Circuits
Uploaded by
En En BelthereCircuits
Uploaded by
En En BelthereELECTRIC CIRCUITS WORKSHEET
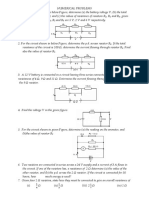
1. A circuit consists of a 12 V battery connected across a single resistor. If the current in the circuit is 3 A, calculate the
size of the resistor.(4 W)
2. Two 5 W resistors are connected in series with a 12 V battery. Determine: (a) the potential difference across each
resistor; and (b) the current flowing in the circuit. (6 V, 1.2 A)
3. Two resistors of size 10 W and 5 W are connected in parallel as shown below.
a. If 3.6 A of current flows into the parallel branch, determine the current flowing in each of the resistors.
(2.4 A in the top resistor & 1.2 A in the bottom resistor)
b. What is the potential difference across each of the resistors? (12 V)
c. How much current will flow out of the parallel branch? (3.6 A)
4. Consider the following circuit and then answer the questions below.
a. State the potential difference between X and Z.
b. State the potential difference between X and Y.
c. State the potential difference between Y and Z.
(Answers: (a) 12 V, (b) 8 V, (c) 4 V)
5. The circuit below shows a resistor, R, connected in series to a 12 V battery across an open switch,
a. If R = 6 W, how much current flows in the circuit with the switch open?
b. While the switch remains open, determine the potential difference between:
i. A and B
ii.A and C
iii. B and C
c. When the switch is closed and R = 6W, determine:
i. The current in the circuit.
ii. The potential difference between A and B.
iii. The potential difference between B and C.
Answers: (a) 0 A / (b)(i) 12 V, (ii) 12 V, (iii) 0 V / (c)(i) 2 A, (ii) 0 V, (iii) 12 V
6. Find the current in the 20 W and 5 W resistors in the following circuit.
(Answers: I20 = 0.045 A and I5 = 0.18 A)
7. In the circuit below, the reading on the ammeter is 3.2 A.
Determine:
a. The reading on the voltmeter.
b. The potential difference across the 40 W resistor.
c. The current in the 40 W resistor.
(Answers: (a) 32 V, (b) 18 V, (c) 0.45 A)
8.
For the circuit above:
a. Determine the total resistance.
b. Find the reading on the ammeter.
c. Draw a voltmeter in the correct place to measure the potential difference across the 0.3 W resistor.
d. Draw an ammeter in the correct place to measure the current in the 0.3 W resistor.
e. Determine the readings on the meters mentioned in parts (c) and (d) above.
(Answers: (a) 100.19 W, (b) 0.2 A, (c) voltmeter in parallel across the resistor, (d) ammeter in series with the resistor, (e)
ammeter reading = 0.125 A and voltmeter reading = 0.0375 V)
You might also like
- NPCIL Question Papers For Electronics BranchNo ratings yetNPCIL Question Papers For Electronics Branch6 pages
- (25366) 2. H Electrical Circuits QuestionsNo ratings yet(25366) 2. H Electrical Circuits Questions10 pages
- Be The Resultant Resistance?: Combination of Resistances (Or Resistors)No ratings yetBe The Resultant Resistance?: Combination of Resistances (Or Resistors)6 pages
- Physics 3204 Unit 2 Current Electricity - Worksheet 4 Ohms Law 2016-2017No ratings yetPhysics 3204 Unit 2 Current Electricity - Worksheet 4 Ohms Law 2016-20174 pages
- Electric Current & Circuits Multiple Choice-2013!07!02No ratings yetElectric Current & Circuits Multiple Choice-2013!07!027 pages
- Ch12 Electricity Ohms Law and Combination of ResistorsNo ratings yetCh12 Electricity Ohms Law and Combination of Resistors10 pages
- Further Problems On Electricity: MBS3211 - Engineering Science For BS Electricity - TutorialsNo ratings yetFurther Problems On Electricity: MBS3211 - Engineering Science For BS Electricity - Tutorials4 pages
- Easy(er) Electrical Principles for General Class Ham License (2015-2019)From EverandEasy(er) Electrical Principles for General Class Ham License (2015-2019)5/5 (1)
- Design of Electrical Circuits using Engineering Software ToolsFrom EverandDesign of Electrical Circuits using Engineering Software ToolsNo ratings yet
- ECENE 1-Fundamentals of Industrial ElectronicsNo ratings yetECENE 1-Fundamentals of Industrial Electronics84 pages
- Serway Physics II Example Questions Chapter 6No ratings yetSerway Physics II Example Questions Chapter 61 page
- Service Manual: Color Television Chassis No. MSANo ratings yetService Manual: Color Television Chassis No. MSA28 pages
- 003 Electrostatic Potential and Capacitance DPP 07of Lec 11No ratings yet003 Electrostatic Potential and Capacitance DPP 07of Lec 113 pages
- Study Guide Series and Parallel Circuits Student Editable - Eman 10ANo ratings yetStudy Guide Series and Parallel Circuits Student Editable - Eman 10A6 pages
- Hazard Defi Nitions: 500 Series Troubleshooting Guide For N1509 and N1511 Alternators100% (1)Hazard Defi Nitions: 500 Series Troubleshooting Guide For N1509 and N1511 Alternators8 pages
- 12.SMART - Drive.ecoinnovation Smart Drive Applications For DIY ProjectsNo ratings yet12.SMART - Drive.ecoinnovation Smart Drive Applications For DIY Projects52 pages
- GMDSS Batteries: Tests and Checks Mariners Must Know: Written by On January 31, 2016No ratings yetGMDSS Batteries: Tests and Checks Mariners Must Know: Written by On January 31, 201622 pages