Chapter 2 Alkanes
Chapter 2 Alkanes
Uploaded by
Shan TiCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 2 Alkanes
Chapter 2 Alkanes
Uploaded by
Shan TiCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Copyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 2 Alkanes
Chapter 2 Alkanes
Uploaded by
Shan TiCopyright:
Available Formats
Centre for Foundation Studies, UTAR
Chapter Scopes FHSC1124 Organic Chemistry Alkanes
Chapter 2 IUPAC Nomenclature / naming Physical properties Free-radical reactions Crude oil and cracking Cycloalkanes
Objectives
After this chapter, you will be able to: Name alkanes using IUPAC Draw the correct structure of simple alkanes Draw/write the product of an organic chemical reaction Understand reactions of alkanes and be able to write out the chemical reactions.
Introduction to Alkanes
Simplest members of hydrocarbon family Paraffins Aliphatic compounds open chain / acyclic compounds General formula of alkanes = CnH2n+2 The names of alkanes end with suffix -ane. Saturated hydrocarbon as only have CC & CH single bonds & contain the max. possible number of H per C.
IUPAC Nomenclature
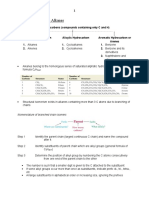
IUPAC International Union of Pure & Applied Chemistry The IUPAC nomenclature system is a set of logical rules devised and used by organic chemists to name the organic compounds. Prefix Parent Suffix What are the How many What family? substituents? carbons?
IUPAC Rules
1. Select the longest continuous C chain as parent chain (use root word for the no. of C) 2. Name each of the branch/substituents as an alkyl / aryl group 3. Number the C chain begin from the end nearest to the branch branch/substituents appear at the lowest no. possible
FHSC1124 ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
Centre for Foundation Studies, UTAR
IUPAC Rules
4. Name each substituent according to its chemical identity & the no. of the C atom to which it is attached For identical substituent, use the prefix di, tri & write appropriate C no. for each substituent 5. Separate no. from no. by commas (,) & no. from letters by hyphens (-) 6. List the substituents alphabetically by name di, tri. dont count
Base Names
Root No. of Name Carbons (n) Meth 1 Eth 2 Prop 3 But 4 Pent 5 Root Name Hex Hept Oct Non Dec No. of Carbons (n) 6 7 8 9 10
Straight-Chain Alkyl Groups, R
Alkyl group Name (abbreviation) Methyl (Me) CH3 Ethyl (Et) CH2CH3 Propyl (Pr) CH2CH2CH3 Butyl (Bu) CH2CH2CH2CH3 Pentyl CH2CH2CH2CH2CH3 Alkyl groups are named by replacing the ane ending of the parent alkane with an yl ending
Example: Naming Alkanes
PHYSICAL PROPERTIES OF ALKANES
Condensed structural formula
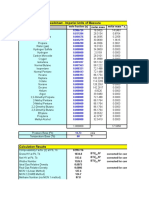
Name Methane Ethane Propane Butane Pentane Hexane Heptane Octane Nonane Decane BP (oC) -161.7 -88.6 -42.2 -0.5 36.1 68.7 98.4 125.6 150.7 174.0 MP (oC) State at 25oC Density -182.6 Gas 0.424 -172.0 Gas 0.546 -187.1 Gas 0.582 -135.0 Gas 0.579 -129.7 Liquid 0.626 -94.0 Liquid 0.659 -90.5 Liquid 0.684 -56.8 Liquid 0.703 -53.7 Liquid 0.718 -29.7 Liquid 0.730
Carbon skeleton
1 2 3 4 5 6
1. Longest continuous C chain is 6 hex 2. All C & H with single bonds ane 3. Parent name: hexane 4. Two methyl groups on 2nd C & 5th C dimethyl 5. Use 2,5-dimethylhexane
FHSC1124 ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
Centre for Foundation Studies, UTAR
Boiling Points of Alkanes
Alkanes have relatively low bp (e.g.: methane bp~ -161 oC) because: Alkanes are ____________ molecules which held by _____________________________. BP of alkanes increase as number of carbon increase because: As the number of C , molecules get ______, Van der Waals forces become ___________ and more energy needed to break the bond
Comparison of BP: Branched-Chain & Straight-Chain
Isomer pentane 2-methylbutane 2,2-dimethylpropane BP (K) 309.2 301.0 282.6
The more branched the chain, the _______ the boiling point tends to be.
Comparison of BP: Branched-Chain & Straight-Chain
The branched-chain isomer will have a lower bp compared to the straight-chain isomer because: Branched-chain alkanes are short, fat & spherical in shape. Thus this reduces the surface area that is exposed to Van der Waals forces. Less energy needed, bp decreases.
Reaction of Alkanes
Combustion / oxidation of Alkanes
Free Radical Halogenation
1. Combustion / Oxidation of Alkanes
Alkanes burn in excess air or O2, to formed CO2 and H2O CxHy +
y x + O 4 2 4
2. Free Radical Halogenation of Alkanes
Alkanes react with chlorine or bromine: When the mixture is heated at 300 400 oC, OR At room temperature under the influence of UV light which act as catalysts.
xCO2 +
4
y 2
H2O
CH4 + 1 + 4 O2 CO2 + 2 H2O CH4 + 2O2 CO2 + 2H2O
XX + Halogens
light / heat X = Br, Cl
X + HX
Haloalkanes / alkyl halides
FHSC1124 ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
Centre for Foundation Studies, UTAR
Chlorination of Methane
Mechanism of Halogenation
Chlorination or bromination of alkanes is by a free-radical substitution mechanism. Involved 3 steps: Step 1: Initiation Step 2: Propagation Step 3: Termination
Mechanism of Halogenation: Step 1: Initiation
Heat or UV light cause the weak halogen bond to undergo ____________ cleavage to generate two bromine radicals and starting the chain process.
Mechanism of Halogenation: Step 2: Propagation
(a) Br radical abstracts a H to form HBr and a methyl radical (b) The methyl radical abstracts a Br atom from another molecule of Br2 to form the methyl bromide and another bromine radical, which can then itself undergo reaction 2(a) creating a cycle that can repeat.
Mechanism of Halogenation: Step 2: Propagation
Mechanism of Halogenation: Step 3: Termination
Various reactions between possible pairs of radicals allow the formation of ethane, Br2 or the product, methyl bromide. These reactions remove radicals and do not perpetuate the cycle.
(a)
(b)
FHSC1124 ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
Centre for Foundation Studies, UTAR
Crude Oil / Petroleum
Alkanes occur naturally in petroleum and natural gas. Petroleum, brownish to black liquid, formed from dead organisms that sank to the bottom shallow seas and were subsequently covered by clay & silt. Pressure heating caused by burial changed these organic matter slowly, after million years, to petroleum. Raw petroleum consists of a mixture of hydrocarbon of various sizes separated by distillation before they used.
Cracking of Alkanes
Cracking involves the _____________ of large alkane molecules into a mixture of smaller-sized alkanes and alkenes.
Cracking of Alkanes
Cracking of Alkanes Catalytic Cracking Thermal/Steam Cracking
Catalytic Cracking
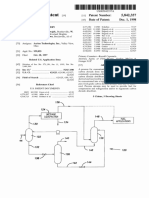
Modern cracking uses zeolites as the _____________. Zeolites = complex aluminosilicates, and are large lattices of aluminium, silicon and oxygen atoms carrying a negative charge. The alkane is brought into contact with the catalyst at a T of about 500 and C moderately low P.
Thermal / Steam Cracking
In thermal cracking, high T (typically in the range of 450 to 750 & P (up to C C) about 70 atm) are used to break the large hydrocarbons into smaller ones. Thermal cracking gives mixtures of products containing high proportions of hydrocarbons with double bonds alkenes.
FHSC1124 ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
Centre for Foundation Studies, UTAR
Cycloalkanes: Cyclic Structures of Alkanes
Halogenation of Cycloalkanes
The reactions of the cycloalkanes are generally just the same as the alkanes, e.g. free radical substitution, oxidation & halogenation.
+ Br2
Br + HBr
Summary
To learn the naming of alkanes Understand reactions of alkanes and be able to write out the chemical reactions.
FHSC1124 ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
You might also like
- Introduction To Organic ChemistryDocument142 pagesIntroduction To Organic ChemistryHafiz Hamidi100% (2)
- Saturated HydrocarbonDocument60 pagesSaturated HydrocarbonMarvin K. Candor100% (2)
- ALKANESDocument10 pagesALKANESJue MayaNo ratings yet
- Topic 2Document32 pagesTopic 2KAI YANG LIMNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry Notes for MBChBDocument66 pagesOrganic Chemistry Notes for MBChBalbertkilonzo4No ratings yet
- Chapter 2 AlkanesDocument61 pagesChapter 2 AlkanesKonoli NuingNo ratings yet
- Org1 Chap2 Saturated HC-ISH-TAB (Feb2023)Document50 pagesOrg1 Chap2 Saturated HC-ISH-TAB (Feb2023)Tapan K LaiNo ratings yet
- 04. HydrocarbonDocument25 pages04. HydrocarbonsoundslikesafuNo ratings yet
- Al KanesDocument9 pagesAl KanesJue MayaNo ratings yet
- Mod 1 Revision Guide Organic2Document6 pagesMod 1 Revision Guide Organic2Saifulahmed49No ratings yet
- Chm457: Fundamental of Organic Chemistry: Alkanes and CycloalkanesDocument97 pagesChm457: Fundamental of Organic Chemistry: Alkanes and CycloalkanesAIMAN IMAN SHAIFUDDIN100% (1)
- CHM 004 AlkaneDocument53 pagesCHM 004 Alkanesamuelosagieainetor11No ratings yet
- 3 - AlkanesDocument34 pages3 - AlkanesSean Gabriel LacambraNo ratings yet
- Alkanes: Draw Out and Name The Structural Isomers of C H and C HDocument7 pagesAlkanes: Draw Out and Name The Structural Isomers of C H and C Hsayma_akhter5074No ratings yet
- CHE 112 - Lecture 2Document103 pagesCHE 112 - Lecture 2Martias WambiNo ratings yet
- Organic Compounds:: - Alkanes 1828: Friedrich Wohler First Synthesized An Organic Compound From An Inorganic SourceDocument30 pagesOrganic Compounds:: - Alkanes 1828: Friedrich Wohler First Synthesized An Organic Compound From An Inorganic SourcePermana PakpahanNo ratings yet
- Revised Organic Chemistry I NotesDocument76 pagesRevised Organic Chemistry I NotesalicegesareNo ratings yet
- Essential Organic Chemistry: An Introduction To Organic CompoundsDocument101 pagesEssential Organic Chemistry: An Introduction To Organic CompoundsJane Limsan PaglinawanNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry - Alkanes: Hydrocarbons (Compounds Containing Only C and H)Document6 pagesOrganic Chemistry - Alkanes: Hydrocarbons (Compounds Containing Only C and H)Jojo LeongNo ratings yet
- Wa0001Document64 pagesWa0001Burhan ButtNo ratings yet
- Alkanes: Draw Out and Name The Structural Isomers of C H and C HDocument7 pagesAlkanes: Draw Out and Name The Structural Isomers of C H and C H897291868No ratings yet
- INTRO To ORGANIC CHEMISTRYDocument60 pagesINTRO To ORGANIC CHEMISTRYNailah KaharNo ratings yet
- Functional Groups and Hydrocarbons: Lecture #2 Melchor Cerdania Dept. of Chemistry, Silliman UniversityDocument45 pagesFunctional Groups and Hydrocarbons: Lecture #2 Melchor Cerdania Dept. of Chemistry, Silliman UniversityGlayzell AltrinnaNo ratings yet
- Organic Compound NomenclatureDocument31 pagesOrganic Compound Nomenclaturetasneem100% (2)
- 02. Aliphatic HydrocarbonsDocument42 pages02. Aliphatic Hydrocarbonsselr3898No ratings yet
- Al KanesDocument32 pagesAl KanesEsther OgelekaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 McmurryDocument26 pagesChapter 3 Mcmurrymuhammad_asim_10No ratings yet
- Session 10. Alkynes of Pharmaceutical ImportanceDocument22 pagesSession 10. Alkynes of Pharmaceutical Importanceharrytonymgaya359No ratings yet
- Aldehydes (Aldehid) & Ketones (Keton)Document29 pagesAldehydes (Aldehid) & Ketones (Keton)Irianto Rizaldi FaturrahmanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3-AlkenesDocument87 pagesChapter 3-AlkenesNURUL BALQIS DZULKIFLINo ratings yet
- Chemistry 30 9.1 9.2 Alkanes PilipchukDocument55 pagesChemistry 30 9.1 9.2 Alkanes Pilipchuksarahlee2608No ratings yet
- 22 Organic FamiliesDocument19 pages22 Organic Familiescivilndlovu13100% (1)
- Organic Chemistry Organic Chemistry: Alkanes Alkanes & & Alkanes Alkanes & & Cycloalkanes CycloalkanesDocument61 pagesOrganic Chemistry Organic Chemistry: Alkanes Alkanes & & Alkanes Alkanes & & Cycloalkanes CycloalkanesRSLNo ratings yet
- As Level Chem1 NotesDocument5 pagesAs Level Chem1 Notesbookman786No ratings yet
- ALKANESDocument20 pagesALKANESLaely INNo ratings yet
- HydrocarbonsDocument28 pagesHydrocarbonsamongus.7624No ratings yet
- Aldehydes and Ketones Lecture NotesDocument12 pagesAldehydes and Ketones Lecture Notesnassirfred2676No ratings yet
- Alkanes & Cycloalkanes: Three Classes of HydrocarbonsDocument20 pagesAlkanes & Cycloalkanes: Three Classes of Hydrocarbonsvxb7vvj9rb100% (1)
- Organic ChemistryDocument24 pagesOrganic ChemistryNivas KaruppananNo ratings yet
- Topic 5a - Introduction To Organic Chemistry Revision Notes: 1) FormulaeDocument5 pagesTopic 5a - Introduction To Organic Chemistry Revision Notes: 1) FormulaeThuvarakaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Alkenes PDFDocument63 pagesChapter 3 - Alkenes PDFSITI NUR ALISSA BINTI AHMAD RASMANNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry CurrentDocument48 pagesOrganic Chemistry CurrentBierzo JomarNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 OrgDocument39 pagesUnit 2 OrgTilahun TesemaNo ratings yet
- Alkanes and Cycloalkanes - ClassDocument16 pagesAlkanes and Cycloalkanes - ClassMartina BugejaNo ratings yet
- Alkanes SlideDocument14 pagesAlkanes Slidevictoryayapaye147No ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry -NamingDocument26 pagesOrganic Chemistry -NamingbnoitaestrellaNo ratings yet
- AlkanesDocument11 pagesAlkanesДмитрий ЛегаNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Organic ChemsitryDocument36 pagesIntroduction To Organic ChemsitryRyanNo ratings yet
- (A) Homologous Series and Functional Group: Chapter 1 Introduction To Organic ChemistryDocument7 pages(A) Homologous Series and Functional Group: Chapter 1 Introduction To Organic ChemistryChristinaNo ratings yet
- Alkanes An Introduction: The Alkanes Are Aliphatic Hydrocarbons Having Only C - CDocument41 pagesAlkanes An Introduction: The Alkanes Are Aliphatic Hydrocarbons Having Only C - CFendi TricksterNo ratings yet
- Alkanes and Cycloalkanes CHM457Document87 pagesAlkanes and Cycloalkanes CHM457AIMAN IMAN SHAIFUDDINNo ratings yet
- Organic Chem CH2 Med Lab.Document150 pagesOrganic Chem CH2 Med Lab.nimonayoseph27No ratings yet
- Lecture 02 Alkane Structures-6119-16921771397377Document62 pagesLecture 02 Alkane Structures-6119-16921771397377Akeanan SroithongmoonNo ratings yet
- Cell Exam QuestionsDocument52 pagesCell Exam QuestionsNabindra RuwaliNo ratings yet
- Alkanes Dr. ShimaaDocument71 pagesAlkanes Dr. Shimaafffaaa21992No ratings yet
- Systematic Nomenclature of AlkanesDocument10 pagesSystematic Nomenclature of AlkanesOliverEmilSkytteGlueNo ratings yet
- Alkanes and Cycloalkanes 2017pptxDocument96 pagesAlkanes and Cycloalkanes 2017pptxEgbebessemenow oben ashuNo ratings yet
- 3.3. Organic Chemistry I-2Document31 pages3.3. Organic Chemistry I-2Cathy Kathy Cathy100% (1)
- Chapter 2 Alkanes - 2Document49 pagesChapter 2 Alkanes - 2farah amaniNo ratings yet
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Organic ChemistryFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Organic ChemistryRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- 0 - Year 2 Lab 1 - Alkanes and Alkenes PersonalDocument6 pages0 - Year 2 Lab 1 - Alkanes and Alkenes Personalakeisha kingNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry Functional GroupDocument79 pagesOrganic Chemistry Functional GroupDumppyNo ratings yet
- Section 3 D6022486 Environmental ProtectionDocument57 pagesSection 3 D6022486 Environmental ProtectionJulianNo ratings yet
- Combustion Engineering-52949589Document23 pagesCombustion Engineering-52949589Justine BoqsNo ratings yet
- EBS Full ReportDocument74 pagesEBS Full ReportEd SalangaNo ratings yet
- Baseline Study of Contaminants in The Swan and Canning Catchment Drainage SystemDocument168 pagesBaseline Study of Contaminants in The Swan and Canning Catchment Drainage SystemJavier Arturo Gaspar PrialéNo ratings yet
- Reviews of Geophysics - 2010 - Kutcherov - Deep Seated Abiogenic Origin of Petroleum From Geological Assessment ToDocument30 pagesReviews of Geophysics - 2010 - Kutcherov - Deep Seated Abiogenic Origin of Petroleum From Geological Assessment ToMuh Zulkarnain SyahNo ratings yet
- AGA5 Calculation-Imperial UnitDocument24 pagesAGA5 Calculation-Imperial UnitlubangjarumNo ratings yet
- محاضرات النفط كاملةDocument180 pagesمحاضرات النفط كاملةOikjng Frdrswa100% (1)
- Saes A 014 PDFDocument20 pagesSaes A 014 PDFSuman TamilselvanNo ratings yet
- Lecture - 1-Petroleum Composition and ProductsDocument34 pagesLecture - 1-Petroleum Composition and Productsmuhammad.ali.shehzad22No ratings yet
- Alkene Exercise Eng Module-4Document21 pagesAlkene Exercise Eng Module-4Raju SinghNo ratings yet
- Sylhet Gas Fields Limited (SGFL) : Natural Gas Processing at Molecular Sieve Turbo Expander (MSTE) Plant of SGFLDocument80 pagesSylhet Gas Fields Limited (SGFL) : Natural Gas Processing at Molecular Sieve Turbo Expander (MSTE) Plant of SGFLRafsan Bin Sorwar100% (3)
- Nordstrom Valves: Sealants and Sealant EquipmentDocument12 pagesNordstrom Valves: Sealants and Sealant EquipmentHrushikesh ReddyNo ratings yet
- CH Test f4Document5 pagesCH Test f4cazmi AndirahmanNo ratings yet
- United States Patent: 73 Assignee: Acrion Technologies, Inc., Valley View, 3. E. em (I. R35Document10 pagesUnited States Patent: 73 Assignee: Acrion Technologies, Inc., Valley View, 3. E. em (I. R35jeremyhoveNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry Foundation Revision Activity MatDocument2 pagesOrganic Chemistry Foundation Revision Activity MatHồng Ngọc VõNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Jan 2023 Paper 2 Non-Regional Marking SchemeDocument12 pagesChemistry Jan 2023 Paper 2 Non-Regional Marking SchemeKenzyNo ratings yet
- Guess Paper of Chemistry 10 Class: M.Cqs. 1X12 Short - Qs. 15/24 15X2 Long Q 2/3 2X9Document3 pagesGuess Paper of Chemistry 10 Class: M.Cqs. 1X12 Short - Qs. 15/24 15X2 Long Q 2/3 2X9ADLG Layyah100% (1)
- CB426: Petroleum Refinery & Petrochemicals: LTPC 3-0-0-6Document136 pagesCB426: Petroleum Refinery & Petrochemicals: LTPC 3-0-0-6Ujjwal AnandNo ratings yet
- Facts at Your Fingertips-48-60Document13 pagesFacts at Your Fingertips-48-60Aatish ChandrawarNo ratings yet
- # 4 and 7 Distillation (1 &2) (Compatibility Mode)Document141 pages# 4 and 7 Distillation (1 &2) (Compatibility Mode)jesiNo ratings yet
- Mineral Base Oils: E-Books Download Weblog: Water Engineering WeblogDocument5 pagesMineral Base Oils: E-Books Download Weblog: Water Engineering WeblogalbertofgvNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Propylene Concentrates: Standard Guide ForDocument4 pagesAnalysis of Propylene Concentrates: Standard Guide ForahmedNo ratings yet
- Modern Chemistry Chapter 4 Homework 4-8Document6 pagesModern Chemistry Chapter 4 Homework 4-8afmcuafnh100% (1)
- Air Quality:: Definitions, Characteristics, and PerspectivesDocument37 pagesAir Quality:: Definitions, Characteristics, and Perspectives^nana^No ratings yet
- Science: The Carbon Compounds and Chemical BondsDocument19 pagesScience: The Carbon Compounds and Chemical BondsAnnie Bagalacsa Cepe-Teodoro100% (1)
- Industrial ProcessDocument64 pagesIndustrial Processgm0047No ratings yet
- EFuel ReportDocument52 pagesEFuel ReportMassimiliano ZocchiNo ratings yet
- STPM Sem 3 Chemistry Note - Chapter AlkanesDocument21 pagesSTPM Sem 3 Chemistry Note - Chapter AlkanesSTPMBAHARU100% (3)