0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
43 viewsEuro Pharma Furosemide
Euro Pharma Furosemide
Uploaded by
ashleiy17Furosemide is a loop diuretic used to treat edema associated with congestive heart failure, liver cirrhosis, and renal disease. It works by inhibiting sodium chloride reabsorption in the ascending loop of Henle, resulting in increased excretion of sodium, chloride, and to a lesser extent potassium and bicarbonate ions. Common adverse reactions include fluid and electrolyte imbalances like hypokalemia. It can interact with other drugs like aminoglycoside antibiotics which may increase ototoxicity risk. Nursing considerations include using cautiously in patients with hepatic disease or sulfonamide allergies.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Euro Pharma Furosemide
Euro Pharma Furosemide
Uploaded by
ashleiy170 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
43 views2 pagesFurosemide is a loop diuretic used to treat edema associated with congestive heart failure, liver cirrhosis, and renal disease. It works by inhibiting sodium chloride reabsorption in the ascending loop of Henle, resulting in increased excretion of sodium, chloride, and to a lesser extent potassium and bicarbonate ions. Common adverse reactions include fluid and electrolyte imbalances like hypokalemia. It can interact with other drugs like aminoglycoside antibiotics which may increase ototoxicity risk. Nursing considerations include using cautiously in patients with hepatic disease or sulfonamide allergies.
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Furosemide is a loop diuretic used to treat edema associated with congestive heart failure, liver cirrhosis, and renal disease. It works by inhibiting sodium chloride reabsorption in the ascending loop of Henle, resulting in increased excretion of sodium, chloride, and to a lesser extent potassium and bicarbonate ions. Common adverse reactions include fluid and electrolyte imbalances like hypokalemia. It can interact with other drugs like aminoglycoside antibiotics which may increase ototoxicity risk. Nursing considerations include using cautiously in patients with hepatic disease or sulfonamide allergies.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as doc, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
43 views2 pagesEuro Pharma Furosemide
Euro Pharma Furosemide
Uploaded by
ashleiy17Furosemide is a loop diuretic used to treat edema associated with congestive heart failure, liver cirrhosis, and renal disease. It works by inhibiting sodium chloride reabsorption in the ascending loop of Henle, resulting in increased excretion of sodium, chloride, and to a lesser extent potassium and bicarbonate ions. Common adverse reactions include fluid and electrolyte imbalances like hypokalemia. It can interact with other drugs like aminoglycoside antibiotics which may increase ototoxicity risk. Nursing considerations include using cautiously in patients with hepatic disease or sulfonamide allergies.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as doc, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 2
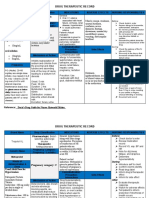
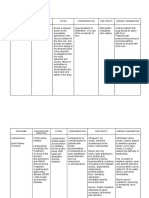
Euro Pharma Furosemide
Generic Name Indication Mechanism Contraindication Adverse Drug Interaction Nursing
Action Reaction Consideration
Edema associated Inhibits the re Most common Aminoglycoside Use cautiously in
Furosemide With CHF hepatic absorption of Anuria, fluid & antibiotics, patients with
Cirrhosis renal sodium chloride Hypersentivity to electrolyte cisplatin: hepatic cirrhosis
disease & is the drug,,severe renal inbalanced after potentiated and in those
ascending loop of disease associated either single ototoxicity. Use allergic to
henle this result in with azotemiaand largedoses is together sulfonamides.
Classification: the excretion of oliguria,hepatic prolonged cautiously. Furosemide should
sodium, chloride coma associated admin.allergy Amphotericin B, be used during
Cardiovascular & to a lesser with electrolyte nausea,diarrhea, corticosteroids, pregnancy only if
drugs degree, potassium depletion Blurred corticotropin, potential benefits
& bicarbonate vision,dizziness, metolazone: clearly outweigh
ions headache, increased risk of possible risks to
The resulting pancreatitis hypokalemia. fetus.
Dosage: urine is more Monitor
acid.the diuretics potassium levels To prevent
action is closely. nocturia, give P.O.
independent of Antidiabetics: and I.M.
changes acid – decreased preparations in the
base balance hypoglycemic morning. Give
effects. Monitor second dose in
blood glucose early afternoon.
levels.
Antihypertensives t-resistant
: increased risk of container to
hypotension. Use prevent
together discoloration
cautiously. (doesn't affect
Cardiac potency). Don't use
glycosides, discolored (yellow)
neuromuscular
blockers: inject able
increased toxicity preparation.
of these drugs Refrigerate oral
from furosemide- furosemide
induced solution to ensure
hypokalemia. drug stability.
Monitor
potassium levels.
Ethacrynic acid:
may increase risk
of ototoxicity.
Don't use
concomitantly.
Lithium:
decreased lithium
excretion,
resulting in
lithium toxicity.
Monitor lithium
level.
NSAIDs: inhibited
diuretic response.
Use together
You might also like
- CP-122 HSE Code of Practice - PDO PDFDocument96 pagesCP-122 HSE Code of Practice - PDO PDFEmre Cengiz100% (3)
- Zang Fu - The Organ Systems of Traditional Chinese Medicine (2ed) - Jeremy RossDocument274 pagesZang Fu - The Organ Systems of Traditional Chinese Medicine (2ed) - Jeremy RossFrancisco_A_Ribeiro67% (3)
- Guidelines For Ship Installation Collision Avoidance PDFDocument88 pagesGuidelines For Ship Installation Collision Avoidance PDFMurat Yilmaz100% (1)
- Techniques of Rational Emotive Behavioral Therapy (REBT)Document30 pagesTechniques of Rational Emotive Behavioral Therapy (REBT)Aamna Haneef81% (27)
- Drug Study 2Document4 pagesDrug Study 2EARL GERALD RICAFRANCANo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument4 pagesDrug StudyKaye Aligato ParaderoNo ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY - FurosemideDocument2 pagesDRUG STUDY - FurosemideVANESSA PAULA ALGADORNo ratings yet
- Drug Study LosartanDocument3 pagesDrug Study LosartanQueenie Mae ReyesNo ratings yet
- Furosemide: Agranulocytosis, Leukopenia, Thrombocytopen Ia, Anemia, Aplastic AnemiaDocument9 pagesFurosemide: Agranulocytosis, Leukopenia, Thrombocytopen Ia, Anemia, Aplastic AnemiaRanee Diane AnanayoNo ratings yet
- Emergency DrugsDocument10 pagesEmergency DrugsnieacatleyaNo ratings yet
- Er Drugs StudyDocument80 pagesEr Drugs StudyJobelle AcenaNo ratings yet
- Amphoterici N: Drug Pharmacokinetic Drug InteractionDocument4 pagesAmphoterici N: Drug Pharmacokinetic Drug InteractionJA BerzabalNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument7 pagesDrug StudyAlhadzra AlihNo ratings yet
- Oral-Revalida GDocument19 pagesOral-Revalida GJasmine CorreosNo ratings yet
- Drug Study 2.1Document2 pagesDrug Study 2.17y7f66q2qfNo ratings yet
- Final Drug StudyDocument81 pagesFinal Drug StudyMinaNo ratings yet
- DRUG ANALYSIS - AcetaminophenDocument1 pageDRUG ANALYSIS - AcetaminophenDaniel Andre S. SomorayNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument2 pagesDrug StudyJEWEL DEEN VILLARMENTE OQUIANANo ratings yet
- Cardiac Medication ListDocument2 pagesCardiac Medication Listgemma.parkerNo ratings yet
- Drug Analysis OB WardDocument9 pagesDrug Analysis OB WardTroy MirandaNo ratings yet
- DRUGS. Hypertensive Pantoloc, Diamicron Vit B, Furosemide CozaarDocument9 pagesDRUGS. Hypertensive Pantoloc, Diamicron Vit B, Furosemide CozaarEzron Kendrick DuranNo ratings yet
- Drug Study and NCP For Eamc Ob-Gyne Ward Case PresDocument4 pagesDrug Study and NCP For Eamc Ob-Gyne Ward Case PresvirnzrobzNo ratings yet
- FUROSEMIDEDocument2 pagesFUROSEMIDEjbespiritu100% (3)
- Generic Name:: Antituberculot IcDocument9 pagesGeneric Name:: Antituberculot IcPrincess Erika C. MendozaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study 1Document3 pagesDrug Study 1avreblora5193valNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument5 pagesDrug StudyanelyukiNo ratings yet
- Nursing Implication: OB, Lactation, Pedi: GeriDocument29 pagesNursing Implication: OB, Lactation, Pedi: GeriGlyssa CabarrubiasNo ratings yet
- Drugstudy JRODDocument4 pagesDrugstudy JRODPeyjeyNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - AtorvastatinDocument4 pagesDrug Study - Atorvastatinronaliza.guimbaolibot.cvtNo ratings yet
- Maylynn Renal Lasix MonographDocument1 pageMaylynn Renal Lasix MonographAORN2008No ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument6 pagesDrug StudyRosemarie CarpioNo ratings yet
- Generic Name: Atorvastatin Brand Name: Lipitor Dosage and RouteDocument3 pagesGeneric Name: Atorvastatin Brand Name: Lipitor Dosage and RouteRamsam UayanNo ratings yet
- Any Up-Dates Are To Be Completed in Different Color Ink. The Student Is Expected To Document All Meds The Client Is Currently ReceivingDocument1 pageAny Up-Dates Are To Be Completed in Different Color Ink. The Student Is Expected To Document All Meds The Client Is Currently Receivinggeorgeloto12No ratings yet
- Drugs Affecting Blood PressureDocument32 pagesDrugs Affecting Blood PressureJenica ManuntagNo ratings yet
- Cilostazol (Pletal)Document4 pagesCilostazol (Pletal)Maria Leonie Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Drugs and NCPDocument4 pagesDrugs and NCPApril Anne CostalesNo ratings yet
- Metformin Drug StudyDocument2 pagesMetformin Drug StudyArone SebastianNo ratings yet
- Ramiso 1Document2 pagesRamiso 1trialnumber0No ratings yet
- Generic Name (Brand Name) Classification Dosage Indication/ Contraindication Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument3 pagesGeneric Name (Brand Name) Classification Dosage Indication/ Contraindication Nursing ResponsibilitiesJoe Anne Maniulit, MSN, RNNo ratings yet
- Drug Study (Fluimicil, Atorvastatin, Piperacillin + Tazobactam..etc.)Document3 pagesDrug Study (Fluimicil, Atorvastatin, Piperacillin + Tazobactam..etc.)Kate PedzNo ratings yet
- Clonidine & Furosemide Drugs StudyDocument3 pagesClonidine & Furosemide Drugs StudyGrape JuiceNo ratings yet
- StudyDocument5 pagesStudyWestley RubinoNo ratings yet
- Drug Study (HERLINA)Document7 pagesDrug Study (HERLINA)Winnie Salazar AriolaNo ratings yet
- NCP DS NCM114 RleDocument12 pagesNCP DS NCM114 RleAllysa Kyle AlfonsoNo ratings yet
- Paracetamol Drug StudyDocument2 pagesParacetamol Drug StudyKyla Lota0% (1)
- Drug Name Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindication Side Effects Nursing Responsibility Generic NameDocument4 pagesDrug Name Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindication Side Effects Nursing Responsibility Generic NameDan HizonNo ratings yet
- Mefenamic Acid Drug StudyDocument4 pagesMefenamic Acid Drug StudyJay Ann Joy PerudaNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument33 pagesDrug Studyjefwy8No ratings yet
- Drug Therapeutic RecordDocument3 pagesDrug Therapeutic RecordMajojay AmadorNo ratings yet
- DTR PediaDocument3 pagesDTR PediaMajojay AmadorNo ratings yet
- IndapamideDocument2 pagesIndapamideNovi Yuliana100% (1)
- Drug StudyDocument7 pagesDrug StudyMelody Forca FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Drug Study DRDocument3 pagesDrug Study DRGershom Perez AcaboNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument3 pagesDrug StudyfortunelobsterNo ratings yet
- Kremil S CsDocument2 pagesKremil S Csunkown userNo ratings yet
- CNS: Dizziness, Assessment History: Allergy ToDocument7 pagesCNS: Dizziness, Assessment History: Allergy To6teen_gurlNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: Aspirin (Asa)Document5 pagesDrug Study: Aspirin (Asa)Shara Lailanie A. AzisNo ratings yet
- AspirinDocument2 pagesAspirinKarl Lourenz DeysolongNo ratings yet
- Practical Drug InteractionDocument5 pagesPractical Drug InteractionSantosh SinghNo ratings yet
- CarvedilolDocument2 pagesCarvedilolKarl Lourenz DeysolongNo ratings yet
- Name of Drug Dosage, Route, Frequency and Timing Mechanism of Action Indication Adverse Reactions Special Precautions Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument2 pagesName of Drug Dosage, Route, Frequency and Timing Mechanism of Action Indication Adverse Reactions Special Precautions Nursing ResponsibilitiesKarl Lourenz DeysolongNo ratings yet
- Austria - Drug Study - ObDocument1 pageAustria - Drug Study - ObRiczhelle AustriaNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument3 pagesDrug Studyanne_ayala_1No ratings yet
- Critical Care Medications: Anti-Arrhythmics Study Guide: Critical Care EssentialsFrom EverandCritical Care Medications: Anti-Arrhythmics Study Guide: Critical Care EssentialsNo ratings yet
- Nurse Practioner Syllabus RegulationsDocument69 pagesNurse Practioner Syllabus RegulationsSanthu SuNo ratings yet
- What Is Kashaya - Kashayalu & How To Prepare Kashaya - Wholesome TalesDocument3 pagesWhat Is Kashaya - Kashayalu & How To Prepare Kashaya - Wholesome TalesManisha MalikNo ratings yet
- Untitled Presentation PDFDocument118 pagesUntitled Presentation PDFSam MitraNo ratings yet
- A Review of The Community Health Club Literature Describing Water, Sanitation, and Hygiene OutcomesDocument33 pagesA Review of The Community Health Club Literature Describing Water, Sanitation, and Hygiene OutcomesJheyDyraNo ratings yet
- DesigningforUncertainty HannemannWerthmannHauck2015Document31 pagesDesigningforUncertainty HannemannWerthmannHauck2015Juliana Quintero MarinNo ratings yet
- 5Document1 page5Damian WayneNo ratings yet
- Title: Important Dates Meta DescriptionDocument5 pagesTitle: Important Dates Meta DescriptionShivangi SinghNo ratings yet
- Aeronid: SSRJVLPHR /JQ K P J/JL FGQDocument1 pageAeronid: SSRJVLPHR /JQ K P J/JL FGQSaifur Rahman SuzonNo ratings yet
- Carilex CentriusDocument4 pagesCarilex Centriusosmar.miteroNo ratings yet
- Heart, Nerve and Mucsle, Membrane Transport Mcqs With KeyDocument8 pagesHeart, Nerve and Mucsle, Membrane Transport Mcqs With KeyMudassar Roomi100% (7)
- Effect of Diammonium Glycyrrhizinate On Pharmacokinetics of Omeprazole by Regulating Cytochrome P450 Enzymes and Plasma Protein Binding RateDocument7 pagesEffect of Diammonium Glycyrrhizinate On Pharmacokinetics of Omeprazole by Regulating Cytochrome P450 Enzymes and Plasma Protein Binding RateFitra AlfaniNo ratings yet
- Eriochrome Black T Msds PDFDocument2 pagesEriochrome Black T Msds PDFDonaldNo ratings yet
- Citrus Sinensis PDFDocument17 pagesCitrus Sinensis PDFwiliersNo ratings yet
- Targeted Individuals - CIA MIND CONTROLLING YOU - 2nd Level - Press Release - Thewhiteroseii - Wordpress.com - PsyopsDocument221 pagesTargeted Individuals - CIA MIND CONTROLLING YOU - 2nd Level - Press Release - Thewhiteroseii - Wordpress.com - PsyopsGustav-Schneeclaus100% (3)
- Canon JudgeDocument69 pagesCanon JudgeHazel-mae LabradaNo ratings yet
- Summary of Clinical RotationDocument2 pagesSummary of Clinical RotationbulikakoNo ratings yet
- The Penn State Worry QuestionnaireDocument13 pagesThe Penn State Worry Questionnairecarolccy54No ratings yet
- HCA Healthcare/HealthONE's North Suburban Medical Center Announces New Chief Nursing OfficerDocument2 pagesHCA Healthcare/HealthONE's North Suburban Medical Center Announces New Chief Nursing OfficerPR.comNo ratings yet
- Aggelos Terzakis - Elliniki Epopoiia 1940 - 1941Document5 pagesAggelos Terzakis - Elliniki Epopoiia 1940 - 1941ryk74No ratings yet
- Yuk Mun Trading - Maq161y11076922021Document2 pagesYuk Mun Trading - Maq161y11076922021Agro Export and importNo ratings yet
- NDSRIs 0-2 AndreRaw WorkshopOverviewDocument5 pagesNDSRIs 0-2 AndreRaw WorkshopOverviewايناس ماجدNo ratings yet
- Clinical Study: Department of Pharmacology Faculty of Medicine Tadulako UniversityDocument38 pagesClinical Study: Department of Pharmacology Faculty of Medicine Tadulako UniversityMuh Ghaly SyadzalyNo ratings yet
- Peme Not ExploratoryDocument6 pagesPeme Not ExploratoryAldos Medina Jr.No ratings yet
- D.A.V Senior Secondary School: Biology Investigatory ProjectDocument22 pagesD.A.V Senior Secondary School: Biology Investigatory ProjecthashimNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Pediatric VentilationDocument41 pagesIntroduction To Pediatric Ventilationedderj2585No ratings yet
- Bioclix Remedies PCD Product SheetDocument4 pagesBioclix Remedies PCD Product SheetSudhir TripathiNo ratings yet