0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
29 viewsFuel ECU
Fuel ECU
Uploaded by
mohamedThe document is a glossary that defines key components of fuel injection systems for 1974-1979 Volkswagen Beetle vehicles. It provides diagrams labeled A through O that define various parts through their purpose, operation, and known alternate names. For each part, it gives a brief 1-2 sentence description of the component's function and relevance to the fuel injection system. The glossary acts as a reference guide for maintenance and troubleshooting of the early electronic fuel injection systems used in these vehicles.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Fuel ECU
Fuel ECU
Uploaded by
mohamed0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
29 views3 pagesThe document is a glossary that defines key components of fuel injection systems for 1974-1979 Volkswagen Beetle vehicles. It provides diagrams labeled A through O that define various parts through their purpose, operation, and known alternate names. For each part, it gives a brief 1-2 sentence description of the component's function and relevance to the fuel injection system. The glossary acts as a reference guide for maintenance and troubleshooting of the early electronic fuel injection systems used in these vehicles.
Original Description:
Fuel ecu
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
The document is a glossary that defines key components of fuel injection systems for 1974-1979 Volkswagen Beetle vehicles. It provides diagrams labeled A through O that define various parts through their purpose, operation, and known alternate names. For each part, it gives a brief 1-2 sentence description of the component's function and relevance to the fuel injection system. The glossary acts as a reference guide for maintenance and troubleshooting of the early electronic fuel injection systems used in these vehicles.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
29 views3 pagesFuel ECU
Fuel ECU
Uploaded by
mohamedThe document is a glossary that defines key components of fuel injection systems for 1974-1979 Volkswagen Beetle vehicles. It provides diagrams labeled A through O that define various parts through their purpose, operation, and known alternate names. For each part, it gives a brief 1-2 sentence description of the component's function and relevance to the fuel injection system. The glossary acts as a reference guide for maintenance and troubleshooting of the early electronic fuel injection systems used in these vehicles.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 3
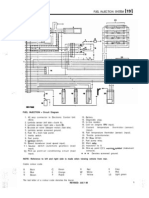
Glossary Key...
(A) - Purpose
(B) - Operation
(C) - “Also known as"
(M) - Maintenance Item
(service per manufacturers'
recommendations)
1974-1977 Standard Beetle & 1974-1979 Super Beetle
1600cc Engine Electronic Control Unit (ECU)
Diagram “A” FUEL FILTER (M) Diagram “C” AUXILIARY AIR VALVE
A) To maintain the high degree of fuel cleanliness A) The auxiliary air valve opens a cross-sectional air bypass
critical to proper fuel injection operation and component around the closed throttle blades to maintain an acceptable
longevity. idle during cold engine operation.
B) Fuel must pass through a paper element, a fibrous B) A precisely calibrated bi-metallic strip governs the cross
“fluff trap”, and finally through a mesh strainer - when sectional area of an internal gate which meters the amount of
replaced at proper intervals as specified by the vehicle extra air admitted to the engine during the warm-up period.
manufacturer, the fuel filter will allow no particles larger The bi-metallic strip has its regulating time governed by the
than 10 microns to pass through it. use of a ceramic heating element
C) Auxiliary Air Device, Auxiliary Air Regulator
Diagram “B” ELECTRIC FUEL PUMP
A) Creates continual pressurized fuel supply of specific Diagram “D” AIR FLOW SENSOR / METER
volume to central fuel metering area. A) The air flow sensor provides the ECU with a continuous
B) The electric fuel pump is usually a roller cell design voltage signal as a measure of inducted air volume (engine
driven by a permanent magnet electric motor. Fuel is load). This signal is a major contributor to the injector
scavenged from the vehicle fuel tank and pressurized duration signal from the ECU.
within cavities formed between the individual pump B) Incoming air volume, as controlled by engine load, deflects
rollers. The pressurized fuel exists, the outlet check valve a spring loaded flap, which at one end of its pivot shaft has
as a direct result of the centrifugal sealing action created a potentiometer contact. An inversely proportionate voltage
in the roller chamber during rotation. signal (along with an air temperature signal in some cases)
C) High Pressure Pump, Supply Pump are sent to the ECU to help govern duration of injection.
C) Air Flow Meter, Vane Meter, VAF (Vane Air Flow)
Diagram “E” THERMO-TIME SWITCH Diagram “K” INJECTOR/PRESSURE REGULATOR SEAL (M)
A) The thermo time switch completes the electrical circuit for, A) These flexible rings prevent unmetered air from entering
and limits the duration of operation for the cold start valve. the engine, position the injection valve, and prevent fuel
B) An internal bi-metallic strip, heated both electrically leakage.
and via engine heat, determines cold start valve on time B) Depending upon system design, the injector seal is
by providing a short duration electrical ground. positioned on the injection valve so as to provide a leak
proof seal between the injector and the intake manifold.
Diagram “F” VACUUM LIMITER In many electronic fuel injection systems, an additional
A) This device provides additional air to the engine during seal is fitted between the injector and fuel rail. The pres-
transitional/closed throttle positions to maintain combustion. sure regulator seal is utilized at the junction of the pres-
B) When a specific difference in pressure before and after sure regulator and fuel rail to prevent fuel leakage.
the throttle valve is achieved (as in deceleration) this valve
opens to supply additional air to the engine. Diagram “L” ENGINE TEMPERATURE SENSOR
A) This device measures engine temperature and reports
Diagram “G” DOUBLE RELAY this information to the electronic control units.
A) The relay provides electrical power to the engine man- B) The internal resistor of the temperature sensor decreas-
agement system and provides a safety circuit to prevent es in electrical resistance as the engine warms. Engine
fuel flow when the engine is not running. temperature via this resistance value is reported to the
B) A primary ignition signal is most often used as an input ECU and used as a correction to the output state (injector
to the relay which, when energized, provides power to delivery, etc.).
the fuel pump, ECU, and the heated oxygen sensor if so C) CTS (Coolant Temperature Sensor), Temperature Sensor II
equipped.
Diagram “M” FUEL INJECTION VALVES (Solenoid Types)
Diagram “H” ELECTRONIC CONTROL UNIT A) The solenoid type fuel injection valve precisely meter
A) Operating in a central processing capacity, the electronic fuel into the individual engine intake ports.
control unit calculates the engine management control B) Driven by the electronic control unit, the valve needle
parameters based on data received from various sensors. will lift within the solenoid body to deliver the predeter-
B) Responding to measured variables and sensor input, the mined fuel quantity. Replaceable O-ring seals are provided
control unit adjusts fuel delivery through its controlling to limit vibration and leakage problems, and to ensure
output stage. that characteristic good hot start condition.
C) ECA (Electronic Control Assembly), ECU, ECM, Logic Module,
Trigger Box. Diagram “N” COLD START VALVE
A) Used to provide additional fuel needed to overcome fuel
Diagram “I” THROTTLE VALVE SWITCH condensation and additional friction present during cold
A) Communicates idle and full load position to the elec- engine start-up.
tronic control unit to allow for adjustment in engine B) Dependent on, and operating in series with the ther-
‘management control. mo-time switch, this solenoid operated valve creates an
B) Actuated by the throttle shaft, one set of contacts closes atomized “swirl” mixture, which is injected directly into
at idle with another signaling full-load electronically; all the intake manifold plenum.
dependent on throttle position. Normally, the idle contact C) The “5th” injector, Cold Start Injector, Cold Start Device.
assists overrun fuel cutoff and idle speed actuator con-
trolling functions, while the full-load contact acts to signal Diagram “O” FUEL PRESSURE REGULATOR
need for additional fuel under wide open throttle. A) The (EFI-multi port type) fuel pressure regulator main-
C) Throttle switch, load switch tains required system specific fuel pressure in a differential
relationship between fuel pressure and manifold vacuum.
Diagram “J” RESISTOR UNIT This device directs excess fuel back to the fuel tank.
A) The resistor unit reduces the voltage supplied to the port B) A spring loaded diaphragm (assisted by a vacuum
fuel injectors. chamber opposite the fuel side) exerts a preset pressure on
B) Battery voltage, supplied to the port injectors continuously the incoming fuel flow, and by deflecting slightly to allow
when the vehicle is running, is reduced by the resistor unit through flow, assures precise fuel rail pressure. The vac-
prior to reaching the injection valves. Only certain L-Jetronic uum chamber receives and responds quickly to the signal
port injectors are designed to operate on this reduced voltage. from the intake manifold.
C) Dropping Resistors, Ballast Pack, Resistor Pack.
special emphasis given to breaker point condition and
correct dwell. All fuel injection system components and
wiring whould be tested.
When troubleshooting the fuel injection system, you need
to test a component that connects to the control unit. Never
attempt to make tests at the terminals of the control unit
itself. Always disconnect the battery ground strap before you
remove the plug from the electronic control unit.
If for any reason you must install a replacement control
unit, make sure that the new control unit has the same
part number as the original control unit. A number of
changes were made since the first fuel injection models
were introduced in 1975.
Before replacing the electronic control unit, the follow-
ing procedures should be observed. The engine compres-
sion should be measured and found within specifications.
The ignition system should be thoroughly checked, with
special emphasis given to breaker point condition and
correct dwell. All fuel injection system components and
wiring should be tested.
Fuel Injected
1600cc Engine Electronic
When troubleshooting the fuel injection system, you need
Control Unit (ECU). Item #317-921 to test a component that connects to the control unit. Never
attempt to make tests at the terminals of the control unit
itself. Always disconnect the battery ground strap before you
Keep All of your Volkswagen’s Electronic System remove the plug from the electronic control unit.
functions running smoothly with this technical tip. If for any reason you must install a replacement control
Before replacing the electronic control unit, the follow- unit, make sure that the new control unit has the same
ing procedures should be observed. The engine compres- part number as the original control unit. A number of
sion should be measured and found within specifications. changes were made since the first fuel injection models
The ignition system should be thoroughly checked, with were introduced in 1975. MAM
You might also like
- 1K 2KD Fuel Injection Volume ValueDocument12 pages1K 2KD Fuel Injection Volume ValueJimmy100% (3)
- Br710-A2 Engine DescriptionDocument19 pagesBr710-A2 Engine Descriptionmuters100% (1)
- 14cux Fuel InjectionDocument80 pages14cux Fuel InjectionJuanjo Chamizo Naranjo100% (2)
- Practical Guides to Testing and Commissioning of Mechanical, Electrical and Plumbing (Mep) InstallationsFrom EverandPractical Guides to Testing and Commissioning of Mechanical, Electrical and Plumbing (Mep) InstallationsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (4)
- MODULE-14 Previous Questions: World'$ of AmeDocument50 pagesMODULE-14 Previous Questions: World'$ of AmeRobNo ratings yet
- VW Digifant ManualDocument43 pagesVW Digifant ManualChris Rimmer100% (6)
- Renault ClioDocument2 pagesRenault ClioGeorgian Cranta100% (1)
- Air Cooled VW VW Fuel Injection L-Jetronic Trouble Shooting Guide - Mid America MotorworksDocument2 pagesAir Cooled VW VW Fuel Injection L-Jetronic Trouble Shooting Guide - Mid America MotorworksWesley FernandesNo ratings yet
- Section 2 EngineDocument14 pagesSection 2 EngineMarco OlivettoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 72Document24 pagesChapter 72DavidfigamNo ratings yet
- Fuel Control and MonitoringDocument8 pagesFuel Control and Monitoringanarko arsipelNo ratings yet
- Fueling System of SI and CI Engines: by Zewdie Alemayehu (Automotive Eng.)Document67 pagesFueling System of SI and CI Engines: by Zewdie Alemayehu (Automotive Eng.)ahmed jemalNo ratings yet
- Electronic Diesel Systems PGDocument221 pagesElectronic Diesel Systems PGredaei beyeneNo ratings yet
- SKI-DOO E-TEC Direct Fuel Injection (SUMMIT X) - Shop Manual - 04cciuAAA - SM11Y015S01 - enDocument46 pagesSKI-DOO E-TEC Direct Fuel Injection (SUMMIT X) - Shop Manual - 04cciuAAA - SM11Y015S01 - enkaenenbox109No ratings yet
- 13 and 14 MarkDocument6 pages13 and 14 MarkM S BharanidharanNo ratings yet
- Diesel Engine ManagementDocument56 pagesDiesel Engine Managementbravo6dNo ratings yet
- N8489B Gyro Copter Doc SDocument13 pagesN8489B Gyro Copter Doc Spadmaraj_pjNo ratings yet
- Nissan Diagnostico de Iacv y AacvDocument7 pagesNissan Diagnostico de Iacv y AacvJose Luis Velasquez RomeroNo ratings yet
- Engine 55-L-714Document92 pagesEngine 55-L-714Georgios Roumpies100% (1)
- 2019-ISB CM2150 IntroductionDocument7 pages2019-ISB CM2150 Introductionralph arisNo ratings yet
- E5050 Diesel Engines Electronic Management (TCT Transmission, 170 HPDocument9 pagesE5050 Diesel Engines Electronic Management (TCT Transmission, 170 HPomid yadegariNo ratings yet
- 2025-ISB/ISC/ISL CM2150 Control SystemDocument7 pages2025-ISB/ISC/ISL CM2150 Control Systemralph arisNo ratings yet
- 2020-ISB CM2150 Shop TalkDocument7 pages2020-ISB CM2150 Shop Talkralph arisNo ratings yet
- 2024-ISB/ISC/ISL CM2150 Crankcase BreatherDocument7 pages2024-ISB/ISC/ISL CM2150 Crankcase Breatherralph arisNo ratings yet
- 2013-QSC8.3 & QSL9 CM850 Shop TalkDocument6 pages2013-QSC8.3 & QSL9 CM850 Shop Talkralph arisNo ratings yet
- Investigation of Electro Mechanical Fuel SystemDocument11 pagesInvestigation of Electro Mechanical Fuel Systemomarsalahomar555No ratings yet
- 2022-ISC/ISL CM2150 Shop TalkDocument7 pages2022-ISC/ISL CM2150 Shop Talkralph arisNo ratings yet
- 2023-ISC/ISL CM2150 Fuel SystemDocument7 pages2023-ISC/ISL CM2150 Fuel Systemralph arisNo ratings yet
- Engine Testing TechniqueDocument8 pagesEngine Testing TechniqueNur YakhinNo ratings yet
- Simulation of A Prototype Electrically Powered Integrated Actuator For Civil AircraftDocument14 pagesSimulation of A Prototype Electrically Powered Integrated Actuator For Civil AircraftdavpaffNo ratings yet
- Service Manual FD200Document210 pagesService Manual FD200Hải TiếnNo ratings yet
- Individual Cylinder Air-Fuel Ratio Control With A Single EGO SensorDocument7 pagesIndividual Cylinder Air-Fuel Ratio Control With A Single EGO SensorcristopuloNo ratings yet
- WM Claas CeltisDocument1,537 pagesWM Claas Celtisboylers95100% (1)
- 27 Appendix D Technical Reference & SpecificationsDocument17 pages27 Appendix D Technical Reference & SpecificationspapipapiiNo ratings yet
- Sfi SystemDocument96 pagesSfi SystemWawan SatiawanNo ratings yet
- Development and Testing of A Multi-Type Air Conditioner Without Using AC InvertersDocument11 pagesDevelopment and Testing of A Multi-Type Air Conditioner Without Using AC InvertersArifRahmanNo ratings yet
- Electrical Systems & Traction Alternator Design & Aux. System DesignDocument11 pagesElectrical Systems & Traction Alternator Design & Aux. System DesignVangara HarshuNo ratings yet
- Unit Injectors: Unit Injector Hold-Down Clamp Rack Plunger Injector NozzleDocument14 pagesUnit Injectors: Unit Injector Hold-Down Clamp Rack Plunger Injector NozzleGovea HeduNo ratings yet
- E - Theory/Operation Article TextDocument6 pagesE - Theory/Operation Article Textalex.mos.408No ratings yet
- 1020-HPI-TP Unit Injector SystemsDocument4 pages1020-HPI-TP Unit Injector Systemsralph arisNo ratings yet
- Cummins CRDocument40 pagesCummins CRАлексей Миронов90% (10)
- Fuel Servo Pressure: The Fuel Metering Valve in The Hydro Mechanical Unit of A F A D E C System Is Operated byDocument2 pagesFuel Servo Pressure: The Fuel Metering Valve in The Hydro Mechanical Unit of A F A D E C System Is Operated byMC ManojNo ratings yet
- Fuel System Engine Control System Hydraulic sYSTEMDocument3 pagesFuel System Engine Control System Hydraulic sYSTEMlamborghini1991No ratings yet
- (VOLKSWAGEN) Manual de Taller Volkswagen CC 1990 1991Document15 pages(VOLKSWAGEN) Manual de Taller Volkswagen CC 1990 1991Luis TroieNo ratings yet
- 1026-Fuel System Electrical ProblemsDocument4 pages1026-Fuel System Electrical Problemsralph arisNo ratings yet
- Electronic Diesel Control (EDC) : System OverviewDocument2 pagesElectronic Diesel Control (EDC) : System OverviewRajni Devi100% (1)
- 1025-Fuel Sub-System Component MalfuntionsDocument4 pages1025-Fuel Sub-System Component Malfuntionsralph arisNo ratings yet
- Aircraft Maintenance B2 Course - M14 PDFDocument140 pagesAircraft Maintenance B2 Course - M14 PDFAnonymous AV90SAXa5VNo ratings yet
- Cabriolet 85 System Cis eDocument33 pagesCabriolet 85 System Cis ediazNo ratings yet
- Fuel InjectionDocument4 pagesFuel InjectionWeyih ReganNo ratings yet
- Engine 714Document92 pagesEngine 714xrayx360No ratings yet
- Volumetric Float Type Fuel Quantity IndicationDocument2 pagesVolumetric Float Type Fuel Quantity IndicationmarianaNo ratings yet
- Engine Instrument QuestionsDocument12 pagesEngine Instrument QuestionsjhonyNo ratings yet
- MECH 435 - IC Engine Laboratory ExperimentDocument9 pagesMECH 435 - IC Engine Laboratory Experimentdesie yalewNo ratings yet
- Untitled 1Document35 pagesUntitled 1sametgencagNo ratings yet
- Control of DC Motor Using Different Control StrategiesFrom EverandControl of DC Motor Using Different Control StrategiesNo ratings yet
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Rating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (3)
- Construction and Manufacture of AutomobilesFrom EverandConstruction and Manufacture of AutomobilesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Simulation of Some Power System, Control System and Power Electronics Case Studies Using Matlab and PowerWorld SimulatorFrom EverandSimulation of Some Power System, Control System and Power Electronics Case Studies Using Matlab and PowerWorld SimulatorNo ratings yet
- Allied-How-to-Use-Your-VOM-and-VTVM1968Document98 pagesAllied-How-to-Use-Your-VOM-and-VTVM1968mohamedNo ratings yet
- Byte-1979-06Document288 pagesByte-1979-06mohamedNo ratings yet
- Fun Way Electronics 2Document133 pagesFun Way Electronics 2mohamedNo ratings yet
- Telegraph Age 1901 01Document72 pagesTelegraph Age 1901 01mohamedNo ratings yet
- Dumont-Cathoder-Ray-Equipment-8th-1951Document220 pagesDumont-Cathoder-Ray-Equipment-8th-1951mohamedNo ratings yet
- 753296Document132 pages753296mohamedNo ratings yet
- Audio Anthology 1950Document127 pagesAudio Anthology 1950mohamedNo ratings yet
- TAB IC Projects Green 1971Document196 pagesTAB IC Projects Green 1971mohamedNo ratings yet
- Marine Electronics Evaluation Project 'Radar' (PDFDrive)Document164 pagesMarine Electronics Evaluation Project 'Radar' (PDFDrive)mohamedNo ratings yet
- كتاب التكنولوجيا الجزء الاول الثالثة ثانويDocument70 pagesكتاب التكنولوجيا الجزء الاول الثالثة ثانويmohamedNo ratings yet
- Practical Electronics 1970 August (PDFDrive)Document84 pagesPractical Electronics 1970 August (PDFDrive)mohamedNo ratings yet
- Elfrink Fuel Injection Manual 4th EditionDocument89 pagesElfrink Fuel Injection Manual 4th EditionmohamedNo ratings yet
- WEBER Carburatori Tuning ManualDocument64 pagesWEBER Carburatori Tuning ManualmohamedNo ratings yet
- Woko Manual de OperaçãoDocument12 pagesWoko Manual de OperaçãoRicardo Fernandes Sales100% (1)
- Wireless Data and Voice Communication Through Infra-Red LEDDocument25 pagesWireless Data and Voice Communication Through Infra-Red LEDManisha SafayaNo ratings yet
- 90294-1.04 Flyer mini-ATOSDocument2 pages90294-1.04 Flyer mini-ATOSRanderson MoraisNo ratings yet
- Summary Switches DevicesDocument3 pagesSummary Switches DevicesmoriNo ratings yet
- Bosch PSB 6000 ReDocument18 pagesBosch PSB 6000 ResysvNo ratings yet
- Circuit Theory - Solved Assignments - Spring 2009Document33 pagesCircuit Theory - Solved Assignments - Spring 2009Muhammad UmairNo ratings yet
- Kaust Repository: Micromachined On-Chip Dielectric Resonator Antenna Operating at 60 GHZDocument9 pagesKaust Repository: Micromachined On-Chip Dielectric Resonator Antenna Operating at 60 GHZm_sushil29No ratings yet
- Operation Manual: MA-3800KIIDocument12 pagesOperation Manual: MA-3800KIIhim neNo ratings yet
- Overcurrent Protection Study For A Power Network PDFDocument132 pagesOvercurrent Protection Study For A Power Network PDFprathap394No ratings yet
- TP Job Information Sheets Aug - Jan - I PDFDocument365 pagesTP Job Information Sheets Aug - Jan - I PDFMohan kumar G100% (1)
- ElectrochemistryDocument91 pagesElectrochemistryShivam TachaleNo ratings yet
- Apc Materials PropertiesDocument2 pagesApc Materials PropertiesShaneNo ratings yet
- Lab 5 - BJT As InverterDocument3 pagesLab 5 - BJT As InverterKamal ChapagainNo ratings yet
- Agfeo K Modul 544 0076Document12 pagesAgfeo K Modul 544 0076Francisco GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Experiment III Transmission LinesDocument10 pagesExperiment III Transmission LinesJoseGarciaRuizNo ratings yet
- EPsolar Product CatalogueDocument29 pagesEPsolar Product CatalogueilhamNo ratings yet
- PMU261110Document4 pagesPMU261110Muhammad NomanNo ratings yet
- Logic Circuit Gates Design Using Organic P-Type Material Based Thin-Film TransistorsDocument6 pagesLogic Circuit Gates Design Using Organic P-Type Material Based Thin-Film TransistorsiamnurentsquareNo ratings yet
- What Is A Buck Boost ConverterDocument4 pagesWhat Is A Buck Boost ConverterXavierNo ratings yet
- Problem Set 1Document2 pagesProblem Set 1Biswajit BeheraNo ratings yet
- fdc2212 q1Document60 pagesfdc2212 q1lolikNo ratings yet
- B737CL Electrical PowerDocument30 pagesB737CL Electrical PowerKenton CharlesNo ratings yet
- JVC 43' LED Smart HD TV LT-43C790 (A) ManualDocument64 pagesJVC 43' LED Smart HD TV LT-43C790 (A) ManualwNo ratings yet
- Network Analysis Practical Viva-Voce QuestionsDocument44 pagesNetwork Analysis Practical Viva-Voce QuestionshksaifeeNo ratings yet
- RectifierDocument4 pagesRectifiertearamisueNo ratings yet
- Am-11.65.030 Kdl32-Mono InstalDocument82 pagesAm-11.65.030 Kdl32-Mono InstalMike Rushe100% (1)
- SmartLiving - Quick GuideDocument2 pagesSmartLiving - Quick GuidegrespanNo ratings yet
- VF-747 UHF RFID Fixed ReaderDocument17 pagesVF-747 UHF RFID Fixed Readerlikhon100No ratings yet
- Sensors-and-Measurements ApplicationDocument1 pageSensors-and-Measurements ApplicationAll Engineering ElectronicsNo ratings yet
- EX600 Profibus DPDocument87 pagesEX600 Profibus DPalberto240174No ratings yet