Série de TD 1
Série de TD 1
Uploaded by
femafafrabdCopyright:
Available Formats
Série de TD 1
Série de TD 1
Uploaded by
femafafrabdCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Copyright:
Available Formats
Série de TD 1
Série de TD 1
Uploaded by
femafafrabdCopyright:
Available Formats
Abou Bekr Belkaid University of Tlemcen. 1st grade LMD (2024/2025).
Faculty of Sciences, Mathematics departement M-MI, Exersices serie N 4:
Chapiter 4 : Limits and continuity
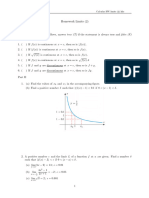
Exercise 1
Find the domain of the following functions:
x+1 1 p 1
1=f (x) = 1 ; 2=f (x) = p ; 3=f (x) = x2 1 e 1 x ;
1 e x sin x
p
1 1 x 2 si x > 1
4=f (x) = (1 + ln x) x ; 5=f (x) = ; 6=f (x) = :
E(x) ln(x + 2) si x 1
Exercise 2
Find the limit of the following functions when it exists:
1 1 x sin (2x) tan x
1) lim x sin ; 2) lim x sin ; 3) lim ; 4) lim
x!0 x x!+1 x x!0 x + sin (3x) x!0 x
p p p
sin x cos x sin(x ln x) x a+ x a
5) lim ; 6) lim ; 7) lim p ;
x! 4 1 tan x x!0 x2 x!0
> x2 a2
x
1 p p x
8) lim 1+ ; 9) lim sin x + 1 sin x ; 10) lim (1 x) tan :
x!+1 x x!+1 x!1 2
Exercise 3
Using the de…nition of the limit, show that:
3x 1 3 4
1= lim (2x 1) = 7; 2/ lim = ; 3/ lim ln x = +1; 4/ lim = +1
x!4 x!+1 2x +1 2 x!+1 > x + 3
x! 3
Exercise 4:
1. We consider the two following functions f and g de…ned over R by:
( 8 1
1
x
if x 6= 0 < xe x if x < 0
f (x) = ex +1 and g(x) = 0 if x = 0
0 if x = 0 : 2
x ln( x1 + 1) if x > 0
Discuss the continuity of the functions f and g on R:
2. Study the continuous extention of the following functions on R :
1 sin ( x)
2) f (x) = xearctan( x2 ) ;
1
1) f (x) = cos ; 3) f (x) =
x 1 x
x+1
3. Let be the functions f (x) = x+2 ; g(x) = x1 :Show that f is uniformly continuous on [0; +1[; but g isn’t on ]0; 1]:
4. Show that, any continuous function f from [a; b] into it self admits a …xed point.
You might also like
- Mathslabmanual VtuDocument84 pagesMathslabmanual VtuDeeba Mushtaq Aga100% (1)
- Cls Jeead-17-18 Xii Mat Target-6 Set-2 Chapter-5Document84 pagesCls Jeead-17-18 Xii Mat Target-6 Set-2 Chapter-5Sagar MalhotraNo ratings yet
- Problems and Solutions in Engineering Mathematics - Edition T.c.guptaDocument830 pagesProblems and Solutions in Engineering Mathematics - Edition T.c.guptacarlos henrique90% (10)
- Lesson 6Document22 pagesLesson 6marianollavejrNo ratings yet
- AMA1110 Tutorial - 4sDocument8 pagesAMA1110 Tutorial - 4sBrian LiNo ratings yet
- JEE Main Limits, Continuity and Differentiability Limits Revision Notes - Free PDF DownloadDocument9 pagesJEE Main Limits, Continuity and Differentiability Limits Revision Notes - Free PDF DownloadherooNo ratings yet
- Série 4limits and ContinuityDocument3 pagesSérie 4limits and Continuitysalimderradj99No ratings yet
- 1 Limit and Continuity: Review Final Exam Math1003 Math Learning Centre Department of MATH & STATSDocument4 pages1 Limit and Continuity: Review Final Exam Math1003 Math Learning Centre Department of MATH & STATSPenellapheNo ratings yet
- Calculate LimitsDocument2 pagesCalculate LimitsSwapnaneel BhattacharyyaNo ratings yet
- 2024-25 Tute I (MAN101) - 240807 - 155250Document3 pages2024-25 Tute I (MAN101) - 240807 - 155250neoa5108No ratings yet
- Hello WorldDocument3 pagesHello WorldBimal Kumar SahooNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document3 pagesAssignment 1Ronan CarrollNo ratings yet
- Exercises MEF - 5 - 2018 - SolutionDocument6 pagesExercises MEF - 5 - 2018 - SolutionrtchuidjangnanaNo ratings yet
- Guided Lecture Sheet Module 1 Part 2Document9 pagesGuided Lecture Sheet Module 1 Part 2ghazialkhatib100No ratings yet
- A F X Centered at X A XaDocument2 pagesA F X Centered at X A XaAtharvaNo ratings yet
- Differential Calculus (Exercises With Detailed Solutions)Document5 pagesDifferential Calculus (Exercises With Detailed Solutions)yancha1973No ratings yet
- Function 27737867Document11 pagesFunction 27737867Ashree KesarwaniNo ratings yet
- С.2 Derivative - HW - 2Document1 pageС.2 Derivative - HW - 2PashaNo ratings yet
- HW - Calculus - ContinuityDocument5 pagesHW - Calculus - Continuityhty2225833180No ratings yet
- ECG1 Interro27 23-24Document4 pagesECG1 Interro27 23-24jpmanga43No ratings yet
- lim.cont.diff. tdDocument2 pageslim.cont.diff. tdDouaa DcNo ratings yet
- Calculus Limits and Continuity Assignment 2Document4 pagesCalculus Limits and Continuity Assignment 2kamlesh agrahariNo ratings yet
- Maths BTechDocument2 pagesMaths BTechRunit JainNo ratings yet
- 00math EngDocument82 pages00math EngBarış UlukanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 PDFDocument3 pagesChapter 2 PDFMakobela MmakwenaNo ratings yet
- Serie 4Document3 pagesSerie 4mathNo ratings yet
- DerivativesDocument5 pagesDerivativesnochekervinpaulNo ratings yet
- 20-Limits, Continuity and DifferntiabilityDocument14 pages20-Limits, Continuity and Differntiabilityteensdepressed774No ratings yet
- PS1ADocument1 pagePS1ARdmstNo ratings yet
- Limits and Continuity & Differentiability (LCD) - Short NotesDocument3 pagesLimits and Continuity & Differentiability (LCD) - Short NotesvatsalkumarshahiNo ratings yet
- Basic Calculus q3 w6 Lesson 61 Determine The Relationship Between Diffentiability and Continuity of A FunctionDocument5 pagesBasic Calculus q3 w6 Lesson 61 Determine The Relationship Between Diffentiability and Continuity of A FunctionRachell MacasoNo ratings yet
- 00math EngDocument82 pages00math EngMahmoud AlnawajhaNo ratings yet
- ws10Document1 pagews10tunagenc999No ratings yet
- Math 180 Midterm Review: Chapter 2: Quick Response QuestionsDocument5 pagesMath 180 Midterm Review: Chapter 2: Quick Response QuestionsMario AgudeloNo ratings yet
- 1 Tan 6 6 Cos) Lim) Lim Cos) Lim 3 2 1 1 Sin (7) 3 3 5 1) Lim) Lim) Lim 4 2 10 6 10 2 1 1, 3 2 3 3) Lim ?) Lim 12 2, 3 3 2 1 1 Co) Lim) Lim 2 S SinDocument3 pages1 Tan 6 6 Cos) Lim) Lim Cos) Lim 3 2 1 1 Sin (7) 3 3 5 1) Lim) Lim) Lim 4 2 10 6 10 2 1 1, 3 2 3 3) Lim ?) Lim 12 2, 3 3 2 1 1 Co) Lim) Lim 2 S SinEng-Mukhtaar CatooshNo ratings yet
- Assignment 13Document1 pageAssignment 13prakashgupta12082000No ratings yet
- MATH 175 Calculus I - 2020-2021 Fall Worksheet 5Document4 pagesMATH 175 Calculus I - 2020-2021 Fall Worksheet 5malafikokamilNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Practice ItemsDocument4 pagesUnit 2 Practice ItemsNe IlNo ratings yet
- 00math EngDocument90 pages00math EngBünyamin DemirNo ratings yet
- Tejlorova FormulaDocument2 pagesTejlorova FormulaZoranNo ratings yet
- 103 Limit Sheet 1658299638237Document44 pages103 Limit Sheet 1658299638237Shashwat NiranjanNo ratings yet
- Mathematics Formula: Topic Phase-4Document14 pagesMathematics Formula: Topic Phase-4testerNo ratings yet
- Additional Exercise 6Document4 pagesAdditional Exercise 6n28tykqh6yNo ratings yet
- Série 4 DL El MortadDocument2 pagesSérie 4 DL El Mortadnaimhamouda200605No ratings yet
- Serie Les Primitives FR ArabDocument1 pageSerie Les Primitives FR ArabHoda HouriNo ratings yet
- CD & AD ANS KEYDocument10 pagesCD & AD ANS KEYyashvi0123456789No ratings yet
- LCD 13Document4 pagesLCD 13Anusha SinghalNo ratings yet
- 201 Nya 05 2016 3Document4 pages201 Nya 05 2016 3rhl5761No ratings yet
- Worksheet 4Document3 pagesWorksheet 4sswengsNo ratings yet
- MATH119 Fall 2024 Recitation 2Document1 pageMATH119 Fall 2024 Recitation 2sanogit436No ratings yet
- С.4 Taylor Series HW4Document1 pageС.4 Taylor Series HW4PashaNo ratings yet
- Additional Exercise 6 SolutionDocument22 pagesAdditional Exercise 6 Solutionn28tykqh6yNo ratings yet
- F24Lab6Document2 pagesF24Lab6gtristanyangNo ratings yet
- Sample Paper For CalculusDocument4 pagesSample Paper For Calculusritikajuyal01230No ratings yet
- ContlimDocument6 pagesContlimsoufianehmid90No ratings yet
- Worksheet 3 SolutionsDocument8 pagesWorksheet 3 SolutionsXuze ChenNo ratings yet
- Assign 3Document1 pageAssign 320230551No ratings yet
- Mat 1120 Tutorial Sheet 8 2022 23Document2 pagesMat 1120 Tutorial Sheet 8 2022 23musamugabazi68No ratings yet
- Week3 - 117 - 2024-1 IDocument1 pageWeek3 - 117 - 2024-1 Iyaseminoral06No ratings yet
- Worksheet 6 Solutions -F23Document3 pagesWorksheet 6 Solutions -F23sarimNo ratings yet
- Factoring and Algebra - A Selection of Classic Mathematical Articles Containing Examples and Exercises on the Subject of Algebra (Mathematics Series)From EverandFactoring and Algebra - A Selection of Classic Mathematical Articles Containing Examples and Exercises on the Subject of Algebra (Mathematics Series)No ratings yet
- Cables: Theory of Structure - IDocument20 pagesCables: Theory of Structure - IUmer KhanNo ratings yet
- Melosh 1963Document7 pagesMelosh 1963Matheus Garcia GoncalvesNo ratings yet
- Performance Task 1-2Document4 pagesPerformance Task 1-2Gerald Maimad100% (1)
- Quadratic EquationsDocument18 pagesQuadratic Equationstanvip16No ratings yet
- Midterm SolutionDocument8 pagesMidterm SolutionAnonymous 94I9knNo ratings yet
- Applications of DerivativesDocument24 pagesApplications of DerivativesDHRUV .C.K.No ratings yet
- Fundamental of Probability TheoryDocument12 pagesFundamental of Probability TheoryRahul KumarNo ratings yet
- Assignment 5 (11-13)Document13 pagesAssignment 5 (11-13)Midhun MNo ratings yet
- 10th Class Anual Plan PDFDocument1 page10th Class Anual Plan PDFAbdul Sami MomandNo ratings yet
- Discret HamzaouiDocument19 pagesDiscret HamzaouiPRED ROOMNo ratings yet
- Geometric CalculusDocument7 pagesGeometric CalculusjosgauNo ratings yet
- Microsoft PowerPoint - Strip TheoryDocument48 pagesMicrosoft PowerPoint - Strip Theoryphantom29No ratings yet
- Bcom - Ca - SyllabusDocument96 pagesBcom - Ca - Syllabuspranavveda64No ratings yet
- Simulated Annealing: by Rohit Ray ESE 251Document20 pagesSimulated Annealing: by Rohit Ray ESE 251shilpi lavaniaNo ratings yet
- Bayesian Modeling of Uncertainty in Low-Level VisionDocument27 pagesBayesian Modeling of Uncertainty in Low-Level VisionSivaloges SingamNo ratings yet
- 1 Shapes of Cubic FunctionsDocument7 pages1 Shapes of Cubic FunctionsHuỳnh Thái ĐinhNo ratings yet
- Probabilistic Methods in Combinatorics: 1 Warm-UpDocument7 pagesProbabilistic Methods in Combinatorics: 1 Warm-UpSrikar VaradarajNo ratings yet
- MATH 135 Course NoteDocument342 pagesMATH 135 Course NoteWilliam XiangNo ratings yet
- Fourier Series NotesDocument18 pagesFourier Series NotesHaziq PazliNo ratings yet
- Calculus Task MSKDocument16 pagesCalculus Task MSKSamantha AnyangoNo ratings yet
- 2 - Solving QE by ExtractingDocument24 pages2 - Solving QE by ExtractingKenzei AzumiNo ratings yet
- Grades 7 and 8 (First Quarter) : Weeks Grade 7 Act/Material Feedback Grade 8 Act/Material FeedbackDocument14 pagesGrades 7 and 8 (First Quarter) : Weeks Grade 7 Act/Material Feedback Grade 8 Act/Material FeedbackAlbec Sagrado BallacarNo ratings yet
- CB_GD_12_ Mathematics (041) _Practicals and Projects_2024 - 25Document1 pageCB_GD_12_ Mathematics (041) _Practicals and Projects_2024 - 25kaiserwilhelm39No ratings yet
- Chapter 2-Optimal Operation of Thermal Power PlantsDocument55 pagesChapter 2-Optimal Operation of Thermal Power PlantsVõ Quang SangNo ratings yet
- NBHM Question Paper 2015Document8 pagesNBHM Question Paper 2015signumsNo ratings yet
- The Laplace Transform of Step Functions (Sect. 6.3) .: OverviewDocument11 pagesThe Laplace Transform of Step Functions (Sect. 6.3) .: OverviewIsaac PangNo ratings yet
- DSP Lab ReportDocument28 pagesDSP Lab ReportKaaviyaNo ratings yet
- Revision Questions - Day 1 To 10Document13 pagesRevision Questions - Day 1 To 10hiteshgamer87No ratings yet