Feed Additives
Feed Additives
Uploaded by
Sunny MalikCopyright:
Available Formats
Feed Additives
Feed Additives
Uploaded by
Sunny MalikCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Copyright:
Available Formats
Feed Additives
Feed Additives
Uploaded by
Sunny MalikCopyright:
Available Formats
Feed additives
Feed additives are products used in animal nutrition for purposes of improving the quality of feed and the quality of food from animal origin, or to improve the animals performance and health, e.g. providing enhanced digestibility of the feed materials. Feed additives may not be put on the market unless authorisation has been given following a scientific evaluation demonstrating that the additive has no harmful effects, on human and animal health and on the environment.
A feed additive is a vitamin for farm animals that can't get enough nutrients from regular meals that the farmers provide. [1] In some cases if an animal does not have some type of feed in its diet it may not grow properly. Nutritional content of an animal feed is influenced not only by nutrient content but also by many other aspects such as, feed presentation, hygiene, digestibility, and effect on intestinal health to name a few. Even with all of the benefits of feed most of a farm animals diet still consist of maize, wheat and soybean meal because of the cost of quality feed
.Types of feed additives
A sensory additive is an additive that stimulates the appetite, improving the voluntary intake of a diet. A nutritional additive provides specific nutrients for an animal for optimal growth. A zootechnical additive improves the nutritional value of a diet. It doesn't give nutrients directly to the animal, but through its diet. A coccidiostats and histomonostats controls the health of poultry through direct effects.
Technological additives. This classification refers to a group of additives which
influences the technological aspects of the feed. This does not directly influence the nutritional value of the feed but may do indirectly by improving its handling or hygiene characteristics, for example. An example of such an additive would be an organic acid for preservation of feed. Sensory additives. This refers to a group of additives which improve the palatability (i.e. voluntary intake) of a diet by stimulating appetite, usually through the effect these products have on the flavour or colour of the diet. For example, a vanilla extract may well encourage piglets to eat a ration. Nutritional additives. Such additives supply specific nutrient(s) required by the animal for optimal growth. An example would be a vitamin, amino acid or trace mineral. In most cases, such additives are simply concentrated forms of nutrients supplied in natural ingredients in the diet. Zootechnical additives. These additives improve the nutrient status of the animal, not by providing specific nutrients, but by enabling more efficient use of the nutrients present in the diet. An example of such an additive would be an enzyme or direct fed microbial product, both of which enhance the conditions of the intestinal tract, thus enabling more effective nutrient extraction from the diet. In this respect they are often referred to as pronutrients, ie products which improve the nutritional value of a diet without necessarily providing nutrients directly. Other additives are used for environmental benefits that they provide to animal husbandry and others are targeted for specific physiological functions. Coccidiostats and Histomonostats. These products are used to control intestinal health of poultry through direct effects on the parasitic organism concerned. They are not classified as antibiotics.
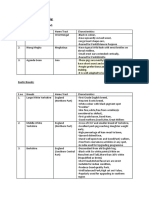
Classification of feed additives 1 nutritives 2 non-nutrutivespple Nutritives
1. Mineral supplements 2. Vitamin supplements 3. Amino acids
Non-nutrutives
1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Antibiotics Hormones Probiotics Acidifiers Medicaments
You might also like
- Final Animal Feeds and Nutrition 2nd Year VetDocument263 pagesFinal Animal Feeds and Nutrition 2nd Year Vetfamiabadir13No ratings yet
- Ansc321 Lab Exam Study GuideDocument7 pagesAnsc321 Lab Exam Study Guideapi-585093321No ratings yet
- AG SCI 209 - Advance Pasture and Fodder Crop Maintenance and Utilization SyllabusDocument4 pagesAG SCI 209 - Advance Pasture and Fodder Crop Maintenance and Utilization SyllabusKRIZZAPEARL VERNo ratings yet
- Role of Feed Additives in Bangladesh Poultry Industries in 2003Document10 pagesRole of Feed Additives in Bangladesh Poultry Industries in 2003Md. Morshed AlamNo ratings yet
- Vitamin in Ruminants NutritionDocument35 pagesVitamin in Ruminants NutritionMoh Dwi HariyonoNo ratings yet
- Feed AdditivesDocument2 pagesFeed AdditivesSunny MalikNo ratings yet
- Feed AdditivesDocument3 pagesFeed AdditivesManzoor AhmadNo ratings yet
- PR Forage and Pasture Crops Beta 362080 1Document104 pagesPR Forage and Pasture Crops Beta 362080 1Jerome RodriguezNo ratings yet
- TN70 Sow Feeding and ManagementDocument8 pagesTN70 Sow Feeding and Managementthanh ba matNo ratings yet
- Swine ProductionDocument52 pagesSwine Productionbstudent136100% (1)
- Swine Management Manual: Agricultural InstructionalDocument129 pagesSwine Management Manual: Agricultural InstructionaljaiNo ratings yet
- PiggeryDocument16 pagesPiggeryAmeya KannamwarNo ratings yet
- Breeds, Breeding and Reproduction - PDFDocument95 pagesBreeds, Breeding and Reproduction - PDFRoxan Mae Amplayo100% (1)
- Feeding Diary CowDocument12 pagesFeeding Diary CowBhat Najibul0% (1)
- Domestication of Farm AnimalsDocument24 pagesDomestication of Farm AnimalsMELITO JR. CATAYLO100% (1)
- Nutrient Requirements of Sheep and GoatsDocument20 pagesNutrient Requirements of Sheep and GoatsSABABA FATIMANo ratings yet
- Feeding and NutritionDocument22 pagesFeeding and NutritionViktor Mikhael Roch BarbaNo ratings yet
- ANSCI2 (The Poultry Industry)Document43 pagesANSCI2 (The Poultry Industry)Madelyn ArimadoNo ratings yet
- Khadkeshwara Broiler FeedsDocument7 pagesKhadkeshwara Broiler FeedsVINODKOSKEWAR100% (1)
- Principles of Material Handling in Relation To The Feed Milling Industry Written ReportDocument30 pagesPrinciples of Material Handling in Relation To The Feed Milling Industry Written ReportCaptainPatsNo ratings yet
- Feeds & Feeding AssignmentDocument12 pagesFeeds & Feeding AssignmentRoseannae ParkNo ratings yet
- Swine Management - Eg'sDocument88 pagesSwine Management - Eg'sJanelle Faye100% (2)
- Lecture 22,23 Feeding of PigsDocument6 pagesLecture 22,23 Feeding of Pigskushal NeupaneNo ratings yet
- Animal Science Rview 2012Document57 pagesAnimal Science Rview 2012Ophalene Althea Odoya100% (1)
- Feed AdditivesDocument53 pagesFeed AdditivesAbhi Sharma100% (2)
- 10 ExerciseDocument2 pages10 ExerciseAngel IloNo ratings yet
- Ruminant Lab 4. 04 24 23Document4 pagesRuminant Lab 4. 04 24 23Christine Joyce Navarro100% (1)
- Animal Selection and Evaluation - Carcass Evaluation PP PresentationDocument82 pagesAnimal Selection and Evaluation - Carcass Evaluation PP PresentationCk_psihNo ratings yet
- Breeds of Poultry SpeciesDocument5 pagesBreeds of Poultry SpeciesJennie Grace MaloomNo ratings yet
- Ans143 - Housing and Equipment in Swine ProductionDocument43 pagesAns143 - Housing and Equipment in Swine ProductionEgie Bulawin100% (1)
- Breeding of SwineDocument16 pagesBreeding of SwineJoy SolamilloNo ratings yet
- 5-6. General Management Practices and Animal Health Program - PDFDocument61 pages5-6. General Management Practices and Animal Health Program - PDFRoxan Mae AmplayoNo ratings yet
- Ration FormulationDocument87 pagesRation FormulationMustee Tefera100% (1)
- Fats in Poultry Nutrition Digestive Physiology and FactorsDocument21 pagesFats in Poultry Nutrition Digestive Physiology and Factorskerko resto100% (1)
- Introduction To Swine HealthDocument38 pagesIntroduction To Swine HealthAnsatsu Kyoushitsu100% (1)
- MODULE 3 Intro To Livestock and PoultryDocument21 pagesMODULE 3 Intro To Livestock and PoultryJessa PabilloreNo ratings yet
- Poultry NutritionDocument54 pagesPoultry Nutritionjohn david alcala100% (1)
- 2 Filipino FarmersDocument32 pages2 Filipino Farmersbeltejarpaul100% (1)
- Module 4 LivestockDocument37 pagesModule 4 LivestockDeejay BeekayNo ratings yet
- ANP 202 Principles of Animal Production PDFDocument207 pagesANP 202 Principles of Animal Production PDFBELKYS100% (1)
- Anp 302 Ruminant Animal ProductionDocument88 pagesAnp 302 Ruminant Animal ProductionDavid OluwapelumiNo ratings yet
- Effects of Different Feed Forms On Performance in Broiler ChickensDocument5 pagesEffects of Different Feed Forms On Performance in Broiler ChickensKhaeraniMahdinurAwliaNo ratings yet
- Module 1 IntroductionDocument15 pagesModule 1 Introductioncristine abridaNo ratings yet
- Indigenous Breed of Pig:: MakingDocument3 pagesIndigenous Breed of Pig:: MakingelanthamizhmaranNo ratings yet
- ASS 122 - Module 2 Breeds of Dairy CattleDocument12 pagesASS 122 - Module 2 Breeds of Dairy CattleGene Rose Gonzales100% (1)
- Sweet Potato Pig FeedDocument12 pagesSweet Potato Pig FeedTrevaughn Cyrus100% (1)
- Chapter One Introducing Poultry Production and Describing The Biology of The FowlDocument47 pagesChapter One Introducing Poultry Production and Describing The Biology of The FowlTamiru LegesseNo ratings yet
- ANSCI44A Lab Exercise 1Document2 pagesANSCI44A Lab Exercise 1Myrielle Timtim100% (1)
- Pork Evaluation ManualDocument38 pagesPork Evaluation Manualจุรรัตน์ ทองแก้วNo ratings yet
- Native Chicken ProductionDocument40 pagesNative Chicken ProductionTOt's VinNo ratings yet
- Facilities & Equipmemt in SwineDocument29 pagesFacilities & Equipmemt in SwineAlliah Dela RosaNo ratings yet
- Animal NutritionDocument28 pagesAnimal NutritionIonela HoteaNo ratings yet
- The Challenge of Cost Effective Poultry and Animal NutritionDocument9 pagesThe Challenge of Cost Effective Poultry and Animal NutritionvetbcasNo ratings yet
- Poultry Nutrition and FeedingDocument16 pagesPoultry Nutrition and FeedingYaserAbbasiNo ratings yet
- Ruminant ProductionDocument92 pagesRuminant ProductionLeonard Villanueva100% (1)
- Beef Cattle Production Lesson 5Document4 pagesBeef Cattle Production Lesson 5Kenneth Manuel RepoleNo ratings yet
- MANAGEMENT OF PIGS PresentDocument34 pagesMANAGEMENT OF PIGS PresentquarozNo ratings yet
- Livestock Feeding PracticesDocument12 pagesLivestock Feeding Practicesbaskar100% (1)
- AnSc 22 Laboratory Exercise No. 1Document5 pagesAnSc 22 Laboratory Exercise No. 1Kheng Lee100% (2)
- Pests of Field Crops and Pastures: Identification and ControlFrom EverandPests of Field Crops and Pastures: Identification and ControlPT BaileyNo ratings yet
- Poultry diseases: Causes, symptoms and treatment, with notes on post-mortem examinationsFrom EverandPoultry diseases: Causes, symptoms and treatment, with notes on post-mortem examinationsNo ratings yet
- EFSA Journal - 2015 - Scientific Opinion On The Safety and Efficacy of Zinc Chelate of L Lysinate HCL As Feed AdditiveDocument20 pagesEFSA Journal - 2015 - Scientific Opinion On The Safety and Efficacy of Zinc Chelate of L Lysinate HCL As Feed AdditiveALEJANDROV71No ratings yet
- Feed AdditivesDocument7 pagesFeed Additivesantonius chaniagoNo ratings yet
- European Union Register of Feed Additives Pursuant-EWAW22007ENN-1Document256 pagesEuropean Union Register of Feed Additives Pursuant-EWAW22007ENN-1uswsrpdlatinlldkegNo ratings yet
- Feed AdditivesDocument7 pagesFeed Additivesantonius chaniagoNo ratings yet