Basic Concept of Oops
Basic Concept of Oops
Uploaded by
ROHANCopyright:
Available Formats
Basic Concept of Oops
Basic Concept of Oops
Uploaded by
ROHANCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Copyright:
Available Formats
Basic Concept of Oops
Basic Concept of Oops
Uploaded by
ROHANCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 6- Basic Concept of OOP
Chapter-6
BASIC CONCEPT OF OOP
Introduction:
Object oriented programming is the principle of design and development of programs using
modular approach.
Object oriented programming approach provides advantages in creation and development of
software for real life application.
The basic element of object oriented programming is the data.
The programs are built by combining data and functions that operate on the data.
Some of the OOP’s languages are C++, Java, C #, Smalltalk, Perl, and Python.
Procedural programming:
The procedural programming focuses on processing of
instructions in order to perform a desired computation.
Therefore it emphasizes more on doing things like algorithms.
This programming is lengthy, increases the complexity of
program, difficult to understand and modify the program.
This technique is used in a conventional programming language such as C and Pascal.
Structured programming:
An organized approach to programming involving
the use of three basic control structures – Sequence,
Conditional and loop.
The top-down concepts to decompose main
functions into lower level components for modular coding purpose.
The major drawback is that it is very difficult to model the real world scenario using this model.
Object oriented programming:
Object oriented programming (OOP) is a concept
that combines both the data and the functions that
operate on that data into a single unit called the
object.
An object is a collection of set of data known as
Smt Devika Lecturer in CS Page 1
Chapter 6- Basic Concept of OOP
member data and the functions that operate on these data known as member function.
OOP follows bottom-up design technique.
Class is the major concept that plays important role in this approach. Class is a template that
represents a group of objects which share common properties and relationships.
Difference between Procedural Programming & Object Oriented
programming:
Procedural Programming Object Oriented Programming
Large programs are divided into
Programs are divided into objects
smaller programs known as
Data is not hidden and can be Data is hidden and cannot be
accessed by external functions accessed by external functions
Follow top down approach in the Follows bottom-up approach
program design in the program design
Data may communicate with each Objects may communicate with each
other through functions other through functions.
Emphasize is on procedure rather Emphasize is on data rather
than data than procedure
Basic Concepts of OOP’ss:
The following are the major characteristics of OOP’s: Important
Objects Overloading
Class Polymorphism
Data abstraction Dynamic Binding
Data encapsulation Message Passing
Inheritance
Smt Devika Lecturer in CS Page 2
Chapter 6- Basic Concept of OOP
Objects
Objects are basic building blocks for designing programs.
An object is a collection of data members and associated member functions.
An object may represent a person, place or a table of data.
Each object is identified by a unique name. Each object must be a member of a particular class.
Example: Apple, orange, mango are the objects of class fruit.
Objects take up space in memory and have address associated with them.
At the time of execution of a program, the objects interact by sending the messages to one another.
The objects can interact with one another without having to know details of data or functions
within an object.
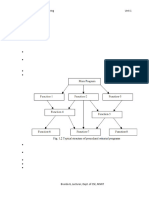
Classes:
The objects can be made user defined data types with the help of a class.
A class is a collection of objects that have identical properties, common
behavior and shared relationship.
Once class is defined, any number of objects of that class is created.
Classes are user defined data taypes. A class can hold both data and
functions.
For example: Planets, sun, moon are member of class solar system.
Data Abstraction:
Data Abstraction refers to the process of representing essential features without including
background details or explanations.
Data Encapsulation:
The wrapping of data and functions into a single unit (class) is called
data encapsulation.
Data encapsulation enables data hiding and information hiding.
Smt Devika Lecturer in CS Page 3
Chapter 6- Basic Concept of OOP
Data hiding is a method used in object oriented programming to hide information within computer
code.
Inheritance:
Inheritance is the process by which one object can
acquire and use the properties of another object.
The existing class is known as base class or super
class.
The new class is known as derived class or sub class.
The derived class shares some of the properties of the base class. Therefore a code from a base
class can be reused by a derived class.
Overloading:
Overloading allows objects to have different meaning depending upon context.
There are two types of overloading viz.
o Operator Overloading
o Function Overloading
When an existing operator operates on new data type is called operator overloading.
Function overloading means two or more function have same, but differ in the number of
arguments or data type of arguments.
Polymorphism:
The ability of an operator and function to take
multiple forms is known as Polymorphism.
The different types of polymorphism are operator
overloading and function overloading.
Dynamic binding:
Binding is the process of connecting one program to another.
Dynamic binding is the process of linking the procedure call to a specific sequence of code or
function at run time or during the execution of the program.
Message Passing:
In OOP’s, processing is done by sending message to objects.
A message for an object is request for execution of procedure.
Smt Devika Lecturer in CS Page 4
Chapter 6- Basic Concept of OOP
Message passing involves specifying the name of the object, the name of the function (message)
and the information to be sent.
Important
Advantage of OOP’s
The programs are modularized based on the principles of classes and objects.
Linking code & object allows related objects to share common code. This reduces code
duplication and code reusability.
Creation and implementation of OOP code is easy and reduces software development time.
The concept of data abstraction separates object specification and object implementation.
Data encapsulated along with functions. Therefore external non-member function cannot access or
modify data, thus proving data security.
Easier to develop complex software, because complexity can be minimized through inheritance.
OOP can communicate through message passing which makes interface description with
outside system very simple.
Disadvantage of OOP’s
Larger program size: OOP’s typically involves more lines of code than procedural programs.
Slower Programs: OOP’s typically slower than procedure based programs, as they typically
require more instructions to be executed.
Not suitable for all types of programs.
To convert a real world problem into an object oriented model is difficult.
OOP’s software development, debugging and testing tools are not standardized.
Polymorphism and dynamic binding also requires processing time, due to overload of function
calls during run time.
Application of OOP’s
Computer graphics applications.
.CAD/CAM software
Object-oriented database.
User-Interface design such as windows
Real-time systems.
Simulation and Modeling
Artificial intelligence and expert systems.
Client-Server Systems.
Smt Devika Lecturer in CS Page 5
Chapter 6- Basic Concept of OOP
Important Questions
2 Marks Question:
1. Explain: Classes, Objects, Data Abstraction, Data Encapsulation, Inheritance, and
Polymorphism.
2. What is Base class and derived class?
5 Marks Question:
1. Distinguish between procedural and object oriented programming.
2. Explain the characteristics of OOP’s.
3. Briefly explain the basic concepts of OOP’s.
4. Explain the advantages of OOP’s.
5. Mention disadvantages of OOP’s.
6. Write the applications of OOP’s.
Smt Devika Lecturer in CS Page 6
You might also like
- Case Study 1 Ahmad Haziq Isp500Document3 pagesCase Study 1 Ahmad Haziq Isp500haziqghz100% (1)
- Chapter 6 OopsDocument6 pagesChapter 6 OopsFaizal KhanNo ratings yet
- OOP Concept NotesDocument6 pagesOOP Concept NotesYou Are Not Wasting TIME Here100% (3)
- Chapter 6 OopsDocument6 pagesChapter 6 Oopsanu xeroxNo ratings yet
- Unit-1 (Part-A) Notes of OOPS by Updesh Kumar - UpdatedDocument29 pagesUnit-1 (Part-A) Notes of OOPS by Updesh Kumar - Updatedviku9267No ratings yet
- UNIT1pdf 2023 07 29 14 43 33Document43 pagesUNIT1pdf 2023 07 29 14 43 33Leeroy MugadzaNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Object Oriented ProgrammingDocument29 pagesFundamentals of Object Oriented ProgrammingkkalyaniNo ratings yet
- Unit - IvDocument63 pagesUnit - IvJit AggNo ratings yet
- 23IT1301 - OOPs - Unit - 1Document84 pages23IT1301 - OOPs - Unit - 1AJAY KRISHNANo ratings yet
- Unit IDocument13 pagesUnit ISeshu ChakravarthyNo ratings yet
- Ooc Notes SvitDocument229 pagesOoc Notes SvitM.A raja100% (1)
- MODULE1-Introduction To OOC PDFDocument50 pagesMODULE1-Introduction To OOC PDFJayanth P ShettyNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 C++Document19 pagesUnit 1 C++priyankaroy8638No ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Object Oriented ConceptsDocument3 pagesChapter 6 Object Oriented ConceptsVansh GuptaNo ratings yet
- Basic Concepts of OOps Assig + NotesDocument4 pagesBasic Concepts of OOps Assig + NotesVithan DineshNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Object Oriented Concepts PDFDocument3 pagesChapter 6 Object Oriented Concepts PDFirshad 10100% (1)
- Chapter 6-Object Oriented Concepts I PUC, MDRPUC, HassanDocument3 pagesChapter 6-Object Oriented Concepts I PUC, MDRPUC, HassanShubham YadavNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Object Oriented ConceptsDocument3 pagesChapter 6 Object Oriented ConceptsP.S. Mithul SouravNo ratings yet
- OOPS NotesDocument3 pagesOOPS Notesmanishgnayaka007No ratings yet
- Unit 1 Principles of OOP: What Is OOPS?Document55 pagesUnit 1 Principles of OOP: What Is OOPS?Kamini SalunkheNo ratings yet
- Chapter-1 ICTDocument18 pagesChapter-1 ICTMashrur Alam KabyaNo ratings yet
- Java - Unit-1 - FinalDocument108 pagesJava - Unit-1 - FinalKondru SirishaNo ratings yet
- 1 Chapter Principal of Object Oriented ProgrammingDocument10 pages1 Chapter Principal of Object Oriented Programmingbasur00basurNo ratings yet
- 01 What Is OOPDocument19 pages01 What Is OOPFarid KhanNo ratings yet
- C Programming Language & C++ Programming Language All Topics Covered.: Programming in C & C++ For Begineers and Advanced LevelDocument90 pagesC Programming Language & C++ Programming Language All Topics Covered.: Programming in C & C++ For Begineers and Advanced LevelShivam KulkarniNo ratings yet
- Basics of OopDocument6 pagesBasics of OopJassica AllenNo ratings yet
- Java Unit-1Document26 pagesJava Unit-1Hemanth GoliNo ratings yet
- What Is Object Oriented Programming? How It Is Differ From Procedure Oriented Programming?Document18 pagesWhat Is Object Oriented Programming? How It Is Differ From Procedure Oriented Programming?اریب صديقيNo ratings yet
- Module1 OOP NotesDocument35 pagesModule1 OOP NotesAkhil AkhiNo ratings yet
- Ooc Mod1@Azdocuments - inDocument50 pagesOoc Mod1@Azdocuments - inabhishekNo ratings yet
- Oops Full NotesDocument285 pagesOops Full Notespassion jobNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Object Oriented Programming Procedure Oriented Programming (POP)Document8 pagesFundamentals of Object Oriented Programming Procedure Oriented Programming (POP)NishanNo ratings yet
- OOSD Unit 1 1Document12 pagesOOSD Unit 1 1kimmisiingh04No ratings yet
- Object Oriented Programing UNIT 1,2,3Document52 pagesObject Oriented Programing UNIT 1,2,3rushabhkansara051No ratings yet
- What Is Procedural Programming?Document27 pagesWhat Is Procedural Programming?KHATRI DHRUVNo ratings yet
- Oodp Unit 1Document30 pagesOodp Unit 1Amp RajasriNo ratings yet
- 30 OOPs Interview Questions and AnswersDocument278 pages30 OOPs Interview Questions and AnswersYeePee IndoNo ratings yet
- Oops NotesDocument79 pagesOops NotesaminNo ratings yet
- Object Oriented Programming With C++Document159 pagesObject Oriented Programming With C++sridharanNo ratings yet
- OOPM UNIT 1 (Cse)Document64 pagesOOPM UNIT 1 (Cse)AnjiNo ratings yet
- OOP Unit1 P1Document25 pagesOOP Unit1 P1sonud96180No ratings yet
- Object Oriented ProgrammingDocument93 pagesObject Oriented ProgrammingSaheli SarkarNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Object Oriented ProgrammingDocument26 pagesFundamentals of Object Oriented ProgrammingGeneral Zorawar SinghNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 - Object Oriented Programming and Methodology - WWW - Rgpvnotes.inDocument16 pagesUnit 1 - Object Oriented Programming and Methodology - WWW - Rgpvnotes.inPiyush MallickNo ratings yet
- IntroductionDocument70 pagesIntroductionkaminisarode1507No ratings yet
- Week 12 Game ProgrammingDocument3 pagesWeek 12 Game Programmingagripino verderaNo ratings yet
- C++ Introduction - BU BCADocument6 pagesC++ Introduction - BU BCASabitha PadmajNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 1-OOP ConceptsDocument63 pagesChapter - 1-OOP ConceptsMik ClashNo ratings yet
- Basic Concepts of Object Oriented ProgrammingDocument3 pagesBasic Concepts of Object Oriented ProgrammingHEMALATHANo ratings yet
- Lecture # 1: Evolution of OOPDocument9 pagesLecture # 1: Evolution of OOPhamzaNo ratings yet
- Java Unit-1 NotesDocument25 pagesJava Unit-1 NotesmouliNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 PDFDocument4 pagesChapter 1 PDFIrfan AhmedNo ratings yet
- OOP in C++ Full Theory NotesDocument93 pagesOOP in C++ Full Theory NotesShantanu GopaleNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Principal of Object Oriented ProgrammingDocument15 pagesChapter 1 - Principal of Object Oriented Programmingbasur00basurNo ratings yet
- Object Oriented Programming Through Java R19 - UNIT-1Document46 pagesObject Oriented Programming Through Java R19 - UNIT-1mahesh vasaNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Object Orinted ProgrammingDocument10 pagesUnit 1 Object Orinted Programmingdaya gautamNo ratings yet
- OOPChapter 01Document6 pagesOOPChapter 01gemechu gebisaNo ratings yet
- Ist Unit 1Document24 pagesIst Unit 1degreecollegeNo ratings yet
- OOPS Notes For 3rd Sem ALL ChaptersDocument62 pagesOOPS Notes For 3rd Sem ALL Chaptersabhishek singh83% (6)
- CH 32 Units and Dimension: Daily Practice Problem 01 Today'S DPPDocument5 pagesCH 32 Units and Dimension: Daily Practice Problem 01 Today'S DPPROHANNo ratings yet
- CH 32 Units and Dimension: Daily Practice Problem 02 Today'S DPPDocument5 pagesCH 32 Units and Dimension: Daily Practice Problem 02 Today'S DPPROHANNo ratings yet
- Kinematics DPP 07Document4 pagesKinematics DPP 07ROHANNo ratings yet
- Kinematics DPP 04Document6 pagesKinematics DPP 04ROHANNo ratings yet
- Kinematics DPP 05Document4 pagesKinematics DPP 05ROHANNo ratings yet
- Ch-Laws of Motion DPP 03Document5 pagesCh-Laws of Motion DPP 03ROHANNo ratings yet
- Basic Mathematics DPP 01Document3 pagesBasic Mathematics DPP 01ROHANNo ratings yet
- Diploma in Electronics Engineering/ Electronics & Communication EngineeringDocument4 pagesDiploma in Electronics Engineering/ Electronics & Communication Engineeringcomic beastNo ratings yet
- Spring Transactions: By, Srinivas Reddy.SDocument20 pagesSpring Transactions: By, Srinivas Reddy.SHarleen DhingraNo ratings yet
- Aermod Userguide PDFDocument333 pagesAermod Userguide PDFMARIA PAULINA TEJERANo ratings yet
- Resume MysqlDocument3 pagesResume MysqlSudheep Chandran C PNo ratings yet
- SYS600 - IEC 60870-5-1-101 Slave ProtocolDocument116 pagesSYS600 - IEC 60870-5-1-101 Slave ProtocolOus-SamaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To PythonDocument20 pagesIntroduction To PythonSebastian OglageNo ratings yet
- The Essential Guide To System RecoveryDocument21 pagesThe Essential Guide To System RecoveryDincerNo ratings yet
- Studio Desk Plans V2 PDFDocument9 pagesStudio Desk Plans V2 PDFDonn PedalesNo ratings yet
- Sb4de36tDocument64 pagesSb4de36tN TNo ratings yet
- Wayne's Geocaching System SolutionsDocument7 pagesWayne's Geocaching System SolutionsNishshanka CJNo ratings yet
- Marantz SR8015 11.2ch 8K AV Receiver With 3D Audio, HEOS® Built-In and Voice ControlDocument2 pagesMarantz SR8015 11.2ch 8K AV Receiver With 3D Audio, HEOS® Built-In and Voice ControljimmymacbootNo ratings yet
- TestCaseTemplate 1Document6 pagesTestCaseTemplate 1Sujith StylishNo ratings yet
- Kubernetes ErrorDocument7 pagesKubernetes ErrorsatyaNo ratings yet
- Vonets VAP11S Quick Setting GuideDocument22 pagesVonets VAP11S Quick Setting GuideManivannan ManikamNo ratings yet
- 1989 SPE771 Christoffersen Whitson TABLEDocument5 pages1989 SPE771 Christoffersen Whitson TABLEPorfirio AguileraNo ratings yet
- Week 1.1 - Orientation ClassDocument18 pagesWeek 1.1 - Orientation ClassShreyasKumarNo ratings yet
- Abhishek TiwariDocument35 pagesAbhishek Tiwarivickyprasadmukandpur2482000No ratings yet
- LP Lab ManualDocument37 pagesLP Lab ManualBhargav Kumar JayanthiNo ratings yet
- Manual FusorDocument10 pagesManual FusorrichiuniNo ratings yet
- Python ModulesDocument4 pagesPython Modulesshivani mNo ratings yet
- 20f208-Java Mini Project - MergedDocument18 pages20f208-Java Mini Project - MergedMohamed Ashraf MANo ratings yet
- Configurations (22%) :: Build and Deployment (8%)Document6 pagesConfigurations (22%) :: Build and Deployment (8%)Vu Minh HuyNo ratings yet
- B.SC - Cyber Forensic SyllabusDocument68 pagesB.SC - Cyber Forensic Syllabussuryarjun23No ratings yet
- Dh-Xvr5116H-I2: 16 Channel Penta-Brid 5M-N/1080P Mini 1U Wizsense Digital Video RecorderDocument3 pagesDh-Xvr5116H-I2: 16 Channel Penta-Brid 5M-N/1080P Mini 1U Wizsense Digital Video RecorderAriadna PeñaNo ratings yet
- 342.01 Win10 Win8 Win7 Winvista Desktop Release NotesDocument47 pages342.01 Win10 Win8 Win7 Winvista Desktop Release NotesShafin JahinNo ratings yet
- Applied Productivity Tools With Advanced Application TechniquesDocument21 pagesApplied Productivity Tools With Advanced Application TechniquesRyan Rojas RicablancaNo ratings yet
- Security GovernanceDocument5 pagesSecurity GovernanceQaiser KhanNo ratings yet
- Assignment 7 - Software Engineering - 2023 (1) .Updated 29thDocument6 pagesAssignment 7 - Software Engineering - 2023 (1) .Updated 29thLiya Wilson100% (1)
- BMW Original Accessories - Snap in AdaptersDocument3 pagesBMW Original Accessories - Snap in AdaptersРоман БерезовськийNo ratings yet