0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
25 viewsWhat Is Data Analytics
What Is Data Analytics
Uploaded by
asila.edu2021Data analytics is the process of extracting useful insights from data to help make better business decisions. It involves manipulating data to identify trends and patterns. There are four main types: predictive analytics which uses data to forecast outcomes; descriptive analytics which analyzes past data; prescriptive analytics which suggests actions based on predictions; and diagnostic analytics which uses historical data to solve problems. Data analytics can benefit many domains like improving decision-making, customer service, operations, and marketing. It has future applications in retail, healthcare, finance, manufacturing, and transportation.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
What Is Data Analytics
What Is Data Analytics
Uploaded by
asila.edu20210 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
25 views3 pagesData analytics is the process of extracting useful insights from data to help make better business decisions. It involves manipulating data to identify trends and patterns. There are four main types: predictive analytics which uses data to forecast outcomes; descriptive analytics which analyzes past data; prescriptive analytics which suggests actions based on predictions; and diagnostic analytics which uses historical data to solve problems. Data analytics can benefit many domains like improving decision-making, customer service, operations, and marketing. It has future applications in retail, healthcare, finance, manufacturing, and transportation.
Original Title
What is Data Analytics
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Data analytics is the process of extracting useful insights from data to help make better business decisions. It involves manipulating data to identify trends and patterns. There are four main types: predictive analytics which uses data to forecast outcomes; descriptive analytics which analyzes past data; prescriptive analytics which suggests actions based on predictions; and diagnostic analytics which uses historical data to solve problems. Data analytics can benefit many domains like improving decision-making, customer service, operations, and marketing. It has future applications in retail, healthcare, finance, manufacturing, and transportation.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
25 views3 pagesWhat Is Data Analytics
What Is Data Analytics
Uploaded by
asila.edu2021Data analytics is the process of extracting useful insights from data to help make better business decisions. It involves manipulating data to identify trends and patterns. There are four main types: predictive analytics which uses data to forecast outcomes; descriptive analytics which analyzes past data; prescriptive analytics which suggests actions based on predictions; and diagnostic analytics which uses historical data to solve problems. Data analytics can benefit many domains like improving decision-making, customer service, operations, and marketing. It has future applications in retail, healthcare, finance, manufacturing, and transportation.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 3
What is Data Analytics?
In this new digital world, data is being generated in an enormous amount which opens new paradigms.
As we have high computing power as well as a large amount of data we can make use of this data to
help us make data-driven decision making. The main benefits of data-driven decisions are that they are
made up by observing past trends which have resulted in beneficial results.
In short, we can say that data analytics is the process of manipulating data to extract useful trends and
hidden patterns which can help us derive valuable insights to make business predictions.
Use of Data Analytics
There are some key domains and strategic planning techniques in which the Data ANlaytics has played
a very important role:
Improved Decision-Making – If we will have supporting data in favor of a decision that then
we will be able to implement them with even more success probability. For example, if a
certain decision or plan has to lead to better outcomes then there will be no doubt in
implementing them again.
Better Customer Service – Churn modeling is the best example of this in which we try to
predict or identify what leads to customer churn and change those things accordingly so, that
the attrition of the customers is as low as possible which is a most important factor in any
organization.
Efficient Operations – Data Analytics can help us understand what is the demand of the
situation and what should be done to get better results then we will be able to streamline our
processes which in turn will lead to efficient operations.
Effective Marketing – Market segmentation techniques have been implemented to target this
important factor only in which we are supposed to find the marketing techniques which will
help us increase our sales and leads to effective marketing strategies.
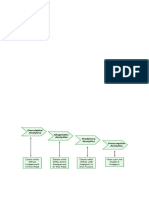
Types of Data Analytics
There are four major types of data analytics:
1. Predictive (forecasting)
2. Descriptive (business intelligence and data mining)
3. Prescriptive (optimization and simulation)
4. Diagnostic analytics
Predictive Analytics
Predictive analytics turn the data into valuable, actionable information. predictive analytics uses data to
determine the probable outcome of an event or a likelihood of a situation occurring. Predictive
analytics holds a variety of statistical techniques from modeling, machine learning, data mining,
and game theory that analyze current and historical facts to make predictions about a future
event. Techniques that are used for predictive analytics are:
Linear Regression
Time Series Analysis and Forecasting
Data Mining
Basic Corner Stones of Predictive Analytics
Predictive modeling
Decision Analysis and optimization
Transaction profiling
Descriptive Analytics
Descriptive analytics looks at data and analyze past event for insight as to how to approach future
events. It looks at past performance and understands the performance by mining historical data to
understand the cause of success or failure in the past. Almost all management reporting such as sales,
marketing, operations, and finance uses this type of analysis.
The descriptive model quantifies relationships in data in a way that is often used to classify customers
or prospects into groups. Unlike a predictive model that focuses on predicting the behavior of a single
customer, Descriptive analytics identifies many different relationships between customer and product.
Common examples of Descriptive analytics are company reports that provide historic reviews
like:
Data Queries
Reports
Descriptive Statistics
Data dashboard
Prescriptive Analytics
Prescriptive Analytics automatically synthesize big data, mathematical science, business rule, and
machine learning to make a prediction and then suggests a decision option to take advantage of the
prediction.
Prescriptive analytics goes beyond predicting future outcomes by also suggesting action benefits from
the predictions and showing the decision maker the implication of each decision option. Prescriptive
Analytics not only anticipates what will happen and when to happen but also why it will happen.
Further, Prescriptive Analytics can suggest decision options on how to take advantage of a future
opportunity or mitigate a future risk and illustrate the implication of each decision option.
For example, Prescriptive Analytics can benefit healthcare strategic planning by using analytics to
leverage operational and usage data combined with data of external factors such as economic data,
population demography, etc.
Diagnostic Analytics
In this analysis, we generally use historical data over other data to answer any question or for the
solution of any problem. We try to find any dependency and pattern in the historical data of the
particular problem.
For example, companies go for this analysis because it gives a great insight into a problem, and they
also keep detailed information about their disposal otherwise data collection may turn out individual
for every problem and it will be very time-consuming. Common techniques used for Diagnostic
Analytics are:
Data discovery
Data mining
Correlations
Future Scope of Data Analytics
1. Retail: To study sales patterns, consumer behavior, and inventory management, data analytics
can be applied in the retail sector. Data analytics can be used by retailers to make data-driven
decisions regarding what products to stock, how to price them, and how to best organize their
stores.
2. Healthcare: Data analytics can be used to evaluate patient data, spot trends in patient health,
and create individualized treatment regimens. Data analytics can be used by healthcare
companies to enhance patient outcomes and lower healthcare expenditures.
3. Finance: In the field of finance, data analytics can be used to evaluate investment data, spot
trends in the financial markets, and make wise investment decisions. Data analytics can be used
by financial institutions to lower risk and boost the performance of investment portfolios.
4. Marketing: By analyzing customer data, spotting trends in consumer behavior, and creating
customized marketing strategies, data analytics can be used in marketing. Data analytics can be
used by marketers to boost the efficiency of their campaigns and their overall impact.
5. Manufacturing: Data analytics can be used to examine production data, spot trends in
production methods, and boost production efficiency in the manufacturing sector. Data
analytics can be used by manufacturers to cut costs and enhance product quality.
6. Transportation: To evaluate logistics data, spot trends in transportation routes, and improve
transportation routes, the transportation sector can employ data analytics. Data analytics can
help transportation businesses cut expenses and speed up delivery times.
You might also like
- IKEA Catalogue 2012Document189 pagesIKEA Catalogue 2012nguyễn thăng vănNo ratings yet
- Cor Vision PlusDocument224 pagesCor Vision PlusAndrei Ivanov67% (3)
- Module 2 Data Analytics and Its TypeDocument9 pagesModule 2 Data Analytics and Its Typerrrf0813No ratings yet
- Unit 2 DSDocument30 pagesUnit 2 DSb3952355No ratings yet
- 1overview of Data AnalysisDocument3 pages1overview of Data AnalysisDivya PrasoonaNo ratings yet
- AnalyticsDocument7 pagesAnalyticsdhairya jainNo ratings yet
- The Role of Data Analytics in Decision Making Process Within Information SystemsDocument11 pagesThe Role of Data Analytics in Decision Making Process Within Information Systemswm364740No ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Big Data & Business Analytics - Assignment - Dec - 2022Document10 pagesFundamentals of Big Data & Business Analytics - Assignment - Dec - 2022Nilesh SatoseNo ratings yet
- 002 - Discover Data Analysis - Overview of Data AnalysisDocument4 pages002 - Discover Data Analysis - Overview of Data AnalysisNeeraj KumarNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Business AnalyticsDocument9 pagesIntroduction To Business AnalyticsTulasiram KandulaNo ratings yet
- Business Analytics IntroductionDocument37 pagesBusiness Analytics IntroductionTejash GannabattulaNo ratings yet
- Business AnalyticsDocument9 pagesBusiness AnalyticsSeven LyxNo ratings yet
- AnalysisDocument4 pagesAnalysisshivamjana40No ratings yet
- Business AnalyticsDocument5 pagesBusiness AnalyticsJake Justine EstoyaNo ratings yet
- Big DataDocument17 pagesBig DataHimanshi YadavNo ratings yet
- BA AssignmentDocument22 pagesBA AssignmentKutty Karthi003No ratings yet
- Unit 1Document18 pagesUnit 1Gaurav SinghNo ratings yet
- Ba Unit 1aDocument18 pagesBa Unit 1areshmibiotechNo ratings yet
- 1 Discover Data AnalysisDocument16 pages1 Discover Data AnalysisJYNo ratings yet
- Data AnalyticsDocument11 pagesData AnalyticsAnonymous X8QppCPYI100% (3)
- The Two-Minute Guide To Understanding and Selecting The Right Descriptive, Predictive, and Prescriptive AnalyticsDocument6 pagesThe Two-Minute Guide To Understanding and Selecting The Right Descriptive, Predictive, and Prescriptive AnalyticsAnonymous f8tAzEb3oNo ratings yet
- 0.introduction To Data AnalyticsDocument6 pages0.introduction To Data Analyticsit21047No ratings yet
- Big Data ApplicationsDocument5 pagesBig Data ApplicationsMohammad KhadeerNo ratings yet
- What Are Different Models of Data AnalysisDocument9 pagesWhat Are Different Models of Data Analysiskin bhNo ratings yet
- Baproduct DevelopmentDocument80 pagesBaproduct Developmentvijay tonnyNo ratings yet
- The Importance of Big Data AnalyticsDocument3 pagesThe Importance of Big Data AnalyticsSuat KamberiNo ratings yet
- Offers Data To Managers Who Help Them To Make Successful Decisions Based On Fundamental Values Rather Than IntuitionsDocument2 pagesOffers Data To Managers Who Help Them To Make Successful Decisions Based On Fundamental Values Rather Than Intuitionssssmitali53No ratings yet
- Analytics and ForecastingDocument15 pagesAnalytics and ForecastingFelix AndohNo ratings yet
- Classification of Big Data AnalyticsDocument13 pagesClassification of Big Data Analyticssanthosh02anandhanNo ratings yet
- Education - Power BiDocument76 pagesEducation - Power Biashwinikr2011100% (1)
- Unit 2Document9 pagesUnit 2Gaurav SinghNo ratings yet
- Mba III Unit I NotesDocument9 pagesMba III Unit I Notesastha shuklaNo ratings yet
- Data AnalyticsDocument16 pagesData AnalyticsRyan FabianNo ratings yet
- Mid 1Document13 pagesMid 1Haritha T.No ratings yet
- Advanced Data AnalyticsDocument54 pagesAdvanced Data Analyticsprincessrevathi25No ratings yet
- Data AnalysisDocument17 pagesData Analysisolabisiesther83No ratings yet
- Power BI - NotesDocument13 pagesPower BI - Notesborade.vijayNo ratings yet
- UNIT-1 Data AnalyticsDocument37 pagesUNIT-1 Data AnalyticsSarfirey GamersNo ratings yet
- Your Modern Business Guide To Data Analysis Methods and Techniques by Bernardita Calzon (2021)Document21 pagesYour Modern Business Guide To Data Analysis Methods and Techniques by Bernardita Calzon (2021)Maria Elliane Querubin RosalesNo ratings yet
- Business Analytics Handout Using Excel 6thDocument12 pagesBusiness Analytics Handout Using Excel 6thPriyanka kumariNo ratings yet
- Prescriptive AnalyticsDocument7 pagesPrescriptive AnalyticsA KarthikeyanNo ratings yet
- Business Analytics CIADocument3 pagesBusiness Analytics CIAJohan PeterNo ratings yet
- Ims-911 Unit-1Document6 pagesIms-911 Unit-1Shanky GujjarNo ratings yet
- What Is Data AnalyticsDocument3 pagesWhat Is Data AnalyticsFatima WahlaNo ratings yet
- Data AnalyticsDocument13 pagesData Analyticsveda shreeNo ratings yet
- Data AnalysisDocument34 pagesData AnalysisDigital CoachingNo ratings yet
- Assignment Sta101Document5 pagesAssignment Sta101SporshoSahaNo ratings yet
- Business AnalyticsDocument10 pagesBusiness AnalyticsDana E. Aranas100% (1)
- 1.0 Business AnalyticsDocument8 pages1.0 Business Analyticsstudent 13No ratings yet
- Big Data Analytics Nep Sem 2 23-24Document15 pagesBig Data Analytics Nep Sem 2 23-24Ganesh PandeyNo ratings yet
- Santhosh AirtcelDocument76 pagesSanthosh Airtcelgeyashnagendhra3465No ratings yet
- AnalyticsDocument3 pagesAnalyticsmishraavinash1025No ratings yet
- Unit-5 Concept of Business AnalyticsDocument45 pagesUnit-5 Concept of Business AnalyticsUP 16 GhaziabadNo ratings yet
- Unit 2Document15 pagesUnit 2shashwat singhNo ratings yet
- Ba Unit 1Document13 pagesBa Unit 1Arunim YadavNo ratings yet
- Module 1Document49 pagesModule 1ambika venkateshNo ratings yet
- Business Analytics-UNIt 1 ReDocument18 pagesBusiness Analytics-UNIt 1 Remayank.rockstarmayank.singh100% (1)
- Business Analytics Model Unit 2Document11 pagesBusiness Analytics Model Unit 2alagumurugan870No ratings yet
- MJV - Business AnalyticsDocument36 pagesMJV - Business AnalyticsJorge SequeiraNo ratings yet
- Types of Analytics: What Is Descriptive Analytics?Document3 pagesTypes of Analytics: What Is Descriptive Analytics?Edgar ElgortNo ratings yet
- Bussiness AnalyticsDocument17 pagesBussiness AnalyticsAbby NavarroNo ratings yet
- Atomic Absorption Spectroscopy - University NotesDocument29 pagesAtomic Absorption Spectroscopy - University NotesLilac44No ratings yet
- 1st Prelim EconDocument3 pages1st Prelim Econmharjun lampaNo ratings yet
- JASO 4 Stroke Motorcycle Engine Oil Code List 2014Document35 pagesJASO 4 Stroke Motorcycle Engine Oil Code List 20146zjptk1okNo ratings yet
- CityU Acct 23/24 Study PlanDocument1 pageCityU Acct 23/24 Study PlanCHUN HEI LUKNo ratings yet
- Questionnaire SampleDocument2 pagesQuestionnaire SampleEkky CecilNo ratings yet
- Unikrn Bermuda LTD Terms of Token Sale Last Updated: September 22, 2017Document20 pagesUnikrn Bermuda LTD Terms of Token Sale Last Updated: September 22, 2017Rony PatahNo ratings yet
- Pretest Posttest AssignmentDocument12 pagesPretest Posttest AssignmentAbdirahmanNo ratings yet
- PDFDocument15 pagesPDFHina Sahar100% (1)
- Trichomonas Vaginalis: Frothy DischargeDocument9 pagesTrichomonas Vaginalis: Frothy DischargeeurocoupeNo ratings yet
- Suy Sing Offerings 2021 WSDocument2 pagesSuy Sing Offerings 2021 WSJayvee BayaniNo ratings yet
- ZyEl 4.5Document42 pagesZyEl 4.5Dan PNo ratings yet
- Beginner Guide For Primavera Part 1Document6 pagesBeginner Guide For Primavera Part 1meshmeshNo ratings yet
- Sony Hcd-gx45 Rg440 Ver-1.2Document78 pagesSony Hcd-gx45 Rg440 Ver-1.2Mario GalvezNo ratings yet
- Acute PancreatitisDocument2 pagesAcute PancreatitisLanh TangcongNo ratings yet
- LaajVanti EbookDocument179 pagesLaajVanti EbookSridhar YvNo ratings yet
- P Block ElementsDocument16 pagesP Block Elementsprakharsample150% (1)
- HR Metrics and Workforce AnalyticsDocument58 pagesHR Metrics and Workforce AnalyticsMuhammad Akmal Hossain100% (1)
- Sustainable Use of Resources - Grade 9Document9 pagesSustainable Use of Resources - Grade 9Tina MoyeniNo ratings yet
- Early Civilizations in China: Powerpoint By: Esther LeeDocument17 pagesEarly Civilizations in China: Powerpoint By: Esther LeeLee EstherNo ratings yet
- Dabur IndiaDocument24 pagesDabur IndiaSauabh Srivastava100% (2)
- De Thi Giao Luu Hoc Sinh Gioi Cap Tinh Mon Tieng Anh 9 Nam 2018 2019 Co Dap An So GD DT Thanh HoaDocument7 pagesDe Thi Giao Luu Hoc Sinh Gioi Cap Tinh Mon Tieng Anh 9 Nam 2018 2019 Co Dap An So GD DT Thanh HoavietanhnotgayNo ratings yet
- mmf2 Develop HelpDocument187 pagesmmf2 Develop HelpStelios LafazanisNo ratings yet
- Physics Experiment Report (Iv) Basic Physics "Oscillation Mathematics"Document8 pagesPhysics Experiment Report (Iv) Basic Physics "Oscillation Mathematics"JkanthNo ratings yet
- Economical Metal Anchor For Drywall and Hollow BlockDocument3 pagesEconomical Metal Anchor For Drywall and Hollow BlockPedro LanuzaNo ratings yet
- Quiz Exercises 9 Reported Speech 9Document2 pagesQuiz Exercises 9 Reported Speech 9Joséphine NancasseNo ratings yet
- KatarakDocument30 pagesKatarakdokter mudaNo ratings yet
- Parkin 13ge Econ IMDocument10 pagesParkin 13ge Econ IMDina SamirNo ratings yet
- A Level Seminar ReadyDocument16 pagesA Level Seminar ReadyOnesmus GumisirizaNo ratings yet