Fibonacci
Fibonacci
Uploaded by
Piron LiveCopyright:
Available Formats
Fibonacci
Fibonacci
Uploaded by
Piron LiveOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Copyright:
Available Formats
Fibonacci
Fibonacci
Uploaded by
Piron LiveCopyright:
Available Formats
Fibonacci numbers
The Fibonacci sequence is named after Italian mathematician Leonardo of Pisa,
known as Fibonacci:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Fibonacci_number
The Fibonacci numbers fn = f(n) are the numbers characterized by the fact that
every number after the first two is the sum of the two preceding ones. They are defined
with the next recurrent relation:
0, if n = 0
f (n) = 1, if n = 1
f (n − 1) + f (n − 2)
So f0 = 0, f1 = 1, fn = fn-1 + fn-2.
The Fibonacci sequence has the form
0, 1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13, 21, 34, 55, …
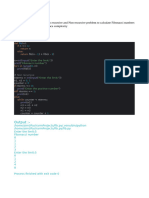
Example. Fill integer array fib with Fibonacci numbers (fib[i] = fi):
#include <stdio.h>
int i, n, fib[47];
int main(void)
{
scanf("%d",&n);
fib[0] = 0; fib[1] = 1;
for(i = 2; i <= n; i++)
fib[i] = fib[i-1] + fib[i-2];
printf("%d\n",fib[n]);
return 0;
}
i 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 ...
fib[i] 0 1 1 2 3 5 8 13 21 34 55 ...
The biggest Fibonacci number that fits into int type is
f46 = 1836311903
The biggest Fibonacci number that fits into long long type is
f92 = 7540113804746346429
If you want to find Fibonacci number fn for n > 92, use BigInteger type.
Example. Find f(n) – the n-th Fibonacci number with recursion:
#include <stdio.h>
int n;
int fib(int n)
{
if (n == 0) return 0;
if (n == 1) return 1;
return fib(n-1) + fib(n - 2);
}
int main(void)
{
scanf("%d",&n);
printf("%d\n",fib(n));
return 0;
}
f(5)
f(4) + f(3)
f(3) + f(2) f(2) + f(1)
f(2) + f(1) f(1) + f(0) f(1) + f(0)
f(1) + f(0)
Example. Find f(n) – the n-th Fibonacci number with recursion + memoization:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
int n, fib[46];
int f(int n)
{
// base case
if (n == 0) return 0;
if (n == 1) return 1;
// if the value fib[n] is ALREADY found, just return it
if (fib[n] != -1) return fib[n];
// if the value fib[n] is not found, calculate and memoize it
return fib[n] = f(n-1) + f(n - 2);
}
int main(void)
{
scanf("%d",&n);
// fib[i] = -1 means that this value is not calculated yet
memset(fib,-1,sizeof(fib));
printf("%d\n",f(n));
return 0;
}
f(5)
f(4) + f(3)
mem
f(3) + f(2)
mem
f(2) + f(1)
f(1) + f(0)
E-OLYMP 4730. Fibonacci Fibonacci numbers is a sequence of numbers F(n),
given by the formula:
F(0) = 1, F(1) = 1, F(n) = F(n – 1) + F(n – 2)
Given value of n (n ≤ 45). Find the n-th Fibonacci number.
► Implement a recursive function with memoization.
E-OLYMP 8295. Fibonacci string generation Generate the n-th Fibonacci string
that is defined with the next recurrent formula:
• f(0) = "a";
• f(1) = "b";
• f(n) = f(n – 1) + f(n – 2), where "+" operation means concatenation
For example, f(3) = f(2) + f(1) = (f(1) + f(0)) + f(1) = "b" + "a" + "b" = "bab".
► Implement a recursive function that generates the n-th Fibonacci string.
string f(int n)
{
if (n == 0) return "a";
if (n == 1) return "b";
return f(n-1) + f(n-2);
}
Read input value of n and print the n-th Fibonacci string.
cin >> n;
cout << f(n) << endl;
You might also like
- QA & QC Final Assignment MCSDocument36 pagesQA & QC Final Assignment MCSSadaf Sumdani NirvikNo ratings yet
- Schematic Diagram For Model 2216: All VersionsDocument1 pageSchematic Diagram For Model 2216: All VersionsZa RacsoNo ratings yet
- Fibonacci Numbers: N If N If N FDocument3 pagesFibonacci Numbers: N If N If N FFutbol ProqnozlariNo ratings yet
- Program For Fibonacci NumbersDocument2 pagesProgram For Fibonacci Numbersjai bachaniNo ratings yet
- RecursionDocument3 pagesRecursionPiron LiveNo ratings yet
- 12.04.dynamic ProgrammingDocument97 pages12.04.dynamic Programmingcurtisandrea242No ratings yet
- Chapter 05 RecursionDocument18 pagesChapter 05 Recursionasdyarash1No ratings yet
- Lecture 2. The Fibonacci SequenceDocument39 pagesLecture 2. The Fibonacci SequenceFlorinda Bautista50% (2)
- Algorithms Lecture 4: Dynamic ProgrammingDocument15 pagesAlgorithms Lecture 4: Dynamic ProgrammingAnirban ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- 05A Dynamic ProgrammingDocument14 pages05A Dynamic ProgrammingNguyen Huynh Lam (K16HCM)No ratings yet
- Module 1 Lesson 2 - FIBONACCI SEQUENCEDocument7 pagesModule 1 Lesson 2 - FIBONACCI SEQUENCEMark Daniel DeTorres GolisaoNo ratings yet
- Recursion TreesDocument21 pagesRecursion TreesJorge RodriguezNo ratings yet
- All About Fibonacci: A Python ApproachDocument5 pagesAll About Fibonacci: A Python ApproachTI Journals PublishingNo ratings yet
- CS8 4:14:15 PDFDocument2 pagesCS8 4:14:15 PDFnovelnerd97No ratings yet
- Data Structures and Algorithms: RecursionDocument27 pagesData Structures and Algorithms: RecursionSaksham SharmaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Algorithms: Dynamic ProgrammingDocument25 pagesIntroduction To Algorithms: Dynamic ProgrammingjaydipNo ratings yet
- 23a-FAZ-Fibonacci Sequence - Road To Dynamic ProgrammingDocument11 pages23a-FAZ-Fibonacci Sequence - Road To Dynamic Programmingtaruna nasutionNo ratings yet
- Dynamic Programming: CSE 301: Combinatorial OptimizationDocument45 pagesDynamic Programming: CSE 301: Combinatorial Optimizationswarna islamNo ratings yet
- 268 L2 Recursion S09Document29 pages268 L2 Recursion S09yoursashmeNo ratings yet
- 2ndweekassignment 1Document4 pages2ndweekassignment 1divyaNo ratings yet
- LESSON 1 Fibonacci NumbersDocument3 pagesLESSON 1 Fibonacci NumbersMarites Peñaranda LebigaNo ratings yet
- DSA With C RecursionDocument11 pagesDSA With C Recursionmeetdave642No ratings yet
- 1st Sem, ITP, Lecture 11-Algorithms & ComputingDocument12 pages1st Sem, ITP, Lecture 11-Algorithms & ComputingM KhattakNo ratings yet
- TheoryDocument21 pagesTheoryNibedan PalNo ratings yet
- 13.1: Finding Fibonacci Numbers RecursivelyDocument2 pages13.1: Finding Fibonacci Numbers RecursivelyRithuik YerrabroluNo ratings yet
- FibonacciDocument15 pagesFibonacciMonirul IslamNo ratings yet
- Lecture 20Document15 pagesLecture 20johnsmith03323315336No ratings yet
- Final Spring19Document4 pagesFinal Spring19aizazNo ratings yet
- InputDocument2 pagesInputrohankpawar30No ratings yet
- Dynamic Programming Lecture 2Document27 pagesDynamic Programming Lecture 2debajyotichakraborty92No ratings yet
- F F F F Fibonacci Number F The Previousterm F Theterm Before FDocument3 pagesF F F F Fibonacci Number F The Previousterm F Theterm Before FRoss Christian ManuelNo ratings yet
- FiboDocument18 pagesFiboIvan MetalnikovNo ratings yet
- L29 L30 Recursive FunctionsDocument25 pagesL29 L30 Recursive FunctionsIshank PatelNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Mathematics in The Modern WorldDocument5 pagesLesson 1 Mathematics in The Modern WorldAUDREY DANCULOSNo ratings yet
- Write The Program To Recursive and Non-Recursive Problem To Calculate Fibonacci Numbers and Analyze Their Time and Space ComplexityDocument2 pagesWrite The Program To Recursive and Non-Recursive Problem To Calculate Fibonacci Numbers and Analyze Their Time and Space Complexityrohankpawar30No ratings yet
- Error EliminatorPython SetDocument3 pagesError EliminatorPython Setsumanthshetty080No ratings yet
- ADA Lab Programs Consolidated 15-4-16Document41 pagesADA Lab Programs Consolidated 15-4-16Spoorthi JNo ratings yet
- Fibonacci SequenceDocument7 pagesFibonacci SequenceneelanshNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals OfalgorithmDocument67 pagesFundamentals OfalgorithmlegharimehjabeenNo ratings yet
- 07 NotesDocument10 pages07 Notessangonomiya21No ratings yet
- Answers For AlgorithmsDocument10 pagesAnswers For AlgorithmsMark DjentNo ratings yet
- Fibonacci Numbers 1Document6 pagesFibonacci Numbers 1Necromancer Gtr75 GtNo ratings yet
- RecursionDocument14 pagesRecursionIshanNo ratings yet
- MMW - FibonacciDocument1 pageMMW - FibonacciDiana Lyn PascualNo ratings yet
- Bu I 7 - Dynamic Programming AlgorithmsDocument119 pagesBu I 7 - Dynamic Programming AlgorithmsPhạm Gia DũngNo ratings yet
- Design & Analysis of Algorithms: Practical FileDocument34 pagesDesign & Analysis of Algorithms: Practical FileaatmashrisanyalNo ratings yet
- Alg Ch1 Part2Document24 pagesAlg Ch1 Part2yarajehadrabNo ratings yet
- Chap 2 RecursionDocument31 pagesChap 2 RecursionChian SoonkaiNo ratings yet
- Dynamic Programming: CSE373: Design and Analysis of AlgorithmsDocument36 pagesDynamic Programming: CSE373: Design and Analysis of AlgorithmsAdrian Anam SifaatNo ratings yet
- Solution Libraries and Recursion WorksheetDocument5 pagesSolution Libraries and Recursion WorksheetBalakrishnan.GNo ratings yet
- Recursion: Prof. Nilesh GambhavaDocument13 pagesRecursion: Prof. Nilesh GambhavaAmogh VaishnavNo ratings yet
- Recursive Functions: 5.13 RecursionDocument7 pagesRecursive Functions: 5.13 RecursionOrinIslamRahaNo ratings yet
- 4 FS - FT and WT - Sept - 2022 PDFDocument120 pages4 FS - FT and WT - Sept - 2022 PDFSahethiNo ratings yet
- RecursionDocument56 pagesRecursionrizi007No ratings yet
- Lp-Iii Lab MannualDocument173 pagesLp-Iii Lab Mannualsnehaldarekar2003No ratings yet
- Lec7 Divide and ConquerDocument25 pagesLec7 Divide and Conquerlsw9020No ratings yet
- Recursive DefinitionsDocument18 pagesRecursive DefinitionsgbikornoNo ratings yet
- FIbonacci Numbers LessonDocument9 pagesFIbonacci Numbers Lessonwinterlilies7No ratings yet
- Dynamic Programming ClassDocument33 pagesDynamic Programming Classrohithkumarasarelly143No ratings yet
- RecursionDocument13 pagesRecursionjigisha kiran shahNo ratings yet
- Functional Operators, Volume 2: The Geometry of Orthogonal SpacesFrom EverandFunctional Operators, Volume 2: The Geometry of Orthogonal SpacesNo ratings yet
- Fitzsimons IndusValleyCivilization 1970Document15 pagesFitzsimons IndusValleyCivilization 1970Piron LiveNo ratings yet
- LawsofUr Nammu v3Document16 pagesLawsofUr Nammu v3Piron LiveNo ratings yet
- Hello WorldDocument19 pagesHello WorldPiron LiveNo ratings yet
- Cin CoutDocument1 pageCin CoutPiron LiveNo ratings yet
- New Digital Qs ClassDocument18 pagesNew Digital Qs ClassPiron LiveNo ratings yet
- Sat Practice Test 3 DigitalDocument56 pagesSat Practice Test 3 DigitalPiron Live100% (1)
- Sat Practice Test 1 DigitalDocument56 pagesSat Practice Test 1 Digitallucifer morningstarNo ratings yet
- March StudentsDocument14 pagesMarch StudentsPiron LiveNo ratings yet
- FactoryTalk - Deleting The RNL FilesDocument8 pagesFactoryTalk - Deleting The RNL FilesJose SierraNo ratings yet
- Ac7114-3 Rev oDocument30 pagesAc7114-3 Rev omrigesh vermaNo ratings yet
- Empowerment Tech Week 5-6 Answer SheetDocument14 pagesEmpowerment Tech Week 5-6 Answer SheetMaestro MertzNo ratings yet
- WhitePaper Changing Approval Level For AppraisalDocument12 pagesWhitePaper Changing Approval Level For AppraisalMuhammad AbubakarNo ratings yet
- Artificial Intelligence Enabled Marketing SolutionDocument14 pagesArtificial Intelligence Enabled Marketing SolutionSalma MamdouhNo ratings yet
- 7 Jurus TerlarangDocument134 pages7 Jurus TerlarangRianta SitanggangNo ratings yet
- Arma 1Document4 pagesArma 1Lâm Anh VũNo ratings yet
- Analysis and Synthesis of Synchronous Sequential CircuitsDocument74 pagesAnalysis and Synthesis of Synchronous Sequential CircuitsANITHA MNo ratings yet
- Sap SD Material 3Document65 pagesSap SD Material 3muddisetty umamaheswarNo ratings yet
- Sharma 2019 J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 1240 012030Document26 pagesSharma 2019 J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 1240 012030Kishan MNo ratings yet
- CapDocument7 pagesCapjarriaga.gonzalezNo ratings yet
- Moiz CompilerDocument11 pagesMoiz CompilerAmmar KhanNo ratings yet
- CSE110 Lab Assignment 4 (String)Document23 pagesCSE110 Lab Assignment 4 (String)Random UseNo ratings yet
- Brochure 2017Document82 pagesBrochure 2017yahyaupsefNo ratings yet
- The Newspaper BusinessDocument42 pagesThe Newspaper BusinessSafin Uddin ShadNo ratings yet
- INSITE 8.5.2 Release NotesDocument15 pagesINSITE 8.5.2 Release Notesorlando de oNo ratings yet
- Python 201 - (Slightly) Advanced Python TopicsDocument69 pagesPython 201 - (Slightly) Advanced Python Topicssandro carNo ratings yet
- Worksheet Class 8 All Chapters Term 1Document12 pagesWorksheet Class 8 All Chapters Term 1areeb9187No ratings yet
- Local Operating Procedure Manual, Terrestrial Radio Communication Services Unit, Nigerian Airspace Management AgencyDocument15 pagesLocal Operating Procedure Manual, Terrestrial Radio Communication Services Unit, Nigerian Airspace Management Agencyjohnogunlola100% (6)
- ZEN 2 Blue Edition - Software GuideDocument309 pagesZEN 2 Blue Edition - Software GuideSakuro19No ratings yet
- EEE 6211 Digital Speech ProcessingDocument40 pagesEEE 6211 Digital Speech ProcessingShoaib SamiNo ratings yet
- Install On A Single Computer - Download & Install - Autodesk Knowledge NetworkDocument11 pagesInstall On A Single Computer - Download & Install - Autodesk Knowledge NetworkSaga MursalNo ratings yet
- Ir21531D (S) & (PBF) : Self-Oscillating Half-Bridge DriverDocument9 pagesIr21531D (S) & (PBF) : Self-Oscillating Half-Bridge DriverErasmo Franco SNo ratings yet
- The Hypdestopt Package: Heiko Oberdiek 2019/12/29 v2.6Document13 pagesThe Hypdestopt Package: Heiko Oberdiek 2019/12/29 v2.6Evan RegazNo ratings yet
- CSW 1×2s Magnet Optic Switch Data Sheet 530701Document3 pagesCSW 1×2s Magnet Optic Switch Data Sheet 530701GLsun MallNo ratings yet
- 1-Dist Part 1Document22 pages1-Dist Part 1Srinivasan MahadevanNo ratings yet
- H To Open The Dictation: Use Voice Recognition in Windows 10 How To Set Up and Test Microphones in Windows 10Document14 pagesH To Open The Dictation: Use Voice Recognition in Windows 10 How To Set Up and Test Microphones in Windows 10pradeepNo ratings yet
- Lab 6 - Circuit Simulation - Rev0Document9 pagesLab 6 - Circuit Simulation - Rev0Muhammad NaguibNo ratings yet