7th Sem Syllabus
7th Sem Syllabus
Uploaded by
Shobhit SinhaCopyright:
Available Formats
7th Sem Syllabus
7th Sem Syllabus
Uploaded by
Shobhit SinhaCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Copyright:
Available Formats
7th Sem Syllabus
7th Sem Syllabus
Uploaded by
Shobhit SinhaCopyright:
Available Formats
COMPUTER SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING/CS
DR. A.P.J. ABDUL KALAM TECHNICAL
UNIVERSITY, UTTAR PRADESH, LUCKNOW
EVALUATION SCHEME & SYLLABUS
FOR
B. TECH. FOURTH (IV) YEAR
(COMPUTER SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING/CS)
AS PER
AICTE MODEL CURRICULUM
[Effective from the Session: 2021-22]
Curriculum & Evaluation Scheme (VII & VIII semester) Page 1
COMPUTER SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING/CS
B.TECH
(COMPUTER SCIENCE & ENGINEERING/CS) CURRICULUM STRUCTURE
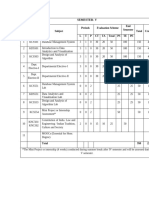
SEMESTER- VII
End
Sl. Subject Periods Evaluation Scheme
Subject Semester Total Credit
No.
Codes L T P CT TA Total PS TE PE
1 KHU701/KHU702 HSMC -1 / HSMC-2 3 0 0 30 20 50 100 150 3
2 KCS07X Departmental Elective-IV 3 0 0 30 20 50 100 150 3
3 KCS07X Departmental Elective-V 3 0 0 30 20 50 100 150 3
4 KOE07X Open Elective-II 3 0 0 30 20 50 100 150 3
The Department may conduct one Lab
of either of the two Electives (4 or 5)
based on the elective chosen for the
5 KCS751A curriculum. The Department shall on 0 0 2 25 25 50 1
its own prepare complete list of
practical for the Lab and arrange for
proper setup and conduct accordingly.
Mini Project or Internship
6 KCS752 0 0 2 50 50 1
Assessment*
7 KCS753 Project 0 0 8 150 150 4
8 MOOCs (Essential for Hons. Degree)
Total 12 0 12 850 18
*The Mini Project or internship (4 - 6 weeks) conducted during summer break after VI semester and will be assessed during VII semester.
SEMESTER- VIII
End
Sl. Subject Periods Evaluation Scheme
Subject Semester Total Credit
No.
Codes L T P CT TA Total PS TE PE
1 KHU801/KHU802 HSMC-1#/HSMC-2# 3 0 0 30 20 50 100 150 3
2 KOE08X Open Elective-III 3 0 0 30 20 50 100 150 3
3 KOE08X Open Elective-IV 3 0 0 30 20 50 100 150 3
4 KCS851 Project 1 0 0 18 100 300 400 9
5 MOOCs (Essential for Hons. Degree)
Total 9 0 18 850 18
Curriculum & Evaluation Scheme (VII & VIII semester) Page 2
COMPUTER SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING/CS
Departmental Elective-IV
1. KCS071 Artificial Intelligence
2. KCS072 Natural language processing
3. KCS073 High Performance Computing
4. KCS074 Cryptography and Network Security
5. KCS075 Design & Development of Applications
6. KCS076 Software Testing
7. KCS077 Distributed Systems
Departmental Elective-V
1. KCS078 Deep Learning
2. KCS079 Service Oriented Architecture
3. KCS710 Quantum Computing
4. KCS711 Mobile Computing
5. KCS712 Internet of Things
6. KCS713 Cloud Computing
7. KCS714 Blockchain Architecture Design
Curriculum & Evaluation Scheme (VII & VIII semester) Page 3
COMPUTER SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING/CS
B.TECH. (CSE/CS)
SEVENT SEMESTER (DETAILED SYLLABUS)
Artificial Intelligence (KCS071)
Course Outcome ( CO) Bloom’s Knowledge Level (KL)
At the end of course , the student will be able to understand
Understand the basics of the theory and practice of Artificial Intelligence as a discipline and K2
CO 1
about intelligent agents.
CO 2 Understand search techniques and gaming theory. K2, K3
The student will learn to apply knowledge representation techniques and problem solving K3 , K4
CO 3
strategies to common AI applications.
CO 4 Student should be aware of techniques used for classification and clustering. K2 , K3
CO 5 Student should aware of basics of pattern recognition and steps required for it. K2 , K4
DETAILED SYLLABUS 3‐0‐0
Proposed
Unit Topic
Lecture
INTRODUCTION :
I Introduction–Definition – Future of Artificial Intelligence – Characteristics of Intelligent Agents– 08
Typical Intelligent Agents – Problem Solving Approach to Typical AI problems.
PROBLEM SOLVING METHODS:
Problem solving Methods – Search Strategies- Uninformed – Informed – Heuristics – Local Search
II Algorithms and Optimization Problems – Searching with Partial Observations – Constraint 08
Satisfaction Problems – Constraint Propagation – Backtracking Search – Game Playing – Optimal
Decisions in Games – Alpha – Beta Pruning – Stochastic Games
KNOWLEDGE REPRESENTATION:
First Order Predicate Logic – Prolog Programming – Unification – Forward Chaining-Backward
III Chaining – Resolution – Knowledge Representation – Ontological Engineering-Categories and 08
Objects – Events – Mental Events and Mental Objects – Reasoning Systems for Categories –
Reasoning with Default Information
SOFTWARE AGENTS:
IV Architecture for Intelligent Agents – Agent communication – Negotiation and Bargaining – 08
Argumentation among Agents – Trust and Reputation in Multi-agent systems.
APPLICATIONS:
AI applications – Language Models – Information Retrieval- Information Extraction – Natural
V 08
Language Processing – Machine Translation – Speech Recognition – Robot – Hardware –
Perception – Planning – Moving
Text books:
1. S. Russell and P. Norvig, “Artificial Intelligence: A Modern Approach‖, Prentice Hall, Third Edition, 2009.
2. I. Bratko, “Prolog: Programming for Artificial Intelligence”, Fourth edition, Addison-Wesley Educational Publishers
Inc., 2011.
3. M. Tim Jones, ―Artificial Intelligence: A Systems Approach(Computer Science)‖, Jones and Bartlett Publishers,
Inc.First Edition, 2008
4. Nils J. Nilsson, ―The Quest for Artificial Intelligence‖, Cambridge University Press, 2009.
5. William F. Clocksin and Christopher S. Mellish,‖ Programming in Prolog: Using the ISO Standard‖, Fifth Edition,
Springer, 2003.
6. Gerhard Weiss, ―Multi Agent Systems‖, Second Edition, MIT Press, 2013.
7. David L. Poole and Alan K. Mackworth, ―Artificial Intelligence: Foundations of Computational Agents‖, Cambridge
University Press, 2010.
Curriculum & Evaluation Scheme (VII & VIII semester) Page 4
COMPUTER SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING/CS
Block chain Architecture Design (KCS714)
Course Outcome ( CO) Bloom’s Knowledge Level (KL)
At the end of course , the student will be able to
CO 1 Describe the basic understanding of Blockchain architecture along with its primitive. K1, K2
CO 2 Explain the requirements for basic protocol along with scalability aspects. K2, K3
CO 3 Design and deploy the consensus process using frontend and backend. K3, K4
Apply Blockchain techniques for different use cases like Finance, Trade/Supply and
CO 4 Government activities. K4, K5
DETAILED SYLLABUS 3-0-0
Unit Topic Proposed
Lecture
Introduction to Blockchain: Digital Money to Distributed Ledgers , Design Primitives: Protocols,
I Security, Consensus, Permissions, Privacy. 08
Blockchain Architecture and Design: Basic crypto primitives: Hash, Signature,) Hashchain to
Blockchain, Basic consensus mechanisms
Consensus: Requirements for the consensus protocols, Proof of Work (PoW), Scalability aspects of
II Blockchain consensus protocols 08
Permissioned Blockchains:Design goals, Consensus protocols for Permissioned Blockchains
Hyperledger Fabric (A): Decomposing the consensus process , Hyperledger fabric components,
III Chaincode Design and Implementation 08
Hyperledger Fabric (B): Beyond Chaincode: fabric SDK and Front End (b) Hyperledger
composer tool
Use case 1 : Blockchain in Financial Software and Systems (FSS): (i) Settlements, (ii) KYC, (iii)
IV Capital markets, (iv) Insurance 08
Use case 2: Blockchain in trade/supply chain: (i) Provenance of goods, visibility, trade/supply
chain finance, invoice management discounting, etc
Use case 3: Blockchain for Government: (i) Digital identity, land records and other kinds of record
V keeping between government entities, (ii) public distribution system social welfare systems 08
Blockchain Cryptography, Privacy and Security on Blockchain
Text books:
1. Mstering Bitcoin: Unlocking Digital Cryptocurrencies, by Andreas Antonopoulos
2. Blockchain by Melanie Swa, O’Reilly
3. Hyperledger Fabric - https://www.hyperledger.org/projects/fabric
4. Zero to Blockchain - An IBM Redbooks course, by Bob Dill, David Smits - https://www.redbooks.ibm.com/
Redbooks.nsf/RedbookAbstracts/crse0401.html
Curriculum & Evaluation Scheme (VII & VIII semester) Page 18
COMPUTER SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING/CS
Cloud Computing (KCS713)
Course Outcome ( CO) Bloom’s Knowledge Level (KL)
At the end of course , the student will be able to understand
CO 1 Describe architecture and underlying principles of cloud computing. K3
CO 2 Explain need, types and tools of Virtualization for cloud. K3, K4
CO 3 Describe Services Oriented Architecture and various types of cloud services. K2, K3
Explain Inter cloud resources management cloud storage services and their providers Assess K2, K4
CO 4
security services and standards for cloud computing.
CO 5 Analyze advanced cloud technologies. K3, K6
DETAILED SYLLABUS 3‐1‐0
Proposed
Unit Topic
Lecture
Introduction To Cloud Computing: Definition of Cloud – Evolution of Cloud Computing –
I Underlying Principles of Parallel and Distributed Computing – Cloud Characteristics – Elasticity in 08
Cloud – On‐demand Provisioning.
Cloud Enabling Technologies Service Oriented Architecture: REST and Systems of Systems – Web
Services – Publish, Subscribe Model – Basics of Virtualization – Types of Virtualization –
II Implementation Levels of Virtualization – Virtualization Structures – Tools and Mechanisms – 08
Virtualization of CPU – Memory – I/O Devices –Virtualization Support and Disaster Recovery.
Cloud Architecture, Services And Storage: Layered Cloud Architecture Design – NIST Cloud
Computing Reference Architecture – Public, Private and Hybrid Clouds – laaS – PaaS – SaaS –
III Architectural Design Challenges – Cloud Storage – Storage‐as‐a‐Service – Advantages of Cloud 08
Storage – Cloud Storage Providers – S3.
Resource Management And Security In Cloud: Inter Cloud Resource Management – Resource
Provisioning and Resource Provisioning Methods – Global Exchange of Cloud Resources – Security
IV Overview – Cloud Security Challenges – Software‐as‐a‐Service Security – Security Governance – 08
Virtual Machine Security – IAM – Security Standards.
Cloud Technologies And Advancements Hadoop: MapReduce – Virtual Box — Google App
V Engine – Programming Environment for Google App Engine –– Open Stack – Federation in the 08
Cloud – Four Levels of Federation – Federated Services and Applications – Future of Federation.
Text books:
1. Kai Hwang, Geoffrey C. Fox, Jack G. Dongarra, “Distributed and Cloud Computing, From Parallel Processing to the
Internet of Things”, Morgan Kaufmann Publishers, 2012.
2. Rittinghouse, John W., and James F. Ransome, ―Cloud Computing: Implementation, Management and Security, CRC
Press, 2017.
3. Rajkumar Buyya, Christian Vecchiola, S. ThamaraiSelvi, ―Mastering Cloud Computing, Tata Mcgraw Hill, 2013.
4. Toby Velte, Anthony Velte, Robert Elsenpeter, “Cloud Computing – A Practical Approach, Tata Mcgraw Hill, 2009.
5. George Reese, “Cloud Application Architectures: Building Applications and Infrastructure in the Cloud: Transactional
Systems for EC2 and Beyond (Theory in Practice), O’Reilly, 2009.
Curriculum & Evaluation Scheme (VII & VIII semester) Page 17
COMPUTER SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING/CS
Cryptography & Network Security ( KCS074)
Course Outcome ( CO) Bloom’s Knowledge Level (KL)
At the end of course , the student will be able to understand
Classify the symmetric encryption techniques and Illustrate various Public key cryptographic K2 , K3
CO 1
techniques.
Understand security protocols for protecting data on networks and be able to digitally sign K1 , K2
CO 2 emails and files.
CO 3 Understand vulnerability assessments and the weakness of using passwords for authentication K4
CO 4 Be able to perform simple vulnerability assessments and password audits K3
CO 5 Summarize the intrusion detection and its solutions to overcome the attacks. K2
DETAILED SYLLABUS 3‐0‐0
Unit Proposed
Topic
Lecture
Introduction to security attacks, services and mechanism, Classical encryption techniques-
substitution ciphers and transposition ciphers, cryptanalysis, steganography, Stream and block
I 08
ciphers. Modern Block Ciphers: Block ciphers principles, Shannon’s theory of confusion and
diffusion, fiestal structure, Data encryption standard(DES), Strength of DES, Idea of differential
cryptanalysis, block cipher modes of operations, Triple DES
Introduction to group, field, finite field of the form GF(p), modular arithmetic, prime and relative
prime numbers, Extended Euclidean Algorithm, Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) encryption
II 08
and decryptionFermat’s and Euler’s theorem, Primarily testing, Chinese Remainder theorem,
Discrete Logarithmic Problem,Principals of public key crypto systems, RSA algorithm, security of
RSA
Message Authentication Codes: Authentication requirements, authentication functions, message
authentication code, hash functions, birthday attacks, security of hash functions, Secure hash
III 08
algorithm (SHA) Digital Signatures: Digital Signatures, Elgamal Digital Signature Techniques,
Digital signature standards (DSS), proof of digital signature algorithm,
Key Management and distribution: Symmetric key distribution, Diffie-Hellman Key Exchange,
IV 08
Public key distribution, X.509 Certificates, Public key Infrastructure. Authentication Applications:
Kerberos, Electronic mail security: pretty good privacy (PGP), S/MIME.
IP Security: Architecture, Authentication header, Encapsulating security payloads, combining
V security associations, key management. Introduction to Secure Socket Layer, Secure electronic, 08
transaction (SET) System Security: Introductory idea of Intrusion, Intrusion detection, Viruses and
related threats, firewalls
Text books:
1. William Stallings, “Cryptography and Network Security: Principals and Practice”, Pearson Education.
2. Behrouz A. Frouzan: Cryptography and Network Security, McGraw Hill .
3. C K Shyamala, N Harini, Dr. T.R.Padmnabhan Cryptography and Security ,Wiley
4. Bruce Schiener, “Applied Cryptography”. John Wiley & Sons
5. Bernard Menezes,” Network Security and Cryptography”, Cengage Learning.
6. AtulKahate, “Cryptography and Network Security”, McGraw Hill
Curriculum & Evaluation Scheme (VII & VIII semester) Page 8
HSMC & OPEN ELECTIVES II LIST 2021-22
2021
DR. A.P.J. ABDU
UL KALAM TECHNICAL UNIVERSITY
UN
UTTAR PRADESH
PRADESH, LUCKNO
OW
EVALUAT
TION SCHEME & SYLLABUS
BUS
FOR
HUMANITIES, SCOCIAL SCIENCE AND
MANAGEMENT COURSE
(HSMC COURSE)
&
OPEN ELECTIVES II LIST
AS PER
AICT
TE MODEL CURRICULUM
ffective from the Session:2021-22]
[Effective 22]
Note:
1. The Student shall choose an opeen Elective from the list in such a manner that he/she
h has not
studied the same course in any fform during the degree programme.
2. * It is mandatory that for these
se subjects (KOE069, KOE076, KOE087,KOE097 & KOE098) only
Trained Faculty (who had donee the FDP for these courses) will teach the coursses.
HSMC & Open Elective List II (VII Semester )2021
)2021-22 Page 1
HSMC & OPEN ELECTIVES II LIST 2021-22
B.Tech. VII Semester (2021-22)
HUMANITIES, SCOCIAL SCIENCE AND MANAGEMENT COURSE
(HSMC COURSE) HSMC1/HSMC2
KHU701/ RURAL DEVELOPMENT: ADMINISTRATION AND PLANNING
KHU801
KHU702/ PROJECT MANAGEMENT & ENTREPRENEURSHIP
KHU802
OPEN ELECTIVE-II
KOE071 FILTER DESIGN
KOE072 BIOECONOMICS
KOE073 MACHINE LEARNING
KOE074 RENEWABLE ENERGY RESOURCES
KOE075 OPERATIONS RESEARCH
KOE076 VISION FOR HUMANE SOCIETY
KOE077 DESIGN THINKING
KOE078 SOIL AND WATER CONSERVATION ENGINEERING
KOE079 INTRODUCTION TO WOMEN’S AND GENDER STUDIES
HSMC & Open Elective List II (VII Semester )2021-22 Page 2
HSMC & OPEN ELECTIVES II LIST 2021-22
KHU701/ RURAL DEVELOPMENT: ADMINISTRATION 3L:0T:0P 3 Credits
KHU801
AND PLANNING
COURSE OUTCOME: After completion of the course student will be able to:
1. Students can understand the definitions, concepts and components of Rural Development
2. Students will know the importance, structure, significance, resources of Indian rural economy.
3. Students will have a clear idea about the area development programmes and its impact.
4. Students will be able to acquire knowledge about rural entrepreneurship.
5. Students will be able to understand about the using of different methods for human resource planning
.
Unit Topics Lectures
I Rural Planning & Development: Concepts of Rural Development, Basic 8
elements of rural Development, and Importance of Rural Development for
creation of Sustainable Livelihoods, An overview of Policies and Programmes for
Rural Development- Programmes in the agricultural sector, Programmes in the
Social Security, Programmes in area of Social Sector.
II Rural Development Programmes: Sriniketan experiment, Gurgaon experiment, 8
marthandam experiment, Baroda experiment, Firkha development scheme, Etawa
pilot project, Nilokheri experiment,approaches to rural community development:
Tagore, Gandhi etc
III Panchayati Raj & Rural Administration: Administrative Structure: 8
bureaucracy, structure of administration; Panchayati Raj Institutions Emergence
and Growth of Panchayati Raj Institutions in India; People and Panchayati Raj;
Financial Organizations in Panchayati Raj Institutions, Structure of rural finance,
Government & Non-Government Organizations / Community Based
Organizations, Concept of Self help group.
IV Human Resource Development in Rural Sector: Need for Human Resource 8
Development, Elements of Human Resource Development in Rural Sector
Dimensions of HRD for rural development-Health, Education, Energy, Skill
Development, Training, Nutritional Status access to basic amenities - Population
composition.
V Rural Industrialization and Entrepreneurship: Concept of Rural 8
Industrialization, Gandhian approach to Rural Industrialization, Appropriate
Technology for Rural Industries, Entrepreneurship and Rural Industrialization-
Problems and diagnosis of Rural Entrepreneurship in India, with special reference
to Women Entrepreneurship; Development of Small Entrepreneurs in India, need
for and scope of entrepreneurship in Rural area.
Text Book:
1. Corporate Social Responsibility: An Ethical Approach - Mark S. Schwartz
2. Katar Singh: Rural Development in India – Theory History and Policy
3. TodaroM.P. Economic Development in III World war
4. Arora R.C – Integrated Rural Development in India
5. Dhandekar V.M and Rath N poverty in India
6. A.N.Agarwal and KundanaLal: Rural Economy of India
7. B.K.Prasad: Rural Development-Sarup& Son’s Publications.
HSMC & Open Elective List II (VII Semester )2021-22 Page 3
HSMC & OPEN ELECTIVES II LIST 2021-22
KOE074 RENEWABLE ENERGY RESOURCES 3L:0T:0P 3 Credits
Unit Topics Lectures
I Introduction: Various non-conventional energy resources- Introduction, 8
availability, classification, relative merits and demerits. Solar Cells:
Theory of solar cells. Solar cell materials, solar cell array, solar cell
power plant, limitations.
II Solar Thermal Energy: Solar radiation, flat plate collectors and their 8
materials, applications and performance, focussing of collectors and
their materials, applications and performance; solar thermal power
plants, thermal energystorage for solar heating and cooling, limitations.
III Geothermal Energy: Resources of geothermal energy, thermodynamics 8
of geo- thermal energy conversion-electrical conversion, non-electrical
conversion, environmental considerations. Magneto-hydrodynamics
(MHD): Principle of working of MHD Power plant, performance
and limitations. Cells: Principle of working of various types of
fuel cells and their working,
performance and limitations.
IV Thermo-electrical and thermionic Conversions: Principle of working, 8
performance and limitations. Wind Energy: Wind power and its
sources, site selection, criterion, momentum theory, classification of
rotors, concentrations and augments, wind characteristics.
Performance and limitations of energy conversion systems.
V Bio-mass: Availability of bio-mass and its conversion theory. Ocean 8
Thermal Energy Conversion (OTEC): Availability, theory and working
principle, performance and limitations. Wave and Tidal Wave:
Principle of working, performance and limitations. Waste Recycling
Plants.
Text Book:
1. Raja etal, “Introduction to Non-Conventional Energy Resources” Scitech
Publications.
2. John Twideu and Tony Weir, “Renewal Energy Resources” BSP Publications, 2006.
3. M.V.R. Koteswara Rao, “Energy Resources: Conventional & Non-Conventional” BSP
Publications,2006.
4. D.S. Chauhan,”Non-conventional Energy Resources” New Age International.
5. C.S. Solanki, “Renewal Energy Technologies: A Practical Guide for Beginners” PHI
Learning.
6. Peter Auer, "Advances in Energy System and Technology". Vol. 1 & II Edited by
Academic Press.
7. Godfrey Boyle,“ Renewable Energy Power For A Sustainable Future”, Oxford
University Press.
Open Elective II 2021-22 K series (VII Semester) Page 8
You might also like
- Q & A Introduction To CriminologyDocument107 pagesQ & A Introduction To CriminologyAngel King Relatives83% (18)
- PLC Programming from Novice to Professional: Learn PLC Programming with Training VideosFrom EverandPLC Programming from Novice to Professional: Learn PLC Programming with Training VideosRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- B.tech - Final Year Computer Science EngineeringDocument60 pagesB.tech - Final Year Computer Science Engineeringlovelesh MauryaNo ratings yet
- Syllabus 4thyearDocument10 pagesSyllabus 4thyearsiddiqueyounus458No ratings yet
- BTech CS 4th Year SyllabusDocument19 pagesBTech CS 4th Year SyllabusRahul Kumar SInhaNo ratings yet
- BTech CS 4th Year SyllabusDocument19 pagesBTech CS 4th Year SyllabusILMA UROOJNo ratings yet
- K - SERIES B.Tech. Computer Science and Design Syllabus 4th Year 2024-25Document19 pagesK - SERIES B.Tech. Computer Science and Design Syllabus 4th Year 2024-25college9899No ratings yet
- BTech. 4th Year - Computer Science and Engineering - Hindi - 2024-25 - v2Document20 pagesBTech. 4th Year - Computer Science and Engineering - Hindi - 2024-25 - v2Thakur SaurabhNo ratings yet
- BTech. 4th Year - Computer Science and Engineering-Artificial Intelligence - 2023-24 - v2Document20 pagesBTech. 4th Year - Computer Science and Engineering-Artificial Intelligence - 2023-24 - v2Abhay shuklaNo ratings yet
- BTech. 4th Year - Computer Science and Engineering-Data Science - 2023-24Document20 pagesBTech. 4th Year - Computer Science and Engineering-Data Science - 2023-24therapidcodingNo ratings yet
- BTech. 4th Year - Computer Science and Engineering-Artificial Intelligence - Machine Learning - 2023-24 AKTU SyllabusDocument21 pagesBTech. 4th Year - Computer Science and Engineering-Artificial Intelligence - Machine Learning - 2023-24 AKTU SyllabusShubhi TomarNo ratings yet
- BTech. 4th Year - Computer Science and Engineering - Internet of Things - 2023-24Document20 pagesBTech. 4th Year - Computer Science and Engineering - Internet of Things - 2023-24Mr. Manoj Kr. Sharma EceNo ratings yet
- AKTU IT 4th YrDocument19 pagesAKTU IT 4th YrMahak SinghNo ratings yet
- B Tech 4th Yr Electronics and Computer Engg 2022 23 RevisedDocument17 pagesB Tech 4th Yr Electronics and Computer Engg 2022 23 RevisedShivangi MishraNo ratings yet
- AKTU 3rd CSE - WatermarkDocument35 pagesAKTU 3rd CSE - WatermarkMahendra KishorNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Engg 4th YearDocument21 pagesMechanical Engg 4th YearPiyush PantNo ratings yet
- B.Tech - CSE and CS Syllabus of 3rd Year 12 Oct 20Document35 pagesB.Tech - CSE and CS Syllabus of 3rd Year 12 Oct 20Basic Of EverythingNo ratings yet
- AKTU ME 4th YrDocument21 pagesAKTU ME 4th YrpthimanshuNo ratings yet
- Aktu ECE 4th Yr SyllabusDocument17 pagesAktu ECE 4th Yr Syllabusabhaymanchanda2004No ratings yet
- B Tech 2nd Year CSE Hindi 2022 23 RevisedDocument15 pagesB Tech 2nd Year CSE Hindi 2022 23 RevisedJobs GlbitmNo ratings yet
- 3rd Year Syllabus 2020-21Document36 pages3rd Year Syllabus 2020-21HarshitNo ratings yet
- BTech. 3rd Year - CSE - Hindi - 2023-24Document33 pagesBTech. 3rd Year - CSE - Hindi - 2023-24AnkitNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Engg 4th Year AktuDocument14 pagesMechanical Engg 4th Year AktuRishabhNo ratings yet
- Automobile Engineering 4th YearDocument11 pagesAutomobile Engineering 4th YearpaoloNo ratings yet
- B.Tech 2nd Year CSAI - CSML - CSDS - CSIOT - 2021-22 0709Document14 pagesB.Tech 2nd Year CSAI - CSML - CSDS - CSIOT - 2021-22 0709sakshamNo ratings yet
- SyllabusDocument37 pagesSyllabusMeme PurNo ratings yet
- B.Tech 2nd Year CSE & CSIT AICTE Model Curriculum 2019-20 PDFDocument14 pagesB.Tech 2nd Year CSE & CSIT AICTE Model Curriculum 2019-20 PDFBrij BihariNo ratings yet
- 202307291442395902Syllabus-CSE-III YearDocument35 pages202307291442395902Syllabus-CSE-III Yearshivamagr111103No ratings yet
- B.tech - CS - Hindi Syllabus of 3rd YearDocument35 pagesB.tech - CS - Hindi Syllabus of 3rd Yearvaibhav0012vNo ratings yet
- 4th Year Effective From 2022 2023Document24 pages4th Year Effective From 2022 2023ia0882326No ratings yet
- Big Data SyllabusDocument5 pagesBig Data SyllabusVani MittalNo ratings yet
- Syllabus of Chemical Engineering 3rd Year 2020 5 April 2021Document57 pagesSyllabus of Chemical Engineering 3rd Year 2020 5 April 2021ShivamNo ratings yet
- B.tech. 2nd Year Chemical EnggDocument22 pagesB.tech. 2nd Year Chemical EnggSumit Rathore100% (1)
- 202108201255246645B Tech IT Third Year SyllabusDocument36 pages202108201255246645B Tech IT Third Year SyllabusSuryansh BaranwalNo ratings yet
- B.Tech - CSE and CS Syllabus of 3rd Year July 2020Document36 pagesB.Tech - CSE and CS Syllabus of 3rd Year July 2020Durgesh MauryaNo ratings yet
- CS2 BTech 2nd Year K Series Syllabus EFS 2019 20 CompressedDocument39 pagesCS2 BTech 2nd Year K Series Syllabus EFS 2019 20 Compressedsouravghanghas777No ratings yet
- B.tech. 2nd Year AICTE Model Curriculum 2019-20 CivilDocument19 pagesB.tech. 2nd Year AICTE Model Curriculum 2019-20 Civilventurimeter effluxNo ratings yet
- BTech Civil Engg 2 ND Year 2122Document19 pagesBTech Civil Engg 2 ND Year 2122Ansh SahuNo ratings yet
- B.Tech. 4th Year Chemical AICTE Model Curriculum 2021-22Document21 pagesB.Tech. 4th Year Chemical AICTE Model Curriculum 2021-22Dhwaj Gupta 2No ratings yet
- 6th Sem SyllabusDocument36 pages6th Sem SyllabusVipin YadavNo ratings yet
- AKTU SyllabusDocument19 pagesAKTU SyllabusGautam NarulaNo ratings yet
- B.Tech - CS - Design 3rd Year Year 2023-24Document33 pagesB.Tech - CS - Design 3rd Year Year 2023-24Aashik HussainNo ratings yet
- B.tech EI 4th Syllabus 2021Document21 pagesB.tech EI 4th Syllabus 2021vanshsachan5No ratings yet
- B.tech. 3rd Yr CSE (AI) 2022 23 RevisedDocument35 pagesB.tech. 3rd Yr CSE (AI) 2022 23 RevisedJobs GlbitmNo ratings yet
- B.tech. 3rd Yr CSE (AIML) 2022 23 RevisedDocument33 pagesB.tech. 3rd Yr CSE (AIML) 2022 23 RevisedJobs GlbitmNo ratings yet
- K Series B Tech 1st Year AICTE Model Curriculum EFS 2020-21-4Document47 pagesK Series B Tech 1st Year AICTE Model Curriculum EFS 2020-21-4Vaibhav KumarNo ratings yet
- B.tech. in Computer Science and Business System-CSBS-Third-Year-2022-23Document69 pagesB.tech. in Computer Science and Business System-CSBS-Third-Year-2022-23mayankchaudhary964No ratings yet
- B.Tech. 3rd Yr CSE (AI) 2022 23Document33 pagesB.Tech. 3rd Yr CSE (AI) 2022 23Harsh SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- B.Tech - IT and CSIT Syllabus of 3rd YearDocument37 pagesB.Tech - IT and CSIT Syllabus of 3rd YearShikhaNo ratings yet
- AKTU Syllabus CS 3rd YrDocument1 pageAKTU Syllabus CS 3rd YrPPDC NAGAURNo ratings yet
- 4. Annexure-IV Lr 23 III & IV Semester SyllabusDocument45 pages4. Annexure-IV Lr 23 III & IV Semester Syllabussyedizaan9876No ratings yet
- Data Sciebce - SemDocument1 pageData Sciebce - SemhollyhocNo ratings yet
- B.Tech - CSE and CS Syllabus of 3rd YearDocument37 pagesB.Tech - CSE and CS Syllabus of 3rd YearShikhaNo ratings yet
- Scheme and Syllabus - 2021-22Document211 pagesScheme and Syllabus - 2021-22AnjanaNo ratings yet
- B.Tech - Final Year - Biotechnology - SyllabusDocument23 pagesB.Tech - Final Year - Biotechnology - SyllabusTubeNo ratings yet
- B Tech 2nd Year AIML, AIDS, Computer SC and Design 2022 23 RevisedDocument14 pagesB Tech 2nd Year AIML, AIDS, Computer SC and Design 2022 23 RevisedJobs GlbitmNo ratings yet
- B - Tech - 2nd - Year - AIML, AIDS, Computer - SC - and - Design - 2022 - 23 - RevisedDocument14 pagesB - Tech - 2nd - Year - AIML, AIDS, Computer - SC - and - Design - 2022 - 23 - RevisedSuresh BhagatNo ratings yet
- Aeronautical Engineering 4th YearDocument19 pagesAeronautical Engineering 4th YearMuskan RawatNo ratings yet
- Aktu Electrical SystemDocument8 pagesAktu Electrical SystemHarshit SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Using Artificial Neural Networks for Analog Integrated Circuit Design AutomationFrom EverandUsing Artificial Neural Networks for Analog Integrated Circuit Design AutomationNo ratings yet
- Pme Unit 1 MamDocument31 pagesPme Unit 1 MamShobhit SinhaNo ratings yet
- Pme Unit 3 NotesDocument9 pagesPme Unit 3 NotesShobhit SinhaNo ratings yet
- Syllabus 8 SemDocument2 pagesSyllabus 8 SemShobhit SinhaNo ratings yet
- Pme Unit1 NotesDocument16 pagesPme Unit1 NotesShobhit SinhaNo ratings yet
- CH 6Document11 pagesCH 6nugusaiyasu4No ratings yet
- How To Solve A Rubiks CubeDocument5 pagesHow To Solve A Rubiks CubeLiezel SanchezNo ratings yet
- 3-5 - Thailand - 20080526 - Thailand Single Window E-Logistics - Seoul v2.0Document38 pages3-5 - Thailand - 20080526 - Thailand Single Window E-Logistics - Seoul v2.0glassyglassNo ratings yet
- Green Supply Chain Management-A Case of Sugar - Rupesh Kumar - OP008Document12 pagesGreen Supply Chain Management-A Case of Sugar - Rupesh Kumar - OP008Arun DevNo ratings yet
- NSS Chemistry Part 2 The Microscopic World HKCEE Past Paper Question The Microscopic World I Ns - Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument32 pagesNSS Chemistry Part 2 The Microscopic World HKCEE Past Paper Question The Microscopic World I Ns - Multiple Choice QuestionsミーチェルNo ratings yet
- Yamaha RX V795ADocument82 pagesYamaha RX V795ADavid F. DealNo ratings yet
- Simple Interest: Day: 74th - 75th Day: 74th - 75thDocument4 pagesSimple Interest: Day: 74th - 75th Day: 74th - 75thShivmNo ratings yet
- What Is Online ShoppingDocument14 pagesWhat Is Online ShoppingMyro DarlandanNo ratings yet
- JENESYS ProgrammeDocument17 pagesJENESYS ProgrammeSophearin PhannNo ratings yet
- Direct Instruction Lesson Siana BergDocument2 pagesDirect Instruction Lesson Siana Bergapi-488045418No ratings yet
- Emlab 2Document21 pagesEmlab 2hafizrahimmitNo ratings yet
- GSM Based Home Security System REPORTDocument51 pagesGSM Based Home Security System REPORTAlok Khatri81% (16)
- 2011 P5 Math SA1 Rosyth PDFDocument36 pages2011 P5 Math SA1 Rosyth PDFPunitha PanchaNo ratings yet
- Math Demo Dec 2 2019 PrintDocument16 pagesMath Demo Dec 2 2019 PrintHazy Jade Hombrog RugaNo ratings yet
- Tda 4661Document6 pagesTda 4661Abubakar SidikNo ratings yet
- Using AI Tools To Lesson Plan - EdutopiaDocument21 pagesUsing AI Tools To Lesson Plan - EdutopiaalraclitasNo ratings yet
- Climate Change and Malaria Predictions Becoming RealityDocument2 pagesClimate Change and Malaria Predictions Becoming Realitygerges8723No ratings yet
- Tyco Form10K 2002 3Document10 pagesTyco Form10K 2002 3TranNo ratings yet
- Infant and Toddler Concussion Guide: Signs & SymptomsDocument2 pagesInfant and Toddler Concussion Guide: Signs & Symptomspeninah annNo ratings yet
- Collage of Computing and Informatics: Wolkite UniversityDocument19 pagesCollage of Computing and Informatics: Wolkite UniversityhabtNo ratings yet
- Bachelor Thesis Finance TopicsDocument4 pagesBachelor Thesis Finance Topicsmak0dug0vuk2100% (2)
- Awaji AnalysisDocument65 pagesAwaji AnalysisVania Estrellita0% (1)
- Lenskart Co. PPT MadhuriDocument16 pagesLenskart Co. PPT MadhuriVishwajeet Vinayak GaikeNo ratings yet
- Adhd Toolkit MedicationsDocument1 pageAdhd Toolkit MedicationsreneezNo ratings yet
- PNC Bank Statement GERALD WILLIAM KACAKDocument2 pagesPNC Bank Statement GERALD WILLIAM KACAKDAVID JOLLEYNo ratings yet
- Common Rail Direct InjectionDocument60 pagesCommon Rail Direct InjectionSapari VelNo ratings yet
- Submis 2Document14 pagesSubmis 2Cao Chen-RuiNo ratings yet
- Activity Sheets: Government Property Not For Sale Allotted ToDocument2 pagesActivity Sheets: Government Property Not For Sale Allotted ToSally Consumo KongNo ratings yet
- Dominic P. E. Dickson, Frank J. Berry-Mossbauer Spectroscopy (2005)Document286 pagesDominic P. E. Dickson, Frank J. Berry-Mossbauer Spectroscopy (2005)Jorge AndradeNo ratings yet