Hooke's Law (New)
Hooke's Law (New)
Uploaded by
Samantha ReemaCopyright:
Available Formats
Hooke's Law (New)
Hooke's Law (New)
Uploaded by
Samantha ReemaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Copyright:
Available Formats
Hooke's Law (New)
Hooke's Law (New)
Uploaded by
Samantha ReemaCopyright:
Available Formats
Semester 2 29, EAC14 Engineering Dynamics, Laboratory session
Hooke's law and Simple harmonic motion
Introduction:
Hooke`s Law states that when an elastic material, such as springs, experienced a
Iorce which cause it to extend or compress, there will be an equal and opposite
Iorce called restoring Iorce which exerts on the spring, this Iorce tries to return the
spring to its original length. This relationship can be shown by equation
F
s
-kx
where F
s
known as the restoring Iorce or spring Iorce, k known as spring constant,
x known as the displacement oI the spring Irom its original length (Walker,2007).
The negative sign in the equation means that the direction oI the restoring Iorce is
opposite to the direction oI the extension or compression at all times. When the
stretched oI spring exceed its elastic limit, the spring will not restore to its original
length.
Objective:
O To determine the spring constant k oI an individual spring by using Hooke`s
Law and the properties oI an oscillating spring-mass system.
IM:
O To measure the extension oI spring by adding static loads
O To calculate the oscillation oI spring periodically under a dynamic loading.
!!#%&$:
Three sets oI unequal stiIIness springs, Range oI slotted weights with hangers, One
meter wooden ruler, Digital stopwatch
!#OCED&#E:
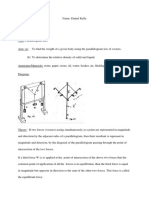
(Statics) 1. k is determined Irom Hooke`s law
i. The physical system is set up with one end oI the spring is attached onto the
O-ring and the other end is attached to the hanger (as shown in the Iigure).
ii. An initial slotted-weight is located to the spring such that the coils just starts
to separate, subsequent spring extensions are measured relative to this
reIerence point.
iii. A series oI additional masses is added to the spring in the order oI equal
increments.
iv. The weight oI the masses (in Newtons) and the resultant position oI the
system (in meters) are recorded down when the system has come to a rest
aIter the mass increment is placed on the hanger.
v. iii and iv is repeated Ior Iive times to take more accurate readings.
(Dynamics) 2. Period oI oscillations is depend on mass by equation T 2a(m/k)
1/2
i. The period oI oscillation, T, is determine Irom 4 diIIerent masses which
hanging on each spring.
ii. The suitable amount oI slotted weights to start oII is decided and gradually
increases them. Prevent to start oII the oscillation with the heaviest mass.
iii. Time is recorded down aIter 10 oscillations Ior each mass.
iv. iii is repeated Ior two times to obtain average readings.
%,ble:
Static:
(i) First spring
Weight, N Displacement, m
3.940 0.008
4.905 0.012
5.886 0.016
6.867 0.020
7.848 0.025
(ii) Second spring
Weight, N Displacement, m
0.000 0.000
2.940 0.085
3.920 0.093
4.910 0.100
5.890 0.109
(iii) Third spring
Weight, N Displacement, m
2.940 0.093
3.920 0.099
4.910 0.104
5.890 0.110
6.870 0.116
Dynamic:
(i) First spring
Time period, T/s Mass, m/kg m`(-2)
0.000 0.000 0.000
0.251 0.300 0.548
0.306 0.400 0.632
0.333 0.500 0.707
0.369 0.600 0.775
(ii) Second spring
Time period, T/s Mass, m/kg m`(-2)
0.000 0.000 0.000
0.337 0.300 0.548
0.362 0.400 0.632
0.394 0.500 0.707
0.419 0.600 0.775
(iii) Third spring
Time period, T/s Mass, m/kg m`(-2)
0.000 0.000 0.000
0.275 0.300 0.548
0.324 0.400 0.632
0.362 0.500 0.707
0.375 0.600 0.775
r,5:
Static:
(i) First spring
(ii) Second spring
0
1
2
3
4
3
6
7
8
9
0 001 002 003
W
e
|
g
h
t
]
N
D|sp|acement ] m
WelghL/ n
ulsplacemenL / m
Llnear (WelghL/ n
ulsplacemenL / m)
1
0
1
2
3
4
3
6
7
0 003 01 013
W
e
|
g
h
t
]
N
D|sp|acement ] m
Second Sprlng (SLaLlc)
Llnear (Second Sprlng
(SLaLlc))
(iii) Third spring
Dynamic:
(i) First spring
0
1
2
3
4
3
6
7
8
0 003 01 013
W
e
|
g
h
t
]
N
D|sp|acement ] m
1hlrd Sprlng (SLaLlc)
ulsplacemenL / m
Llnear (1hlrd Sprlng
(SLaLlc) ulsplacemenL /
m)
003
0
003
01
013
02
023
03
033
04
0 02 04 06 08 1
1
|
m
e
e
r
|
o
d
1
]
s
D|sp|acement ] m
llrsL SLrlng (uymanlcs)
Llnear (llrsL SLrlng
(uymanlcs))
(ii) Second spring
(iii) Third spring
0
003
01
013
02
023
03
033
04
043
03
0 02 04 06 08 1
1
|
m
e
e
r
|
o
d
1
]
s
D|sp|acement ] m
Second Sprlng
(uynamlc)
Llnear (Second Sprlng
(uynamlc))
0
003
01
013
02
023
03
033
04
043
0 023 03 073 1
1
|
m
e
e
r
|
o
d
1
]
s
D|sp|acement ] m
1hlrd Sprlng (uynamlc)
Llnear (1hlrd Sprlng
(uynamlc))
Discussion:
omparing both the experiment, the value oI the spring constant, k is not the same
Ior the three diIIerent lengths oI springs used. This is due to several errors that
occur which causes the value oI k to be diIIerent.
One oI the common errors that happen during the experiment is the random error.
For instance, the position oI the ruler was not placed parallel to the position oI the
spring which caused the reading to be lack oI precision. The solution to this
problem is by using a clamp to hold the ruler beside the spring to ensure that the
position oI the ruler is parallel to the spring. Besides that, variation in the eye
position when taking the reading will cause the precision oI the reading to
decreases. This event normally happens when the observer`s eyes are not
perpendicular to the reading oI the ruler. In order to solve the problem, the
observer has to repeat the experiment a Iew times to get the average reading to
increase the precision oI the result.
Systematic error is another common error occurs during the experiment. This oIten
happen when the spring loss its elasticity due to the long usage by a lot oI people
which caused the reading to be lack oI accuracy. With this, the experimenters have
to observe the spring beIore using it and should get a new spring Irom the tutor to
ensure a more accurate reading. The scale oI the ruler is another systematic error
that occurs while doing the experiment due to the scale used is too small that will
reduce the accuracy oI the result. ThereIore, the ruler should replace by other more
scale apparatus like the electronic apparatus to get a more accurate reading.
Beside the error Iorming, there are also some diIIiculties that make the reading to
be inaccurate and imprecise. Some oI these diIIiculties can lead to the Iormation oI
these errors. One oI the diIIiculties is the catching the exact timing Ior the 10
oscillation oI the spring in the dynamic experiment. This is due to observer who
are unable to react Iast when the taking the time taken Ior the oscillation oI the
spring. With this, the experiment has to be repeated a Iew times to get the average
reading to ensure correct reading obtain. The inconsistent oI the vibration oI the
spring in the dynamic experiment is another diIIiculties that will Iaced by the
experimenter. This is due to the Iorce applied on the spring is not consistent which
made the spring to move in all direction. The way to solve this problem is by the
attach a string to the spring to make vibration vertical because the Iorce is Iocus at
the centre oI the spring which will reduce the spring Irom moving in all direction.
There are diIIiculties Iaced when measuring the extension oI the spring by using a
ruler because extension oI the spring is too small which cause the reading to be
inaccurate. The solution to this problem is by measuring the length oI the spring
using a string so that the string can attach to the spring to ensure that the small
change in the length oI the spring can be observed.
As comparing both the experiment, the graph Ior the Iirst spring used in the
dynamic is more accurate and precise as compare to the static. For the reading oI
the second spring used in the dynamic is more consistent but lack oI accuracy.
Whereas Ior the spring used in the static graph show that the readings are not
accurate and precise. For the graph oI the third spring used in static and dynamic
show the reading are all precise but not accurate.
Conclusion:
Spring constant is the same Ior both the static and dynamic experiment. Even
though there are a Iew changes in the experiment, but it would not change the
value Ior the spring constant, k provided the same type oI the springs is used in the
experiment.
#eference:
Walker, J. & Halliday & Resnick (2007), ' Work-Kinetic Energy Theorem,
Fundamentals oI Physics, 8
th
edn, John Wiley & Sons.
You might also like
- Physics Report HOOKE'S LAWDocument6 pagesPhysics Report HOOKE'S LAWHulwan Mukhlis82% (44)
- Hooke's Law Lab ReportDocument5 pagesHooke's Law Lab Reportdanproxy100% (1)
- Toyota Camry 2002 2006 Workshop ManualDocument20 pagesToyota Camry 2002 2006 Workshop Manualbelinda100% (61)
- Lab Report 3 - Lab 6 - Hooke's LawDocument13 pagesLab Report 3 - Lab 6 - Hooke's LawDennis Enderson100% (2)
- Cantilever Beam ExperimentDocument2 pagesCantilever Beam ExperimentJosh MacneilageNo ratings yet
- Lab Report - Simple PendulumDocument12 pagesLab Report - Simple PendulumAnanyaNo ratings yet
- Lab Report Experiment 2 Phy 433 1 1 PDFDocument18 pagesLab Report Experiment 2 Phy 433 1 1 PDFHANY NUR AQILAH YUSOFNo ratings yet
- Method Statement For Installation of Pipes and FittingsDocument4 pagesMethod Statement For Installation of Pipes and Fittingsadeniyi abiolaNo ratings yet
- Lab Report Hooke's LawDocument8 pagesLab Report Hooke's LawLeila JakupovicNo ratings yet
- The Simple Pendulum LabDocument2 pagesThe Simple Pendulum LabMichael ComradeGeneral Chenko100% (3)
- Pendulum Lab ReportDocument4 pagesPendulum Lab Reportapi-452150993No ratings yet
- Lab Report Physics 1Document18 pagesLab Report Physics 1Nisa AzrinNo ratings yet
- Physics Vibrating String LabDocument9 pagesPhysics Vibrating String LabBrooke McNally100% (3)
- Mechanic Machine Friction (Inclined Plane)Document4 pagesMechanic Machine Friction (Inclined Plane)limakupang_mat100% (1)
- CAPE Unit1 Physics Lab #5 Parallelogram LawDocument9 pagesCAPE Unit1 Physics Lab #5 Parallelogram LawDaniel Kelly50% (2)
- Hardness Test (Lab Report)Document14 pagesHardness Test (Lab Report)Kavin VarmaNo ratings yet
- Penske 7800 Technical ManualDocument12 pagesPenske 7800 Technical ManualgeorgeNo ratings yet
- Simple Harmonic Motion Group 1Document9 pagesSimple Harmonic Motion Group 1Abu HuzaifahNo ratings yet
- Hooke's LawDocument15 pagesHooke's LawHisyamAl-Muhammadi100% (1)
- Simple Pendulum Lab WriteDocument5 pagesSimple Pendulum Lab WriterezzmanNo ratings yet
- Hooke's Law Lab ReportDocument3 pagesHooke's Law Lab ReportNur Syahirah Hanafi75% (4)
- Lab Report 1 The Simple PendulumDocument3 pagesLab Report 1 The Simple PendulumMohammedSalahNo ratings yet
- Lab Report Physics Hooke's LawDocument11 pagesLab Report Physics Hooke's LawAbu Huzaifah100% (1)
- Basic Masurment and UncertainlyDocument29 pagesBasic Masurment and UncertainlyHelny LydarisboNo ratings yet
- Hooke's Law Lab ReportDocument5 pagesHooke's Law Lab ReportÖzgür Sarımaden100% (1)
- Kinetic Friction: Experiment #13Document8 pagesKinetic Friction: Experiment #13kate anne del castroNo ratings yet
- Physics Lab Assessment 7 PARTA - The Conservation of Energy (Elastic Potential Energy) Practical ReportDocument8 pagesPhysics Lab Assessment 7 PARTA - The Conservation of Energy (Elastic Potential Energy) Practical ReportMark Riley67% (3)
- Value of G by Compound PendulumDocument8 pagesValue of G by Compound PendulumMohammad Ameer hamzaNo ratings yet
- Physics LAB Report Simple PendulumDocument7 pagesPhysics LAB Report Simple PendulumDoom Doo100% (1)
- Lab Report Mass Spring System Omar Nizar2Document31 pagesLab Report Mass Spring System Omar Nizar2Omar MustafaNo ratings yet
- Physic Lab Report 1 (Correction)Document16 pagesPhysic Lab Report 1 (Correction)Khairun HusnaNo ratings yet
- Hooke's LawDocument7 pagesHooke's LawamiraaikharahNo ratings yet
- The Simple Pendulum: ObjectiveDocument5 pagesThe Simple Pendulum: ObjectiveAlexo ManNo ratings yet
- Expt2 Simplependulum PDFDocument7 pagesExpt2 Simplependulum PDFSharifuddin RumanNo ratings yet
- Physics Lab Report 10Document3 pagesPhysics Lab Report 10Catherine Linsley100% (6)
- Simple PendulumDocument5 pagesSimple PendulumMaliha KhanNo ratings yet
- This Study Resource Was: Ryerson UniversityDocument8 pagesThis Study Resource Was: Ryerson Universitychris paulNo ratings yet
- Simple Harmonic MotionDocument18 pagesSimple Harmonic Motionieja03100% (2)
- Hooke's Law and Simple Harmonic MotionDocument5 pagesHooke's Law and Simple Harmonic MotionmandoolalaNo ratings yet
- Latent Heat VaporizationDocument3 pagesLatent Heat VaporizationerorkinNo ratings yet
- Local Acceleration Due To Gravity Using Simple PendulumDocument9 pagesLocal Acceleration Due To Gravity Using Simple PendulumAshu t100% (2)
- Lab Report Phy 3Document4 pagesLab Report Phy 3Eri SkcNo ratings yet
- Lab Report: Ripple TestDocument12 pagesLab Report: Ripple TestSyedlakhtehassanNo ratings yet
- Experiment 08 Simple PendulumDocument8 pagesExperiment 08 Simple PendulumAnonymous rswF6CNo ratings yet
- Report 1 Measurement Physics 6Document10 pagesReport 1 Measurement Physics 6rodneyperu88% (25)
- Experiment 2 (Viscosity - A4)Document16 pagesExperiment 2 (Viscosity - A4)Jamiel Catapang100% (1)
- The Simple PendulumDocument8 pagesThe Simple PendulumInu Kag100% (2)
- Group 3 Section (H) (Lab Report 3)Document9 pagesGroup 3 Section (H) (Lab Report 3)Shoaib KhanNo ratings yet
- Lab Reports Mechanics, Heat & VibrationsDocument79 pagesLab Reports Mechanics, Heat & VibrationsNabeel AhmadNo ratings yet
- Resistance Lab ReportDocument14 pagesResistance Lab Reportalsaffar2010100% (4)
- Lab Report Lab 1 Thermistor Temperature CoefficientDocument20 pagesLab Report Lab 1 Thermistor Temperature Coefficientഅരുൺ പി.കെ100% (1)
- Physics Report Simple PendulumDocument3 pagesPhysics Report Simple PendulumGracey- Ann Johnson100% (3)
- Experiment 1 - Simple Harmonic MotionDocument5 pagesExperiment 1 - Simple Harmonic MotionAngelica UyNo ratings yet
- 2 Literature ReviewDocument15 pages2 Literature ReviewstuartwwNo ratings yet
- Inclined Plane: Experiment No: 1Document14 pagesInclined Plane: Experiment No: 1Dilshan SudarshanaNo ratings yet
- Pendulum LabDocument5 pagesPendulum Labmt9260100% (6)
- Laboratory Report FinalDocument26 pagesLaboratory Report Finallemigobena12100% (2)
- Hooke's Law LAB REPORTDocument9 pagesHooke's Law LAB REPORTOmar MustafaNo ratings yet
- General Physics Lab. ReportDocument10 pagesGeneral Physics Lab. ReportBa LamNo ratings yet
- Lab 5 Lab ReportDocument5 pagesLab 5 Lab Reportapi-272572831100% (7)
- Lab Report 1Document7 pagesLab Report 1api-241362194No ratings yet
- Lab 2 Moment of InertiaDocument10 pagesLab 2 Moment of InertiaChing Wai Yong100% (1)
- Free Harmonic Oscillations Formal Report UploadDocument9 pagesFree Harmonic Oscillations Formal Report UploadPassionFruitBowlNo ratings yet
- Piezas Polipasto Dh-325Document32 pagesPiezas Polipasto Dh-325Alejandro Rodriguez FloresNo ratings yet
- Suction Pile and FoundationDocument19 pagesSuction Pile and Foundationhaydarburedah100% (1)
- 04 Multi V ENGDocument44 pages04 Multi V ENGsellabiNo ratings yet
- ER CRANE 77002R-0400A.prnDocument25 pagesER CRANE 77002R-0400A.prnjarekNo ratings yet
- Intake DesignDocument2 pagesIntake DesignmanwarkhanNo ratings yet
- Be Entluefungsventile Prospekt Hawle en 12 2018Document12 pagesBe Entluefungsventile Prospekt Hawle en 12 2018Santosh KumarNo ratings yet
- DC Motor Speed ModelingDocument4 pagesDC Motor Speed ModelingAvinash TrivediNo ratings yet
- Module 2 - Fall 2023Document38 pagesModule 2 - Fall 2023Muhammad FahimNo ratings yet
- Cold-Drawn, Stress-Relieved Carbon Steel Bars Subject To Mechanical Property RequirementsDocument4 pagesCold-Drawn, Stress-Relieved Carbon Steel Bars Subject To Mechanical Property RequirementsSofiaJabadanEspulgarNo ratings yet
- Cylinder Liner: Item Code Item Description Engine Name Model Name Bore Dia Oem No O.E. NumberDocument49 pagesCylinder Liner: Item Code Item Description Engine Name Model Name Bore Dia Oem No O.E. NumberDuvacy0% (1)
- Etasr 3317Document9 pagesEtasr 3317Zatul IzattyNo ratings yet
- Anti-Lock Braking System (Abs) and Electronic Stability Control (Esc)Document73 pagesAnti-Lock Braking System (Abs) and Electronic Stability Control (Esc)新一泉No ratings yet
- Placa de OrificioDocument74 pagesPlaca de OrificioAriely Menacho MontenegroNo ratings yet
- M/S.Ameenji Rubber Pvt. LTD.: Customer Ref. NoDocument1 pageM/S.Ameenji Rubber Pvt. LTD.: Customer Ref. NoSainath AmudaNo ratings yet
- Packer 7in Crest-II Sapex SpecDocument3 pagesPacker 7in Crest-II Sapex SpecbayuNo ratings yet
- 2132 Radome ECU Spec SheetDocument2 pages2132 Radome ECU Spec SheetCanhCuaCàMuốiNo ratings yet
- Mechanics 1 ClassifiedDocument472 pagesMechanics 1 Classifiedkunihiramelinda25No ratings yet
- Service Information No.: 990923-Required SI: PM Energy Saving PackageDocument2 pagesService Information No.: 990923-Required SI: PM Energy Saving PackageAndrei 26No ratings yet
- Ship Stability Center of Gravity and Center of BuoyancyDocument8 pagesShip Stability Center of Gravity and Center of BuoyancyAmin Al QawasmehNo ratings yet
- BOQ Plumbing+HvacDocument3 pagesBOQ Plumbing+HvacOmar MhmmadNo ratings yet
- PT Manual CalculationDocument4 pagesPT Manual CalculationrishiNo ratings yet
- ZF 5HP19HL PDFDocument4 pagesZF 5HP19HL PDFwilderNo ratings yet
- Fabricated "Y" Strainers: Features OptionsDocument2 pagesFabricated "Y" Strainers: Features OptionsGourav SharmaNo ratings yet
- Special Edition Tensioner JuneDocument3 pagesSpecial Edition Tensioner JuneDjebali MouradNo ratings yet
- Worksheet On Kinetic ParticleDocument3 pagesWorksheet On Kinetic ParticlePontuChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- Válvulas Borboletas Posi FlateDocument4 pagesVálvulas Borboletas Posi FlateRodrigo MilaniNo ratings yet
- LG Spareparts: Parts Forhome A Pplia N CesDocument14 pagesLG Spareparts: Parts Forhome A Pplia N CeschuminhNo ratings yet