Ext Ping Trace
Ext Ping Trace
Uploaded by
Sandhya KumariCopyright:
Available Formats
Ext Ping Trace
Ext Ping Trace
Uploaded by
Sandhya KumariCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Copyright:
Available Formats
Ext Ping Trace
Ext Ping Trace
Uploaded by
Sandhya KumariCopyright:
Available Formats
Cisco - Using the Extended ping and Extended traceroute Commands
Using the Extended ping and Extended traceroute Commands
Contents
Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions The ping Command The Extended ping Command ping Command Field Descriptions The traceroute Command The Extended traceroute Command traceroute Command Field Descriptions Cisco Support Community - Featured Conversations Related Information
TAC Notice: What's Changing on TAC Web
Help us help you.
Please rate this document.
Excellent Good Average Fair Poor
This document solved my problem.
Yes
Introduction
This document illustrates how to use the extended ping and extended traceroute commands. Standard ping and traceroute commands are covered extensively in these documents: Understanding the ping and traceroute Commands Using the traceroute Command on Operating Systems
No Just browsing
Suggestions for improvement:
Prerequisites
Requirements
This document requires an understanding of the ping and traceroute commands which are described in detail in the links given in the Introduction section of this document.
(256 character limit)
Send
Components Used
The information in this document is based on these software and hardware versions: Cisco IOS Software Release 12.2(10b) All Cisco series routers
http://kbase/paws/servlet/ViewFile/13730/ext_ping_trace.xml?convertPaths=1[3/16/2010 8:51:55 AM]
Cisco - Using the Extended ping and Extended traceroute Commands
The information in this document was created from the devices in a specific lab environment. All of the devices used in this document started with a cleared (default) configuration. If your network is live, make sure that you understand the potential impact of any command.
Conventions
Refer to Cisco Technical Tips Conventions for more information on document conventions.
The ping Command
The ping (Packet InterNet Groper) command is a very common method for troubleshooting the accessibility of devices. It uses two Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) query messages, ICMP echo requests, and ICMP echo replies to determine whether a remote host is active. The ping command also measures the amount of time it takes to receive the echo reply. The ping command first sends an echo request packet to an address, and then it waits for a reply. The ping is successful only if the ECHO REQUEST gets to the destination, and the destination is able to get an ECHO REPLY back to the source of the ping within a predefined time interval.
The Extended ping Command
When a normal ping command is sent from a router, the source address of the ping is the IP address of the interface that the packet uses to exit the router. If an extended ping command is used, the source IP address can be changed to any IP address on the router. The extended ping is used to perform a more advanced check of host reachability and network connectivity. The extended ping command works only at the privileged EXEC command line. The normal ping works both in the user EXEC mode and the privileged EXEC mode. In order to use this feature, enter ping at the command line and press Return. You are prompted for the fields as given in the ping Command Field Descriptions section of this document.
ping Command Field Descriptions
This table lists the ping command field descriptions. These fields can be modified with the use of the extended ping command.
Field
Description
Protocol [ip]:
Prompts for a supported protocol. Enter appletalk, clns, ip, novell, apollo, vines, decnet, or xns. The default is ip.
Target IP address:
Prompts for the IP address or host name of the destination node you plan to ping. If you have specified a supported protocol other than IP, enter an appropriate address for that protocol here. The default is none.
Repeat count
Number of ping packets that are sent to the
http://kbase/paws/servlet/ViewFile/13730/ext_ping_trace.xml?convertPaths=1[3/16/2010 8:51:55 AM]
Cisco - Using the Extended ping and Extended traceroute Commands
[5]:
destination address. The default is 5.
Datagram size [100]:
Size of the ping packet (in bytes). Default: 100 bytes.
Timeout in seconds [2]:
Timeout interval. Default: 2 (seconds). The ping is declared successful only if the ECHO REPLY packet is received before this time interval.
Extended Specifies whether or not a series of additional commands [n]: commands appears. The default is no.
The interface or IP address of the router to use as a source address for the probes. The router normally picks the IP address of the outbound interface to use. The interface can also be mentioned, but with Source address the correct syntax as shown here: or interface:
Source address or interface: ethernet 0
Note: This is a partial output of the extended ping command. The interface cannot be written as e0.
Type of service [0]:
Specifies the Type of Service (ToS). The requested ToS is placed in each probe, but there is no guarantee that all routers process the ToS. It is the Internet service's quality selection. The default is 0.
Set DF bit in IP header? [no]:
Specifies whether or not the Don't Fragment (DF) bit is to be set on the ping packet. If yes is specified, the Don't Fragment option does not allow this packet to be fragmented when it has to go through a segment with a smaller maximum transmission unit (MTU), and you will receive an error message from the device that wanted to fragment the packet. This is useful for determining the smallest MTU in the path to a destination. The default is no.
Validate reply data? [no]:
Specifies whether or not to validate the reply data. The default is no.
Data pattern [0xABCD]
Specifies the data pattern. Different data patterns are used to troubleshoot framing errors and clocking problems on serial lines. The default is [0xABCD].
http://kbase/paws/servlet/ViewFile/13730/ext_ping_trace.xml?convertPaths=1[3/16/2010 8:51:55 AM]
Cisco - Using the Extended ping and Extended traceroute Commands
IP header options. This prompt offers more than one option to be selected. They are: Verbose is automatically selected along with any other option. Record is a very useful option because it displays the address(es) of the hops (up to nine) the packet goes through. Loose allows you to influence the path by specifying the address(es) of the hop(s) you want the packet to go through. Loose, Strict, Record, Timestamp, Verbose[none]: Strict is used to specify the hop(s) that you want the packet to go through, but no other hop(s) are allowed to be visited. Timestamp is used to measure roundtrip time to particular hosts. The difference between using the Record option of this command and using the traceroute command is that, the Record option of this command not only informs you of the hops that the echo request (ping) went through to get to the destination, but it also informs you of the hops it visited on the return path. With the traceroute command, you do not get information about the path that the echo reply takes. The traceroute command issues prompts for the required fields. Note that the traceroute command places the requested options in each probe. However, there is no guarantee that all routers (or end nodes) process the options. The default is none.
Sweep range of sizes [n]:
Allows you to vary the sizes of the echo packets that are sent. This is used to determine the minimum sizes of the MTUs configured on the nodes along the path to the destination address. Performance problems caused by packet fragmentation is thus reduced. The default is no.
!!!!!
Each exclaimation point (!) denotes receipt of a reply. A period (.) denotes that the network server timed out while waiting for a reply. Refer to ping characters for a description of the remaining characters.
Percentage of packets successfully echoed back to
http://kbase/paws/servlet/ViewFile/13730/ext_ping_trace.xml?convertPaths=1[3/16/2010 8:51:55 AM]
Cisco - Using the Extended ping and Extended traceroute Commands
Success rate is the router. Anything less than 80 percent is usually 100 percent considered problematic.
round-trip Round-trip travel time intervals for the protocol min/avg/max = echo packets, including minimum/average/maximum 1/2/4 ms (in milliseconds).
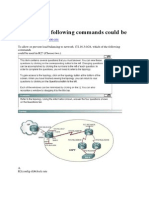
In this diagram, Host 1 and Host 2 are unable to ping each other. You can troubleshoot this problem on the routers in order to determine if there is a routing problem, or if one of the two hosts does not have its default gateway correctly set.
In order for the ping from Host 1 to Host 2 to succeed, each host needs to point its default gateway to the router on its respective LAN segment, or the host needs to exchange network information with the routers that use a routing protocol. If either host does not have its default gateway set correctly, or it does not have the correct routes in its routing table, it is not able to send packets to destinations not present in its Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) cache. It is also possible that the hosts cannot ping each other because one of the routers does not have a route to the subnet from which the host is sourcing its ping packets. Example This is an example of the extended ping command sourced from the Router A Ethernet 0 interface and destined for the Router B Ethernet interface. If this ping succeeds, it is an indication that there is no routing problem. Router A knows how to get to the Ethernet of Router B, and Router B knows how to get to the Ethernet of Router A. Also both hosts have their default gateways set correctly. If the extended ping command from Router A fails, it means that there is a routing problem. There could be a routing problem on any of the three routers. Router A could be missing a route to the subnet of Router B's Ethernet, or to the subnet between Router C and Router B. Router B could be missing a route to the subnet of Router A's subnet, or to the subnet between Router C and Router A; and Router C could be missing a route to the subnet of Router A's or Router B's Ethernet segments. You should correct any routing problems, and then Host 1 should try to ping Host 2. If Host 1 still cannot ping Host 2, then both hosts' default gateways should be checked. The connectivity between the Ethernet
http://kbase/paws/servlet/ViewFile/13730/ext_ping_trace.xml?convertPaths=1[3/16/2010 8:51:55 AM]
Cisco - Using the Extended ping and Extended traceroute Commands
of Router A and the Ethernet of Router B is checked with the extended ping command. With a normal ping from Router A to Router B's Ethernet interface, the source address of the ping packet would be the address of the outgoing interface, that is, the address of the serial 0 interface (172.31.20.1). When Router B replies to the ping packet, it replies to the source address (that is, 172.31.20.1). This way, only the connectivity between the serial 0 interface of Router A (172.31.20.1) and the Ethernet interface of Router B (192.168.40.1) is tested. In order to test the connectivity between Router A Ethernet 0 (172.16.23.2) and Router B Ethernet 0 (192.168.40.1), use the extended ping command. With extended ping, you get the option to specify the source address of the ping packet, as shown here.
Router A>enable Router A#ping Protocol [ip]: Target IP address: 192.168.40.1 !--- The address to ping. Repeat count [5]: Datagram size [100]: Timeout in seconds [2]: Extended commands [n]: y Source address or interface: 172.16.23.2 !---Ping packets are sourced from this address. Type of service [0]: Set DF bit in IP header? [no]: Validate reply data? [no]: Data pattern [0xABCD]: Loose, Strict, Record, Timestamp, Verbose[none]: Sweep range of sizes [n]: Type escape sequence to abort. Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 162.108.21.8, timeout is 2 seconds: !!!!! Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 36/97/132 ms !--- Ping is successful. Router A#
This is an example with extended commands and sweep details:
Router A>enable Router A#ping Protocol [ip]: !--- The protocol name. Target IP address: 192.168.40.1 !--- The address to ping. Repeat count [5]: 10 !--- The number of ping packets that are sent to the destination address. Datagram size [100]: !--- The size of the ping packet in size. The default is 100 bytes. Timeout in seconds [2]: !--- The timeout interval. The ping is declared successful only if the !--- ECHO REPLY packet is received before this interval. Extended commands [n]: y
http://kbase/paws/servlet/ViewFile/13730/ext_ping_trace.xml?convertPaths=1[3/16/2010 8:51:55 AM]
Cisco - Using the Extended ping and Extended traceroute Commands
!--- You choose yes if you want extended command options !--- (Loose Source Routing, Strict Source Routing, Record route and Timestamp). Source address or interface: 172.16.23.2 !--- Ping packets are sourced from this address and must be the IP address !--- or full interface name (for example, Serial0/1 or 172.16.23.2). Type of service [0]: !--- Specifies Type of Service (ToS). Set DF bit in IP header? [no]: !--- Specifies whether or not the Dont Fragment (DF) bit is to be !--- set on the ping packet. Validate reply data? [no]: !--- Specifies whether or not to validate reply data. Data pattern [0xABCD]: !--!--!--!--!--Specifies the data pattern in the ping payload. Some physical links might exhibit data pattern dependent problems. For example, serial links with misconfigured line coding. Some useful data patterns to test include all 1s (0Xffff), all 0s (0x0000) and alternating ones and zeros (0Xaaaa).
Loose, Strict, Record, Timestamp, Verbose[none]: !--- IP header options. Sweep range of sizes [n]: y !--- Choose yes if you want to vary the sizes on echo packets that are sent. Sweep min size [36]: Sweep max size [18024]: Sweep interval [1]: Sending 179890, [36..18024]-byte ICMP Echos to 162.108.21.8, timeout is 2 seconds: !--- The count 179890 depends on the values of min sweep, !--- max sweep, sweep interval and repeat count. Calculations are based on: !--!--!--!--!--!--!--!--18024(high end of range) - 36(low end of range) = 17988(bytes in range) 17988(bytes in range) / 1(sweep interval) = 17988 (steps in range) 17988(bytes in range) + 1 (first value) = 17989(values to be tested) 17989(values to be tested) * 10(repeat count) = 179890 (pings to be sent) In order to decrease the value, increase the sweep interval or decrease the repeat count, or you can even decrease the difference between Minimum and Maximum sweep size. Based on the previous example, the number 17890 is an expected value and tries to ping 17890 times.
Packet sent with a source address of 172.16.23.2 !!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!! !!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!! !!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!! !!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!! !!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!! !!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!! !!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!! !!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!! !!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!! !!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!! !!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!! !!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!! !!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!! Success rate is 100 percent, round-trip min/avg/max = 1/2/4 ms
http://kbase/paws/servlet/ViewFile/13730/ext_ping_trace.xml?convertPaths=1[3/16/2010 8:51:55 AM]
Cisco - Using the Extended ping and Extended traceroute Commands
!--- Ping is successful. Router A#
The traceroute Command
Where ping can be used to verify connectivity between devices, the traceroute command can be used to discover the paths packets take to a remote destination, as well as where routing breaks down. The purpose behind the traceroute command is to record the source of each ICMP "time exceeded" message in order to provide a trace of the path the packet took to reach the destination. The device that executes the traceroute command sends out a sequence of User Datagram Protocol (UDP) datagrams, each with incrementing Time-To-Live (TTL) values, to an invalid port address (Default 33434) at the remote host. First, three datagrams are sent, each with a TTL field value set to 1. The TTL value of 1 causes the datagram to "timeout" as soon as it hits the first router in the path. This router then responds with an ICMP "time exceeded" message which indicates that the datagram has expired. Next, three more UDP messages are sent, each with the TTL value set to 2. This causes the second router in the path to the destination to return ICMP "time exceeded" messages. This process continues until the packets reach the destination and until the system that originates the traceroute receives ICMP "time exceeded" messages from every router in the path to the destination. Since these datagrams try to access an invalid port (Default 33434) at the destination host, the host responds with ICMP "port unreachable" messages that indicate an unreachable port. This event signals the traceroute program to finish. Note: Make sure you have not disabled the ip unreachable command using no ip unreachables under any VLAN. This command makes the packet discard without sending any ICMP error message. In this case, traceroute does not work.
The Extended traceroute Command
The extended traceroute command is a variation of the traceroute command. An extended traceroute command can be used to see what path packets take in order to get to a destination. The command can also be used to check routing at the same time. This is helpful for when you troubleshoot routing loops, or for when you determine where packets are getting lost (if a route is missing, or if packets are being blocked by an Access Control List (ACL) or firewall). You can use the extended ping command in order to determine the type of connectivity problem, and then use the extended traceroute command in order to narrow down where the problem occurs. A "time exceeded" error message indicates that an intermediate communication server has seen and discarded the packet. A "destination unreachable" error message indicates that the destination node has received the probe and discarded it because it could not deliver the packet. If the timer goes off before a response comes in, trace prints an asterisk(*). The command terminates when any of these happens: the destination responds the maximum TTL is exceeded the user interrupts the trace with the escape sequence Note: You can invoke this escape sequence when you simultaneously press Ctrl, Shift and 6.
http://kbase/paws/servlet/ViewFile/13730/ext_ping_trace.xml?convertPaths=1[3/16/2010 8:51:55 AM]
Cisco - Using the Extended ping and Extended traceroute Commands
traceroute Command Field Descriptions
This table lists the traceroute command field descriptions:
Field
Description
Protocol [ip]:
Prompts for a supported protocol. Enter appletalk, clns, ip, novell, apollo, vines, decnet, or xns. The default is ip.
Target IP addres
You must enter a host name or an IP address. There is no default.
Source address:
The interface or IP address of the router to use as a source address for the probes. The router normally picks the IP address of the outbound interface to use.
Numeric display [n]:
The default is to have both a symbolic and numeric display; however, you can suppress the symbolic display.
Timeout in seconds [3]:
The number of seconds to wait for a response to a probe packet. The default is 3 seconds.
Probe count [3]:
The number of probes to be sent at each TTL level. The default count is 3.
Minimum Time to Live [1]:
The TTL value for the first probes. The default is 1, but it can be set to a higher value to suppress the display of known hops.
Maximum Time to Live [30]:
The largest TTL value that can be used. The default is 30. The traceroute command terminates when the destination is reached or when this value is reached.
Port Number [33434]:
The destination port used by the UDP probe messages. The default is 33434.
http://kbase/paws/servlet/ViewFile/13730/ext_ping_trace.xml?convertPaths=1[3/16/2010 8:51:55 AM]
Cisco - Using the Extended ping and Extended traceroute Commands
IP header options. You can specify any combination. The traceroute command issues Loose, Strict, prompts for the required fields. Note that the Record, traceroute command will place the requested Timestamp, options in each probe; however, there is no Verbose[none]: guarantee that all routers (or end nodes) will process the options.
Example
Router A>enable Router A#traceroute Protocol [ip]: Target IP address: 192.168.40.2 !--- The address to which the path is traced. Source address: 172.16.23.2 Numeric display [n]: Timeout in seconds [3]: Probe count [3]: Minimum Time to Live [1]: Maximum Time to Live [30]: Port Number [33434]: Loose, Strict, Record, Timestamp, Verbose[none]: Type escape sequence to abort. Tracing the route to 192.168.40.2 1 172.31.20.2 16 msec 16 msec 16 msec 2 172.20.10.2 28 msec 28 msec 32 msec 3 192.168.40.2 32 msec 28 msec * !--- The traceroute is successful. Router A#
Note: The extended traceroute command can be executed in the privileged EXEC mode only, whereas the normal traceroute command works on both the user and privileged EXEC modes.
Cisco Support Community - Featured Conversations
Cisco Support Community is a forum for you to ask and answer questions, share suggestions, and collaborate with your peers. Below are just some of the most recent and relevant conversations happening right now.
Want to see more? Join us by clicking here ping and extended ping ravisambaji 4 Replies 3 years, 11 months ago Help needed on "Extended ping" srikrishnan.b 3 Replies 4 years, 1 month ago Extended traceroute keepalives 1 Reply 6 years, 9 months ago extended ping rageurdreams 3 Replies 2 years, 3 months ago Can only ping using extended ping garybeach 5 Replies 2 years, 7 months ago
http://kbase/paws/servlet/ViewFile/13730/ext_ping_trace.xml?convertPaths=1[3/16/2010 8:51:55 AM]
Cisco - Using the Extended ping and Extended traceroute Commands
Extended Ping irfan_1505 1 Reply 10 months, 2 weeks ago Extended Ping jeff.koh 2 Replies 6 years, 8 months ago Can only ping using Extended Ping... garybeach 17 Replies 2 years, 10 months ago Extended traceroute not working londint 3 Replies 2 years, 7 months ago extended ping https://supportforums.cisco.com/people/alsayed%40litani.gov.lb 1 Reply 3 years, 9 months ago Start A New Discussion Subscribe
Related Information
TCP/IP Routed Protocols Support Page IP Routing Support Page Technical Support & Documentation - Cisco Systems
Contacts & Feedback | Help | Site Map 2009 - 2010 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Terms & Conditions | Privacy Statement | Cookie Policy | Trademarks of Cisco Systems, Inc.
http://kbase/paws/servlet/ViewFile/13730/ext_ping_trace.xml?convertPaths=1[3/16/2010 8:51:55 AM]
You might also like
- HW 2Document3 pagesHW 2Marina CzuprynaNo ratings yet
- Lab 03Document7 pagesLab 03Ihsan ul HaqNo ratings yet
- Sample Oral Questions With Answers For CNSL Oral PreparationDocument63 pagesSample Oral Questions With Answers For CNSL Oral Preparationchaudharylalit025No ratings yet
- Connectivity Testing With Ping, Telnet, Tracert and PathPingDocument3 pagesConnectivity Testing With Ping, Telnet, Tracert and PathPingSAGALOGNo ratings yet
- Ethernet CablingDocument8 pagesEthernet CablingOctav EnachiNo ratings yet
- BITS-Pilani Hyderabad Campus CS F303 (Computer Networks) Laboratory 1Document7 pagesBITS-Pilani Hyderabad Campus CS F303 (Computer Networks) Laboratory 1pundaNo ratings yet
- Ping Command:: Assignment No: 1Document16 pagesPing Command:: Assignment No: 1Ninad ShetkarNo ratings yet
- Csc261 CCN Lab ManualDocument125 pagesCsc261 CCN Lab ManualasadhppyNo ratings yet
- Networking CommandsDocument5 pagesNetworking CommandsChristina JosephNo ratings yet
- Sample Answers: Network Programming - Spring 2003 Midterm ExamDocument6 pagesSample Answers: Network Programming - Spring 2003 Midterm Examlm_zakaria4420No ratings yet
- Lab 01: Basic Networking Commands: IpconfigDocument9 pagesLab 01: Basic Networking Commands: IpconfigBipin MasalNo ratings yet
- 22 (&!Document24 pages22 (&!Rehman ZamanNo ratings yet
- Ccna TestDocument24 pagesCcna TestArt CamposNo ratings yet
- Certification 2 Sem 4Document27 pagesCertification 2 Sem 4Norman AdimoNo ratings yet
- Practical No.15: Theory: Tracing The Path of Website: It Involves Following StepsDocument13 pagesPractical No.15: Theory: Tracing The Path of Website: It Involves Following StepsRed Light HackersNo ratings yet
- FJJFNVDocument21 pagesFJJFNVRehman ZamanNo ratings yet
- Highcpu InterruptsDocument7 pagesHighcpu InterruptsVillyDangerouslyNo ratings yet
- The Art of Network Debugging With Tcpdump MSamir PDFDocument9 pagesThe Art of Network Debugging With Tcpdump MSamir PDFzennroNo ratings yet
- Ccna2 4p2Document41 pagesCcna2 4p2Alok SharmaNo ratings yet
- Question: What Is A Computer Ping Test?Document7 pagesQuestion: What Is A Computer Ping Test?Preeti KatariaNo ratings yet
- Network ToolsDocument8 pagesNetwork ToolsIas Aspirant AbhiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Interfaces ResumoDocument20 pagesChapter 5 Interfaces ResumoGabrielNo ratings yet
- CMD CommandsDocument27 pagesCMD CommandsAbhishek gargNo ratings yet
- How To Troubleshoot Network Adapter Problems in WindowsDocument41 pagesHow To Troubleshoot Network Adapter Problems in WindowsShivakumar S KadakalNo ratings yet
- 307 Pract8 1 FTPDocument36 pages307 Pract8 1 FTPRanjay PrajapatiNo ratings yet
- Fgrep: Nslookup ( - Option) ... Host (Server)Document12 pagesFgrep: Nslookup ( - Option) ... Host (Server)Vaishali ChughNo ratings yet
- Experiment No. 1: Name: - Aditi A Jadhav Class: - Be/Extc ROLL NO: - 114 Subject: - Internet Communication EngineeringDocument6 pagesExperiment No. 1: Name: - Aditi A Jadhav Class: - Be/Extc ROLL NO: - 114 Subject: - Internet Communication EngineeringAditi JadhavNo ratings yet
- CommandsDocument39 pagesCommandsMythili NatarajanNo ratings yet
- Tshoot CCNPDocument19 pagesTshoot CCNPJamez STNo ratings yet
- 300-101 New Dump Oct 2016 PDFDocument21 pages300-101 New Dump Oct 2016 PDFjustanotherrandomdudeNo ratings yet
- CN Lab1Document12 pagesCN Lab1f20201862No ratings yet
- Eigrp CiscoDocument47 pagesEigrp CiscojkararrigasNo ratings yet
- Digital Communication and Computer Networking Lab ManualDocument66 pagesDigital Communication and Computer Networking Lab ManualJoey TribianniNo ratings yet
- Internet Protocols g10 Chs EdzDocument49 pagesInternet Protocols g10 Chs EdzJoan Sarahan100% (1)
- Computer Networks Quest SolsDocument3 pagesComputer Networks Quest SolsRajesh TiwaryNo ratings yet
- Tshoot 300-315Document19 pagesTshoot 300-315Paulo DembiNo ratings yet
- CS-356 Computer Networks Lab 1Document13 pagesCS-356 Computer Networks Lab 1atishkumar20180No ratings yet
- CN Practical10Document8 pagesCN Practical10permggohil12No ratings yet
- CCN Exp1bDocument10 pagesCCN Exp1bsatyam142857No ratings yet
- 7 Network Layer IPv4Document33 pages7 Network Layer IPv4raj25comNo ratings yet
- Cisco Doc 16406 EigrpDocument44 pagesCisco Doc 16406 EigrpStuart CampbellNo ratings yet
- Assignment 4 SolDocument7 pagesAssignment 4 Soljazib1921No ratings yet
- CN Unit Iv QBSDocument17 pagesCN Unit Iv QBS82Neha PalNo ratings yet
- CCNA 1 Final 2012 Exam AnswersDocument65 pagesCCNA 1 Final 2012 Exam Answerserzza storeNo ratings yet
- Lab 1 To 4Document41 pagesLab 1 To 4asifa AdilNo ratings yet
- Modules 8 - 10 - EnglishDocument34 pagesModules 8 - 10 - EnglishChabi HonoratNo ratings yet
- 1 Network Familiarization CommandsDocument7 pages1 Network Familiarization Commandskingmaster208143No ratings yet
- Network Connectivity Checking Procedures and TechniquesDocument31 pagesNetwork Connectivity Checking Procedures and TechniquesLeonardo Noran Jr100% (1)
- Lab 10 CCNDocument15 pagesLab 10 CCNMalik WaqarNo ratings yet
- ICND1 Practice ExamDocument208 pagesICND1 Practice ExamJoshua Limakwe100% (2)
- Name: K.Sai Manas Reddy REG NUM: 19BIT0027: Data Communication and Computer Networks Digital Assesment 1Document19 pagesName: K.Sai Manas Reddy REG NUM: 19BIT0027: Data Communication and Computer Networks Digital Assesment 1Manas ReddyNo ratings yet
- Muzamil Interview Prepration NotesDocument30 pagesMuzamil Interview Prepration NotesMuzamil AbbasNo ratings yet
- PingDocument7 pagesPingricardoso5549No ratings yet
- Assignment Cs349 WiresharkDocument8 pagesAssignment Cs349 WiresharkRitvik SarafNo ratings yet
- DOS Network Tools CommandsDocument5 pagesDOS Network Tools CommandstommyyjaykalNo ratings yet
- CSS G10 Q1 - Wk8 - Ping CommandDocument11 pagesCSS G10 Q1 - Wk8 - Ping CommandBryce PandaanNo ratings yet
- CCNA Quick Notes Before ExamDocument10 pagesCCNA Quick Notes Before ExamFranco GilsonNo ratings yet
- LEARN MPLS FROM SCRATCH PART-B: A Beginners guide to next level of networkingFrom EverandLEARN MPLS FROM SCRATCH PART-B: A Beginners guide to next level of networkingNo ratings yet
- CISCO PACKET TRACER LABS: Best practice of configuring or troubleshooting NetworkFrom EverandCISCO PACKET TRACER LABS: Best practice of configuring or troubleshooting NetworkNo ratings yet
- Pg150 Ultrascale Memory IpDocument528 pagesPg150 Ultrascale Memory IpMohammed Nawaz ShaikNo ratings yet
- Chapter24 Nosql DbsDocument35 pagesChapter24 Nosql DbsNora SalehNo ratings yet
- The Semi Colon Is Used at The End of Proc SQL StatementDocument5 pagesThe Semi Colon Is Used at The End of Proc SQL StatementOm Prakash100% (1)
- Esubmit: Technical Specifications For Rai and Supporting Documentation Electronic SubmissionsDocument11 pagesEsubmit: Technical Specifications For Rai and Supporting Documentation Electronic SubmissionsSabteNo ratings yet
- SnowflakeDocument3 pagesSnowflakeimanonNo ratings yet
- User Account Features 9090909090909900Document6 pagesUser Account Features 9090909090909900urva ahmedNo ratings yet
- Installation LogDocument13 pagesInstallation LogAdrianoNo ratings yet
- Access Control Lists (ACLs)Document67 pagesAccess Control Lists (ACLs)Senan AlkaabyNo ratings yet
- Read File BinaryDocument3 pagesRead File BinaryJuliusNo ratings yet
- LP Lab ProgramsDocument42 pagesLP Lab ProgramsAmjath KhanNo ratings yet
- Starting and Stopping SAP Systems and Instances Using Commands (Unix)Document5 pagesStarting and Stopping SAP Systems and Instances Using Commands (Unix)shambhu guptaNo ratings yet
- Introducing Low-Density Parity-Check CodesDocument84 pagesIntroducing Low-Density Parity-Check Codesmohamedezzelden30No ratings yet
- C Programming Lesson On One-Dimensional ArraysDocument3 pagesC Programming Lesson On One-Dimensional Arraysroyce542No ratings yet
- STM32F107 Ethernet IntroductionDocument25 pagesSTM32F107 Ethernet Introductionkit2100% (3)
- Dumpsfree: Dumpsfree Provide High-Quality Dumps Vce & Dumps DemoDocument4 pagesDumpsfree: Dumpsfree Provide High-Quality Dumps Vce & Dumps DemoDeepak KumarNo ratings yet
- Splunk vs. ELK The Risk Focus Way: Case StudyDocument16 pagesSplunk vs. ELK The Risk Focus Way: Case Studyضراب آسمانیNo ratings yet
- Ccna 4 Packet Tracer Lab AnswersDocument5 pagesCcna 4 Packet Tracer Lab AnswersSagar Solo NandigamaNo ratings yet
- Docs Jboss Org Hibernate Orm 5 2 Userguide HTML Single HiberDocument365 pagesDocs Jboss Org Hibernate Orm 5 2 Userguide HTML Single HiberASDNo ratings yet
- 01-Block DiagramDocument1 page01-Block Diagramkhoi vuNo ratings yet
- AACS2034 Fundamentals of Computer Networks Tutorial 1A: Introduction To NetworksDocument3 pagesAACS2034 Fundamentals of Computer Networks Tutorial 1A: Introduction To NetworksM1JoeKillerNo ratings yet
- Sap FaqDocument31 pagesSap FaqsakergayenrNo ratings yet
- Wadminep Reference w97Document1 pageWadminep Reference w97Demetrio RussoNo ratings yet
- 01 Installation and AdministrationDocument28 pages01 Installation and AdministrationAlyssa Marie CadeliñaNo ratings yet
- Just Enough Dump: by Gabe GargiuloDocument18 pagesJust Enough Dump: by Gabe GargiuloLalit KumarNo ratings yet
- Tpcds Workload Analysis PDFDocument12 pagesTpcds Workload Analysis PDFthak123No ratings yet
- DVD File LayoutDocument3 pagesDVD File LayoutPipe DavilaNo ratings yet
- Difference Between AX-2009 To Ax-2012: Anil Kumar Chowdary Minds2Mentor Technology PVT LTD 2/11/2012Document5 pagesDifference Between AX-2009 To Ax-2012: Anil Kumar Chowdary Minds2Mentor Technology PVT LTD 2/11/2012Vinod PasupuletiNo ratings yet
- Faisal Akkawi Akkawi@cs - Iit.edu Department of Computer Science Illinois Institute of Technology Chicago, IL 60616Document43 pagesFaisal Akkawi Akkawi@cs - Iit.edu Department of Computer Science Illinois Institute of Technology Chicago, IL 60616Sachi BagdeNo ratings yet
- Test PT Verificare e A CuaskdasdasdDocument2 pagesTest PT Verificare e A CuaskdasdasdCatalin TobaNo ratings yet
- Understand and Use Essential Tools: in Preparation Study Points For The ExamDocument6 pagesUnderstand and Use Essential Tools: in Preparation Study Points For The ExamAravinth KumarNo ratings yet