D - Absorption and Variable Costing
D - Absorption and Variable Costing
Uploaded by
ian dizonCopyright:
Available Formats
D - Absorption and Variable Costing
D - Absorption and Variable Costing
Uploaded by
ian dizonCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Copyright:
Available Formats
D - Absorption and Variable Costing
D - Absorption and Variable Costing
Uploaded by
ian dizonCopyright:
Available Formats
1/5
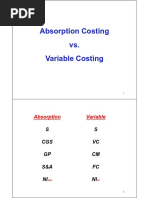
Absorption and Variable Costing
Absorption Costing Variable Costing
Full Costing Other Names Direct Costing
GAAP Costing Marginal Costing
External Reporting Purpose Internal Reporting
Product Cost Treatment of Fixed FOH Period Cost
Initially inventoried then expensed (FFOH) Fully expensed in the period
as part of CGS when sold incurred regardless if units are
sold or not
FFOH is necessary to produce Reason FFOH is incurred with or without
units production
DM, DL, VFOH, and FFOH Product Cost DM, DL, and VFOH
Higher than VC Lower than AC
Selling and GAE Period Cost FFOH, Selling, and GAE
Lower than AC
Seldom segregates costs into
variable and fixed costs 24
Cost Segregation
Higher than VC
Segregates costs into variable
and fixed costs
20
Compliant Matching Principle Non-compliant
Compliance
Functional (Product vs. Period) Behavioral (Variable vs. Fixed)
CGS Format CM Format
Sales xx Sales xx
h
CGS (xx) Income Statement Format Variable (xx)
GP xx CM xx
tc
OE (xx) Fixed (xx)
Profit xx Profit xx
Profit is influenced by production Profit fluctuates with sales
Ba
Financial Statements CVP Analysis
Reporting to BIR and SEC Uses Pricing Decisions
Relevant Costing
Absorption Costing Profit vs. Variable Costing Profit
Situation Implication Explanation
P=S ACP = VCP End Inv = Beg Inv thus FFOH in AC = FFOH in VC
P>S ACP > VCP End Inv > Beg Inv thus FFOH in AC < FFOH in VC
P<S ACP < VCP End Inv < Beg Inv thus FFOH in AC > FFOH in VC
Where: P - Production; S - Sales; ACP - Absorption Costing Profit; VCP - Variable Costing Profit
Management Services College of Business Studies
D - Absorption and Variable Costing Don Honorio Ventura State University
2/5
Accounting for Difference in Profit
The difference in profit represents the amount of fixed factory overhead charged to inventory (treated
as asset).
Δ Profit = Δ Inventory x Unit FFOH
Where: Δ Profit = ACP - VCP
Δ Inventory = Ending Inventory - Beginning Inventory / Production - Sales
Unit FFOH = Total FOH ÷ Production / AC Cost per Unit - VC Cost per Unit
Reconciliation of ACP and VCP
Absorption Costing Profit xx
ADD: Fixed FOH in the Beginning Inventory xx
LESS: Fixed FOH in the Ending Inventory (xx)
Variable Costing Profit xx
Problem I
In 2022, UST company’s production was equal to its normal capacity of 1,000 units. It
sold 900 units at a price of P 50 per unit. The following costs were incurred during that
year:
Direct Materials
Direct Labor
Variable FOH
Fixed FOH
P
24
Total Cost
12,000
10,000
8,000
6,000
P
Unit Cost
12
10
8
6
20
Variable Selling & Admin 4,500 5 (4,500 ÷ 900 units sold)
Fixed Selling & Admin 3,000 3
Units Sold 900 units
Determine the following:
1. Product cor per unit under absorption and variable costing.
h
2. Fixed factory overhead per unit.
3. Income under absorption costing.
tc
4. Income under variable costing.
5. Amount of fixed factory overhead charged to inventory.
6. Cost of the ending inventory - absorption.
7. Cost of the ending inventory - variable.
Ba
Problem II
UST produced and sold 12,000 units of a product. Manufacturing and selling costs
incurred were:
Prime Cost P480,000
Variable FOH 108,000
Fixed FOH 24,000
Variable Selling 12,000
1. The product’s unit cost under absorption costing was ______.
2. The product’s unit cost under variable costing was ______.
Management Services College of Business Studies
D - Absorption and Variable Costing Don Honorio Ventura State University
3/5
Problem III
UST began its operations on January 01, 2022. It produces a single product that sells
for P13.50 per unit. The company uses an actual (historical) cost system. During 2022,
150,000 units were produced and 135,000 units were sold. There was no WIP on
December 31, 2022. The cost data of the company were:
Raw Materials - 3.50 per unit produced
Direct Labor - 2.50 per unit produced
Factory Overhead P195,000 1.00 per unit produced
Selling and Administrative 140,000 1.20 per unit sold
1. What is the profit of UST under absorption costing?
2. What is the profit of UST under variable costing?
3. What is the amount of fixed factory overhead charged to inventory?
4. Prepare a reconciliation of the absorption costing and variable costing profits.
5. The cost of ending inventory under the two costing methods were _____ and ____.
Problem IV
UST’s records for the year 2022 show the following data:
Net Sales
Variable Production Cost
Fixed Production Cost
Variable Operating Expense
24
P21,000
9,450
4,725
1,470
Fixed Operating Expense
Units Sold
Units Produced
2,100
6,000 units
7,000 units
20
There was no beginning and ending WIP inventory. Also, there was no beginning FG
inventory.
1. The ending finished goods inventory under absorption costing is _______.
2. The ending finished goods inventory under variable costing is _______.
3. The profit under absorption costing is _______.
h
4. The profit under variable costing is _______.
tc
Other Product Costing Methods
1. Super Variable Costing (Throughput Costing): treats direct materials as the only
variable cost.
Ba
a. Only direct material costs are inventoried. All other costs are expensed
when incurred.
b. WIP and FG are not recorded.
c. It results in lower income than variable costing when production > sales.
d. It penalizes high production and rewards low production.
Sales xx
Direct Materials (xx)
Throughput Margin xx
Other Expenses (xx)
Profit xx
2. Super Absorption Costing: treats costs from all links in the value chain as
inventoriable costs.
Management Services College of Business Studies
D - Absorption and Variable Costing Don Honorio Ventura State University
4/5
Problem V
UST sells its products at P120 per unit. It has a material cost per unit of P30 and
conversion cost of P50 per unit. In 2022, it produced 500 units and sold ¾ of the said
production. It also incurred administrative expenses of P2,000.
Determine the following
1. Profit of UST if it uses throughput costing method.
2. Profit of UST if it uses the super absorption costing method.
3. Cost of ending inventory of UST if it uses throughput costing method.
4. Cost of ending inventory of UST if it uses the super absorption costing method.
Multiple-Choice Questions
1. Which of the following is a product cost under absorption costing but not under variable
costing?
a. Variable marketing costs c. Variable manufacturing costs
b. Fixed marketing costs d. Fixed manufacturing costs
2. Under absorption costing, fixed manufacturing overhead costs are best
described as
a. Direct period costs
b. Direct product costs
3. Under variable costing,
24 c. Indirect period costs
d. Indirect product costs
20
a. All period costs are fixed c. All product costs are fixed
b. All period costs are variable d. All product costs are variable
4. As compared to variable costing inventory cost, inventory cost under absorption
costing is typically
a. Lower
h
b. The same c. Higher
d. The same or lower
Items 5 to 7 are based on the following information:
tc
UST manufactures a single product. Unit variable production costs are P 20 and fixed
production costs are P 150,000. UST uses a normal activity of 10,000 units. UST began
the year with no inventory, produced 12,000 units, and sold 7,500 units.
Ba
5. How much is the unit product cost under variable costing?
a. P 20.00 c. P 32.50
b. P 35.00 d. P 40.00
6. How much is the unit product cost under absorption costing?
a. P 20.00 c. P 32.50
b. 35.00 d. P 40.00
7. What is the volume or capacity variance under absorption costing?
NOTE: volume variance = (actual production – normal production) x unit FFOH
a. P 24,000 unfavorable c. P 24,000 favorable
b. P 30,000 unfavorable d. P 30,000 favorable
8. If production is higher than sales, then absorption costing profit is expected to be
a. Lower than variable costing profit
b. Equal to the variable costing profit
c. Higher than variable costing profit
d. Incomparable with variable costing profit
Management Services College of Business Studies
D - Absorption and Variable Costing Don Honorio Ventura State University
5/5
9. UST produced 10,000 units and sold 9,000 units. Fixed manufacturing overhead
costs were P20,000, and variable manufacturing overhead costs were P 3 per
unit. Which of the following best describes the profit under the absorption
costing method?
a. P 2,000 less than profit under variable costing method
b. P 5,000 less than profit under variable costing method
c. P 2,000 more than profit under variable costing method
d. P 5,000 more than profit under variable costing method
10. If ending inventory is higher than beginning inventory, then absorption costing
profit is expected to be
a. Lower than variable costing profit
b. Equal to the variable costing profit
c. Higher than variable costing profit
d. Incomparable with variable costing profit
11. UST has an operating income of P 50,000 under direct costing. Beginning and
ending inventories were 13,000 units and 18,000 units, respectively. If the fixed
factory overhead application rate is P 2 per unit, then what is the operating
income under the absorption costing?
a. P 70,000 c. P 60,000
b. P 50,000
24 d. P 40,000
12. UST had 16,000 units in its beginning inventory. The company’s variable
production costs were P 6 per unit and its fixed manufacturing overhead costs
were P 4 per unit. The company’s net income for the year was P 24,000 lower
20
under absorption costing than it was under variable costing. How many units
does the company have in its ending inventory?
a. 22,000 units c. 10,000 units
b. 6,000 units d. 4,000 units
13. UST had a net income of P 90,000 using variable costing and net income of P
h
85,500 using absorption costing. Total fixed manufacturing overhead cost was P
150,000 and production was 100,000 units. How did the inventory level change
tc
during the year?
a. 3,000 units increase c. 3,000 units decrease
b. 500 units increase d. 4,500 units decrease
Ba
14. Variable costing profit fluctuates with (A) ____ and does not react to changes in
(B) ____.
a. (A) sales (B) production c. (A) production (B) sales
b. (A) sales (B) demand d. (A) production (B) supply
15. Variable costing is unacceptable for
a. Financial reporting d. Short-term decision making
b. Transfer pricing
c. CVP analysis
References:
1. Roque, R. S. Reviewer in Management Advisory Services (2016). GIC Enterprises & Co., Inc.
2. Review Materials from Review School of Accountancy
Management Services College of Business Studies
D - Absorption and Variable Costing Don Honorio Ventura State University
You might also like
- Absorption and Variable CostingDocument22 pagesAbsorption and Variable CostingJamaica David100% (4)
- Chapter Ten: Criticisms of Absorption Cost Systems: Incentive To OverproduceDocument16 pagesChapter Ten: Criticisms of Absorption Cost Systems: Incentive To Overproducemuudey sheikhNo ratings yet
- ACC803 Advanced Financial Reporting: Week 2: Financial Statement Preparation and PresentationDocument17 pagesACC803 Advanced Financial Reporting: Week 2: Financial Statement Preparation and PresentationRavinesh PrasadNo ratings yet
- Module 4 Variable and Absorption CostingDocument14 pagesModule 4 Variable and Absorption Costingangelicamae.valdezNo ratings yet
- Acctg 402Document9 pagesAcctg 402Marriah Izzabelle Suarez RamadaNo ratings yet
- ABSORPTION-COSTING-AND-VARIABLE-COSTING_053406Document10 pagesABSORPTION-COSTING-AND-VARIABLE-COSTING_053406wanttolearnacctgNo ratings yet
- Absorption and Variable Costing NotesDocument4 pagesAbsorption and Variable Costing NotesGerald Nitz PonceNo ratings yet
- 3MA 03 Absortion and Variable CostingDocument3 pages3MA 03 Absortion and Variable CostingAbigail Regondola BonitaNo ratings yet
- 04 Variable and Absorption CostingDocument8 pages04 Variable and Absorption CostingJunZon VelascoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7Document4 pagesChapter 7Mixx MineNo ratings yet
- SIM - Variable and Absorption Costing - 0Document5 pagesSIM - Variable and Absorption Costing - 0lilienesieraNo ratings yet
- Presentation - Chapter3 & 9Document49 pagesPresentation - Chapter3 & 9rajeshaisdu009No ratings yet
- Absorption and Variable CostingDocument3 pagesAbsorption and Variable CostingDhona Mae FidelNo ratings yet
- Absorption Vs VariableDocument10 pagesAbsorption Vs VariableRonie Macasabuang CardosaNo ratings yet
- Variable and Absorption CostingDocument21 pagesVariable and Absorption Costingbrabz rayNo ratings yet
- Module 4 Absorption and Variable Costing NotesDocument3 pagesModule 4 Absorption and Variable Costing NotesMadielyn Santarin Miranda100% (3)
- Mas-03: Absorption & Variable CostingDocument4 pagesMas-03: Absorption & Variable CostingClint AbenojaNo ratings yet
- Absorption (Full Costing) Variable (Direct Costing)Document4 pagesAbsorption (Full Costing) Variable (Direct Costing)Leo Sandy Ambe CuisNo ratings yet
- ACT121 - Topic 5Document5 pagesACT121 - Topic 5Juan FrivaldoNo ratings yet
- Absorption and Variable Costing ReviewDocument13 pagesAbsorption and Variable Costing ReviewRodelLabor100% (1)
- Absorption Variable Costing1Document3 pagesAbsorption Variable Costing1Jasmine LimNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7Document12 pagesChapter 7Camille GarciaNo ratings yet
- MODULE 1 Variable and Absorption CostingDocument9 pagesMODULE 1 Variable and Absorption Costingjerico garciaNo ratings yet
- 03 MAS - Var. & Absorption CostingDocument6 pages03 MAS - Var. & Absorption CostingManwol JangNo ratings yet
- Contribution Approach 2Document16 pagesContribution Approach 2kualler80% (5)
- 006 Camist Ch04 Amndd Hs PP 79-102 Branded BW RP SecDocument25 pages006 Camist Ch04 Amndd Hs PP 79-102 Branded BW RP SecMd Salahuddin HowladerNo ratings yet
- Absorption and Direct Costing lecture Aid(1)Document5 pagesAbsorption and Direct Costing lecture Aid(1)xandraitrizhanvillamar7718No ratings yet
- CVP TheoryDocument7 pagesCVP Theoryhassan malikNo ratings yet
- Absorption Costing GclassDocument4 pagesAbsorption Costing GclassDoromal, Jerome A.No ratings yet
- 3 Absorption Vs Variable CostingDocument16 pages3 Absorption Vs Variable CostingXyril MañagoNo ratings yet
- MS 01 - Absorption and Variable CostingDocument5 pagesMS 01 - Absorption and Variable Costingalliahraiz24No ratings yet
- Week 3 Absorption VariableDocument21 pagesWeek 3 Absorption VariableHallie KuronumaNo ratings yet
- Cost and Management Accounting Unit 2Document38 pagesCost and Management Accounting Unit 2Minisha GuptaNo ratings yet
- Managerial Accounting Absorption and Variable Costing 081712Document14 pagesManagerial Accounting Absorption and Variable Costing 081712Mary Ann Jacolbe BaguioNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 04 Marginal Costing and Absorption CostingDocument10 pagesChapter - 04 Marginal Costing and Absorption CostingWolfKing 999No ratings yet
- Chapter 1-Over ViewDocument39 pagesChapter 1-Over ViewMalcolmNo ratings yet
- Management Accounting Absorption and Variable Costing Absorption CostingDocument10 pagesManagement Accounting Absorption and Variable Costing Absorption CostingnaddieNo ratings yet
- TOPIC 9Document49 pagesTOPIC 9zatulsyazirahNo ratings yet
- MAS 02 Variable AbsorptionDocument7 pagesMAS 02 Variable AbsorptionEdwin Bong Ababa Jr.No ratings yet
- M3 Variable Costing As Management ToolDocument6 pagesM3 Variable Costing As Management Toolwingsenigma 00No ratings yet
- 3, Inventory ValuationDocument20 pages3, Inventory ValuationclairecstrattonNo ratings yet
- IWB Chapter 5 - Marginal and Absorption CostingDocument28 pagesIWB Chapter 5 - Marginal and Absorption Costingjulioruiz891No ratings yet
- Topic 7 - Absorption & Marginal CostingDocument8 pagesTopic 7 - Absorption & Marginal CostingMuhammad Alif100% (5)
- Module 4 Absorption Variable Throughput CostingDocument3 pagesModule 4 Absorption Variable Throughput CostingSky Soronoi100% (1)
- Module 4 Absorption Variable Throughput CostingDocument3 pagesModule 4 Absorption Variable Throughput CostingSky SoronoiNo ratings yet
- Variable Costing'Document22 pagesVariable Costing'2023-2-95-013No ratings yet
- Variable & Absorption Costing LectureDocument11 pagesVariable & Absorption Costing LectureElisha Dhowry PascualNo ratings yet
- OR Cost of Inventory: Absorption Costing Variable CostingDocument2 pagesOR Cost of Inventory: Absorption Costing Variable CostingKim TaehyungNo ratings yet
- Absorption Costing & Variable CostingDocument20 pagesAbsorption Costing & Variable Costingsaidkhatib368No ratings yet
- Lesson 4 Absorption Costing and Variable CostingDocument10 pagesLesson 4 Absorption Costing and Variable CostinggracemarypudlaoNo ratings yet
- Costman Variable CostingDocument2 pagesCostman Variable CostingJeremi BernardoNo ratings yet
- Absorption Costing vs. Variable CostinggDocument11 pagesAbsorption Costing vs. Variable CostinggGwyneth Ü ElipanioNo ratings yet
- MI1 Chapter 4Document56 pagesMI1 Chapter 4nchi16586No ratings yet
- Absorption and Variable CostingDocument5 pagesAbsorption and Variable CostingKIM RAGA100% (1)
- AbsVarcosting Handout 2Document6 pagesAbsVarcosting Handout 2Gwy PagdilaoNo ratings yet
- Marginal Costing TYBAFDocument13 pagesMarginal Costing TYBAFAkash BugadeNo ratings yet
- Product-Costing-s.1Document7 pagesProduct-Costing-s.1vppelayoNo ratings yet
- Absorption Costing and Variable CostingDocument29 pagesAbsorption Costing and Variable Costingmikyla malazzabNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 - Marginal and Absorption CostingDocument8 pagesChapter 10 - Marginal and Absorption CostingkundiarshdeepNo ratings yet
- Review Session 01 MA Topics 1-6 BeforeDocument32 pagesReview Session 01 MA Topics 1-6 BeforemisalNo ratings yet
- Equity Valuation: Models from Leading Investment BanksFrom EverandEquity Valuation: Models from Leading Investment BanksJan ViebigNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document28 pagesChapter 4Shibly SadikNo ratings yet
- Unit 6 - Investment DecisionsDocument28 pagesUnit 6 - Investment Decisions2154 taibakhatunNo ratings yet
- Syllabus Finacial Planning & BudgetingDocument5 pagesSyllabus Finacial Planning & BudgetingAdnan MasoodNo ratings yet
- Intermediate Accounting 3 Part 1: Cash Flows Objectives of Cash Flow StatementDocument19 pagesIntermediate Accounting 3 Part 1: Cash Flows Objectives of Cash Flow StatementAG VenturesNo ratings yet
- Retail Industry Financial AnalysisDocument13 pagesRetail Industry Financial AnalysisRishabh MauryaNo ratings yet
- Corporate AccountingDocument59 pagesCorporate AccountingTushar GaurNo ratings yet
- Business Finance Chapter 1Document43 pagesBusiness Finance Chapter 1Arafat UjjamanNo ratings yet
- 6th Practice Qs 99.2Document3 pages6th Practice Qs 99.2BromanineNo ratings yet
- Period and Direct Costing MethodDocument14 pagesPeriod and Direct Costing MethodJames WisleyNo ratings yet
- AlFardan Group FRD Consolidation 1.3Document24 pagesAlFardan Group FRD Consolidation 1.3fahd786No ratings yet
- Group # 5 Financial Ratios AssignmentDocument4 pagesGroup # 5 Financial Ratios AssignmentNavi GuptaNo ratings yet
- Ch8 Income Statement Worksheet AnswersDocument2 pagesCh8 Income Statement Worksheet Answerssalma RamadanNo ratings yet
- Fundamental Accounting Principles Canadian Canadian 14th Edition Larson Test BankDocument35 pagesFundamental Accounting Principles Canadian Canadian 14th Edition Larson Test Bankvictoredana7uz9gw100% (42)
- Unit 5Document15 pagesUnit 5EYOB AHMEDNo ratings yet
- Capital Budgeting - Chaitanya ChemicalsDocument63 pagesCapital Budgeting - Chaitanya ChemicalsNani RoyalNo ratings yet
- Chapter 28 - AnswerDocument6 pagesChapter 28 - Answerwynellamae100% (1)
- (Final) Acco 20113 - Strategic Cost ManagementDocument18 pages(Final) Acco 20113 - Strategic Cost ManagementJona kelssNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 - Financial Statement AnalysisDocument22 pagesChapter 6 - Financial Statement AnalysisRameinor TambuliNo ratings yet
- MFRS 13 FValueDocument14 pagesMFRS 13 FValuefaiez jamilNo ratings yet
- Baf Annual Report 2022Document558 pagesBaf Annual Report 2022Tahir Mustafa ChohanNo ratings yet
- Annual Report 2021 Q3Document71 pagesAnnual Report 2021 Q3Leonita EffendyNo ratings yet
- MMPC 04 PDF EBOOK Merged SECUREDocument74 pagesMMPC 04 PDF EBOOK Merged SECURERakesh dahiyaNo ratings yet
- Axis Card 1Document4 pagesAxis Card 1Om PrakashNo ratings yet
- Capital Struture ChapterDocument50 pagesCapital Struture ChapterAhmed MokhtarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 20 - NEWDocument22 pagesChapter 20 - NEWMaruf AhmedNo ratings yet
- Financial Management - Grinblatt and TitmanDocument68 pagesFinancial Management - Grinblatt and TitmanLuis Daniel Malavé RojasNo ratings yet
- Modern Approach of AccountingDocument24 pagesModern Approach of AccountingParesh ShahNo ratings yet
- BFD Test 1 With Solution Jun 2023 ST AcademyDocument10 pagesBFD Test 1 With Solution Jun 2023 ST AcademyHassan AzamNo ratings yet
- Intern FINALDocument27 pagesIntern FINALSantosh ThapaliyaNo ratings yet