CHM231 - Tuto 1
CHM231 - Tuto 1
Uploaded by
2023502121Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
CHM231 - Tuto 1
CHM231 - Tuto 1
Uploaded by
2023502121Copyright:
Available Formats
CHM231
TUTORIAL 1: INTRODUCTION TO CHEMICAL ANALYSIS
1.1 TYPES AND STEPS IN ANALYSIS
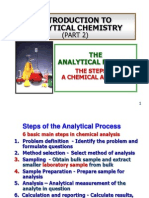
1. Give the main steps in chemical analysis.
Ans:
1) defining the problem
2) selecting the method
3) acquiring the representative sample
4) processing the sample
5) eliminating the interference
6) performing the measurement
7) calculating and presenting the result
2. Differentiate between qualitative analysis and quantitative analysis.
Ans: Quantitative analysis
● Analysis to determine how much of each constituent present in the
sample.
● Quantitative analysis is how much .
Qualitative analysis
● Analysis conducted to identify what are the constituents present in the
sample .
● Qualitative analysis is what .
3. State the type of analysis required for the following statements.
a) To determine and compare the percentage yield of fish oil in siakap and tilapia
fish.
Ans:Quantitative
b) To determine the presence of ascorbic acid in canned fruit juices.
Ans: Qualitative
c) To compare the amount of potassium content in varieties of local durians.
Ans: Quantitative
1.2 TREATMENT OF SAMPLE (TECHNIQUES OF SAMPLING, DRYING AND
WEIGHING)
1. Define the term sampling.
Ans:A process that obtained a representative sample of the whole sample where it can
be taken to laboratory for chemical analysis and the result obtained will be accurate.
2. Differentiate between gross sample and laboratory sample.
Ans:
Gross Sample Laboratory Sample
Consists of several portions of the Consists of small portions of gross
materials to be tested sample made homogenous
3. Describe the techniques of sampling the followings:
a) soil
Ans: Coning and Quartering is used as a method of sampling soil.
b) water
Ans: Water is a example of homogeneous mixture and it is easier to sample. So, since
the sampling techniques depends on the type of liquid, the water is included in the
category of large stationary liquids.
c) gas
Ans: It tends to be homogenous alkjnd requires a large volume of samples because
gases have lower density in states of matter. There are 3 methods that can be used in
this sampling such as air analysis, liquid displacement method and breath method.
4. Describe the problems that occurred when the sample was not handled and stored
properly before the analysis is carried out and suggest how to overcome these
problems.
Ans:
Problems occurred when the sample was Suggestions how to overcome these
not handled and stored properly before problems.
the analysis is carried out
Decomposition of sample from bacterial Samples may need to be stored in
sources refrigerator
Loss of the analyte due to exposure to -Put sample in a completely clean (sterile)
atmosphere or adsorption onto the wall of container or use contaminant-free
the container. containers
- should not be stored in glass container
Decomposition due light, heat or bacteria. Samples requiring preservation should be
preserved as soon as possible after
collection to maintain the integrity of the
sample.
1.3 DISSOLUTION OF SAMPLE AND ELIMINATION OF INTERFERENCES
1. Define the sample dissolution.
Ans: The sample is changed into solution form by dissolving the sample in suitable
solvents.
2. Name four (4) methods can be used in dissolution of samples.
Ans: (1)Partial dissolution, (2) total dissolution, (3)wet digestion, (4)dry ashing
3. Give three (3) differences between dry ashing and wet digestion.
Ans:
Dry ashing Wet digestion
determine the composition of a sample determine the composition of a sample
at its dry state at its aqueous state
Heating at a high temperature in muffle heating in the presence of a strong acid
furnace and an oxidizing agent
the sample in a dry state the sample is in aqueous state
4. Give three (3) sources of errors in decomposition and dissolution of solid samples.
Ans:
1)Light
2)Heat
3)Bacteria
5. Name two (2) common acids which can be used to dissolve organic samples prior to
analysis.
Ans: (1)HNO3 (2)HCl
6. Suggest three (3) separation methods to eliminate the interferences in the sample.
Ans:1)Precipitation
2)Extraction
3)Distillation
7. Give two (2) problems encountered during storage of samples.
Ans: It will cause contamination or alteration and loss of analyte due to exposure to
the atmosphere.
8. Explain why glass containers are inappropriate for sampling and storage of water
samples for trace level of heavy metals.
Ans: Glass containers are inappropriate for sampling and storage of water samples for
trace level of heavy metals because glass can leach small amounts of metal.
You might also like
- smww.1060 Ed 24 2023Document10 pagessmww.1060 Ed 24 2023DenisVYNo ratings yet
- A Novel Behavioral Scoring Model For Estimating Probability of DefaultDocument9 pagesA Novel Behavioral Scoring Model For Estimating Probability of DefaultSYEDA MAHEENNo ratings yet
- Topic 1.2 Analytical ProcessDocument52 pagesTopic 1.2 Analytical ProcessEyzah75% (8)
- Exp 11: Analysis of (Co (NH3) 5Cl) Cl2Document6 pagesExp 11: Analysis of (Co (NH3) 5Cl) Cl2Marla Basa50% (2)
- Chapter 4 Basic Requirements For AnalysisDocument41 pagesChapter 4 Basic Requirements For AnalysisSaffiyah AtiqahNo ratings yet
- Topic 3 - CHM421Document68 pagesTopic 3 - CHM421PUTRI DAYANA BATRIESYA ABDUL HANIFNo ratings yet
- Environmental Analytical ChemistryDocument6 pagesEnvironmental Analytical ChemistrykatlegoNo ratings yet
- Steps and Tools in A Typical Quantitative AnalysisDocument5 pagesSteps and Tools in A Typical Quantitative Analysisjay cNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Total Chloride Content in Concrete: RecommendationDocument3 pagesAnalysis of Total Chloride Content in Concrete: RecommendationKhalid JavedNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - Basic Requirements For AnalysisDocument80 pagesChapter 4 - Basic Requirements For AnalysisSPMUSER9A100% (1)
- Chapter 4 AmnDocument32 pagesChapter 4 Amnnur ilyanaNo ratings yet
- Chm256 c4 Part 1Document32 pagesChm256 c4 Part 1shahera rosdi100% (1)
- 9701 Practical Booklet 06 (Accompanies Scheme of Work 2016)Document19 pages9701 Practical Booklet 06 (Accompanies Scheme of Work 2016)Jonathan StashNo ratings yet
- Lecture 01 Analytical TechniquesDocument14 pagesLecture 01 Analytical TechniquesraowaleedahmadNo ratings yet
- Analitycal ProcessDocument52 pagesAnalitycal ProcessPa77ricioNo ratings yet
- ECE Lab Manual Requirements Sep 2021Document10 pagesECE Lab Manual Requirements Sep 2021supinya bieNo ratings yet
- TOXICITY CHARACTERISTIC LEACHING PROCEDURE-ThompsonDocument16 pagesTOXICITY CHARACTERISTIC LEACHING PROCEDURE-Thompsonptindosains1No ratings yet
- Leaving Certificate Chemistry Student Laboratory Notebook Teacher's ManualDocument42 pagesLeaving Certificate Chemistry Student Laboratory Notebook Teacher's ManualMusdq Chowdhury0% (1)
- Analytical Chemistry 1Document20 pagesAnalytical Chemistry 1Andrew May Ncube100% (1)
- BIO 10 Laboratory ManualDocument55 pagesBIO 10 Laboratory ManualRonneil Bilbao0% (1)
- AP Bio EssaysDocument34 pagesAP Bio EssayshyacyntheNo ratings yet
- ProposalDocument13 pagesProposalJack JackNo ratings yet
- OpQuiz Test122Document2 pagesOpQuiz Test122asifmullaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 THE ANALYSIS OF REAL SAMPLESDocument2 pagesChapter 3 THE ANALYSIS OF REAL SAMPLESChristian EduardoNo ratings yet
- 1.0 Bio150 Laboratory GuidelinesDocument11 pages1.0 Bio150 Laboratory GuidelinesNUR AISHAH MOHAMADNo ratings yet
- 4-Activated Carbon AdsorptionDocument3 pages4-Activated Carbon AdsorptioncenbanaNo ratings yet
- SamplingDocument19 pagesSamplingMae Christine PaduaNo ratings yet
- Analytical Chem-Unit 3Document10 pagesAnalytical Chem-Unit 3Jayson PolinarNo ratings yet
- CE6611 Environmental Engineering Lab ManualDocument44 pagesCE6611 Environmental Engineering Lab ManualArun Pugal100% (3)
- Week 8 - Quantitative Analysis-1Document37 pagesWeek 8 - Quantitative Analysis-1Jose LimNo ratings yet
- Water Andre FriDocument232 pagesWater Andre Friwnew2me428100% (1)
- Redox GravimetricDocument6 pagesRedox GravimetricadillezbaboolalNo ratings yet
- CHEM 130 Lab Manual Fall 2011Document64 pagesCHEM 130 Lab Manual Fall 2011CaledoniaHearthPipesNo ratings yet
- EE II Lab Manual2020Document29 pagesEE II Lab Manual2020Shweta UmaleNo ratings yet
- Inherent in An Experiment Sources of ErrorsDocument9 pagesInherent in An Experiment Sources of ErrorsfynnkohkexuanNo ratings yet
- CO2 LaserDocument75 pagesCO2 Lasersanchanar6No ratings yet
- Anachem (Prelim)Document5 pagesAnachem (Prelim)zzrot1No ratings yet
- 05 Analyze A MixtureDocument9 pages05 Analyze A MixtureBano KhanNo ratings yet
- Lab Manual March 2023Document23 pagesLab Manual March 2023MASYITAH MOHD PADZILNo ratings yet
- Pre Lab Experiment 4 Analysis of Lipids CaliganDocument6 pagesPre Lab Experiment 4 Analysis of Lipids CaliganMary Angelique CaliganNo ratings yet
- Medt25 01 Module Rubrics Urinalysis FecalysisDocument13 pagesMedt25 01 Module Rubrics Urinalysis Fecalysissharon agorNo ratings yet
- Experiment 4: Water Analysis Solids Gallardo, Hans Tristan MDocument7 pagesExperiment 4: Water Analysis Solids Gallardo, Hans Tristan Mjamila milanoNo ratings yet
- EXP 32 - Batch AdsorptionDocument2 pagesEXP 32 - Batch AdsorptionResky Ervaldi SaputraNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Techniques and MethodsDocument5 pagesLaboratory Techniques and MethodsSkyeNo ratings yet
- Top Evaluation Examination - 2016: Biology Combined Paper Form 2 July/AugustDocument7 pagesTop Evaluation Examination - 2016: Biology Combined Paper Form 2 July/Augustpeterrolland22No ratings yet
- SpectrometerDocument17 pagesSpectrometerMazzel Lou BaelNo ratings yet
- STK1121 LabManual 2017 PDFDocument32 pagesSTK1121 LabManual 2017 PDFmirayeollieNo ratings yet
- Environmental LabDocument51 pagesEnvironmental LabTop5 foryouNo ratings yet
- Water Hyacinth Eichhornia Crassipes FingDocument49 pagesWater Hyacinth Eichhornia Crassipes FingBea BaguioNo ratings yet
- The University of Al-Mustansiriyah College of Pharmacy Dep of Pharmaceutical Chemistry &pharmacognosyDocument38 pagesThe University of Al-Mustansiriyah College of Pharmacy Dep of Pharmaceutical Chemistry &pharmacognosyabdul88fNo ratings yet
- First Lab (Compatibility Mode)Document49 pagesFirst Lab (Compatibility Mode)ahmed94062331No ratings yet
- CHE311 Analytical Chemistry Quizzes CollectionDocument161 pagesCHE311 Analytical Chemistry Quizzes CollectionRenee KimNo ratings yet
- Topic 1.2 - Analytical ProcessDocument44 pagesTopic 1.2 - Analytical ProcessHaiqal Aziz100% (1)
- ZOO 120 Laboratory ExperimentsDocument17 pagesZOO 120 Laboratory ExperimentsErica De Guzman100% (1)
- Diffusion and Osmosis LabsDocument2 pagesDiffusion and Osmosis Labsgailluna112795No ratings yet
- 4 UVVis TroubleshootingDocument2 pages4 UVVis TroubleshootingYoya LoyaNo ratings yet
- Proximate AnalysisDocument29 pagesProximate AnalysisAhmad ArifNo ratings yet
- Lecture Note of SamplingDocument17 pagesLecture Note of SamplingSaitrushna JenaNo ratings yet
- LABORATORY MANUAL FOR A MINI PROJECT: MSCB 1113 BIOCHEMISTRY & MICROBIAL PHYSIOLOGYFrom EverandLABORATORY MANUAL FOR A MINI PROJECT: MSCB 1113 BIOCHEMISTRY & MICROBIAL PHYSIOLOGYNo ratings yet
- Standard methods for the examination of water and sewageFrom EverandStandard methods for the examination of water and sewageNo ratings yet
- TM3101 Design Project Report PDFDocument128 pagesTM3101 Design Project Report PDFMd. Mahabubul HassanNo ratings yet
- About HDFC Bank and RoadmapDocument17 pagesAbout HDFC Bank and RoadmapManu GargNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 SummaryDocument3 pagesChapter 1 Summaryparini soniNo ratings yet
- Artificial IntelligenceDocument17 pagesArtificial IntelligenceAppleNo ratings yet
- Order ID 352758453Document6 pagesOrder ID 352758453James NdiranguNo ratings yet
- HW 01Document2 pagesHW 01Wajeeha KhanNo ratings yet
- Nitoflor FC100 PDFDocument4 pagesNitoflor FC100 PDFriverwilliamsNo ratings yet
- Official Te Aho Matua Feb.08Document14 pagesOfficial Te Aho Matua Feb.08Joshua WoodhamNo ratings yet
- ABAP For SAP HANA' Points To RememberDocument170 pagesABAP For SAP HANA' Points To RememberPreethish Reddy Reva100% (2)
- Simplified Method For Performance-Based Siesmic Design of Suction Caisson Supporting Jacket OWTDocument23 pagesSimplified Method For Performance-Based Siesmic Design of Suction Caisson Supporting Jacket OWTDang Quang MinhNo ratings yet
- CV - Spillway Penstocks BidaproDocument6 pagesCV - Spillway Penstocks BidaproCretu DanNo ratings yet
- It's in The Air ... ... Quality Does Indeed Make A Difference!Document2 pagesIt's in The Air ... ... Quality Does Indeed Make A Difference!XIN NIUNIUNo ratings yet
- SyllabusDocument1 pageSyllabusKalyana Sundaram M.SNo ratings yet
- Paper N-Standard Penetration Test (SPT) : Muchammad Lextito Harnadi D100 154 010Document13 pagesPaper N-Standard Penetration Test (SPT) : Muchammad Lextito Harnadi D100 154 010Lextito HarnadiNo ratings yet
- Case Study 2Document3 pagesCase Study 2op bolte broNo ratings yet
- Eng Akrapovic Spec S-Y125SO4-HRSSDocument2 pagesEng Akrapovic Spec S-Y125SO4-HRSSclinic carsNo ratings yet
- Cambridge O Level: BIOLOGY 5090/62Document12 pagesCambridge O Level: BIOLOGY 5090/62Shiromi GnanapriyaNo ratings yet
- Grade 8 Q3 Mod 1Document10 pagesGrade 8 Q3 Mod 1Jami BrianNo ratings yet
- Btftoe605c - Marketing ReasearchDocument3 pagesBtftoe605c - Marketing ReasearchMegha ShuklaNo ratings yet
- Technical Service Information: Ford Motor Company Trucks 1996 and LaterDocument4 pagesTechnical Service Information: Ford Motor Company Trucks 1996 and LaterLUISNo ratings yet
- SOCAP14 Program GuideDocument96 pagesSOCAP14 Program Guidehfaison110% (1)
- BV Cvxbook Extra ExercisesDocument139 pagesBV Cvxbook Extra ExercisesAkhil AmritaNo ratings yet
- Sika PDS - E - Sarnafil G 476 PDFDocument3 pagesSika PDS - E - Sarnafil G 476 PDFlwin_oo2435No ratings yet
- Spe 132704 MSDocument11 pagesSpe 132704 MSJessica King100% (1)
- Hot Man ThesisDocument8 pagesHot Man Thesislaurasmithkansascity100% (1)
- As Members of The IESL Who Are Bound by The IESLDocument4 pagesAs Members of The IESL Who Are Bound by The IESLNipun JamesNo ratings yet
- Thailand Expor OpportunityDocument38 pagesThailand Expor OpportunitySyefrial Abidin FikriyansyahNo ratings yet
- BSBDIV501 Unit of Competency Final Result V2Document1 pageBSBDIV501 Unit of Competency Final Result V2Agus BudionoNo ratings yet
- Risk Assessment Worksheet: AS/NZS 4801 OHSAS 18001 OHS20309 SAI GlobalDocument2 pagesRisk Assessment Worksheet: AS/NZS 4801 OHSAS 18001 OHS20309 SAI GlobalferyanNo ratings yet