0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views06 Hydrogen
06 Hydrogen
Uploaded by
Jainil PanchalCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
06 Hydrogen
06 Hydrogen
Uploaded by
Jainil Panchal0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views7 pagesOriginal Title
06
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views7 pages06 Hydrogen
06 Hydrogen
Uploaded by
Jainil PanchalCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 7
06-Hydrogen
1. Who discovered Hydrogen?
• Henry Cavendish.
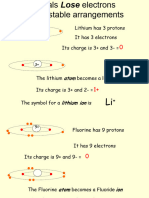
2. Justify the position of Hydrogen in the periodic table.
• Since Hydrogen has atomic number 1, it is placed
in the first group first row. Hence it is the first
element in the periodic table.
3. Why does Hydrogen shows dual nature?
• Hydrogen resembles the alkali metals of group IA
and the halogens of group VIIA.
4. Compare Hydrogen with alkali metals on the basis of : (i)
Ion formation, (ii) Reducing-power, (iii) Reaction with
Oxygen, (iv) Oxide formation.
• (i) Hydrogen and alkali metals can form a cation
by the loss of an electron.
• (ii) Both Hydrogen and alkali metals are reducing
agents.
• (iii) Hydrogen and alkali metals burns in Oxygen
to form Oxides.
• (iv) Hydrogen and alkali metals react with Oxygen
to form Oxides.
5. In what respect does Hydrogen differ from i) Alkali metals,
ii) Halogens?
• (i) Oxides of alkali metals are acidic, while oxide of
hydrogen is neutral.
• (ii) Hydrogen atom has only shell, while halogens
have two or more shells.
6. Which metal is preferred for preparation of hydrogen (i)
from water, (ii) from acids?
• (i) Reactive metals like, Sodium, Potassium and
Calcium are used for the preparing Hydrogen from
water.
• (ii) Metals like, Magnesium, Aluminium, Zinc, and
Iron are used for preparing Hydrogen from acids.
7. The reaction between metals like magnesium, aluminium
and zinc with steam stops after some time. Give reason?
• The oxides of these metals continue sticking to
their surface. This prevents the contact between
steam and the metals, and the reaction stops after
sometime.
8. The reaction between metals like, sodium, potassium and
calcium with dilute sulphuric acid or dilute hydrochloric
acid is not feasible under laboratory conditions. Give
reason.
• Metals like, sodium, potassium and calcium react
violently with dilute acids. The reaction is highly
explosive in nature and hence not feasible under
laboratory conditions.
9. Why nitric acid is not used for the preparation of Hydrogen
from metals?
• Nitric acid is a strong oxidizing agent and form
oxides of nitrogen instead of hydrogen. Hence it is
not used for the preparation of Hydrogen from
metals.
10. Why lead is not used for the preparation of Hydrogen
from dilute acids?
• The lead chloride or lead sulphate formed during
the reaction are insoluble in water and hence,
settle over the surface of lead. This prevents the
contact between lead and acid and hence, reaction
stops.
11. How do you prepare Hydrogen in the laboratory?
• Hydrogen is prepared in the laboratory by
treating granulated zinc with dilute sulphuric acid
at room temperature.
• Zn + Dil. H2SO4 → ZnSO4 + H2
12. Granulated zinc is used for the laboratory
preparation of Hydrogen. Give reason.
• Granulated zinc always contains copper as
impurity, which acts as a catalyst and speeds up
the reaction.
• Granulated zinc provides large surface area, which
speeds up the reaction.
13. Why Aluminium is not used for the preparation of
Hydrogen from dilute acids?
• Aluminium is generally coated with a protective
layer of Aluminium oxide (Al2O3), which does not
allow the acid to react.
14. Why iron is not used for the preparation of Hydrogen
from dilute acids?
• Iron (Fe) reacts slowly with acids and heat is
required. More over H2S and SO2 gases are also
produced due to impurities present in ion.
15. What are the precautions to be taken during the
laboratory preparation of Hydrogen?
• Apparatus should be air tight.
• Allow the first few bubbles of hydrogen gas to
escape, as they contain air and becomes an
explosive mixture.
• Do not bring any naked fire near the apparatus.
• The lower end of the thistle funnel must dip in the
dilute sulphuric acid. Otherwise gas will escape
into the atomosphere.
16. What are the impurities present in the gas prepared
from granulated zinc?
• Arsine gas (AsH3)
• Phospine gas (PH3)
• Hydrogen sulphide (H2S)
• Sulphur dioxide (SO2)
• Carbon dioxide (CO2)
• Oxides of nitrogen (NO2)
• Water vapour (H2O)
17. Hydrogen prepared from granulated zinc has a
characteristic disagreeable odour or fishy smell. Give
reason.
• Granulated Zinc contains a lot of impurities, as a
result along with hydrogen some other gases like,
Arsine, Phosphine, Hydrogen sulphide, Sulphur
dioxide etc will also be produced. Due to the
presence of these gases, hydrogen has a
disagreeable odour or fishy smell.
18. How do you purify Hydrogen prepared from zinc?
• Arsine and phosphine gases are removed by
passing the gas through silver nitrate solution.
• Hydrogen sulphide is removed by passing the gas
through lead nitrate solution.
• Nitrogen dioxide, sulphur dioxide and carbon
dioxide are removed by passing the gas through a
solution of potassium hydroxide.
• Water vapour is removed by passing the gas
through anhydrous calcium chloride.
19. Name the process of industrial method of
preparation of hydrogen.
• Bosch process.
20. How do you prepare water gas? Give relevant
chemical equations.
• When super heated steam (170oC) is passed over
white hot coke a mixture of equal volumes of
carbon monoxide and hydrogen forms. This
mixture is called water gas.
• C + H2O → [ CO + H2]
21. Explain water gas shift reaction.
• The water gas is mixed with twice the volume of
super heated steam and passed over a mixture of
ferric oxide and chromium oxide maintained
450oC – 500oC, carbon monoxide is oxidised to
carbon dioxide. This reaction is called water gas
shift reaction.
• Catalyst – Ferric oxide – Fe2O3
• Promoter – Chromium oxide – Cr2O3
• Temperature – 450oC – 500oC
• Pressure – Normal atmospherical pressure
• [H2 + CO] + H2O → 2H2 + CO2
22. How do you remove carbon dioxide from the mixture
of gases obtained after water gas shift reaction?
• The mixture of carbon dioxide and hydrogen gases
obtained after the water gas shift reaction, is
compressed to 30 atm pressure and then passed
through water, when CO2 dissolved in water and
hydrogen bubbles out.
• H2O + CO2 → H2CO3 (carbonic acid)
23. How do you remove the traces of carbon monoxide
present in hydrogen produced by Bosch process?
•Traces of carbon monoxide is removed by
bubbling the gas through ammoniacal cuprous
chloride solution.
• CuCl + CO + 2H2O → CuCl.CO.2H2O (addition
compound)
24. How do you remove moisture from hydrogen gas
produced by Bosch process?
• The moisture is removed by cooling the gas to -
20oC, when water vapour freezes.
25. How do you produce hydrogen from natural gas?
• Natural gas contains Methane, which reacts with
steam to give hydrogen.
• CH4 + H2O → CO + 3H2
• Catalyst – Nickel
• Temperature – 800oC
• Carbon monoxide is separated from Hydrogen by
water gas shift reaction.
26. Explain oxidation.
• The oxidation of a substance takes place when:
• (i) there is addition of oxygen to a substance,
• (ii) there is removal of hydrogen from a substance.
• 2Cu + O2 → 2CuO :: Oxygen is added to copper,
therefore copper is oxidized to copper oxide.
27. Explain oxidizing agent.
• The substance that causes addition of oxygen or
removal of hydrogen is called oxidizing agents.
• Some common oxidizing agents are : Oxygen (O2),
Ozone (O3), Chlorine (Cl2), Hydrogen peroxide
(H2O2), Nitric Acid (HNO3) and Sulphuric acid
(H2SO4)
28. Explain reduction.
• The reduction of a substance takes place when:
• (i) when there is addition of hydrogen to a
substance,
• (ii) there is removal of oxygen from a substance.
• CuO + H2 → Cu + H2O :: Copper oxide is reduced to
copper on account of loss of oxygen.
29. Explain reducing agents.
• The substances that causes addition of hydrogen
or removal oxygen is called reducing agents.
• Some important reducing agents are : Active
metals (Na, K, Ca, Al, Zn), Hydrogen, Carbon,
Carbon monoxide, Sulphur dioxide, Hydrogen
sulphide.
30. What do you mean by redox reaction.
• In a chemical reaction, if the oxidation and
reduction takes place simultaneously is called
redox reaction.
• CuO + H2 → Cu + H2O , here
• Oxygen is removed from CuO, so reduction takes
place.
• Oxygen is added to hydrogen to form H2O, so
oxidation takes place.
31. How do the following reaction with water? Write
balanced chemical equations:
• Potassium hydride
• Potassium hydride react with water
producing potassium hydroxide and
hydrogen gas.
• KH + H2O → KOH + H2
• Calcium hydride
• Calcium hydride react with water
producing calcium hydroxide and water.
• CaH2 + 2H2O → Ca(OH)2 + 2H2
32. K, Na, Ca, Mg, Al, Zn, Fe, Sn, Pb, H, Cu, Hg, Ag, Au is the
activity series. Answer the following questions.
• Name the metal which react fastest with cold
water.
• K
• Name the metal which does not react with cold
water, but reacts with boiling hot water very
slowly.
• Mg
• Name the metal which on heating reacts with
steam, but reaction is reversible.
• Fe
• Name a metal which reacts explosively with dilute
HCl.
• K or Na or Ca
• Name a metal which reacts violently with dilute
HCl.
• K or Na or Ca
• Name a metal which displaces hydrogen very
slowly from dilute HCl.
• Pb
• Name a metal which does not react with water or
dilute HCl.
• Cu
You might also like
- Question # 01: AnswerDocument9 pagesQuestion # 01: AnswerKhushnoodNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Chapter 6 NotesDocument4 pagesChemistry Chapter 6 Notesmeenakshikumawat601No ratings yet
- Chemical Reactions and EquationsDocument31 pagesChemical Reactions and EquationsShubhada WarakeNo ratings yet
- All Reactions - PadhleDocument18 pagesAll Reactions - Padhlerakshitham603No ratings yet
- Hydrogen Is The of The Periodic Table.: First ElementDocument5 pagesHydrogen Is The of The Periodic Table.: First Elementnofodic311No ratings yet
- Non MetalDocument54 pagesNon Metalchinyegaamadi2022No ratings yet
- Lesson 2 Non-Metals and Moles G11Document61 pagesLesson 2 Non-Metals and Moles G11Jodell CampbellNo ratings yet
- Amazing Chemical Reactions EditedDocument23 pagesAmazing Chemical Reactions EditedMahbub Al-HaqiNo ratings yet
- Summary On Preparation of GasesDocument31 pagesSummary On Preparation of Gasesl6995212No ratings yet
- a3a2c5a2 1f08 429c 8f03 b17c5ad01c94 S2 Chemistry Notes Water and Hydrogen 2020Document13 pagesa3a2c5a2 1f08 429c 8f03 b17c5ad01c94 S2 Chemistry Notes Water and Hydrogen 2020pakistanpower196No ratings yet
- HydrogenDocument10 pagesHydrogenAyush DasNo ratings yet
- Folio ChemistryDocument32 pagesFolio Chemistrybella21893No ratings yet
- Chemistry Form 2 Notes PDFDocument122 pagesChemistry Form 2 Notes PDFGeorge SombeNo ratings yet
- Hydrogen 1698636337Document9 pagesHydrogen 1698636337Shazia ParveenNo ratings yet
- 3 BodyPartDocument70 pages3 BodyPartAhmed ThaerNo ratings yet
- Hydrogen CL 8 2024-25Document6 pagesHydrogen CL 8 2024-25Pratima SenNo ratings yet
- Science 2Document68 pagesScience 2Satyajit SwainNo ratings yet
- All Chemical Reactions 2023Document29 pagesAll Chemical Reactions 2023Aryan MishraNo ratings yet
- Sulphuric Acid 3613517c 7b1e 42b4 Be9c E88be08ae32dDocument9 pagesSulphuric Acid 3613517c 7b1e 42b4 Be9c E88be08ae32dshaikhkhushnuma601No ratings yet
- Ques. Ans XI Inorganic GSSDocument16 pagesQues. Ans XI Inorganic GSSเชี่ย คุณNo ratings yet
- Some Gases PArt 1 (Hydrogen, Oxygen and Nitrogen)Document20 pagesSome Gases PArt 1 (Hydrogen, Oxygen and Nitrogen)Nitesh PanditNo ratings yet
- Hydrogen CH 7 202122 ChemDocument19 pagesHydrogen CH 7 202122 Chembhavyakapadia149No ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Acid and BasesDocument56 pagesChapter 7 Acid and BasesThanabalan Munuswamy100% (1)
- Chapter 9 Folio: Manufactured Substances in Industry.: ChemistryDocument15 pagesChapter 9 Folio: Manufactured Substances in Industry.: ChemistryFaizul IzhamNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Topic 4Document10 pagesChemistry Topic 4manahilimrNo ratings yet
- Exercise 6c ChemistryDocument7 pagesExercise 6c Chemistryapi-533545229No ratings yet
- Production of Sulfuric Acid PDFDocument70 pagesProduction of Sulfuric Acid PDFزهراء عادل عبد الزهرة إسماعيلNo ratings yet
- Balancing Chemical Equations Worksheet Student Instructions: Acids Alkalis (Bases)Document5 pagesBalancing Chemical Equations Worksheet Student Instructions: Acids Alkalis (Bases)Gopal PenjarlaNo ratings yet
- Pak Studies BookDocument10 pagesPak Studies Bookibrahimmkhan777No ratings yet
- Hydrogen 1547134840Document9 pagesHydrogen 1547134840Aditya DubeyNo ratings yet
- P Blockelements 1608Document51 pagesP Blockelements 1608د.حاتممرقهNo ratings yet
- All Chemical ReactionsDocument29 pagesAll Chemical ReactionsManeet SinghNo ratings yet
- Acid, Salt and Salt PreparationDocument13 pagesAcid, Salt and Salt PreparationLiton DasNo ratings yet
- Preparation of HydrogenDocument9 pagesPreparation of HydrogenDavies Masumba67% (3)
- Acids Bases Revision 2021 BRNDocument37 pagesAcids Bases Revision 2021 BRNlinaya.princessNo ratings yet
- G10 Revised Acids, Bases and SaltsDocument81 pagesG10 Revised Acids, Bases and Saltsandrew.mooreNo ratings yet
- Chemical Reactions and Equations: Worksheet ScienceDocument4 pagesChemical Reactions and Equations: Worksheet ScienceGitesh AndhariNo ratings yet
- UjianDocument18 pagesUjianYeni PurwatiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10Document14 pagesChapter 10Happy RoyNo ratings yet
- Acids Bases Salts Notes Icse 10Document10 pagesAcids Bases Salts Notes Icse 10mrnobodycaresaboutNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 testDocument2 pagesChapter 1 testsunidhiojhaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Acids Bases & Salts - Part 2 NotesDocument10 pagesChemistry Acids Bases & Salts - Part 2 Notesancy45No ratings yet
- Chapter 10. Sulphuric Acid: Short QuestionsDocument14 pagesChapter 10. Sulphuric Acid: Short QuestionsAbhay VishwakarmaNo ratings yet
- Lkali and Alkaline Earth Metals Lkali Metals Periodic Discussion and General CharacteristicsDocument33 pagesLkali and Alkaline Earth Metals Lkali Metals Periodic Discussion and General CharacteristicsKawasoti HoNo ratings yet
- Hydrogen and Its CompoundsDocument14 pagesHydrogen and Its Compoundsenochobaro2No ratings yet
- Group 16Document10 pagesGroup 16mithusutradhar.01No ratings yet
- Remedial-Chemical Equations and Reaction-Grade 10Document14 pagesRemedial-Chemical Equations and Reaction-Grade 10solrr786No ratings yet
- 12) Acids, Bases and SaltsDocument11 pages12) Acids, Bases and Saltsbushramahmud6468No ratings yet
- selfstudys_com_file (11)Document14 pagesselfstudys_com_file (11)saptarshinandi24No ratings yet
- Hydrogen, Ammonia, HCl, PaintDocument30 pagesHydrogen, Ammonia, HCl, PaintPriyanshu VarshneyNo ratings yet
- Trends in Period 3 Elements (2018 - 04 - 16 01 - 41 - 52 UTC)Document35 pagesTrends in Period 3 Elements (2018 - 04 - 16 01 - 41 - 52 UTC)tsteadmanNo ratings yet
- SS2 2ND TERM NewDocument59 pagesSS2 2ND TERM Newpalmer okiemuteNo ratings yet
- Acid BaseDocument18 pagesAcid BasechaitanyaNo ratings yet
- Group 01Document34 pagesGroup 01Muhammad MugheeraNo ratings yet
- Study of Components Sulphuric AcidDocument4 pagesStudy of Components Sulphuric AcidKavya YadavNo ratings yet
- 8.6 OxidesDocument6 pages8.6 Oxides29seolaiscooltbhNo ratings yet
- Chemical Reactions of Group IV Elements (3) CompressedDocument9 pagesChemical Reactions of Group IV Elements (3) CompressedTahera McsweenNo ratings yet
- A System of Instruction in the Practical Use of the BlowpipeFrom EverandA System of Instruction in the Practical Use of the BlowpipeNo ratings yet
- A System of Instruction in the Practical Use of the Blowpipe: Being A Graduated Course Of Analysis For The Use Of Students And All Those Engaged In The Examination Of Metallic CombinationsFrom EverandA System of Instruction in the Practical Use of the Blowpipe: Being A Graduated Course Of Analysis For The Use Of Students And All Those Engaged In The Examination Of Metallic CombinationsNo ratings yet
- Why Do Metals Rust? An Easy Read Chemistry Book for Kids | Children's Chemistry BooksFrom EverandWhy Do Metals Rust? An Easy Read Chemistry Book for Kids | Children's Chemistry BooksNo ratings yet
- Teem Scrubber QuestionnaireDocument2 pagesTeem Scrubber QuestionnaireJulius T. PaglinawanNo ratings yet
- Electrostatic Potential and Capacitance Study Module Lakshya NEETDocument42 pagesElectrostatic Potential and Capacitance Study Module Lakshya NEETShreya sachiNo ratings yet
- SSRN-id3814712 TCMDocument13 pagesSSRN-id3814712 TCMamirali2015No ratings yet
- wch11 01 Que 20221012Document28 pageswch11 01 Que 20221012AthenaNo ratings yet
- Digital Notes (Organic Chemistry)Document10 pagesDigital Notes (Organic Chemistry)Adri versouisseNo ratings yet
- Multiple Choice Quiz-Pericyclic ChemistryDocument14 pagesMultiple Choice Quiz-Pericyclic ChemistryChandrashekhar Singh52% (25)
- Lecture 2 PDFDocument12 pagesLecture 2 PDFBvvvvvNo ratings yet
- Rotational Raman SpectrosDocument17 pagesRotational Raman SpectrosAnonymous SVy8sOsvJDNo ratings yet
- Ii Iiiii Iii Ii: l8 - D:'R - RR O/-'R-Rvt "'IDocument12 pagesIi Iiiii Iii Ii: l8 - D:'R - RR O/-'R-Rvt "'IIndah Azhari MawaddahNo ratings yet
- 2 Reciprocal LatticeDocument48 pages2 Reciprocal LatticeHasan MarzukiNo ratings yet
- Wet Electrostatitc PrecipitatorsDocument23 pagesWet Electrostatitc PrecipitatorsEmmanuel ChibweNo ratings yet
- Obtaining Cellulose Nanofibers With A Uniform Width of 15 NM From WoodDocument3 pagesObtaining Cellulose Nanofibers With A Uniform Width of 15 NM From Wooddhy182No ratings yet
- Heat Exchanger Thermal Analysis: Lecture-4Document13 pagesHeat Exchanger Thermal Analysis: Lecture-4Usama IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Optimal Tech Coating News Vol 20Document2 pagesOptimal Tech Coating News Vol 20Javeria Ahmed100% (1)
- Cellulose NanocrystalsDocument8 pagesCellulose NanocrystalsWilson PiresNo ratings yet
- Progress in Structural Characterization of Functional PolysaccharidesDocument40 pagesProgress in Structural Characterization of Functional PolysaccharidesMuhammad Irfan SahabNo ratings yet
- Study of Heat Affected Zone (HAZ) in Friction Welding ProcessDocument7 pagesStudy of Heat Affected Zone (HAZ) in Friction Welding Processsam_aresNo ratings yet
- TDS LOCTITE ABLESTIK 968 2 Issue 10 14Document2 pagesTDS LOCTITE ABLESTIK 968 2 Issue 10 14digiarkanandNo ratings yet
- 4 ThermochemistryDocument34 pages4 ThermochemistryNurl Aina100% (1)
- Dissipative Kerr Solitons in Optical Microresonators: Review SummaryDocument13 pagesDissipative Kerr Solitons in Optical Microresonators: Review SummaryLichtNo ratings yet
- Dos and Don'ts of Vapor Line Blind (VLB) - FCC Refinery Training NetworkDocument3 pagesDos and Don'ts of Vapor Line Blind (VLB) - FCC Refinery Training NetworkNaiduJagarapuNo ratings yet
- Development of Ethanol Gas Sensors Using Ternary Metal Oxide Thick FilmsDocument10 pagesDevelopment of Ethanol Gas Sensors Using Ternary Metal Oxide Thick FilmsTJPRC PublicationsNo ratings yet
- What Is A SemiconductorDocument3 pagesWhat Is A Semiconductorshubhamkr91234No ratings yet
- Cooling LoadDocument39 pagesCooling LoadMohtasham NaeemNo ratings yet
- Intermolecular Forces: © 20 Pearson Education, IncDocument26 pagesIntermolecular Forces: © 20 Pearson Education, IncKJ AlinsasaguinNo ratings yet
- MR Sir Blank Ques Slide (@parasspandit)Document5 pagesMR Sir Blank Ques Slide (@parasspandit)unknownman2129No ratings yet
- CM3110: Lecture Notes 21 March18, 2004: Heat Transfer To Solids in A Flowing Fluid Flow Parallel To A Flat PlateDocument4 pagesCM3110: Lecture Notes 21 March18, 2004: Heat Transfer To Solids in A Flowing Fluid Flow Parallel To A Flat PlateStrive Tadiwanashe GarapoNo ratings yet
- W4 - SE1 - Semiconductor Junction 1Document41 pagesW4 - SE1 - Semiconductor Junction 1wjsdnwjd9219No ratings yet
- QCP521 Koh Chia Ho Specific Heat Capacity SlidesDocument24 pagesQCP521 Koh Chia Ho Specific Heat Capacity SlidesANJALI RANANo ratings yet