DRUG STUDY (Furosemide)
DRUG STUDY (Furosemide)
Uploaded by
Glenn ConcepcionCopyright:
Available Formats
DRUG STUDY (Furosemide)
DRUG STUDY (Furosemide)
Uploaded by
Glenn ConcepcionOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Copyright:
Available Formats
DRUG STUDY (Furosemide)
DRUG STUDY (Furosemide)
Uploaded by
Glenn ConcepcionCopyright:
Available Formats
DRUG STUDY (Furosemide)
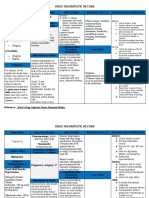
NAME OF ADVERSE NURSING
DRUG USE INDICATIONS/DOSAGES CONTRAINDICATIONS REACTIONS RESPONSIBILITIES
Furosemide ● Furosemide is used ● Acute pulmonary edema ● Contraindicated in CNS:vertigo, headache, ● To prevent
(Lasix) to treat hypertension Adults: 40mg I.V. injected clients dizziness, paresthesia, nocturia, give
(high blood slowly over 1 to 2 minutes; then hypersensitive to weakness, restlessness, P.O. and I.M.
pressure). It is also 80mg I.V. in 60 to 90 minutes if drug and in those fever. preparations in
used to treat edema. needed. with anuria. the morning.
This is swelling due CV: orthostatic Give second
to fluid buildup in ● Edema ● Use cautiously in hypotension, dose in early
the body. Edema can Adults: 20 to 80mg P.O. daily in clients with hepatic thrombophlebitis with afternoon.
be caused by other the morning. If response is cirrhosis and in I.V. administration.
medical conditions inadequate, give a second dose, those allergic to ● Alert: Monitor
such as heart failure,
and each succeeding dose, every sulfonamides. Use EENT: transient weight, blood
cirrhosis of the liver,
6 to 8 hours. Carefully increase during pregnancy deafness, blurred or pressure and
or kidney disease. dose in 20 to 40mg increments up only if potential yellowed vision, pulse rate
to 600mg daily. Once an effective benefits to the tinnitus. routinely with
● Furosemide may be dose is attained, may give once or mother clearly long-term use
used as part of a twice daily. Or, 20 to 40mg I.V. outweigh risks to GI: abdominal and during
combination therapy or I.M., increased by 20mg every the fetus. discomfort and pain, rapid diuresis.
to treat high blood 2 hours until desired effect diarrhea, anorexia, Use can lead to
pressure. This means achieved. nausea, vomiting, profound water
you may need to constipation, and electrolyte
take it with other Infants and Children: 2mg/kg pancreatitis. depletion.
medications. P.O. daily, increased by 1 to 2
mg/kg in 6 to 8 hours if needed; GU: nocturia, polyuria, ● If oliguria or
carefully adjusted up to 6mg/kg frequent urination, azotemia
daily if needed. oliguria. develops or
increases, drug
● Hypertension Hematologic: may need to be
Adults: 40mg P.O. b.i.d. Dosage agranulocytosis, stopped.
adjusted based on response. May aplastic anemia,
be used as adjunct to other leukopenia, ● Monitor fluid
antihypertensives if needed. thrombocytopenia, intake and
azotemia, anemia. output and
Children: 0.5 to 2mg/kg P.O. electrolyte,
once or twice daily. Increase dose Hepatic: hepatic BUN and
as needed up to 6mg/kg daily. dysfunction, jaundice. carbon dioxide
levels
I.V. Administration Metabolic: volume frequently.
● If it is discolored yellow, depletion and
don’t use it. dehydration, ● Watch for signs
● For direct injection, give asymptomatic of hypokalemia,
over 1 to 2 minutes. hyperuricemia, such as muscle
● For infusion, dilute with impaired glucose weakness and
D5W, normal saline tolerance, hypokalemia, cramps.
solution, or Lactated hypochloremic
Ringer solution. alkalosis, ● Consult
● To avoid ototoxicity, hyperglycemia, prescriber and
infuse no more than dilutional dietitian about a
4mg/minute. hyponatremia, high-potassium
● Use prepared infusion hypocalcemia, diet or
solutions within 24 hours. hypomagnesemia. potassium
supplements.
Musculoskeletal: Foods rich in
muscle spasm. potassium
include citrus
Skin: dermatitis, fruits, tomatoes,
purpura, bananas, dates
photosensitivity and apricots.
reactions, transient pain
at I.M. injection site. ● Monitor
glucose level in
Other: gout. diabetic clients.
● Drugs may not
be well
absorbed orally
in clients with
severe heart
failure. Drugs
may need to be
given I.V. even
if the client is
taking other
oral drugs.
● Monitor uric
acid level,
especially in
clients with a
history of gout.
● Store tablets in
light-resistant
containers to
prevent
discoloration
(doesn’t affect
potency).
Refrigerate oral
solution to
ensure drug
stability.
● Look
alike-sound
alike: Don’t
confuse
furosemide
with torsemide
or Lasix with
Lonox, Lidex
or Luvox.
DRUG STUDY (Prednisone)
NAME OF ADVERSE NURSING
DRUG USE INDICATIONS/DOSAGES CONTRAINDICATIONS REACTIONS RESPONSIBILITIES
Prednisone ● Prednisone is used to ● Severe inflammation, ● Contraindicated CNS: euphoria, ● Determine
(Prednisone treat conditions such immunosuppression with clients insomnia, psychotic whether the
Intensol) as arthritis, blood Adults: 5 to 60mg P.O. daily in a hypersensitive to behavior, pseudotumor client is
disorders, breathing single dose or as two to four drug or its cerebri, vertigo, sensitive to
problems, severe divided doses. Maintenance dose ingredients, in headache, paresthesia, other
allergies, skin given once daily or every other those with seizures. corticosteroids.
diseases, cancer, eye day. Dosage must be systemic fungal
problems, and individualized. infections, and in CV: heart failure, ● Drugs may be
immune system those receiving hypertension, edema, used for
disorders. Children: 0.14 to 2mg/kg or 4 to immunosuppressiv arrhythmias, alternate-day
Prednisone belongs 60mg/m2 daily P.O. in four e doses together thrombophlebitis, therapy.
to a class of drugs divided doses. with live-virus thromboembolism.
known as vaccines. ● Always adjust
corticosteroids. It ● Contact dermatitis; EENT: cataracts, to the lowest
decreases your poison ivy ● Use cautiously in glaucoma. effective dose.
immune system's Adults: Initially, 30mg (six 5-mg clients with recent
response to various tablets); taper by 5mg daily until MI, GI ulcer, renal GI: peptic ulceration, ● Most adverse
diseases to reduce 21 tablets have been given. disease, pancreatitis, GI reactions to
symptoms such as hypertension, irritation, increased corticosteroids
swelling and osteoporosis, appetite, nausea, are dose- or
allergic-type ● Acute exacerbations of diabetes mellitus, vomiting. duration-depen
reactions. multiple sclerosis hypothyroidism, dent.
Adults: 200mg P.O. daily for 7 cirrhosis, active GU: menstrual
days; then 80mg P.O. every other hepatitis, irregularities, increased ● For better
day for 1 month. diverticulitis, urine calcium level. results and less
nonspecific toxicity, give a
● Advanced pulmonary ulcerative colitis, Metabolic: once-daily dose
tuberculosis recent intestinal hypokalemia, in the morning.
Adults: 40 to 60mg P.O. daily for anastomoses, hyperglycemia,
30 days; taper over 4 to 8 weeks. thromboembolic hypocalcemia, ● Unless
disorders, seizures, carbohydrate contraindicated,
● Tuberculosis meningitis myasthenia gravis, intolerance, give oral dose
Adults: 1mg/kg P.O. daily for heart failure, hypercholesterolemia. with food when
30days; taper over several weeks. tuberculosis, ocular possible to
herpes simplex, Musculoskeletal: reduce GI
● Adjunctive treatment in emotional growth suppression in irritation.
Pneumocystis jiroveci instability, and children, muscle Clients may
(carinii) pneumonia in psychotic weakness, osteoporosis. need
clients with AIDS tendencies or in medication to
Adults and Children age 13 and breastfeeding Skin: hirsutism, delayed prevent GI
older: 40mg P.O. b.i.d. For 5 women. wound healing, acne, irritation.
days; then 40mg P.O. daily for 5 various skin eruptions.
days; then 20mg P.O. daily for 11 ● The oral
days or until completion of Other: cushingoid state, solution may be
anti-infective therapy. susceptibility to diluted in juice
infections, acute adrenal or other
insufficiency, after flavored diluent
increased stressor or semi-solid
abrupt withdrawal after food such as
long-term therapy. applesauce
before using.
After abrupt
withdrawal: rebound ● Monitor client’s
inflammation, fatigue, blood pressure,
weakness, arthralgia, sleep patterns
fever, dizziness, and potassium
lethargy, depression, level.
fainting, orthostatic
hypotension, dyspnea, ● Weigh clients
anorexia, hypoglycemia. daily; report
After prolonged use, sudden weight
sudden withdrawal may gain to
be fatal. prescriber.
● Monitor client
for cushingoid
effects,
including moon
face, buffalo
hump, central
obesity,
thinning hair,
hypertension
and increased
susceptibility to
infection.
● Drugs may
mask or worsen
infections,
including latent
amebiasis.
● Unless
contraindicated,
give a
low-sodium
diet that’s high
in potassium
and protein.
Give potassium
supplements, as
needed.
You might also like
- How To Find Out Anything About A Person - The Best Tutorial You Can FindDocument37 pagesHow To Find Out Anything About A Person - The Best Tutorial You Can Find0x 1switch100% (3)
- Prova Final Inter 1Document4 pagesProva Final Inter 1IMEITA 02No ratings yet
- Gentamycin Drug StudyDocument2 pagesGentamycin Drug StudyShin Guevara100% (3)
- HydrocortisoneDocument2 pagesHydrocortisoneIvanne Hisoler100% (15)
- DrugsDocument11 pagesDrugsedmond callenNo ratings yet
- Furosemide 1Document1 pageFurosemide 1Marck A. AlcedoNo ratings yet
- Paracetamol Drug StudyDocument2 pagesParacetamol Drug StudyKyla Lota0% (1)
- Maylynn Renal Lasix MonographDocument1 pageMaylynn Renal Lasix MonographAORN2008No ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument4 pagesDrug StudyMary AllizaNo ratings yet
- Drug Information Worksheet: Hypertension - 40 Twice DailyDocument57 pagesDrug Information Worksheet: Hypertension - 40 Twice DailyMichelle Davis-JacksonNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument7 pagesDrug StudyAlhadzra AlihNo ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY - FurosemideDocument2 pagesDRUG STUDY - FurosemideVANESSA PAULA ALGADORNo ratings yet
- Group 3 ActivityDocument5 pagesGroup 3 Activityspes.paasa.cocNo ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY Methotrexate and AntidoteDocument4 pagesDRUG STUDY Methotrexate and AntidoteSaidinaNo ratings yet
- Name of Drug Dosage, Frequency, Route, Timing Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effect Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument13 pagesName of Drug Dosage, Frequency, Route, Timing Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effect Nursing Responsibilitieskev mondaNo ratings yet
- IndapamideDocument2 pagesIndapamideNovi Yuliana100% (1)
- Drug Study ParacetamolDocument2 pagesDrug Study ParacetamolAhliah MauhayNo ratings yet
- FUROSEMIDEDocument2 pagesFUROSEMIDEjbespiritu100% (3)
- ParacetamolDocument2 pagesParacetamolKristine YoungNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Maam MJ (11-19)Document6 pagesDrug Study Maam MJ (11-19)Arevalo, Denisse S.No ratings yet
- DTR PediaDocument3 pagesDTR PediaMajojay AmadorNo ratings yet
- Drug Therapeutic RecordDocument3 pagesDrug Therapeutic RecordMajojay AmadorNo ratings yet
- Go SPIRONOLACTONE-PODocument4 pagesGo SPIRONOLACTONE-POSAMANTHA T. MODESTONo ratings yet
- GenericDocument1 pageGenericRaine NicolasNo ratings yet
- Final Drug StudyDocument81 pagesFinal Drug StudyMinaNo ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY - FurosemideDocument2 pagesDRUG STUDY - FurosemideKian HerreraNo ratings yet
- Drug Study 2Document4 pagesDrug Study 2EARL GERALD RICAFRANCANo ratings yet
- Bumetanide Drug Study WWW RNpedia ComDocument2 pagesBumetanide Drug Study WWW RNpedia ComYuuki Chitose (tai-kun)No ratings yet
- Furosemide Drug ProfileDocument34 pagesFurosemide Drug ProfileNur Ilmi SofiahNo ratings yet
- Clonidine HydrochlorideDocument1 pageClonidine HydrochloridebluetonksNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - ParacetamolDocument2 pagesDrug Study - ParacetamolNE TdrNo ratings yet
- FUROSEMIDEDocument6 pagesFUROSEMIDEPark JeongyeonNo ratings yet
- Hydralazine.1 3Document1 pageHydralazine.1 3SNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument2 pagesDrug StudyJan Lianne BernalesNo ratings yet
- Euro Pharma FurosemideDocument2 pagesEuro Pharma Furosemideashleiy17No ratings yet
- Ziprasidone Drug StudyDocument4 pagesZiprasidone Drug Studyshadow gonzalez100% (1)
- AmloDocument1 pageAmloamy navajaNo ratings yet
- EnalaprilDocument4 pagesEnalaprilGwyn RosalesNo ratings yet
- LisinoprilDocument3 pagesLisinoprilLIEZEL GRACE VELAYONo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument20 pagesDrug StudyLore Anne Mhae SantosNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - OB WardDocument8 pagesDrug Study - OB WardCheska YsabelleNo ratings yet
- Anti EpilepticsDocument4 pagesAnti EpilepticsWajih FarhanNo ratings yet
- Furosemid Citicoline Clexane, LevofloxacinDocument9 pagesFurosemid Citicoline Clexane, Levofloxacincotyboy50% (2)
- Case Presentation Station 3B Drug Study LosartanDocument3 pagesCase Presentation Station 3B Drug Study Losartanhahahahaaaaaaa100% (1)
- High Risk DrugsDocument50 pagesHigh Risk DrugsRuchi PaulNo ratings yet
- MethimazoleDocument3 pagesMethimazoleRenNo ratings yet
- Drugstudy JRODDocument4 pagesDrugstudy JRODPeyjeyNo ratings yet
- Diuretic Therapy and Drugs For Renal Failure: DiureticsDocument7 pagesDiuretic Therapy and Drugs For Renal Failure: DiureticsApple MaeNo ratings yet
- Drug Classification Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument17 pagesDrug Classification Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesAsterlyn ConiendoNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - AcetaminophenDocument2 pagesDrug Study - AcetaminophenVANESSA PAULA ALGADORNo ratings yet
- Drug Study For PsychosisDocument4 pagesDrug Study For PsychosisHoney Bee S. PlatolonNo ratings yet
- Anti PsychotisDocument21 pagesAnti Psychotissuresh sataguniNo ratings yet
- Zamora - Colon Cancer 2Document25 pagesZamora - Colon Cancer 2Kristel PunoNo ratings yet
- Lisinopril, TAB: Generic Name of Medication: Brand/trade Name of MedicationDocument6 pagesLisinopril, TAB: Generic Name of Medication: Brand/trade Name of MedicationCliff by the seaNo ratings yet
- 312-Rle-Drug StudyDocument4 pages312-Rle-Drug StudyRogelyn PatriarcaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study (Amiodarone)Document8 pagesDrug Study (Amiodarone)Justine Conui100% (1)
- ANTIPSYCHOTICSDocument25 pagesANTIPSYCHOTICSCheetahboi Shopee100% (4)
- NCP DS NCM114 RleDocument12 pagesNCP DS NCM114 RleAllysa Kyle AlfonsoNo ratings yet
- ACE InhibitorsDocument22 pagesACE InhibitorsHaidee GervacioNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument3 pagesDrug StudyCyril_Cybernat_1553No ratings yet
- Of Active Duodenal Ulcer: 40 MG PO orDocument3 pagesOf Active Duodenal Ulcer: 40 MG PO orAbie Jewel Joy RoqueNo ratings yet
- Critical Care Medications: Anti-Arrhythmics Study Guide: Critical Care EssentialsFrom EverandCritical Care Medications: Anti-Arrhythmics Study Guide: Critical Care EssentialsNo ratings yet
- 10h Air Hiroshima Reading PacketDocument13 pages10h Air Hiroshima Reading Packetapi-263744910No ratings yet
- To Splint or Not To Splint: The Current Status of Periodontal SplintingDocument15 pagesTo Splint or Not To Splint: The Current Status of Periodontal SplintingmailaNo ratings yet
- 1 PBDocument12 pages1 PBdewi arumNo ratings yet
- 02 ACF Bonds Stocks Projects CompaniesDocument67 pages02 ACF Bonds Stocks Projects CompaniesFlaminiaNo ratings yet
- Customer Course CatalogDocument108 pagesCustomer Course CatalogSanghwi HwangNo ratings yet
- 02-18-005 BIM Revit Modeling RFP FinalDocument12 pages02-18-005 BIM Revit Modeling RFP FinalSantosh NathanNo ratings yet
- Sets - Word ProblemsDocument2 pagesSets - Word ProblemsCamille LopezNo ratings yet
- Daan v. SandiganbayanDocument2 pagesDaan v. SandiganbayanMACNo ratings yet
- The Influence of Brand Image, Design, Feature, and Price On Purchasing Decision of Apple iOS Smartphone in Surakarta, IndonesiaDocument5 pagesThe Influence of Brand Image, Design, Feature, and Price On Purchasing Decision of Apple iOS Smartphone in Surakarta, Indonesiassagr123No ratings yet
- Blackbox BN2T Islander TutorialDocument32 pagesBlackbox BN2T Islander TutorialGraham WaterfieldNo ratings yet
- Basic 1-Practice 1ADocument2 pagesBasic 1-Practice 1ALesly Zapata ToribioNo ratings yet
- Learning Journal Unit 3 CS1104 FinalDocument3 pagesLearning Journal Unit 3 CS1104 FinalKareem NabilNo ratings yet
- Juan ClimacoDocument3 pagesJuan ClimacoAubrey CañeteNo ratings yet
- La Resiliencia Como Predictora Del Impacto NegativoDocument36 pagesLa Resiliencia Como Predictora Del Impacto NegativoRenee LissethNo ratings yet
- National Training of Teachers Grade 11 Career Guidance ModulesDocument31 pagesNational Training of Teachers Grade 11 Career Guidance Modulesmicai dpbNo ratings yet
- 1.3.3 Bruner's Inductive Learning TheoryDocument10 pages1.3.3 Bruner's Inductive Learning TheoryNurul Syafiqah NasirNo ratings yet
- The Magic Love Spell Herb That Will Make You IrresistibleDocument2 pagesThe Magic Love Spell Herb That Will Make You IrresistiblePamela Ann MooreNo ratings yet
- Bach's Mass in B Minor As Musical IconDocument12 pagesBach's Mass in B Minor As Musical IconscribdscribdjlpNo ratings yet
- Sale of Land AgreementDocument3 pagesSale of Land AgreementAjjas Insuranceagency100% (1)
- Role of An EntrepreneurDocument42 pagesRole of An EntrepreneurRohitkumarilu0% (1)
- This Study Resource Was: Page 1 of 5Document6 pagesThis Study Resource Was: Page 1 of 5LJBernardoNo ratings yet
- Leave Benefits (Cecilia Nacional)Document81 pagesLeave Benefits (Cecilia Nacional)Bhenjhan AbbilaniNo ratings yet
- A Place For Pluto Read Aloud 3 Lesson Plan Template 3105 1 3Document6 pagesA Place For Pluto Read Aloud 3 Lesson Plan Template 3105 1 3api-488277855No ratings yet
- CDCP Vs CuencaDocument5 pagesCDCP Vs CuencaJeanne CalalinNo ratings yet
- Cohesive DevicesDocument2 pagesCohesive DevicesMd SaifullahNo ratings yet
- The Green GenerationDocument3 pagesThe Green GenerationEstherNo ratings yet
- 05 Daftar Pustaka NewDocument3 pages05 Daftar Pustaka NewDanuSusantoNo ratings yet
- NWIE RepairDocument29 pagesNWIE RepairNosaErnest50% (2)