HRLB With Multi Band Booster
HRLB With Multi Band Booster
Uploaded by
Noorul ameenCopyright:
Available Formats
HRLB With Multi Band Booster
HRLB With Multi Band Booster
Uploaded by
Noorul ameenCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Copyright:
Available Formats
HRLB With Multi Band Booster
HRLB With Multi Band Booster
Uploaded by
Noorul ameenCopyright:
Available Formats
Configuring Multi-Band Booster with
Hierarchical Radio Link Bonding (hRLB)
Operating Instructions
912/1543-HRA 901 20/11 Uen L Commercial in confidence
Copyright
© Ericsson AB 2020–2022. All rights reserved. No part of this document may be
reproduced in any form without the written permission of the copyright owner.
Disclaimer
The contents of this document are subject to revision without notice due to
continued progress in methodology, design and manufacturing. Ericsson shall
have no liability for any error or damage of any kind resulting from the use of this
document.
Commercial in confidence 912/1543-HRA 901 20/11 Uen L | 2022-11-23
Contents
Contents
1 Overview 1
2 Planning and Preparing 3
2.1 Prerequisites 3
2.2 Limitations 3
2.3 Planning Advice 5
2.4 Required Documentation 5
2.5 Safety Information 6
3 Configuring Multi-Band Booster with DCN Using CLI 7
3.1 Configuring DCN Using Separate Cables 7
3.2 Configuring DCN Using In-Band Routed DCN 10
4 Configuring Multi-Band Booster with Hierarchical Radio Link
Bonding using CLI 16
4.1 Configure Multi-Band Booster with hRLB on MINI-LINK 6352
(CLI) 16
4.2 Configure Multi-Band Booster with hRLB on MINI-LINK 6600
(CLI) 16
5 Configuring Multi-Band Booster with Hierarchical Radio Link
Bonding Using In-band Routed DCN with MINI-LINK 6352 in
Fast EQP Configuration Using CLI 19
5.1 Configure Hierarchical Radio Link Bonding Using In-band
Routed DCN with MINI-LINK 6352 in Fast EQP Mode 20
6 Configuring Multi-Band Booster with Hierarchical Radio Link
Bonding using MINI-LINK Node-GUI 26
6.1 Configure Multi-Band Booster with hRLB on MINI-LINK 6352
(GUI) 26
6.2 Configure Multi-Band Booster with hRLB on MINI-LINK 6600
(GUI) 28
912/1543-HRA 901 20/11 Uen L | 2022-11-23 Commercial in confidence
Configuring Multi-Band Booster with Hierarchical Radio Link Bonding (hRLB)
Commercial in confidence 912/1543-HRA 901 20/11 Uen L | 2022-11-23
Overview
1 Overview
The main principle for Multi-Band Booster is to use two radio links in different
frequency regions, one low-frequency region and one high-frequency region.
Usually, the low-frequency region carries also the TDM traffic, and the high-
frequency region carries only Ethernet.
Multi-Band Booster increases the performance of microwave backhaul and can
increase network capacity. It supports flexible bonding of different carriers and
frequency band combinations. Multi-Band Booster provides more efficient use
of diverse backhaul spectrum assets, using higher frequencies over much wider
geographical areas.
Figure 1 gives examples of multi-band possibilities.
Limit without fading
99.9% availability, mild climate
99.9% availability, severe climate
99.999% availability, mild climate
99.999% availability, severe climate
Distance (km) Multi-band potential
25
20
Ch1 Ch2
15
10
5
Ch1 Ch2
0
0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90
Bands
Frequency (GHz)
18038
Figure 1 Distances and Frequency Bands Relevant for Multi-Band Booster
Hierarchical Radio Link Bonding (hRLB) is a Layer-1 (L1) technology that can
be used for improving the Multi-Band Booster function, that is, for bonding an
E-Band radio link with a traditional Radio Link Terminal (RLT). It can also be
used for bonding separately configured RLTs into one hRLB interface to achieve a
higher radio link capacity.
A maximum of two hRLB groups are supported in a Multi-Band Booster scenario.
912/1543-HRA 901 20/11 Uen L | 2022-11-23 Commercial in confidence 1
Configuring Multi-Band Booster with Hierarchical Radio Link Bonding (hRLB)
Bonding an E-Band radio link with a traditional RLT creates a Multi-Band
Booster scenario and requires a MINI-LINK 6352. MINI-LINK 6352 can be
connected to MINI-LINK 6600 using a 10 Gbps LAN interface. The supported
hRLB configurations are listed in MINI-LINK 6600 R1 Compatibility.
This document describes how to configure hRLB in a Multi-Band Booster
scenario through an example of a (1+0) + AOD hRLB group configured from
a 1+0 E-Band radio link (MINI-LINK 6352) and a 1+0 traditional RLT.
It is also possible to configure Multi-Band Booster with Hierarchical Radio
Link Bonding using in-band routed DCN with MINI-LINK 6352 in 1+0 Radio
Link, in 2+0 Radio Link Bonding (RLB) Pair Mode, and in 2+0 RLB Pair Mode
XPIC (requires MINI-LINK 6352/2 or MINI-LINK 6352/3) with fast Equipment
Protection (EQP) configuration.
2 Commercial in confidence 912/1543-HRA 901 20/11 Uen L | 2022-11-23
Planning and Preparing
2 Planning and Preparing
This section includes information about the required preparation before
configuring Multi-Band Booster with hRLB.
2.1 Prerequisites
— hRLB requires an NPU 1005, MMU 1005 or MINI-LINK 6651/4.
— Since hRLB uses existing RLTs, previously configured RLTs are needed.
— To access a MINI-LINK 6600 NE remotely through MINI-LINK Node GUI, a
MINI-LINK Node GUI license is required on that specific NE.
— hRLB requires bonding licenses.
— When configuring DCN with a separate cable:
• A separate cable is required for DCN connection towards MINI-LINK
6352.
For more information, see Configuring Multi-Band Booster with DCN Using
CLI on page 7.
— When configuring DCN using in-band routed DCN:
• An additional /30 subnet mask
• A specific VLAN
For more information, see Configuring DCN Using In-Band Routed DCN on
page 10.
2.2 Limitations
— The group capacity can be up to 10 Gbps. However, this capacity is not
guaranteed when using small frame sizes. In case of one group configured
the hRLB packet processing capacity is 7.5 Mpps. For example, with an
RFC 2544 throughput test that uses 64-byte or 128-byte frames, it is not
expected to reach the 10 Gbps capacity. In case of two groups are configured
the hRLB capacity is 4 Mpps per group. Considering RFC2544 throughput
test with 64, 128, 256 bytes frames the 10Gbps capacity should not be
expected.
— The maximum supported frame size over an hRLB link is 9212 bytes.
— MINI-LINK 6352 supports the following radio link configurations for hRLB:
912/1543-HRA 901 20/11 Uen L | 2022-11-23 Commercial in confidence 3
Configuring Multi-Band Booster with Hierarchical Radio Link Bonding (hRLB)
• 1+0
• 2+0 RLB Virtual Node
• 2+0 RLB Virtual Node XPIC
• 2+0 RLB Pair Mode with Fast EQP
• 2+0 RLB Pair Mode XPIC with Fast EQP
— Traffic Aware Power Save (TAPS) is not supported with hRLB. Therefore,
TAPS must be disabled on all radio carriers involved in an hRLB group.
— Multi-Layer Header Compression (MLHC) is not supported with hRLB.
Therefore, MLHC must be disabled on all radio carriers involved in an hRLB
group.
— Adding and removing hRLB members on MINI-LINK 6651 and MINI-LINK
6654 can result in a short traffic disturbance on that interface and other
connected interfaces. A short outage in DCN connectivity is also possible.
— The smallest subnet size for in-band routed DCN is /30.
— The L3 VLAN subinterface must be tagged for the in-band routed DCN.
— When a second hRLB group is configured and both are using in-band
routed DCN, then the VLAN ID for the L3 VLAN subinterface on the two
LAN members must be the same. For example, if the first hRLB group has
L3 VLAN subinterface with VLAN ID 100 configured directly on the LAN
interface for the in-band DCN, then the second hRLB group’s L3 VLAN
subinterface on the LAN interface must also use VLAN ID 100.
— When using a separate cable for DCN connectivity of MINI-LINK 6352, the
DCN VLAN used for the separate cable must be different than the DCN VLAN
through the hRLB interface. This is applicable for both DCN over VLAN and
routed DCN.
— A LAN interface only with 10 Gbps line speed can be added as a member. It
can be added to an hRLB group as either a 10 Gbps or a 2.5 Gbps capacity
member.
— RLT ports are allowed only as 2.5 Gbps capacity members, except on MMU
1005 where RLT can be added as 10Gbps capacity member.
— On NPU1005 the second hRLB group can only be configured if the first has
no 10Gbps capacity members.
— HRLB has total capacity of 17 Gbps on ML6651/4.
4 Commercial in confidence 912/1543-HRA 901 20/11 Uen L | 2022-11-23
Planning and Preparing
2.3 Planning Advice
To ensure proper node and network function, all configuration activities must be
planned in advance by skilled personnel. Before taking any actions, make sure
that only authorized persons have access to the NE.
When using CLI commands, the configuration can be prepared offline and
transferred to the node in the form of a CLI script, either remotely (when
modifying the configuration for an installed node) or on site (when installing
a new node).
When using MINI-LINK Node GUI, the configuration can also be performed
either remotely or on site.
In hRLB mode, MINI-LINK 6352 uses the configured minimum modulation as
a safety zone to avoid packet drops in case the E-Band fades out, therefore
configured minimum modulation cannot be equal with configured maximum
modulation.
To maximize utilization it is recommended to configure minimum modulation to
the lowest supported modulation.
For MINI-LINK 6352, the v11 or v12 physical mode must be used.
It is recommended to perform a limited clear on MINI-LINK 6352 as a first
step when configuring hRLB—for example, RSTP must be disabled on the ports
involved in hRLB configuration. The reason is that there is a chance that the old
configuration conflicts with the hRLB-related configuration.
If Virtual Node (VN) or Pair Mode is planned to be used in the future, it is not
advised to use LAN 1/4 as an hRLB port on MINI-LINK 6352.
If Precision Time Protocol (PTP) is used, MINI-LINK 6352 can only be in
Transparent Clock (TC) mode. For more information, see Configuring Network
Synchronization. Because PTP requires frequency synchronization, the SyncE
feature must be configured on the LAN interfaces between MINI-LINK 6600 and
MINI-LINK 6352. Furthermore, it is recommended to configure the SyncE feature
also on the MINI-LINK 6352 WAN ports.
2.4 Required Documentation
Read through this document. Make sure that the referenced documentation is
available during the configuration process.
— Finding Information in the CPI Library
— Accessing a Network Element
— CLI User Guide
912/1543-HRA 901 20/11 Uen L | 2022-11-23 Commercial in confidence 5
Configuring Multi-Band Booster with Hierarchical Radio Link Bonding (hRLB)
— CLI Tool User Guide
— CLI Descriptions
— MINI-LINK Node GUI User Guide
— MINI-LINK Node GUI Descriptions
2.5 Safety Information
Make sure that the information in the following documents have been
understood by the persons performing the procedures:
— Personal Health and Safety Information
— System Safety Information
— Supplementary Safety Information for MINI-LINK
6 Commercial in confidence 912/1543-HRA 901 20/11 Uen L | 2022-11-23
Configuring Multi-Band Booster with DCN Using CLI
3 Configuring Multi-Band Booster with DCN
Using CLI
To achieve DCN connectivity for all nodes in a Multi-Band Booster setup with
hRLB, the operator has to use a separate DCN cable or an in-band routed DCN
cable. If the operator uses separate DCN cables, then they are going to need an
additional set of cables for both MINI-LINK 6352 nodes.
3.1 Configuring DCN Using Separate Cables
When separate cables are used, an additional VLAN is required for MINI-LINK
6352 beside the original DCN VLAN used for every node on the same Layer-2
(L2) domain. To prevent loops between the MINI-LINK 6600 and MINI-LINK
6352 nodes, the original DCN VLAN must be untagged on the MINI-LINK 6600
side and re-tagged on the MINI-LINK 6352 side with the additional VLAN ID.
The additional VLAN is possible to reuse on all MINI-LINK 6352 nodes in Multi-
Band Booster with hRLB hops in the network.
LAN WAN WAN LAN
2 5 5 2
A B
LAN LAN
3 3
LAN LAN LAN
1/4/6 LAN 1/4/6
1/4/7 1/4/7
LAN WAN WAN LAN
1/4/8 1/4/50 1/4/50 1/4/8
RLT RLT
1/1/1 1/1/1
C D
Separate cable for DCN connection
Optical cable
Radio Connection
MINI-LINK 6600 DCN
Untagged MINI-LINK 6352 DCN
Figure 2 DCN with Separate Cables
In general, the near-end MINI-LINK 6600 and MINI-LINK 6352 are reached
from the interface towards the core and through the separate cable between the
two nodes. The far-end nodes are always reached with the hRLB tunneling the
DCN VLAN between the two MINI-LINK 6600 nodes and onto the separate cable
between the far-end nodes.
912/1543-HRA 901 20/11 Uen L | 2022-11-23 Commercial in confidence 7
Configuring Multi-Band Booster with Hierarchical Radio Link Bonding (hRLB)
If the MINI-LINK 6352 radio link is down, the nodes are reached in the following
order:
1. The near-end MINI-LINK 6600 is reached from the northbound 1/4/8
interface.
2. The near-end MINI-LINK 6352 is reached from the 1/4/6 interface of the
near-end MINI-LINK 6600 with an untagged DCN that is re-tagged with a
different VLAN tag.
3. The far-end MINI-LINK 6600 is reached from the near-end MINI-LINK 6600
through the traditional radio link.
4. The far-end MINI-LINK 6352 is reached from the 1/4/6 interface of the
far-end MINI-LINK 6600 with an untagged DCN that is re-tagged with a
different VLAN tag.
When the traditional radio link between the MINI-LINK 6600 nodes is down,
reaching the far-end nodes is different, as follows:
1. The far-end MINI-LINK 6600 is reached the following way:
a. Near-end MINI-LINK 6600
b. Near-end MINI-LINK 6352
c. Far-end MINI-LINK 6352
d. Far-end MINI-LINK 6600
2. The far-end MINI-LINK 6352 forwards its own DCN frames as traffic, then
the far end MINI-LINK 6600 removes the VLAN tag and forwards it through
the separate cable. The path is the following:
a. Near-end MINI-LINK 6600
b. Near-end MINI-LINK 6352
c. Far-end MINI-LINK 6352 forwarding the DCN as L2 traffic
d. Far-end MINI-LINK 6600 forwarding as untagged
e. Far-end MINI-LINK 6352 receiving as DCN traffic
3.1.1 Configure DCN on MINI-LINK 6600
On the MINI-LINK 6600 side, the configuration requires only one VLAN. The
separate cable and the local DCN must be configured as untagged. The priority of
the re-tagging on the separate cable can be changed to the required preferences.
In the following example, the highest priority is used to make sure that the
nodes are always reachable and user traffic always leaves room for the DCN
connectivity. This can be changed if required.
8 Commercial in confidence 912/1543-HRA 901 20/11 Uen L | 2022-11-23
Configuring Multi-Band Booster with DCN Using CLI
Steps
1. Use this example script to configure DCN:
Example
! In Global Configuration mode, change to the (config-eth) submode,
! and configure the selected interface:
! (config)#interface ethernet <R/S/P>
! Make sure that the correct R/S/P values are used.
! This example changes to the (config-eth) submode on interface 1/4/6:
interface ethernet 1/4/6
! Change to the (config-bridgeport) submode:
! (config)#bridge-port
! This example changes to the (config-bridgeport) submode:
bridge-port
! Set the port role:
! (config-bridgeport)#role {uni | inni | mirror | cep | cnp | layer1}
! This example sets the port role to uni:
role uni
! Set the default network priority:
! (config-bridgeport)#default-network-priority <PRIORITY>
! This example sets the default network priority to 7:
default-network-priority 7
! Exit the (config-bridgeport) submode:
! (config-eth)#exit
exit
! Exit the (config-eth) submode:
! (config-eth)#exit
exit
! In Global Configuration mode, change to the (config-vlan) submode:
! (config)#[no] vlan <VLANID> [<NAME>]
! This example changes to the (config-vlan) submode
! and creates a VLAN with VLAN ID 1:
vlan 1
! Select egress ports:
! (config-vlan)#[no] egressports <PORTLIST>
! Make sure that the correct R/S/P values are used.
! This example adds ports 1/4/0, 1/4/6, 1/4/8, and 1/4/50 to the port list for the created VLAN:
egressports 1/4/0,1/4/6,1/4/8,1/4/50
! Select untagged ports:
! (config-vlan)#[no] untagged-ports <PORTLIST>
! This command is valid for UNI ports in customer mode and for CN-UNI ports in provider mode.
! Make sure that the correct R/S/P values are used.
! This example selects ports 1/4/0 and 1/4/6 as untagged ports:
untagged-ports 1/4/0,1/4/6
! Exit the (config-vlan) submode:
! (config-vlan)#exit
exit
3.1.2 Configure DCN on MINI-LINK 6352
On the MINI-LINK 6352 nodes, the original DCN VLAN must not be added to the
configuration, but another VLAN needs to be configured to terminate the DCN
traffic from the separate cable.
Steps
1. Create a VLAN.
912/1543-HRA 901 20/11 Uen L | 2022-11-23 Commercial in confidence 9
Configuring Multi-Band Booster with Hierarchical Radio Link Bonding (hRLB)
Example
# This example configures the VLAN:
#
end; config switch vlan 2
2. Change the DCN port to the interface of the separate cable and define a new
VLAN to send untagged DCN traffic.
Example
# This example configures a new VLAN to send untagged DCN traffic:
#
end; config switch vlan 2 port 1 2
end; config slot 1 lan 1 2 switchport mode cnp switchport default-vlan 2
end; config dcn-mgmtvlan mgmt-vlan id 2
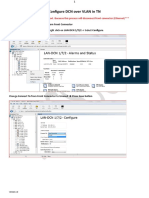
3.2 Configuring DCN Using In-Band Routed DCN
Note: When OSPF is configured on MINI-LINK 6352 it is advised not to
have static routes configured to networks learned through OSPF and/or
pointing to a default gateway.
In-band routed DCN can be configured with either using numbered or
unnumbered IP addresses. In case of numbered IP addresses, configuration
requires an extra /30 subnet mask. Both solutions require a specific VLAN that is
not used on other interfaces on the MINI-LINK 6600 nodes. The VLAN can be the
same for both MINI-LINK 6352s in the hop.
Figure 3 In-Band Routed DCN towards MINI-LINK 6352
10 Commercial in confidence 912/1543-HRA 901 20/11 Uen L | 2022-11-23
Configuring Multi-Band Booster with DCN Using CLI
In general, the near-end MINI-LINK 6600 and MINI-LINK 6352 nodes are
reached (from their interface towards the core) through the 10G optical cable
between the two nodes. The far-end MINI-LINK nodes are always reached with
the hRLB tunneling the Layer 3 DCN between the two MINI-LINK 6600 nodes,
routing and forwarding onto the 10G optical cable between the far-end nodes.
If the MINI-LINK 6352 radio link is down, the nodes are reached in the following
order:
1. The near-end MINI-LINK 6600 is reached from the northbound 1/4/8
interface.
2. The near-end MINI-LINK 6352 is reached from the 1/4/7 interface of the
near-end MINI-LINK 6600 after the packets have been routed.
3. The far-end MINI-LINK 6600 is reached from the near-end MINI-LINK 6600
through the traditional radio link. Packets are routed between the 1/4/50
hRLB interfaces.
4. The far-end MINI-LINK 6352 is reached from the 1/4/7 interface of the
far-end MINI-LINK 6600 after the packets have been routed.
When the traditional radio link between the MINI-LINK 6600 nodes is down,
reaching the far-end nodes is different, as follows:
1. The far-end MINI-LINK 6600 is reached the following way:
a. The near-end MINI-LINK 6600 routing the packets
b. The near-end MINI-LINK 6352 forwarding in hRLB mode
c. The far-end MINI-LINK 6352 forwarding in hRLB mode
d. The far-end MINI-LINK 6600
2. The far-end MINI-LINK 6352 forwards its own DCN frames as traffic, then
the far end MINI-LINK 6600 routes the DCN packets and forwards it through
the 1/4/7 optical cable. The path is the following:
a. The near-end MINI-LINK 6600 routing the packets
b. The near-end MINI-LINK 6352 forwarding in hRLB mode
c. The far-end MINI-LINK 6352 forwarding the DCN in hRLB mode
d. The far-end MINI-LINK 6600 routing back towards the MINI-LINK 6352
e. The far-end MINI-LINK 6352 receiving as DCN traffic
912/1543-HRA 901 20/11 Uen L | 2022-11-23 Commercial in confidence 11
Configuring Multi-Band Booster with Hierarchical Radio Link Bonding (hRLB)
3.2.1 Configure In-Band Routed DCN on MINI-LINK 6600
3.2.1.1 Configure In-Band Routed DCN on the NPU
Prerequisites
— Have routed DCN already available for the MINI-LINK 6600 nodes: L3
VLAN subinterface on the hRLB interface and either OSPF or IS-IS routing
process including the hRLB interface. For more information, see Planning
and Dimensioning DCN and Configuring Routed DCN.
— hRLB already configured with 10G LAN
Then configure in-band routed DCN on MINI-LINK 6600 towards the MINI-LINK
6352:
Steps
1. Add a new L3 VLAN subinterface with an arbitrary VLAN ID on the 10G LAN
member of the hRLB interface. Use this example script to configure a new
Layer 3 VLAN subinterface:
Do!
The VLAN ID for the L3 VLAN subinterface must not be used on the hRLB group.
The same VLAN ID cannot be used to create L3 VLAN subinterfaces on the hRLB
group and it’s HLAN member port. In case of dual hop hRLB on the interconnection
node that has two hRLB instances the VLAN ID for each hop must be different. For
example, the first WAN hRLB interface L3 VLAN ID is 200 and it's LAN member’s L3
VLAN ID is 100, and the second WAN hRLB interface L3 VLAN ID is 300 and it's LAN
member’s L3 VLAN ID is 400. In case of multiple dual hop configurations, the same
VLAN ID structure can be reused as long as on the interconnection node the VLAN
IDs are different.
Example
! In Global Configuration mode, change to the (config-eth) submode,
! and configure the selected interface:
! (config)#interface ethernet <R/S/P>
! Make sure that the correct R/S/P values are used.
! This example changes to the (config-eth) submode on interface 1/4/7:
interface ethernet 1/4/7
! Change to the (config-bridgeport) submode:
! (config)#bridge-port
! This example changes to the (config-bridgeport) submode:
bridge-port
! Create an L3 VLAN subinterface:
! (config-bridgeport)#l3enable [untagged]
! This example creates an L3 VLAN subinterface with VLAN number 100:
l3enable 100
! Exit the (config-bridgeport) submode:
12 Commercial in confidence 912/1543-HRA 901 20/11 Uen L | 2022-11-23
Configuring Multi-Band Booster with DCN Using CLI
! (config-eth)#exit
exit
! Exit the (config-eth) submode:
! (config-eth)#exit
exit
3.2.1.2 Configure In-Band Routed DCN on MMU1005
Prerequisites
— Have routed DCN already available for the MINI-LINK 6600 nodes: L3
VLAN subinterface on the hRLB interface and either OSPF or IS-IS routing
process including the hRLB interface. For more information, see Planning
and Dimensioning DCN and Configuring Routed DCN.
— hRLB already configured with 10G LAN
Then configure in-band routed DCN on MINI-LINK 6600 towards the MINI-LINK
6352:
Steps
1. Add a new L3 VLAN subinterface with an arbitrary VLAN ID on the 10G LAN
member of the hRLB interface. Use this example script to configure a new
Layer 3 VLAN subinterface:
Do!
The VLAN ID for the L3 VLAN subinterface must not be used on the hRLB group. If
the same VLAN ID is used to configure a L3 VLAN subinterface on the hRLB group
and on the 10G LAN member, then the two conflicts resulting in an unstable DCN
connection. In case of dual hop hRLB on the interconnection node that has two
hRLB instances, the VLAN ID for each hop must be different. For example, WAN
hRLB interface L3 VLAN ID is 200, first hRLB instance LAN member VLAN ID 100,
and second hRLB instance LAN member. In case of multiple dual hop configurations,
the same VLAN ID structure can be reused as long as on the interconnection node
the VLAN IDs are different.
Example
! In Global Configuration mode, change to the (config-eth) submode,
! and configure the selected interface:
! (config)#interface ethernet <R/S/P>
! Make sure that the correct R/S/P values are used.
! This example changes to the (config-eth) submode on interface 1/4/7:
interface ethernet 1/4/7
! Change to the (config-bridgeport) submode:
! (config)#bridge-port
! This example changes to the (config-bridgeport) submode:
bridge-port
! Create an L3 VLAN subinterface:
912/1543-HRA 901 20/11 Uen L | 2022-11-23 Commercial in confidence 13
Configuring Multi-Band Booster with Hierarchical Radio Link Bonding (hRLB)
! (config-bridgeport)#l3enable [untagged]
! This example creates an L3 VLAN subinterface with VLAN number 100:
l3enable 100
! Exit the (config-bridgeport) submode:
! (config-eth)#exit
exit
! Exit the (config-eth) submode:
! (config-eth)#exit
exit
2. Use this example script to configure the interface as unnumbered:
Example
! In Global Configuration mode, configure the IP parameters of the L3 VLAN subinterface:
! (config)#interface ip {<IFNAME_VLAN> | <IFNAME_RSP_VLAN>}
! Make sure that the correct R/S/P values are used.
! This example selects subinterface 1/4/7.100
! and changes to the (config-router-if) submode:
interface ip 1/4/7.100
! Set the IP address of the L3 VLAN subinterface:
! (config-router-if)#ip address <ADDR/PREFIX>
! This example sets the IP address of the subinterface to 192.168.40.1/30:
ip address unnumbered
! Enable the L3 VLAN subinterface:
! (config-router-if)#[no] shutdown
! This example the L3 VLAN subinterface:
no shutdown
! Exit the (config-router-if) submode:
! (config-router-if)#exit
exit
Since the loopback address is already added to the routing instance before
starting the configuration, it is not needed to add the interface separately to
the OSPF network.
3.2.2 Configure In-Band Routed DCN on MINI-LINK 6352
Use the same VLAN as on the L3 VLAN subinterface on the MINI-LINK 6600 10G
LAN hRLB member interface. In case of hRLB mode, the LAN interface of the
hRLB link can only be configured with one L3 VLAN subinterface while the WAN
interface cannot have any L3 interfaces.
Steps
1. Configure the Router ID and the loopback address, then assign it to the
OSPF:
Note: If Router ID is configured with an existing IP address, then to use
unnumbered IP addresses on an L3 interface, a loopback address
must also be configured.
Example
# This example configures the Router ID and loopback address:
#
end; config ip routerid 10.10.10.10
14 Commercial in confidence 912/1543-HRA 901 20/11 Uen L | 2022-11-23
Configuring Multi-Band Booster with DCN Using CLI
end; config ip ospf interface 80 area 0.0.0.0
end; config ip ospf enable enabled
2. Configure an unnumbered L3 VLAN subinterface with OSPF:
Example
# This example configures a L3 VLAN subinterface and attaches it to OSPF:
#
end; config switch l3-vlan sub-interface 1 3 100
end; config ip interface 6001 type unnumbered
end; config ip ospf interface 6001 area 0.0.0.0 network p2p
912/1543-HRA 901 20/11 Uen L | 2022-11-23 Commercial in confidence 15
Configuring Multi-Band Booster with Hierarchical Radio Link Bonding (hRLB)
4 Configuring Multi-Band Booster with
Hierarchical Radio Link Bonding using CLI
4.1 Configure Multi-Band Booster with hRLB on MINI-LINK
6352 (CLI)
1. Enable Multi-Band Booster with hRLB.
Example
# Enable Multi-Band Booster with hRLB:
#
end; config mbb hrlb enabled
2. Configure Layer 1 on the traffic ports used for hRLB.
Example
# Configure Layer 1 on the traffic ports used for hRLB:
#
end; slot 1 lan 1 3 capability l1
end; slot 1 wan 1 5 capability l1
Note: There can be only one LAN port that has L1 capability on the node.
4.2 Configure Multi-Band Booster with hRLB on MINI-LINK
6600 (CLI)
1. Use this example script to configure a (1+0) + AOD hRLB group configured
from an 1+0 E-Band radio link (MINI-LINK 6352) and an 1+0 traditional
RLT, which are already set up on the modem:
Example
! In Global Configuration mode, create an hRLB group
! and change to hRLB Configuration submode:
! (config)#[no] hrlb <RSP>
! Make sure that the correct R/S/P values are used.
! The following example creates an hRLB group on 1/4/50:
hrlb 1/4/50
! Add member interfaces to an hRLB group:
! (config-hrlb)#add-member <RSP> [<CAPACITY>]
! Make sure that the correct R/S/P values are used.
! Capacity is optional, it can be 10G or 2500M.
! The following example adds the E-Band radio link to the group
! by selecting a LAN interface used to connect the MINI-LINK 6352:
add-member 1/4/7
16 Commercial in confidence 912/1543-HRA 901 20/11 Uen L | 2022-11-23
Configuring Multi-Band Booster with Hierarchical Radio Link Bonding using CLI
! Add member interfaces to an hRLB group:
! (config-hrlb)#add-member <RSP> [<CAPACITY>]
! Make sure that the correct R/S/P values are used.
! Capacity is optional, it can be 10G or 2500M.
! The following example adds the RLT to the hRLB group:
add-member 1/1/1
! Optionally, enable the Degraded Service alarm:
! (config-hrlb)#[no] alarm-enable-degraded-service
! The following example enables the Degraded Service alarm:
alarm-enable-degraded-service
! Optionally, enable the No Traffic alarm:
! (config-hrlb)#[no] alarm-enable-no-traffic
! The following example enables the No Traffic alarm:
alarm-enable-no-traffic
! Exit to Global Configuration mode:
! (config-hrlb)#exit
exit
2. Use this example script to configure the real speed of the external radio link
on MINI-LINK 6600:
Example
! In Global Configuration mode, change to the (config-eth) submode:
! (config)#interface ethernet <RSP>
! Make sure that the correct R/S/P values are used.
! The following example changes to the (config-eth) submode in interface 1/4/7:
interface ethernet 1/4/7
! In the (config-eth)submode, change to the (config-lan) submode:
! (config-eth)#lan
lan
! In the (config-lan) submode, specify the maximum radio link speed of an
! All Outdoor (MINI-LINK 6352) hRLB member node in the hRLB group:
! (config-lan)#[no] external-rl-speed <SPEED>
! The following example specifies the maximum radio link speed:
external-rl-speed 3371
! Exit to the (config-eth) submode:
! (config-lan)#exit
exit
! Exit to Global Configuration mode:
! (config-eth)#exit
exit
3. Use this example script to confirm the configuration:
912/1543-HRA 901 20/11 Uen L | 2022-11-23 Commercial in confidence 17
Configuring Multi-Band Booster with Hierarchical Radio Link Bonding (hRLB)
Example
! Exit Global Configuration mode:
! (config)#exit
exit
! In Privileged Exec mode, display information about hRLB groups:
! #show hrlb {<RSP> | group-info}
! Make sure that the correct R/S/P values are used.
! The following example displays information about hRLB group 1/4/50:
show hrlb 1/4/50
Output example:
ML66#show hrlb 1/4/50
hrlb 1/4/50
add-member 1/4/7 10G
add-member 1/1/1 2500M
alarm-enable-degraded-service
alarm-enable-no-traffic
exit
! Display information about hRLB groups:
! #show hrlb {<RSP> | group-info}
! The following example displays information about all hRLB groups:
show hrlb group-info
Output example:
ML66>#show hrlb group-info
hrlb 1/4/50
capacity of group: 10000 Mbps
speed of group: 3923 Mbps
member port:1/4/7, max capacity: 3371 Mbps
member port:1/1/1, max capacity:552 Mbps
! Change to Global Configuration mode:
! #configure
configure
18 Commercial in confidence 912/1543-HRA 901 20/11 Uen L | 2022-11-23
Configuring Multi-Band Booster with Hierarchical Radio Link Bonding Using In-band Routed DCN with MINI-LINK 6352 in
Fast EQP Configuration Using CLI
5 Configuring Multi-Band Booster with
Hierarchical Radio Link Bonding Using In-
band Routed DCN with MINI-LINK 6352 in
Fast EQP Configuration Using CLI
Note: When OSPF is configured on MINI-LINK 6352 it is advised not to
have static routes configured to networks learned through OSPF and/or
pointing to a default gateway.
The configuration example below uses the following setup:
— Hierarchical Radio Link Bonding configured on MINI-LINK 6600 nodes
— Fast EQP configured on MINI-LINK 6352 nodes
— DCN connection towards MINI-LINK 6352 nodes uses in-band routed DCN
with unnumbered interfaces
Figure 4 Configuration of hRLB with in-band routed DCN with MINI-LINK 6352 nodes in fast EQP
912/1543-HRA 901 20/11 Uen L | 2022-11-23 Commercial in confidence 19
Configuring Multi-Band Booster with Hierarchical Radio Link Bonding (hRLB)
5.1 Configure Hierarchical Radio Link Bonding Using In-
band Routed DCN with MINI-LINK 6352 in Fast EQP
Mode
Prerequisites
— Fast EQP is configured on MINI-LINK 6352 nodes
Steps
1. Configure Hierarchical Radio Link Bonding on MINI-LINK 6600.
For detailed description see Configuring Hierarchical Radio Link Bonding
(hRLB).
Example
! Configure Hierarchical Radio Link Bonding on MINI-LINK 6600
! In Global Configuration mode, create an hRLB group
! and change to hRLB Configuration submode:
! (config)#[no] hrlb <RSP>
! Make sure that the correct R/S/P values are used.
! The following example creates an hRLB group on 1/4/50:
hrlb 1/4/50
! Add member interfaces to an hRLB group:
! (config-hrlb)#add-member <RSP> [<CAPACITY>]
! Make sure that the correct R/S/P values are used.
! Capacity is optional, it can be 10G or 2500M.
! The following example adds the E-Band radio link to the group
! by selecting a LAN interface used to connect the MINI-LINK 6352:
add-member 1/4/7
! Add member interfaces to an hRLB group:
! (config-hrlb)#add-member <RSP> [<CAPACITY>]
! Make sure that the correct R/S/P values are used.
! Capacity is optional, it can be 10G or 2500M.
! The following example adds the RLT to the hRLB group:
add-member 1/1/1
! Optionally, enable the Degraded Service alarm:
! (config-hrlb)#[no] alarm-enable-degraded-service
! The following example enables the Degraded Service alarm:
alarm-enable-degraded-service
! Optionally, enable the No Traffic alarm:
! (config-hrlb)#[no] alarm-enable-no-traffic
! The following example enables the No Traffic alarm:
20 Commercial in confidence 912/1543-HRA 901 20/11 Uen L | 2022-11-23
Configuring Multi-Band Booster with Hierarchical Radio Link Bonding Using In-band Routed DCN with MINI-LINK 6352 in
Fast EQP Configuration Using CLI
alarm-enable-no-traffic
! Exit to Global Configuration mode:
exit
! Configure the real speed of the external radio link on MINI-LINK 6600
! In Global Configuration mode, change to the (config-eth) submode:
! (config)#interface ethernet <RSP>
! Make sure that the correct R/S/P values are used.
! The following example changes to the (config-eth) submode in interface 1/4/7:
interface ethernet 1/4/7
! In the (config-eth)submode, change to the (config-lan) submode:
! (config-eth)#lan
lan
! In the (config-lan) submode, specify the maximum radio link speed of an
! All Outdoor (MINI-LINK 6352) hRLB member node in the hRLB group:
! (config-lan)#[no] external-rl-speed <SPEED>
! The following example specifies the maximum radio link speed:
external-rl-speed 6742
! Exit to Global Configuration mode:
exit
exit
Note: If the external radio link’s maximum speed is higher than the speed
of the hRLB LAN member interface, then configuring the external
radio link’s maximum speed is not needed.
2. Configure MINI-LINK 6352 Fast EQP.
For detailed information see the MINI-LINK 6352 library.
3. Configure Hierarchical Radio Link Bonding mode on MINI-LINK 6352 nodes.
For detailed description see Configuring Hierarchical Radio Link Bonding
(hRLB).
Note: MINI-LINK 6352 in fast EQP configuration must have all
configuration done on the passive node as well.
Example
! Configure Hierarchical Radio Link Bonding mode (Layer 1) on MINI-LINK 6352 no →
des
# Enable Multi-Band Booster with hRLB:
#
end; config mbb hrlb enabled
912/1543-HRA 901 20/11 Uen L | 2022-11-23 Commercial in confidence 21
Configuring Multi-Band Booster with Hierarchical Radio Link Bonding (hRLB)
# Configure Layer 1 on the traffic ports used for hRLB:
#
end; slot 1 lan 1 3 capability l1
end; slot 1 wan 1 5 capability l1
Note: There can be only one LAN port that has L1 capability on the node.
4. Configure routed DCN on hRLB interface on MINI-LINK 6600.
For detailed description see Planning and Dimensioning DCN and
Configuring Routed DCN.
Example
! In Global Configuration mode, set the DCN mode to DCN-Mode Routed:
! (config)#dcn-mode {vlan | routed}
! This example sets the DCN mode to DCN-Mode Routed:
dcn-mode routed
! In Global Configuration mode, change to the (config-router-lo) submode:
! (config)#interface lo
! The following example changes to the (config-router-lo) submode:
interface lo
! Set the IP address of the router loopback interface:
! (config-router-lo)#ip address <ADDR/PREFIX>
! The following example sets the ip address of the router loopback interface:
ip address 1.1.1.1/32
! Change to Global Configuration mode:
exit
! Set the host interface for DCN-Mode Routed:
! (config)#ip host interface [<IFNAME_RSP_H> | <IFNAME_VLAN> | <IFNAME_RSP_VLAN> →
| lo]
! The following example sets the host interface:
ip host interface lo
! In Global Configuration mode, change to the (config-router-ospf) submode:
! (config)#[no] router ospf [<PROC_ID> [vrf <VRF>]]
! The following example changes to the (config-router-ospf) submode:
router ospf
! Add the loopback interface network to the OSPF area:
! (config-router-ospf)#network <IPADDR/PREFIX> area <AREA> [instance-id <INSTANCE_I →
D>]
! The following example adds the loopback interface network:
network 1.1.1.1/32 area 0
! Change to Global Configuration mode:
exit
22 Commercial in confidence 912/1543-HRA 901 20/11 Uen L | 2022-11-23
Configuring Multi-Band Booster with Hierarchical Radio Link Bonding Using In-band Routed DCN with MINI-LINK 6352 in
Fast EQP Configuration Using CLI
! In Global Configuration mode, change to (config-eth) submode:
! (config)#interface ethernet <RSP>
! The following example changes to (config-eth) submode:
interface ethernet 1/4/50
! Change to (config-bridgeport) submode:
! (config-eth)#bridge-port
! The following example changes to (config-bridgeport) submode:
bridge-port
! Create an L3 VLAN subinterface:
! (config-bridgeport)#l3enable <VLAN_ID> [untagged | port-based]
! The following example creates an L3 VLAN subinterface:
l3enable 200
! Change to Global Configuration mode:
exit
exit
! In Global configuration mode, change to the (config-router-if) submode
! to configure the IP parameters of the L3 VLAN subinterface:
! (config)#interface ip <IFNAME_RSP_VLAN>
! The following example changes to the (config-router-if) submode:
interface ip 1/4/50.200
! Set the L3 VLAN subinterface to unnumbered:
! (config-router-if)#ip unnumbered
! The following example sets the L3 VLAN subinterface to unnumbered:
ip unnumbered
! Set the Administrative Status of an L3 interface to enabled:
! (config-router-if))# [no] shutdown
! The following example sets the Administrative Status of an L3 interface to en →
abled:
no shutdown
! Change to Global Configuration mode:
exit
5. Configure in-band routed DCN on MINI-LINK 6600 and MINI-LINK 6352
including ICC.
For detailed description see Configuring DCN Using In-Band Routed DCN on
page 10.
Example
! Configure in-band routed DCN on MINI-LINK 6600
! In Global Configuration mode, switch to the (config-eth) submode,
! and configure the selected interface:
! (config)#interface ethernet <R/S/P>
912/1543-HRA 901 20/11 Uen L | 2022-11-23 Commercial in confidence 23
Configuring Multi-Band Booster with Hierarchical Radio Link Bonding (hRLB)
! The following example changes to the (config-eth) submode:
interface ethernet 1/4/7
! Switch to the (config-bridgeport) submode:
! (config)#bridge-port
! The following example changes to the (config-bridgeport) submode
bridge-port
! Create an L3 VLAN subinterface:
! (config-bridgeport)#l3enable <VLAN-ID> [untagged | port-based]
! The following example creates the L3 VLAN subinterface:
l3enable 100 port-based
! Change to Global Configuration mode:
exit
exit
! In Global Configuration mode, configure the IP parameters of the L3 VLAN subi →
nterface:
! (config)#interface ip {<IFNAME_VLAN> | <IFNAME_RSP_VLAN>}
! The following example sets the IP parameters of the L3 VLAN subinterface:
interface ip 1/4/7.100
! Set the IP address of the L3 VLAN subinterface to unnumbered:
! (config-router-if)#ip unnumbered
! The following example sets the IP address of the L3 VLAN subinterface to unnu →
mbered:
ip unnumbered
! Set the Administrative Status of an L3 interface to enabled:
! (config-router-if))#[no] shutdown
! The following example sets the Administrative Status of an L3 interface to en →
abled:
no shutdown
! Change to Global Configuration mode:
exit
Note: 6352 in fast EQP configuration must have all configuration done on
the passive node as well. IP address used on the passive node must
be different.
Example
# Configure in-band routed DCN on MINI-LINK 6352 including ICC
# This example configures the Router ID and loopback address and enables OSPF:
#
end; config ip routerid 10.10.10.10
end; config ip ospf interface 80 area 0.0.0.0
end; config ip ospf enable enabled
24 Commercial in confidence 912/1543-HRA 901 20/11 Uen L | 2022-11-23
Configuring Multi-Band Booster with Hierarchical Radio Link Bonding Using In-band Routed DCN with MINI-LINK 6352 in
Fast EQP Configuration Using CLI
# This example configures a L3 VLAN subinterface and attaches it to OSPF:
#
end; config switch l3-vlan sub-interface 1 3 100
end; config ip interface 6001 type unnumbered
end; config ip ospf interface 6001 area 0.0.0.0 network p2p
# This example configures a L3 VLAN subinterface and attaches it to OSPF:
#
end; config slot 1 lan 1 4 capability l2-l3
end; config switch l3-vlan sub-interface 1 4 101
end; config ip interface 6002 type unnumbered
end; config ip ospf interface 6002 area 0.0.0.0 network p2p
912/1543-HRA 901 20/11 Uen L | 2022-11-23 Commercial in confidence 25
Configuring Multi-Band Booster with Hierarchical Radio Link Bonding (hRLB)
6 Configuring Multi-Band Booster with
Hierarchical Radio Link Bonding using MINI-
LINK Node-GUI
6.1 Configure Multi-Band Booster with hRLB on MINI-LINK
6352 (GUI)
1. Log on to the Node GUI. For information about accessing the Node GUI, see
MINI-LINK 6352 Accessing a Network Element. The Overview page opens.
2. In the menu on the left, click Multinode System.
3. Under Multi-Band Booster, check the configured EtherType for LAN and
WAN interfaces.
26 Commercial in confidence 912/1543-HRA 901 20/11 Uen L | 2022-11-23
Configuring Multi-Band Booster with Hierarchical Radio Link Bonding using MINI-LINK Node-GUI
912/1543-HRA 901 20/11 Uen L | 2022-11-23 Commercial in confidence 27
Configuring Multi-Band Booster with Hierarchical Radio Link Bonding (hRLB)
4. Set the EtherType of the interfaces, if needed.
5. Set the WAN port and exactly one LAN port to Layer 1, using the Layer 1
capability check boxes.
6. Enable hRLB.
7. Click Save and then OK.
6.2 Configure Multi-Band Booster with hRLB on MINI-LINK
6600 (GUI)
1. In the Management tree, on the Packet tab, expand Packet.
2. Right-click Ethernet, point to Configure, and click Hierarchical Radio Link
Bonding
MINI-LINK Node GUI displays the Hierarchical Radio Link Bonding page.
3. On the Hierarchical Radio Link Bonding Groups tab, in the General panel,
select the member interfaces from the 10G Members and 2.5G Members
drop-down lists.
4. Click Save to apply changes.
Result: The hRLB interfaces are displayed:
Figure 5 Example Multi-Band Booster with hRLB Configuration
28 Commercial in confidence 912/1543-HRA 901 20/11 Uen L | 2022-11-23
Configuring Multi-Band Booster with Hierarchical Radio Link Bonding using MINI-LINK Node-GUI
5. Optionally, disable No Traffic alarm or Degraded Service alarm by selecting
the No traffic alarm or Degraded service alarm and click Save.
6. To specify the maximum radio link speed of an All Outdoor (MINI-LINK
6352) hRLB member node in the hRLB group, click on the External Radio
Link Speed tab.
MINI-LINK Node GUI displays the External Radio Link Speed tab.
7. Under RL speed (Mbit/s) specify the maximum radio link speed and click
Save.
Note: Setting this value properly is essential to have correct WAN
bandwidth utilization report for the hRLB group WAN interface.
Result: The maximum radio link speed is displayed:
Figure 6 Example Maximum Radio Link Speed Configuration
912/1543-HRA 901 20/11 Uen L | 2022-11-23 Commercial in confidence 29
You might also like
- Baseband ConnectionsBaseband 6648Document26 pagesBaseband ConnectionsBaseband 6648Sát Thủ Sân CỏNo ratings yet
- Switched Network Project - Comp1154Document19 pagesSwitched Network Project - Comp1154purpleblaze0201No ratings yet
- Ericsson Minilink PDFDocument2 pagesEricsson Minilink PDFStuartNo ratings yet
- 4 1551-Lza7016012 1uen.a2.pico6Document47 pages4 1551-Lza7016012 1uen.a2.pico6roy100% (1)
- RFL - FiberServiceC3794 - 5 - 20 - 13 PDFDocument20 pagesRFL - FiberServiceC3794 - 5 - 20 - 13 PDFRaj and Milissa Gandhi100% (1)
- HRLBDocument13 pagesHRLBNoorul ameenNo ratings yet
- Understanding UMTS Radio Network Modelling, Planning and Automated Optimisation: Theory and PracticeFrom EverandUnderstanding UMTS Radio Network Modelling, Planning and Automated Optimisation: Theory and PracticeMaciej NawrockiNo ratings yet
- Mini-Link 6000: Enabling 5G Transport EverywhereDocument8 pagesMini-Link 6000: Enabling 5G Transport EverywhereEdmilsonNo ratings yet
- MINI-LINK 6352 Eband - CommissioningDocument23 pagesMINI-LINK 6352 Eband - CommissioningmohaelexNo ratings yet
- Full Outdoor Eband MW - ML6352Document20 pagesFull Outdoor Eband MW - ML6352mohaelexNo ratings yet
- MINI-LINK 6600 L3 ServicesDocument16 pagesMINI-LINK 6600 L3 ServicesDiHLoSNo ratings yet
- Dual Band AntennaDocument6 pagesDual Band AntennaMohammad WagiallaNo ratings yet
- Ericsson MINI-LINK 6600 DatasheetDocument2 pagesEricsson MINI-LINK 6600 DatasheetIboro PeterNo ratings yet
- Ericsson Microwave-MobilisDocument33 pagesEricsson Microwave-Mobilisyacine bouazni100% (1)
- E Band AntennaDocument2 pagesE Band Antennawriterse1No ratings yet
- 01 - MINI LINK LH Product PresentationDocument35 pages01 - MINI LINK LH Product PresentationCesh CordisNo ratings yet
- Mini-Link Outdoor MW Access From Indoor UnitsDocument11 pagesMini-Link Outdoor MW Access From Indoor Unitszakariya nooman syed100% (1)
- ML IndoorDocument77 pagesML IndoorElfatih Hashim100% (1)
- Ericsson MINI-LINK Family Leads The Microwave Backhaul Market - EricssonDocument4 pagesEricsson MINI-LINK Family Leads The Microwave Backhaul Market - EricssonAhmad Badius Zaman0% (1)
- Chojnacota (5434) : ANT3 1.8 7/8 HPXDocument3 pagesChojnacota (5434) : ANT3 1.8 7/8 HPXCristobal Carrillo100% (1)
- License SystemDocument22 pagesLicense SystemJakoba FetindrainibeNo ratings yet
- Production Faulty Buffer Repair EducationDocument11 pagesProduction Faulty Buffer Repair EducationRaimundo Moura100% (2)
- Minilink5g BrochureDocument8 pagesMinilink5g BrochureuuiuiueNo ratings yet
- 1 28701 FGC 101 3441 Router 6471 Datasheet Rev G PDFDocument2 pages1 28701 FGC 101 3441 Router 6471 Datasheet Rev G PDFtariq mehmoodNo ratings yet
- Visibility Script For BasebandDocument16 pagesVisibility Script For BasebandWAQAS ASLAMNo ratings yet
- Ericsson at MWC 2015 ": We Enable Change-Makers"Document33 pagesEricsson at MWC 2015 ": We Enable Change-Makers"lumnwiNo ratings yet
- MINI-LINK Microwave NetworksDocument20 pagesMINI-LINK Microwave NetworksDIAMONDNo ratings yet
- Release 21Q1: Miroslaw Tarka Mikael Öhberg Massimiliano TornarDocument23 pagesRelease 21Q1: Miroslaw Tarka Mikael Öhberg Massimiliano TornarX XNo ratings yet
- MOP For L3 Configuration On ML6692Document6 pagesMOP For L3 Configuration On ML6692Emoka KingsleyNo ratings yet
- Installing and Managing Licenses MLTNDocument24 pagesInstalling and Managing Licenses MLTNMatar NiangNo ratings yet
- DCN Over VlanDocument14 pagesDCN Over VlanHedi PrimaNo ratings yet
- High Capacity Microwave Solution BriefDocument12 pagesHigh Capacity Microwave Solution BriefabdullahNo ratings yet
- Configuration Script CSG - ATN910C-B.HUIZUCAR - PHEONIX.01Document5 pagesConfiguration Script CSG - ATN910C-B.HUIZUCAR - PHEONIX.01AlexNo ratings yet
- Small Form-Factor Pluggable (SFP) Copper and Optical Fiber TransceiversDocument6 pagesSmall Form-Factor Pluggable (SFP) Copper and Optical Fiber TransceiversHari PrashannaNo ratings yet
- 06 RN31566EN40GLA0 NSN Radio Network Solution RU40 3.0Document35 pages06 RN31566EN40GLA0 NSN Radio Network Solution RU40 3.0Jimoh YunusNo ratings yet
- RBS 6000 Commissioning Procedure - PA1Document17 pagesRBS 6000 Commissioning Procedure - PA1He Ro90% (10)
- Split Mount MW - Indoor PartDocument40 pagesSplit Mount MW - Indoor Partmohaelex100% (1)
- SIU ComandDocument1 pageSIU ComandIoan Lapadus100% (1)
- Cli Command Guide For FD 24gbps NTDocument2,754 pagesCli Command Guide For FD 24gbps NTszejkdudiNo ratings yet
- 5216 1Document36 pages5216 1RogerioNo ratings yet
- Minilink BasDocument174 pagesMinilink BaspeterNo ratings yet
- SAU DescriptionDocument11 pagesSAU DescriptionИнга ТурчановаNo ratings yet
- MLTNDocument61 pagesMLTNMuhammad AyatullahNo ratings yet
- Minilink CN R2 SpesificationsDocument2 pagesMinilink CN R2 SpesificationsAjun Wicaksono0% (1)
- Introducing The Ericsson Rbs 6000 Series: BTS Field & Radio High Level SupportDocument22 pagesIntroducing The Ericsson Rbs 6000 Series: BTS Field & Radio High Level Supportcalvin mavakiseNo ratings yet
- Install Radio 2203Document41 pagesInstall Radio 2203YousufaLi Moiz Hussain0% (1)
- SIR & SDM in SDE MobileDocument42 pagesSIR & SDM in SDE Mobileisaac brine100% (1)
- 6352 DS PDFDocument2 pages6352 DS PDFLafi FahedNo ratings yet
- Ericsson Minilink Series: Transport Network ProductsDocument3 pagesEricsson Minilink Series: Transport Network ProductsMaz MoektiNo ratings yet
- Eric MiniLink Brochure 150608 LowresDocument5 pagesEric MiniLink Brochure 150608 Lowrespierre dumarchandNo ratings yet
- Ericsson UMTS RBS6000 NodeB Integration PDFDocument63 pagesEricsson UMTS RBS6000 NodeB Integration PDFRAYENNE AYOUBENo ratings yet
- 7302 7330 ISAM R2 5 Product InformationDocument112 pages7302 7330 ISAM R2 5 Product InformationMILTONBARRERANo ratings yet
- UMTS-BTS-Fault-Analysis 2020 PDFDocument516 pagesUMTS-BTS-Fault-Analysis 2020 PDFNaftal MassingueNo ratings yet
- Method of Procedure Semi Auto Integration On Site XL Axiata ProjectDocument10 pagesMethod of Procedure Semi Auto Integration On Site XL Axiata ProjectbintangNo ratings yet
- MOP For Controller 6610 IntegrationDocument39 pagesMOP For Controller 6610 Integrationstelco231100% (2)
- BaseBand Integration SAMYDocument16 pagesBaseBand Integration SAMYBOURAS Ihabe - بوراس إيهابNo ratings yet
- Antenna Interface For Microwave AntennasDocument11 pagesAntenna Interface For Microwave AntennasYassin100% (2)
- How To Upgrade TDM1001 in UbootDocument9 pagesHow To Upgrade TDM1001 in UbootAbdul GhaffarNo ratings yet
- LTE Self-Organising Networks (SON): Network Management Automation for Operational EfficiencyFrom EverandLTE Self-Organising Networks (SON): Network Management Automation for Operational EfficiencySeppo HämäläinenNo ratings yet
- Backhauling / Fronthauling for Future Wireless SystemsFrom EverandBackhauling / Fronthauling for Future Wireless SystemsKazi Mohammed Saidul HuqNo ratings yet
- Maazhasnain167 9a CCN PPRDocument8 pagesMaazhasnain167 9a CCN PPRMaaz ChauhannNo ratings yet
- Exchanging Data Over The Network Using DelphiDocument4 pagesExchanging Data Over The Network Using DelphiHiLmawan SikoboiSundaNo ratings yet
- Comcast Business IP Gateway User GuideDocument25 pagesComcast Business IP Gateway User GuidedeoptimaNo ratings yet
- 2nd Edition PDFDocument32 pages2nd Edition PDFjayaprasanna1230% (1)
- Fa19-Bcs-068 - 4D - DCCN Lab 6 TasksDocument6 pagesFa19-Bcs-068 - 4D - DCCN Lab 6 TasksHamza ZbNo ratings yet
- Welcome To Ccna: Lead by Eng AbyadDocument46 pagesWelcome To Ccna: Lead by Eng AbyadAbdifatah SaidNo ratings yet
- A07D12HS Datasheet: Quick SpecsDocument3 pagesA07D12HS Datasheet: Quick SpecsflacocNo ratings yet
- Creating LUN in NetApp Using CLIDocument2 pagesCreating LUN in NetApp Using CLIanon_326668689No ratings yet
- Documentatie Integrare EDI 01-03-2022Document10 pagesDocumentatie Integrare EDI 01-03-2022ralucaNo ratings yet
- DS-2CD2786G2-IZS Datasheet V5.5.98 20190902 Draft-1Document6 pagesDS-2CD2786G2-IZS Datasheet V5.5.98 20190902 Draft-1jorge solanoNo ratings yet
- Switch Ports MerakiDocument10 pagesSwitch Ports MerakiCarlos Torres MoranNo ratings yet
- ITP Standard Installation Procedure v1.1Document23 pagesITP Standard Installation Procedure v1.1Anonymous 4DHysinkAuNo ratings yet
- EPC Principle TestDocument8 pagesEPC Principle Testlaralym2No ratings yet
- CCNP Enterprise BrochureDocument6 pagesCCNP Enterprise BrochureAnataTumongloNo ratings yet
- Communications: Introduction To Telecommunications by GokhaleDocument60 pagesCommunications: Introduction To Telecommunications by GokhalePradnya Sarkale-DalviNo ratings yet
- 20-Port Mirroring CommandDocument10 pages20-Port Mirroring CommandArnon PipatbanjongNo ratings yet
- Troubleshooting OSI Layers 1 3Document7 pagesTroubleshooting OSI Layers 1 3Bhushan ZopeNo ratings yet
- DS-2CD3T56G2-4IS Posicionada Na Revisão OkaDocument7 pagesDS-2CD3T56G2-4IS Posicionada Na Revisão OkaPablo MenezesNo ratings yet
- TeSys T LTM R - Instruction SheetDocument4 pagesTeSys T LTM R - Instruction SheetDavid GarciaNo ratings yet
- 7.1.3.6 Lab Configuring Advanced EIGRP For IPv4 Features 1Document9 pages7.1.3.6 Lab Configuring Advanced EIGRP For IPv4 Features 1белимNo ratings yet
- School of Computer Science and IT: Question Bank Sub: 20mcasct303 - Desinging Enterprise NetworkDocument8 pagesSchool of Computer Science and IT: Question Bank Sub: 20mcasct303 - Desinging Enterprise NetworkNishant KumarNo ratings yet
- Mop Bb5216 Single GSM New Site g2 Oss ProcedureDocument25 pagesMop Bb5216 Single GSM New Site g2 Oss ProcedureMohamed Elhadi100% (2)
- Virtual LANDocument63 pagesVirtual LANVo Ngoc HoangNo ratings yet
- RW 7400 8008Document4 pagesRW 7400 8008Amos GoldmanNo ratings yet
- HSS9860 V900R008C20 Data Configuration and O&M (LTE)Document51 pagesHSS9860 V900R008C20 Data Configuration and O&M (LTE)sirjimyNo ratings yet
- Tasks Involved in Sending A LetterDocument37 pagesTasks Involved in Sending A LetterAnkur SodhiNo ratings yet
- X-WAY Driver On TCP/IP Installation and Start-Up GuideDocument40 pagesX-WAY Driver On TCP/IP Installation and Start-Up Guideعبد الكريم ملوحNo ratings yet
- CCNA Chapter 3 Study GuideDocument5 pagesCCNA Chapter 3 Study GuideSansribal AlonNo ratings yet
- MIS 6314 Long Quiz 4Document18 pagesMIS 6314 Long Quiz 4mary annNo ratings yet