7S
7S
Uploaded by
bijankumar88Copyright:
Available Formats
7S
7S
Uploaded by
bijankumar88Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Copyright:
Available Formats
7S
7S
Uploaded by
bijankumar88Copyright:
Available Formats
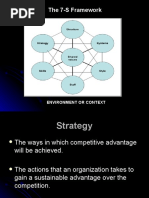
7-S Framework of McKinsey
The 7-S framework of McKinsey is a Value Based Management (VBM) model that describes how one can holistically and effectively organize a company. Together these factors determine the way in which a corporation operates. Shared Value The interconnecting center of McKinsey's model is: Shared Values. What does the organization stands for and what it believes in. Central beliefs and attitudes.
Strategy Plans for the allocation of a firms scarce resources, over time, to reach identified goals. Environment, competition, customers.
Structure
The way the organization's units relate to each other: centralized, functional divisions (topdown); decentralized (the trend in larger organizations); matrix, network, holding, etc. System The procedures, processes and routines that characterize how important work is to be done: financial systems; hiring, promotion and performance appraisal systems; information systems.
Staff Numbers and types of personnel within the organization.
Style Cultural style of the organization and how key managers behave in achieving the organizations goals. Management Styles.
Skill Distinctive capabilities of personnel or of the organization as a whole. Core Competences.
Element of 7S model
Application to digital marketing team
Key issues from practice and literature
Strategy
The significance of digital marketing in influencing and Gaining appropriate budgets supporting organisations' strategy and demonstrating / delivering value and ROI from budgets. Annual planning approach. Techniques for using digital marketing to impact organisation strategy Techniques for aligning digital strategy with organisational and marketing strategy
Structure
The modification of organizational structure to support digital marketing. Integration of team with other management, marketing (corporate
communications, brand marketing, direct marketing) and IT staff Use of cross-functional teams and steering groups Insourcing vs. outsourcing The development of specific processes, procedures or Campaign planning approach-integration information systems to support digital marketing Systems
Managing/sharing customer information Managing content quality Unified reporting of digital marketing effectiveness In-house vs. external bestof-breed vs. external integrated technology solutions Staff The breakdown of staff in terms of their background and characteristics such as IT vs. Marketing, use of contractors/consultants, age and sex. Insourcing vs. outsourcing
Achieving senior management buyin/involvement with digital marketing Staff recruitment and retention. Virtual working Staff development and training Includes both the way in which key managers behave Relates to role of digital in achieving the organizations' goals and the cultural marketing team in influencing strategy style of the organization as a whole. it is it dynamic and influential or conservative and looking for a voice Skills Distinctive capabilities of key staff, but can be interpreted as specific skill-sets of team members. Staff skills in specific areas: supplier selection, project management, Content management, specific e-
Style
marketing approaches (SEO,PPC, affiliate marketing, e-mail marketing, online advertising) The guiding concepts of the digital marketing organisation which are also part of shared values and culture. The internal and external perception of these goals may vary Improving the perception of the importance and effectiveness of the digital marketing team amongst senior managers and staff it works with (marketing generalists and IT)
Superordinate goals
What is 7-S Model? The Seven-Ss is a framework for analyzing organizations and their effectiveness. It looks at the seven key elements that make the organizations successful, or not: strategy; structure; systems; style; skills; staff; and shared values. Consultants at McKinsey & Company developed the 7S model in the late 1970s to help managers address the difficulties of organizational change. The model shows that organizational immune systems and the many interconnected variables involved make change complex, and that an effective change effort must address many of these issues simultaneously. 7-S Model A Systemic Approach to Improving Organizations
The 7-S model is a tool for managerial analysis and action that provides a structure with which to consider a company as a whole, so that the organization's problems may be diagnosed and a strategy may be developed and implemented. The 7-S diagram illustrates the multiplicity interconnectedness of elements that define an organization's ability to change. The theory helped to change manager's thinking about how companies could be improved. It says that it is not just a matter of devising a new strategy and following it through. Nor is it a matter of setting up new systems and letting them generate improvements. There is no starting point or implied hierarchy - different factors may drive the business in any one organization. Shared Values Shared values are commonly held beliefs, mindsets, and assumptions that shape how an organization behaves its corporate culture. Shared values are what engender trust. They are an interconnecting center of the 7Ss model. Values are the identity by which a company is known throughout its business areas, what the organization stands for and what it believes in, it central beliefs and attitudes. These values must be explicitly stated as both corporate objectives and individual values. Structure Structure is the organizational chart and associated information that shows who reports to whom and how tasks are both divided up and integrated. In other words, structures describe the hierarchy of authority and accountability in an organization, the way the organization's units relate to each other: centralized, functional divisions (top-down); decentralized (the trend in larger organizations); matrix, network, holding, etc. These relationships are frequently diagrammed in organizational charts. Most organizations use some mix of structures - pyramidal, matrix or networked ones - to accomplish their goals. Strategy Strategy are plans an organization formulates to reach identified goals, and a set of decisions and actions aimed at gaining a sustainable advantage over the competition. Systems Systems define the flow of activities involved in the daily operation of business, including its core processes and its support systems. They refer to the procedures, processes and routines that are used to manage the organization and characterize how important work is to be done. Systems include: Business System Business Process Management System (BPMS) Management information system Innovation system Performance management system Financial system/capital allocation system Compensation system/reward system
Style
Customer satisfaction monitoring system
"Style" refers to the cultural style of the organization, how key managers behave in achieving the organization's goals, how managers collectively spend their time and attention, and how they use symbolic behavior. How management acts is more important that what management says. Staff "Staff" refers to the number and types of personnel within the organization and how companies develop employees and shape basic values. Skills "Skills" refer to the dominant distinctive capabilities and competencies of the personnel or of the organization as a whole.
You might also like
- Netflix's Organisational CultureDocument11 pagesNetflix's Organisational CultureAnkita Das100% (5)
- Case Study 5 The ABC Training Program: in Partial Fulfillment of The Requirements For The SubjectDocument10 pagesCase Study 5 The ABC Training Program: in Partial Fulfillment of The Requirements For The SubjectKlester Kim Sauro ZitaNo ratings yet
- Mis in HondaDocument25 pagesMis in Hondadivyagaba2160% (5)
- CHAPTER 7 - ORGANIZATIONAL STRUCTURE AND DESIGN Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument19 pagesCHAPTER 7 - ORGANIZATIONAL STRUCTURE AND DESIGN Multiple Choice QuestionsKAINAT MUSHTAQ90% (10)
- McKinsey 7S Framework of Nestle LTD ScribdDocument2 pagesMcKinsey 7S Framework of Nestle LTD Scribdsreeya57% (7)
- Educational AdministrationDocument15 pagesEducational AdministrationAISWARYA. S100% (3)
- SM II-handout 05-Mckinsey 7s ModelDocument6 pagesSM II-handout 05-Mckinsey 7s ModelAkshay sachanNo ratings yet
- Marketing ImplementationDocument24 pagesMarketing ImplementationMohammad Raihanul HasanNo ratings yet
- McKinsey 7sDocument10 pagesMcKinsey 7sKiran Kumar S SNo ratings yet
- Chapter Three: Values, Attitudes, Emotions, and Culture: The Manager As A PersonDocument51 pagesChapter Three: Values, Attitudes, Emotions, and Culture: The Manager As A PersonAiTheruMinasseNo ratings yet
- Mckinsey 7s FrameworkDocument7 pagesMckinsey 7s FrameworkPraveen KumarNo ratings yet
- Mckinsey's 7-S FramewrokDocument4 pagesMckinsey's 7-S FramewrokMonirul AlamNo ratings yet
- 7-S Framework of Mckinsey Management TheoriesDocument26 pages7-S Framework of Mckinsey Management Theoriesवरूणी रंजन शर्माNo ratings yet
- What Is 7-S Model?: Organizational ChangeDocument2 pagesWhat Is 7-S Model?: Organizational Changesahilchopra17No ratings yet
- McKinsey 7SDocument14 pagesMcKinsey 7SVijay HalalliNo ratings yet
- The McKinsey 7S ModelDocument4 pagesThe McKinsey 7S ModelAmey VartakNo ratings yet
- 7s Framework For EcommerceDocument4 pages7s Framework For EcommerceKarthik Hegde0% (1)
- 7 S MckinseyDocument3 pages7 S MckinseyBriand DaydayNo ratings yet
- Mckinsey 7-S Framework ModelDocument9 pagesMckinsey 7-S Framework ModelhajashareefNo ratings yet
- Seven "S" Model: Nirma University Institute of Law 2 SemesterDocument18 pagesSeven "S" Model: Nirma University Institute of Law 2 SemesterMishika Shah100% (1)
- MC Kinsey 7S Model Its Implementation in InfosysDocument24 pagesMC Kinsey 7S Model Its Implementation in InfosysAbdul Halim JoharNo ratings yet
- Basic Models For Organisation DesignDocument14 pagesBasic Models For Organisation Designpulkitkhurana104599No ratings yet
- 202003291621085882smitasingh McKinsey 7s ModelDocument6 pages202003291621085882smitasingh McKinsey 7s ModelJanice MkhizeNo ratings yet
- Mckinsey 7-S Framework ModelDocument9 pagesMckinsey 7-S Framework Modelferry hascaryantoNo ratings yet
- Shared ValuesDocument2 pagesShared ValuesyudipaluNo ratings yet
- 7-S Framework of McKinseyDocument13 pages7-S Framework of McKinseymba9988No ratings yet
- MC Kinsey ModelDocument9 pagesMC Kinsey ModelJuhika SharmaNo ratings yet
- Assignment Number 2 - FinalDocument8 pagesAssignment Number 2 - FinalCuster CoNo ratings yet
- SM Unit-5Document11 pagesSM Unit-5shiva12mayNo ratings yet
- Written ReportDocument5 pagesWritten Reportlee jong sukNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 Strategic ManagementDocument18 pagesUnit 4 Strategic ManagementMadhu ShrivastavNo ratings yet
- 7 SDocument2 pages7 SAthul znNo ratings yet
- The 7-S Framework: Environment or ContextDocument21 pagesThe 7-S Framework: Environment or ContextSorin SpiridonNo ratings yet
- McKinsey 7S ModelDocument12 pagesMcKinsey 7S Modelmahmoud elsrogyNo ratings yet
- McKinsey 7-S FrameworkDocument4 pagesMcKinsey 7-S FrameworkSOHEB TADVINo ratings yet
- The Easy Guide To The McKinsey 7S ModelDocument4 pagesThe Easy Guide To The McKinsey 7S ModelRose DumayacNo ratings yet
- MC Kinsey 7-S FrameworkDocument26 pagesMC Kinsey 7-S FrameworkCraig WilliamsNo ratings yet
- Mckinsey 7'S Framework: The Soft Elements Are As FollowsDocument5 pagesMckinsey 7'S Framework: The Soft Elements Are As FollowsPrakriti SinghNo ratings yet
- 7 - S FrameworkDocument23 pages7 - S FrameworkRitika AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Small Unit Supervision (McKinsey 7S Model)Document4 pagesSmall Unit Supervision (McKinsey 7S Model)PEMS Ivan Theodore P LopezNo ratings yet
- The McKinsey 7S FrameworkDocument6 pagesThe McKinsey 7S FrameworkMathan Raj75% (4)
- Mckinsey 7-S Framework: Making Every Part of Your Organization Work in HarmonyDocument10 pagesMckinsey 7-S Framework: Making Every Part of Your Organization Work in HarmonyDaiserie Mae AguilarNo ratings yet
- 7S FrameworkDocument10 pages7S FrameworkAshwini SudheerNo ratings yet
- 7 S ModelDocument16 pages7 S ModelTedwinThomasNo ratings yet
- BA 550 2 Org DesignDocument30 pagesBA 550 2 Org DesignRuchi_Gulati_4764No ratings yet
- McKinsey 7S ModelDocument6 pagesMcKinsey 7S ModelNikhil Manocha100% (1)
- 7 S Model PresentationDocument16 pages7 S Model PresentationTedwinThomas100% (2)
- Mcckinsey 7s Short SummaryDocument7 pagesMcckinsey 7s Short SummaryBarış TunçbilekNo ratings yet
- McKinsey Framework2Document4 pagesMcKinsey Framework2Enna L LebarimNo ratings yet
- Intro To Org DesignDocument2 pagesIntro To Org DesignShariq KhurshidNo ratings yet
- Ge9 CellDocument8 pagesGe9 Cellsneha bhongadeNo ratings yet
- Strategy Implementation The 7S FrameworkDocument16 pagesStrategy Implementation The 7S FrameworkVignesh StrykerNo ratings yet
- McKinsey 7s ModelDocument11 pagesMcKinsey 7s ModelAnilKotthur0% (1)
- The McKinsey 7S Framework - Strategy Skills From MindToolsDocument7 pagesThe McKinsey 7S Framework - Strategy Skills From MindToolstani100% (1)
- Organizational Structure and DesignDocument11 pagesOrganizational Structure and Designsathvic kNo ratings yet
- BSCIStrategicManagementMaturityModel PDFDocument8 pagesBSCIStrategicManagementMaturityModel PDFAdriana Q.No ratings yet
- Strategic Management AssignmentDocument17 pagesStrategic Management Assignmentshiv mehra100% (1)
- 7 SDocument9 pages7 SAliyaNo ratings yet
- Mckinsey 7 Dimensions and Hofstede SMMDocument18 pagesMckinsey 7 Dimensions and Hofstede SMMLyna EvaNo ratings yet
- 7S Framework: Presented by - Chandan Kumar Das 1502051Document13 pages7S Framework: Presented by - Chandan Kumar Das 1502051ChandanNo ratings yet
- McKinsey 7 S FrameworkDocument6 pagesMcKinsey 7 S FrameworkDeepank GuptaNo ratings yet
- 7S FrameworkDocument2 pages7S FrameworkSanjay GhodadraNo ratings yet
- Compentanices forIncreasingOrganizational Effectiveness11012020Document3 pagesCompentanices forIncreasingOrganizational Effectiveness11012020Siya SunilNo ratings yet
- Building Winning Organisations: A complete guide to sustaining best-in-class performance for all organisationsFrom EverandBuilding Winning Organisations: A complete guide to sustaining best-in-class performance for all organisationsNo ratings yet
- Currents Trends in MGTDocument23 pagesCurrents Trends in MGTsuganthi rajesh kanna100% (1)
- The Differences and Similarities Between IHRM and HRMDocument16 pagesThe Differences and Similarities Between IHRM and HRMMohamed SobahNo ratings yet
- Corporate Strategy MCQDocument38 pagesCorporate Strategy MCQFakeha ShahidNo ratings yet
- IWB Chapter 1 - The Context of Management AccountingDocument22 pagesIWB Chapter 1 - The Context of Management Accountingjulioruiz891No ratings yet
- Brand Stewardship: by Karl D. SpeakDocument13 pagesBrand Stewardship: by Karl D. SpeakSandrine RolandNo ratings yet
- OD Interventions in Relation With Client SystemDocument8 pagesOD Interventions in Relation With Client SystemnavaneeNo ratings yet
- Esbm MaterialDocument30 pagesEsbm Materialsudheer rickyNo ratings yet
- BBDM 1013 BC - Chapter 1Document10 pagesBBDM 1013 BC - Chapter 1nsiva1011No ratings yet
- Strategic Management: Creating Competitive Advantages: Chapter OneDocument54 pagesStrategic Management: Creating Competitive Advantages: Chapter OneDolhadi ZainudinNo ratings yet
- Enabling Sustainable Transformation Hybrid OrganizDocument18 pagesEnabling Sustainable Transformation Hybrid OrganiznabellaromaNo ratings yet
- MboDocument19 pagesMboPriyaranjan JoseNo ratings yet
- Quality Management in TourismDocument10 pagesQuality Management in TourismJa NiceNo ratings yet
- All PBI Sample QuestionsDocument9 pagesAll PBI Sample QuestionsHarry SmithNo ratings yet
- PM7 - Business Markets and Business Buyer BehaviorsDocument22 pagesPM7 - Business Markets and Business Buyer BehaviorsRHam VariasNo ratings yet
- Ates Et AlDocument27 pagesAtes Et AlMtra Isabel MedelNo ratings yet
- BC Block 4 Unit 2Document22 pagesBC Block 4 Unit 2ASHWININo ratings yet
- Human Resource ManagementDocument12 pagesHuman Resource Managementarunkr14318No ratings yet
- TOYOTADocument30 pagesTOYOTAlanoyjessicaellahNo ratings yet
- 2019 Examiningthe Impactof Transformational LeadershipontheDocument9 pages2019 Examiningthe Impactof Transformational Leadershiponthesaleh alqatanNo ratings yet
- ch1 QuizDocument10 pagesch1 QuizBhavika GholapNo ratings yet
- OrganogramDocument5 pagesOrganogramPema ChuklaNo ratings yet
- 04 Research Methods NGOmgmtDocument12 pages04 Research Methods NGOmgmtAnkita NalawadeNo ratings yet
- Bechky - Okhuysen - 2011 - Expecting The UnexpectedDocument24 pagesBechky - Okhuysen - 2011 - Expecting The UnexpectedJean ValjeanNo ratings yet
- DANIEL DOC BM 405Document8 pagesDANIEL DOC BM 405Pascal MasekesaNo ratings yet