Demineralization of Water by Ion Exchange
Demineralization of Water by Ion Exchange
Uploaded by
DeenaCopyright:
Available Formats
Demineralization of Water by Ion Exchange
Demineralization of Water by Ion Exchange
Uploaded by
DeenaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Copyright:
Available Formats
Demineralization of Water by Ion Exchange
Demineralization of Water by Ion Exchange
Uploaded by
DeenaCopyright:
Available Formats
Demineralization of water by Ion exchange or
Demineralization process – (An External treatment)
Softening or conditioning of water
• The process of removing hardness producing salt from water.
• Two methods are (a) External treatment (b) internal treatment
Ion exchange or demineralization process
• The process in which removal of almost all the ions (both anion and
cation) present in the hard water.
• The soft water, produced by lime-soda and zeolite processes, does
not contain hardness producing Ca and Mg ions, but it will contain
2+ 2+
other ions like Na+, K+, SO42–, Cl– etc.,
• On the other hand demineralised (DM) water does not contain both
anions and cations.
• Thus soft water is not demineralised water, whereas demineralised water
is soft water.
Demineralization process
• This process is carried out by using ion exchange resins, which are
long chain, cross linked, insoluble organic polymers.
• The functional groups of present in resins are responsible for the
ion exchanging properties.
Cation exchanger
• Resins containing acidic functional groups (–COOH, – SO3H).
• Acidic resins are capable of exchanging their H + ions with other cation
present in hard water.
• Cation exchange resin is represented as RH2.
Examples: Sulphonatedcoals, Sulphonated polystyrene, R–SO3H; R–
COOH ≡ RH2.
Anion Exchanger
• Resins containing basic functional groups (–NH2, –OH).
• Basic resins are capable of exchanging their anions with other
anions present in hard water.
• Anion exchange resin is represented as R (OH)2.
Examples: Cross-linked quaternary ammonium salts, Urea-
formaldehyde resin, R–NR3OH; R–OH; R–NH2 ≡ R (OH)2
Process
• The hard water first passed through a cation exchange which absorbs
all the cations like Ca2+, Mg2+ Na+, K+ from the hard water.
RH2 + CaCl2 → RCa + 2HCl
RH2 + MgSO4 → RMg + H2SO4
RH + NaCl → RNa + HCl
• The cation free water is then passed through anion exchange column.
• Cation exchange column absorbs all the anions like Cl–, SO42-, HCO3–,
from the hard water.
R' (OH)2 + 2HCl → R'Cl2 + 2H2O
R'(OH)2 + H2SO4 → R'SO4 + 2H2O
• The water coming out of the anion exchanger completely free from
cations and anions.
• This water is known as demineralised water or deionised water.
Regeneration
• The exhausted cation exchange resin can be regenerated by passing a
solution of dil.HCl or dil.H2SO4.
RCa + 2HCl → RH2 + CaCl2
RNa + HCl → RH + NaCl
• Similarly, the exhausted anionic exchange resin can be regenerated by
passing a solution of aq.NaOH.
R’Cl2 + 2 NaOH → R'(OH)2 + 2 NaCl
Advantages
• The obtained water will have very low hardness.
• Highly acidic or alkaline water can be treated by this process.
Disadvantages
• The equipment is costly.
• More explosive chemicals are needed for this process.
• Water containing turbidity, Fe and Mn cannot be treated. Hence
turbidity reduces the output.
Difference between Zeolite and Demineralization process
S.no Zeolite process Deminealization process
1. It exchanges only cation It exchanges both anion and cation
2 Acidic water cannot be treated Acidic water can be treated
3 The treated water contains contain The treated water does not contain
small amount of dissolved salts. small amount of dissolved salts.
Hence priming, foaming, and Hence there is no priming, foaming,
caustic embrittlement are possible. and caustic embrittlement.
4 Water containing turbidity, Fe, Mn Also, Water containing turbidity, Fe,
cannot be treated. Mn cannot be treated.
5 Treated water is not soft water. Treated water is a soft water.
You might also like
- Chemistry Project Topics and MaterialsDocument2 pagesChemistry Project Topics and MaterialsAshiru Nuhu100% (1)
- Softening Methods4Document3 pagesSoftening Methods4Tejas YadavNo ratings yet
- Ion Exchange Method (De-Ionisation or Demineralisation) : I) Cation Exchange ResinsDocument10 pagesIon Exchange Method (De-Ionisation or Demineralisation) : I) Cation Exchange ResinsRaunit VermaNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 Part 3 PPT (1) ChemDocument16 pagesUnit 4 Part 3 PPT (1) Chemneha yarrapothuNo ratings yet
- Removal of Hardness 1Document35 pagesRemoval of Hardness 1KISHAN PATELNo ratings yet
- Rohini 93707242656Document11 pagesRohini 93707242656a97724972No ratings yet
- Unit-I Water TechnologyDocument22 pagesUnit-I Water TechnologyManivannanVenkatesan100% (1)
- Chemistry Materials - QuestionsDocument11 pagesChemistry Materials - QuestionsSanthosh kannaNo ratings yet
- Water Treatment Process: By: - S U Ya SH Ke Di A (L008) Tan Ishq G Upta (L006) Anubhavmaheshwari (L011)Document12 pagesWater Treatment Process: By: - S U Ya SH Ke Di A (L008) Tan Ishq G Upta (L006) Anubhavmaheshwari (L011)Tanishq GuptaNo ratings yet
- 3Document66 pages3Nikhil AroraNo ratings yet
- DM PlantDocument25 pagesDM PlantAbdul BokhariNo ratings yet
- Removal of Hardness Water TreatmentDocument6 pagesRemoval of Hardness Water TreatmentEffat JahanNo ratings yet
- Ion Exchange Theory (Portable Mixed Bed)Document9 pagesIon Exchange Theory (Portable Mixed Bed)Ahmed NizamNo ratings yet
- ZeolitesDocument14 pagesZeolitessamikshamalik1610No ratings yet
- Water Softening Methods and DemineralizationDocument36 pagesWater Softening Methods and DemineralizationPRASADNo ratings yet
- Water Treatment Lectures Week5@Sep18!22!2023Document28 pagesWater Treatment Lectures Week5@Sep18!22!2023Airbus A320No ratings yet
- Ion ExchangeDocument4 pagesIon ExchangeslchemNo ratings yet
- M1 L9 Zeolite Ion ExchangeDocument21 pagesM1 L9 Zeolite Ion Exchangegaurav toppoNo ratings yet
- Water SofteningDocument8 pagesWater SofteningRafio AhmedNo ratings yet
- 1843 159 578 Water-3Document12 pages1843 159 578 Water-3Mercy SajiNo ratings yet
- 1844 159 578 Water-4Document24 pages1844 159 578 Water-4Mercy SajiNo ratings yet
- Unit - I: Water TreatmentDocument127 pagesUnit - I: Water TreatmentAnu ShanthanNo ratings yet
- Caco Mgco MG (OH)Document28 pagesCaco Mgco MG (OH)Shivam KumarNo ratings yet
- BV Water Lecturer 2Document15 pagesBV Water Lecturer 2Prathamesh KumbharNo ratings yet
- Basic Ion Exchange ProcessesDocument12 pagesBasic Ion Exchange ProcessesMd Suzon MahmudNo ratings yet
- Water SofteningDocument20 pagesWater SofteningHassan AliNo ratings yet
- Environmental Chemistry - Causes of Hardness in WaterDocument87 pagesEnvironmental Chemistry - Causes of Hardness in WaterVikas KabburiNo ratings yet
- Hardness of WaterDocument20 pagesHardness of Waterneelesh_rawat100% (1)
- Water Quality Requirements and Auxiliary Chemicals For DyeingDocument27 pagesWater Quality Requirements and Auxiliary Chemicals For DyeingMegatronNo ratings yet
- FALLSEM2022-23 BCHY101L TH VL2022230105172 Reference Material I 20-12-2022 Module-7-Water Softening MethodsDocument81 pagesFALLSEM2022-23 BCHY101L TH VL2022230105172 Reference Material I 20-12-2022 Module-7-Water Softening MethodsVenkat BalajiNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Da1Document6 pagesChemistry Da1Vijayaraj MNo ratings yet
- Water Softening MethodsDocument34 pagesWater Softening MethodsAjitsingh Jagtap100% (1)
- DM PlantDocument9 pagesDM Plantsohag97No ratings yet
- Water Traetment Lecture 4 NewDocument28 pagesWater Traetment Lecture 4 NewMuzamil RaoNo ratings yet
- Dardel InfoDocument7 pagesDardel InfoajwebNo ratings yet
- Ion Exchange ProcessDocument10 pagesIon Exchange Process056 Jatin GavelNo ratings yet
- Water and Its Treatment-7,8Document4 pagesWater and Its Treatment-7,8Tushar SharmaNo ratings yet
- Basic Ion Exchange ProcessesDocument7 pagesBasic Ion Exchange ProcessesandriNo ratings yet
- Hydrogen NotesDocument46 pagesHydrogen Notesmbarwani2812No ratings yet
- Basic Ion Exchange ProcessesDocument9 pagesBasic Ion Exchange ProcessesSAYEDNo ratings yet
- Water 2SDocument35 pagesWater 2SIshan Satya PrakashNo ratings yet
- Guide To Water TechnologyDocument29 pagesGuide To Water TechnologyManjunath NadarajanNo ratings yet
- Reverse Osmosis Fuels and Combustion - LCV, HCV,-29-04-2024Document62 pagesReverse Osmosis Fuels and Combustion - LCV, HCV,-29-04-2024Unbreakable SwordNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Unit 1 Water Technology Part A Question BankDocument4 pagesChemistry Unit 1 Water Technology Part A Question Bankganesh48mpNo ratings yet
- Water Final 2019 20Document40 pagesWater Final 2019 20Maheroz shaikhNo ratings yet
- Watertreatmentandanalysis 2Document19 pagesWatertreatmentandanalysis 2O MNo ratings yet
- Water SofteningDocument6 pagesWater SofteningHuda ShahNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7Document21 pagesChapter 7Solomon DesalegnNo ratings yet
- Softening FinalDocument23 pagesSoftening FinalSonali Jahagirdar100% (1)
- Chemistry FullDocument273 pagesChemistry FullVraj ShahNo ratings yet
- 25 HydrogenDocument53 pages25 HydrogenAbdul MateenNo ratings yet
- I Unit Water TechnologyDocument83 pagesI Unit Water TechnologyRɩsʜʌv SɩŋʛʜNo ratings yet
- Chemical ChangesDocument6 pagesChemical ChangesmahmudswordofjusticeNo ratings yet
- Objectives of HydrometallurgyDocument14 pagesObjectives of HydrometallurgyAnubhav ChandilNo ratings yet
- Removal of ImpuritiesDocument27 pagesRemoval of ImpuritiesAbdullah ZaidNo ratings yet
- RoleofadsorbentDocument32 pagesRoleofadsorbentwood_ksd3251No ratings yet
- Water: Sources of Water Hard and Soft WaterDocument23 pagesWater: Sources of Water Hard and Soft WatersurenNo ratings yet
- 04a HARD+WATER 240606 130115Document27 pages04a HARD+WATER 240606 130115mukanielisha44No ratings yet
- Water TreatmentDocument27 pagesWater TreatmentArya Singh Rathod100% (1)
- Ion Exchange Resins and Adsorbents in Chemical Processing: Second EditionFrom EverandIon Exchange Resins and Adsorbents in Chemical Processing: Second EditionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Permaleic Acid: Baeyer Villiger Oxidation of CyclododecanoneDocument2 pagesPermaleic Acid: Baeyer Villiger Oxidation of CyclododecanoneGustavo RuizNo ratings yet
- FTS 100 P1Document58 pagesFTS 100 P1Abhay MallNo ratings yet
- Determinación de 3 Alkil 2 Metoxipirazinas en Uvas Mostos y VinosDocument9 pagesDeterminación de 3 Alkil 2 Metoxipirazinas en Uvas Mostos y VinosEmmanuel BonninNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Instruction SheetDocument2 pagesLaboratory Instruction SheetberkanNo ratings yet
- Exam Style Answers 6Document3 pagesExam Style Answers 6Thanos GamingNo ratings yet
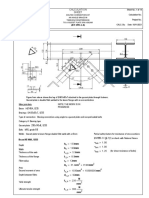
- Mathcad - Angle Bracing Connected To A Gusset Plate On BeamDocument14 pagesMathcad - Angle Bracing Connected To A Gusset Plate On BeamValentinNo ratings yet
- F3 400 PL SPC FJC 0001 - AD Specification For Field Joint CoatingDocument29 pagesF3 400 PL SPC FJC 0001 - AD Specification For Field Joint CoatingDiana MihuNo ratings yet
- Remediation Activity 1 and 2 - Grade 7Document8 pagesRemediation Activity 1 and 2 - Grade 7Shane Catherine Besares100% (1)
- Resource l1HDcxX74pDocument22 pagesResource l1HDcxX74pManlikeibzzzNo ratings yet
- COA of Alpha Lipoic AcidDocument1 pageCOA of Alpha Lipoic AcidPan EmmaNo ratings yet
- Do Sender Chem Brochure - Initiators, Peroxide, Intermediate.Document69 pagesDo Sender Chem Brochure - Initiators, Peroxide, Intermediate.Nick SunNo ratings yet
- BK - Base - Halal Certificate - March 2020 PDFDocument2 pagesBK - Base - Halal Certificate - March 2020 PDFAsep100% (1)
- Frequently Asked Questions About Ceramic Coating For Cars in 2024Document6 pagesFrequently Asked Questions About Ceramic Coating For Cars in 2024trihuynhNo ratings yet
- 10-Coagulation and PrecipitationDocument34 pages10-Coagulation and PrecipitationAnu NNo ratings yet
- WS21.C11.21 - Hydrogen and Its Compounds - 18-09-2021 - 1631937557635 - MH7uxDocument4 pagesWS21.C11.21 - Hydrogen and Its Compounds - 18-09-2021 - 1631937557635 - MH7uxRAVI ANANTHAKRISHNANNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Paper 1 HL-Nov2017 PDFDocument17 pagesChemistry Paper 1 HL-Nov2017 PDFIrfan zameerNo ratings yet
- Miscibility GapDocument11 pagesMiscibility GapChaeyoung SonNo ratings yet
- Lightweight ConcreteDocument8 pagesLightweight ConcreteMADDIBOINA SISINDRINo ratings yet
- Trex Decking Care and Cleaning 010820pdfpdfDocument2 pagesTrex Decking Care and Cleaning 010820pdfpdfSportz KatNo ratings yet
- Bahubali Strategy (Class 10 Science) - : " Trust + Implementation Result Wonderful Result "Document2 pagesBahubali Strategy (Class 10 Science) - : " Trust + Implementation Result Wonderful Result "Moin Ansari100% (1)
- LAB ACTIVITY 3 Edited 2Document9 pagesLAB ACTIVITY 3 Edited 2Hazeljoyce AlcantaraNo ratings yet
- CE341 CE22 Wk03 4 Soil CompactionDocument143 pagesCE341 CE22 Wk03 4 Soil CompactionFaiaz Bin DelworNo ratings yet
- P Block Group - 17 MCQ - With SolDocument7 pagesP Block Group - 17 MCQ - With SolKalp patniNo ratings yet
- Katalis DehidrogenasiDocument17 pagesKatalis DehidrogenasiSigit SuryadiNo ratings yet
- MCQ Questions For Class 7 Science Chapter 4 Heat W+Document9 pagesMCQ Questions For Class 7 Science Chapter 4 Heat W+guruvisnu sureshNo ratings yet
- TARGET: JEE (Main + Advanced) 2020 Course: VIKAAS (JA) NO. B1Document65 pagesTARGET: JEE (Main + Advanced) 2020 Course: VIKAAS (JA) NO. B1rahul tudNo ratings yet
- The Amount of Calcium Carbonate in Toothpaste: SynopsisDocument3 pagesThe Amount of Calcium Carbonate in Toothpaste: SynopsisJonathan SolomonNo ratings yet
- Gas StoichiometryDocument22 pagesGas Stoichiometrykenot100% (1)
- Chemistry Worksheet 5 (Moles)Document6 pagesChemistry Worksheet 5 (Moles)Minal FatimaNo ratings yet