Motor Examination - Rawan Aldhwaihi
Motor Examination - Rawan Aldhwaihi
Uploaded by
kakhazmaliCopyright:
Available Formats
Motor Examination - Rawan Aldhwaihi
Motor Examination - Rawan Aldhwaihi
Uploaded by
kakhazmaliCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Copyright:
Available Formats
Motor Examination - Rawan Aldhwaihi
Motor Examination - Rawan Aldhwaihi
Uploaded by
kakhazmaliCopyright:
Available Formats
Motor Examination
Always Compare
Ask about pain which may interfere with testing.
As a quick review (motor examination)composed of: inspection →tone→ power →reflex
What to examine How to do it
Inspection ▪ Scars, striae, swelling, dilated vein
▪ Abnormal position e.g: Hemiplegia,Mask face,
▪ Abnormal movement, e.g. :tremor or drifting.
▪ Muscle wasting
▪ Deformity, e.g. :Wrist or foot drop,Claw hand.
▪ Fasciculations
Tone 1)on supine position,ask the pt to RELAX
2)Move his\her big joints passively through the range of motions,start from upper limb distal then proximal or vasa
versa:
For upper limb [pronate & supinate the hand→flex & extend the wrist→flex & extend the
elbow→abduct & adduct the shoulder]
For lower limb[ flex & extend the ankle→flex & extend the knee→flex & extend the hip]
Power 1) Pt position: for upper limb power :sitting |For lower limb power :supine.
2)Test the muscle strength of upper \lower limb by asking the pt to do: اقوله يسوي هالحركات وأنا احاول اعكس حركته بيدي
,كت كت! ي
اب اشوف قد ايش عضالته قوية وبتقدر تقاوم حر ي واقوله حاول تقاوم حر ي
UPPER LIMB
Shoulder abduction
Elbow flexion Elbow extension
Wrist extension
Finger extension Finger flexion Finger abduction Thumb
abduction
LOWER LIMB
Hip flexion Hip extension
Knee flexion Knee extension
Ankle dorsiflexion Ankle plantar Great toe extension Ankle eversion Ankle inversion
flexion
3) Compare muscle strength on both sides, and grade it on the MRC Scale:
To test truncal strength اعرفوها عشان تصيروا فنانين اذا سألوكم
ask the patient to sit up from the lying position, or rise from a chair,
without using the arms
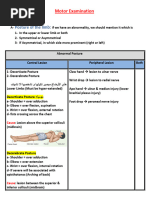
4)pronator drift: Observe the patient with his arms outstretched and
supinated(palms up) and eyes closed for ‘pronator drift’, when one arm starts to
pronate .
*Pronator drift is an early feature of an upper motor neurone lesion
Right cerebral lesion:left side finding
Reflex 1)Ask the patient to lie supine with the limbs exposed. He should be as relaxed and comfortable as possible,
2)Strike the tendon,not the muscle or bone ]فمهم تعرفون تحددون مكان التندون بالزبط
(Deep tendon Testing the deep tendon reflexes of the upper limb:
reflexes) Eliciting the biceps jerk, C5. Triceps jerk, C7. Supinator jerk, C6.
هالنقطه ماتكلموا عنها الدكاتره وماظن مهمه بس لقيتها بالكتاب وخفت يكون عليها درجات بالتشيك ليست
Testing the deep tendon reflexes of the hand.
Hoffmann’s sign. Eliciting a finger
امسك يد المريض نفس, بهوفمن ساين
jer
)الصورة(يد االقزانر هي السمراء
واقوم اخذ االصبع االوسط وأفرك ظفره
طبيعيا بيصير ردة الفعل, رايحه جايه
Adduction of the thumb and
flexion of the index
Testing the deep tendon reflexes of the lower limb:
Eliciting the knee jerk (note that the legs should not Ankle jerk , S1
be in contact with each other), L3, L4.
3)Record the response as:increased-normal-diminished present only with reinforcement-absent.
4)Use reinforcement whenever a reflex appears absent:
→ To reinforce Lower limb reflexes:ask the patient to interlock the fingers and pull one hand against
the other, immediately before you strike the tendon (Jendrassik’s manoeuvre). ال بالصورة عجنب
نفس ي
→ To reinforce upper limb reflexes:ask the patient to clench the teeth or to make a fist with the
contralateral hand.
Reflex Plantar response (S1–2)
(Superficial → How to do it: وامش به عىل باطن القدم بنفس اتجاه السهم يال بالصوة
ي ش حاد زي مفتاح السيارة وال طرف الهامر
خوذوا ي
reflexes)
→ Abnormal findings :An abnormal plantar response is extension of the large toe (extensor plantar or Babinski response).
This is a sign of upper motor neuron damage and is usually associated with other upper motor neurone signs, e.g.
spasticity,lonus and hyperreflexia. Fanning of the toes is normal and not pathological.
Abdominal reflexes (T8–12) not imp just mention it
→ How to do it: The patient should be supine and relaxed. Use an orange stick and briskly, but lightly,
stroke the upperand lower quadrants of the abdomen in a medial direction.The normal response is
contraction of the underlying muscle,
→ Abnormal findings :Superficial abdominal reflexes (T8–12) are lost in upper motor neurone lesions
but are also affected by lower motor neurone damage affecting T8–12. Usually absent in the obese
For males Cremasteric reflex (L1–2): not imp just mention it
→ How to do it:Abduct and externally rotate the patient’s thigh.the upper medial aspect of the thigh.Normally the testis on
the side stimulated will rise .
→ Abnormal findings :The cremasteric reflex in males (L1 and L2) is rarely elicited, but typically is lost in spinal cord or root
lesions.
NOTE:
If they ask you in the osce to do upper limp examination do It in this way:motor examination sensory
examinationcoordination
If they ask you in the osce to do upper limp examination do It in this way:motor examination sensory
examinationcoordination Gait
The details of each examination have been discussed separately
You might also like
- Brunnstrom'S Movement Therapy in HemiplegiaDocument9 pagesBrunnstrom'S Movement Therapy in HemiplegiaLall JingerppangNo ratings yet
- Brunnstrom ApproachDocument9 pagesBrunnstrom Approachavtordaj100% (1)
- Process Industry Practices Coatings: PIP CTSL1000 Application of Internal LiningsDocument23 pagesProcess Industry Practices Coatings: PIP CTSL1000 Application of Internal LiningsSujita Sah100% (1)
- Neuro ExaminationDocument3 pagesNeuro Examinationnickmirad2No ratings yet
- Reflex ExamDocument4 pagesReflex ExamDan Ali100% (1)
- SENSORY EXAMINATON - Rawan AldhwaihiDocument2 pagesSENSORY EXAMINATON - Rawan AldhwaihikakhazmaliNo ratings yet
- 3 Detailed LL Motor Sensory ExamDocument3 pages3 Detailed LL Motor Sensory Exambsm8gf6szxNo ratings yet
- Examination of ReflexesDocument27 pagesExamination of ReflexeslasyabudhavarapuNo ratings yet
- Cns RefelexesDocument25 pagesCns RefelexesNashat SaadiNo ratings yet
- Motor and Sensory Examination: Dr. Bandar Al Jafen, MD Consultant NeurologistDocument36 pagesMotor and Sensory Examination: Dr. Bandar Al Jafen, MD Consultant NeurologistJim Jose Antony100% (1)
- Motor ExaminationDocument36 pagesMotor ExaminationKenneth DizonNo ratings yet
- Deep Tendon Reflex Steps On How To Assess The DTR: Normal Response: DTR GradingDocument2 pagesDeep Tendon Reflex Steps On How To Assess The DTR: Normal Response: DTR GradingElla EvangelistaNo ratings yet
- PHYSIO Expt 15 Reflex Testing - ReformattedDocument1 pagePHYSIO Expt 15 Reflex Testing - ReformattedBrooke PabsNo ratings yet
- ReflexesDocument37 pagesReflexesmishky19No ratings yet
- ReflexesDocument22 pagesReflexesgmpcbpzdysNo ratings yet
- Note 10 Jul 2023Document12 pagesNote 10 Jul 2023Omar AL RashidiNo ratings yet
- The Precise Neurological ExamDocument12 pagesThe Precise Neurological ExamGigiEnergieNo ratings yet
- All Clinical Examinations GuideDocument29 pagesAll Clinical Examinations Guideasalizwa ludlalaNo ratings yet
- HAND ExaminationDocument11 pagesHAND ExaminationEbtesamNo ratings yet
- Neurological ExaminationDocument13 pagesNeurological Examinationsaveetha purushothamanNo ratings yet
- Assessing The Reflexes Bell-Magendie LawDocument9 pagesAssessing The Reflexes Bell-Magendie LawRoger ViloNo ratings yet
- Neuro 1 and 2 LabDocument3 pagesNeuro 1 and 2 LabHardikPatelNo ratings yet
- Forearm, Wrist & Hand Special TestDocument17 pagesForearm, Wrist & Hand Special TestelinelisaNo ratings yet
- Reflexes: Yara George AbdouDocument7 pagesReflexes: Yara George AbdouVivek VijayendraNo ratings yet
- Muscle Strength TestingDocument3 pagesMuscle Strength TestingGiselle Chloe Baluya ico100% (1)
- Neurological History and ExaminationDocument30 pagesNeurological History and ExaminationMaria Agatha100% (1)
- REFLEXESDocument15 pagesREFLEXESSonali Soumyashree100% (2)
- Upper & Lower Limb ExaminationDocument20 pagesUpper & Lower Limb Examinationcvmqx7yppd100% (1)
- Objective Ie. QualimedDocument10 pagesObjective Ie. QualimedPhiliaMelAbarquezNo ratings yet
- Remaining NEUROLOGIC SYSTEMDocument67 pagesRemaining NEUROLOGIC SYSTEMtendi AndriansayahNo ratings yet
- Neurological ExaminationDocument8 pagesNeurological Examinationg8048658No ratings yet
- Medicine 2.3c Reflex TestingDocument5 pagesMedicine 2.3c Reflex TestingelleinasNo ratings yet
- Lower Limb Neurological Assessment: EquipmentDocument15 pagesLower Limb Neurological Assessment: EquipmentShalini RavNo ratings yet
- ReflexesDocument22 pagesReflexesasakingofhNo ratings yet
- YEAR 1 and 2 OSCE Revision: Author: DR Thomas PayneDocument30 pagesYEAR 1 and 2 OSCE Revision: Author: DR Thomas Payneminayoki100% (1)
- Lower Limb NeuroDocument2 pagesLower Limb Neuroquojo041No ratings yet
- Motor SystemDocument8 pagesMotor SystemEman LabNo ratings yet
- Neurologic SystemDocument4 pagesNeurologic SystemDale Ros CollamatNo ratings yet
- Superficialreflexes 150609023712 Lva1 App6891Document1 pageSuperficialreflexes 150609023712 Lva1 App6891Karthik TNo ratings yet
- PTAT 1 Exercise TechniquesDocument18 pagesPTAT 1 Exercise TechniquesANNE RIEN DIGALNo ratings yet
- Musculoskeletal Retdem ScriptDocument1 pageMusculoskeletal Retdem ScriptAllyssaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology Lab Activity 9Document4 pagesAnatomy and Physiology Lab Activity 9Kylene Gayle MoralesNo ratings yet
- Examination of The Hand: o o o oDocument5 pagesExamination of The Hand: o o o oGurunadh OrthoNo ratings yet
- Spine ExamDocument4 pagesSpine ExamSaberNo ratings yet
- Stretch ReflexDocument31 pagesStretch ReflexTots Enriquez Navarro100% (1)
- Lab No4Document5 pagesLab No4Usama JavedNo ratings yet
- Group 9Document2 pagesGroup 9Samantha DollosoNo ratings yet
- Lower Limb Neurological Examination OSCE GuideDocument15 pagesLower Limb Neurological Examination OSCE GuideLeen abusarhanNo ratings yet
- Cranial Nerves Examination, Khaled ElmagrabyDocument4 pagesCranial Nerves Examination, Khaled ElmagrabyTalaat OmranNo ratings yet
- 10 +Manual+Muscle+Testing+of+the+Ankle+Plantar+FlexionDocument36 pages10 +Manual+Muscle+Testing+of+the+Ankle+Plantar+FlexionzelinaokiNo ratings yet
- Brunnstrom ApproachDocument12 pagesBrunnstrom Approachnap caruzNo ratings yet
- PNS Examination 15Document17 pagesPNS Examination 15NolanNo ratings yet
- Neurological ExaminationDocument38 pagesNeurological ExaminationYousif Alaa100% (1)
- Neurological ExaminationDocument7 pagesNeurological ExaminationKalashini SenadheeraNo ratings yet
- Motor ExaminationDocument11 pagesMotor ExaminationHero StoreNo ratings yet
- Medical DisordersDocument22 pagesMedical DisorderskakhazmaliNo ratings yet
- 3 - Management of Labour and Fetal AssessmentDocument20 pages3 - Management of Labour and Fetal AssessmentkakhazmaliNo ratings yet
- L2 - History Taking & Physical Examination - Med441Document20 pagesL2 - History Taking & Physical Examination - Med441kakhazmaliNo ratings yet
- T5 - Puerperium and Puerperal SepsisDocument15 pagesT5 - Puerperium and Puerperal SepsiskakhazmaliNo ratings yet
- Ilovepdf MergedDocument19 pagesIlovepdf MergedkakhazmaliNo ratings yet
- Ilovepdf MergedDocument28 pagesIlovepdf MergedkakhazmaliNo ratings yet
- 4-Oxytocics & TocolyticsDocument11 pages4-Oxytocics & TocolyticskakhazmaliNo ratings yet
- Multiple pregnancy د.عادلDocument34 pagesMultiple pregnancy د.عادلkakhazmaliNo ratings yet
- FibroidDocument8 pagesFibroidkakhazmaliNo ratings yet
- post-natal history د.عادلDocument16 pagespost-natal history د.عادلkakhazmaliNo ratings yet
- Clinic GynecologyDocument13 pagesClinic GynecologykakhazmaliNo ratings yet
- Genital ProlapseDocument6 pagesGenital ProlapsekakhazmaliNo ratings yet
- 16-PCOS Group-FDocument7 pages16-PCOS Group-FkakhazmaliNo ratings yet
- Flat Multi Layer Microwave Absorber - FU-MLDocument2 pagesFlat Multi Layer Microwave Absorber - FU-MLtarun_sheladiyaNo ratings yet
- Chigbo Chibuikem K21PPDocument11 pagesChigbo Chibuikem K21PPAbootlhaNo ratings yet
- Marketing Activities Huyen Tran..Document2 pagesMarketing Activities Huyen Tran..Tuyền Nguyễn Thị ThúyNo ratings yet
- Foundations of PlanningDocument19 pagesFoundations of PlanningAkiNiHandiongNo ratings yet
- The Seven Segment DisplayDocument5 pagesThe Seven Segment DisplayTewodros Kassahun100% (2)
- 2nd LAW THERMO2Document6 pages2nd LAW THERMO2Ervin MogarNo ratings yet
- Unit IiDocument4 pagesUnit Iigunalan gNo ratings yet
- Purestroage Flashbalde Architect Associate Exam Study GuideDocument303 pagesPurestroage Flashbalde Architect Associate Exam Study GuideLuckjoe WamundilaNo ratings yet
- Solution Manual For Business Data Communications Infrastructure Networking and Security 7 e 7th Edition William Stallings Tom CaseDocument9 pagesSolution Manual For Business Data Communications Infrastructure Networking and Security 7 e 7th Edition William Stallings Tom CaseCarlton Caughey100% (47)
- A of (L2) : Critical Appraisal of Gardner's Social-Psychological Theory Second-Language LearningDocument26 pagesA of (L2) : Critical Appraisal of Gardner's Social-Psychological Theory Second-Language LearningTran Ngo TuNo ratings yet
- Junaid Ahmad DarDocument12 pagesJunaid Ahmad Dar7ywtyc8rr7No ratings yet
- Eman Barakat Abu HmeesDocument172 pagesEman Barakat Abu HmeesHama HamaNo ratings yet
- Book 3 - Road Safety at Work Site On Indonesian Roads MPWDocument98 pagesBook 3 - Road Safety at Work Site On Indonesian Roads MPWRahmadirgaNo ratings yet
- Consent Online SurveyDocument2 pagesConsent Online Surveyapi-239920772No ratings yet
- Respiratory System ExaminationDocument46 pagesRespiratory System ExaminationÑäd Éèm100% (1)
- Joe R. Feagin - The White Racial Frame (2013)Document281 pagesJoe R. Feagin - The White Racial Frame (2013)gregcarter100% (1)
- Literasi Dalam Bahasa InggrisDocument8 pagesLiterasi Dalam Bahasa InggrisReza Arya NugrahaNo ratings yet
- ACS350 Technical CatalogueDocument20 pagesACS350 Technical CatalogueJNo ratings yet
- Acephob S - TMEDocument2 pagesAcephob S - TMEanneleiaaaNo ratings yet
- GQ - June 2015 AUDocument162 pagesGQ - June 2015 AUjtora100% (2)
- Hajj, Journey To The Heart of Islam PDFDocument273 pagesHajj, Journey To The Heart of Islam PDFPddfNo ratings yet
- Blank 7E Lesson Plan TemplateDocument5 pagesBlank 7E Lesson Plan TemplateJoshuel AgpasaNo ratings yet
- Gaurang - Reportory LectureDocument42 pagesGaurang - Reportory LectureJayakrishnaNo ratings yet
- Business PlanDocument25 pagesBusiness Plansisondale02No ratings yet
- Rfid Tree Tracking SystemDocument53 pagesRfid Tree Tracking SystemSports addictsNo ratings yet
- Biopapro BrochureDocument22 pagesBiopapro Brochureray1980harishNo ratings yet
- ZV28 Profundo Powered Subwoofer: Owner's ManualDocument10 pagesZV28 Profundo Powered Subwoofer: Owner's ManualKentzNo ratings yet
- Kiwadye Red P-84S-đã chuyển đổiDocument2 pagesKiwadye Red P-84S-đã chuyển đổiperp9018No ratings yet
- ECS-700 System OverviewDocument34 pagesECS-700 System OverviewIrfan AqibNo ratings yet