Animal tissue
Animal tissue
Uploaded by
Elvira SilvaCopyright:
Available Formats
Animal tissue
Animal tissue
Uploaded by
Elvira SilvaCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Copyright:
Available Formats
Animal tissue
Animal tissue
Uploaded by
Elvira SilvaCopyright:
Available Formats
CHAPTER-2
Lesson-Animal Tissue
Tissue means a group of cells with similar origins performing a particular function. The tissue level of
organization begins from the phylum Coelenterates (Cnidaria).
In animals, there are 4 basic types of tissues.
1. Connective Tissue
2. Epithelial Tissue
3. Muscle Tissue
4. Nervous Tissue
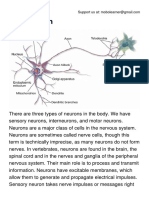
Nervous tissue (Neural tissue)
It is an excitable tissue. Nervous tissue consists of neurons and neuroglial cells. The neuron is the
longest cell in the body.
The nervous system is first formed in the Cnidarians. The nervous system develops from
the ectoderm in embryonic development.
Nervous tissue is made up of
A. Neuron (Nerve cell)
B. Neuroglial cells (Glial cells)
Neuron (Nerve cell)
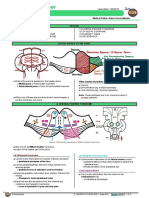
Structure of nerve cell
Neurons are the basic units of the nervous system, and amitotic.
A neuron has a cell body (Soma), dendrites, and Axon.
A cell body of neuron contains nucleus, other cell organelles, and nissel granuels (RNA particles).
Some projections from the cell body, known as dendrites, produce a tremendous surface area to receive
the information (Impulse).
The soma connects to the axon through the axon hillock (refer to your biology notebook to know what
is axon hillock).
An axon transmits the nerve impulse to the next neuron. A myelin sheath protects an axon. In CNS
myelin sheath is formed by oligodendrocytes and in PNS it's formed by individual cells called Schwann
cells.
The small gaps of myelin sheath on an axon are called Ranvier nodes. An axon ends with axon dendrites
or axon terminal synapses (Axon bulbs).
Classification of neurons or types of neurons.
Based on the following criteria neurons have been classified into several types.
1. Based on the structure
A. Nonpolar neurons or apolar neurons
They do not have any polarity. Axons and dendrites are not distinguished in these fibers.
All fibers are of the same kind and can carry information towards or away from the cell
body.
B. Unipolar neurons
Soma gives rise to only one nerve process, which acts as both an axon and a dendron.
The flow of information is unidirectional. These are sensory neurons. They can be found
in invertebrate and vertebrate embryos but not in adults.
C. Bipolar neurons
In bipolar neurons, Soma gives rise to two nerve processes with one dendron and one
axon at opposite poles. These neurons have a unidirectional information flow. They can
be found in the retina of the eyes, as well as the olfactory epithelium.
D. Multipolar neurons
One axon and numerous dendrites make up multipolar neurons, allowing for a one-way
information flow. They can be found in the cerebral cortex of adult vertebrates.
2. Based on the function
A. Sensory neurons / afferent neurons.
Transmits the information from sensory receptors to CNS.
Ex: Unipolar neurons
B. Motor/efferent neurons
Transmits the information from CNS to Muscle or glands.
Ex: Multipolar neurons
C. Interneurons/relay neurons/ association neuron
These neurons help shuttle the signals between afferent and efferent neurons.
Ex: Multipolar neurons in CNS
3. Based on Myelin sheath
A. Myelinated neurons
Schwann cells and Oligodendrocytes envelop myelinated nerve fibers, forming
the myelin sheath around the axon. The nodes of Ranvier are the spaces between two
neighbouring myelin sheaths. These fibers are present in the spinal and cranial nerves.
B. Non-Myelinated neurons
No myelin sheath around the axon surrounds. There are no Ranvier nodes. These fibers can
be found in both the autonomic and somatic nervous systems.
Neuroglial cells (Glial cells)
Muscle Tissue
The study of muscles, their function, and diseases of muscles is called Myology. The Muscular
system develops from mesoderm in embryonic development.
Muscular tissue has been classified into 3 types
Skeletal Muscle
Skeletal muscle is found throughout the body and functions to contract in response to a stimulus.
Skeletal muscle serves many purposes, including producing movement, sustaining body posture and
position, maintaining body temperature, storing nutrients, and stabilizing joints. skeletal muscle
contraction is under voluntary control, receiving neural inputs allowing conscious control of muscles.
You might also like
- Anatomy and Physiology Lecture Notes Chapter 1Document6 pagesAnatomy and Physiology Lecture Notes Chapter 1Cza Mae ArsenalNo ratings yet
- Nervous System Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument26 pagesNervous System Anatomy and PhysiologyKBD100% (4)
- Exercise and Cardiac Health Physiological and Molecular InsightsDocument11 pagesExercise and Cardiac Health Physiological and Molecular InsightsAngélica MuñozNo ratings yet
- BT - EfaDocument94 pagesBT - EfaCharles NepomucenoNo ratings yet
- 9SUMMARYNERVOUSSYSTEMDocument24 pages9SUMMARYNERVOUSSYSTEMArvenBitasNo ratings yet
- The Nervous SystemDocument86 pagesThe Nervous SystemNatukunda Dianah100% (1)
- Nervous SystemDocument20 pagesNervous SystemxoxogeloNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument19 pagesNervous Systemmercaderlorenzo9No ratings yet
- THE HUMAN NERVOUS SYSTEM 24-25Document14 pagesTHE HUMAN NERVOUS SYSTEM 24-25denniswezaaraujoNo ratings yet
- Nervous System ResonanceDocument72 pagesNervous System ResonanceEkta ManglaniNo ratings yet
- Altered Cognitive-Perceptual Patterns: Clients With Neuroligic DisordersDocument96 pagesAltered Cognitive-Perceptual Patterns: Clients With Neuroligic DisordersJobelle AcenaNo ratings yet
- Topic 02A - The NeuronsDocument5 pagesTopic 02A - The NeuronsjmvengineerconsNo ratings yet
- Nscelec4-Week 15Document23 pagesNscelec4-Week 15Jeune Kristine OngNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument12 pagesNervous SystemLeon MarkoNo ratings yet
- The Nervous SystemDocument36 pagesThe Nervous SystemAebie AquinoNo ratings yet
- Animal Nervous System: Logo HereDocument32 pagesAnimal Nervous System: Logo HereAnne Claudette Capin TeofiloNo ratings yet
- Trigeminal NerveDocument39 pagesTrigeminal NerveRanjana RavindranNo ratings yet
- Ervous Ystem: Structural ClassificationDocument95 pagesErvous Ystem: Structural ClassificationJobelle AcenaNo ratings yet
- Second Quarter Grade 10 - Science HANDOUT No.2 On Neurons, Reflex, Reflex Arc & Brain General Information About The Nervous SystemDocument2 pagesSecond Quarter Grade 10 - Science HANDOUT No.2 On Neurons, Reflex, Reflex Arc & Brain General Information About The Nervous SystemMartin ReaporNo ratings yet
- The Nervous SystemDocument66 pagesThe Nervous Systemmatthewcabulong7No ratings yet
- UNIT 4 (Nervous System)Document14 pagesUNIT 4 (Nervous System)Workinesh Kaynabo KambaloNo ratings yet
- 4.2 Nervious TissuesDocument36 pages4.2 Nervious TissuesZaara RashéidNo ratings yet
- Presentation 2Document23 pagesPresentation 2Maria KhanNo ratings yet
- Nervous System 1Document13 pagesNervous System 1wasim akhtarNo ratings yet
- Psy 413 ProjectDocument38 pagesPsy 413 ProjectDumebi AneneNo ratings yet
- Lab 9 Nervous TissueDocument28 pagesLab 9 Nervous TissueSarwar JafarNo ratings yet
- Nervous Tissue PDFDocument4 pagesNervous Tissue PDFFadhil Hussam AhmedNo ratings yet
- FinalDocument14 pagesFinalsukhleenNo ratings yet
- Module 14Document65 pagesModule 14sukhleenNo ratings yet
- Nervous System and TissueDocument3 pagesNervous System and TissueatrideepmNo ratings yet
- Excitable TissueDocument117 pagesExcitable Tissueur.yared21100% (1)
- HongolphDocument6 pagesHongolphfirstmail227No ratings yet
- New Notes Ch12Document7 pagesNew Notes Ch12moorekaleb104No ratings yet
- 1.2 Neuroscience and BehaviourDocument7 pages1.2 Neuroscience and BehaviourDiya MehtaNo ratings yet
- DelaCruz AlbertBryan Activity#4 MED3Document3 pagesDelaCruz AlbertBryan Activity#4 MED3AlbertNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument26 pagesNervous SystemNABIHA NAEEMNo ratings yet
- Types of Neurons PDFDocument2 pagesTypes of Neurons PDFPerry Sin100% (2)
- Excitable Tissues Neurons Autonomic Nervous SystemDocument19 pagesExcitable Tissues Neurons Autonomic Nervous Systemhardworkeffiong14No ratings yet
- N 4Document85 pagesN 4Riya ThakkarNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Nervous TissueDocument54 pagesAnatomy of Nervous TissueNand PrakashNo ratings yet
- Neurons and Nervous SystemDocument10 pagesNeurons and Nervous SystemALWEN ROSE CARILLONo ratings yet
- Neuron and Glial CellsDocument8 pagesNeuron and Glial CellsMurilo Bonet100% (1)
- Nervous TissueDocument25 pagesNervous TissueSumayya KabeerNo ratings yet
- Bio612 Writtenreport Cabaluna NancyDocument10 pagesBio612 Writtenreport Cabaluna NancyNancy Medina CabalunaNo ratings yet
- Ns-Elec-4 - Nervous SystemDocument14 pagesNs-Elec-4 - Nervous SystemONGLENGCO WILSON JAKE V.No ratings yet
- HND HIM-mallam SADIQDocument17 pagesHND HIM-mallam SADIQsadiq rabiu umarNo ratings yet
- Nerve TypeDocument6 pagesNerve Typeabdulbilqees2004No ratings yet
- Histology: Neuron Cells Types and StructureDocument7 pagesHistology: Neuron Cells Types and StructureAli HayderNo ratings yet
- Nervous System-WPS OfficeDocument36 pagesNervous System-WPS OfficeShubhendu Chattopadhyay100% (1)
- Nervous TissueDocument14 pagesNervous Tissueyigermalamanuel32No ratings yet
- 4.d Nerves TissueDocument130 pages4.d Nerves TissueTony Anthony ChikwembaNo ratings yet
- Unit 6 NeuroanatomyDocument212 pagesUnit 6 Neuroanatomyjeptoo006No ratings yet
- Nervous TissueDocument10 pagesNervous TissueWrigley PatioNo ratings yet
- Exercise No. 7 Nervous TissueDocument10 pagesExercise No. 7 Nervous TissueRyan Aaron Cruz ParNo ratings yet
- Ns-Elec-4 - Nervous SystemDocument14 pagesNs-Elec-4 - Nervous SystemONGLENGCO WILSON JAKE V.No ratings yet
- MODULE 2 physioDocument8 pagesMODULE 2 physioriyaanka.sharmaNo ratings yet
- NeuroscienceDocument6 pagesNeuroscienceZerica JohnNo ratings yet
- PsyQuesta SAPE Part 2Document414 pagesPsyQuesta SAPE Part 2abhinavkannan2002No ratings yet
- Science Sofie 10 3 RevDocument11 pagesScience Sofie 10 3 Revjinxtapperhat07No ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument24 pagesNervous System8D cibi chakrawarthyNo ratings yet
- Nervous System Transes 1Document6 pagesNervous System Transes 1Rhodie BatislaonNo ratings yet
- Itzar - Neurohistology PDFDocument186 pagesItzar - Neurohistology PDFahmad aqilNo ratings yet
- Die Sel en Selstrukture GR 10Document57 pagesDie Sel en Selstrukture GR 10zetamouton18No ratings yet
- Meat and Meat Products Technology Including Poultry Products Technology PDFDocument76 pagesMeat and Meat Products Technology Including Poultry Products Technology PDFDhanya M AlexNo ratings yet
- Marchand 2008Document25 pagesMarchand 2008Fernando TeixeiraNo ratings yet
- EOC Review Packet StudentDocument15 pagesEOC Review Packet Studentjjman epicNo ratings yet
- Diabetes Mellitus SeminarDocument35 pagesDiabetes Mellitus SeminarAnkush SinglaNo ratings yet
- CCNDocument39 pagesCCNMann TSha100% (1)
- Class 11 Bio Paper (2) - 240205 - 195646Document6 pagesClass 11 Bio Paper (2) - 240205 - 195646sannnd31No ratings yet
- 5pri - Nat SC WM - Madrid - Apoyo Al AprendizajeDocument43 pages5pri - Nat SC WM - Madrid - Apoyo Al AprendizajeVictoria CristobalNo ratings yet
- Autophagy Provides A Conceptual Therapeutic Framework For Bone Metastasis From Prostate CancerDocument8 pagesAutophagy Provides A Conceptual Therapeutic Framework For Bone Metastasis From Prostate CancerAnnisa RahmaNo ratings yet
- F CKDocument8 pagesF CKfmaximianoNo ratings yet
- An Atlas of Osteoporosis Third Edition John C. Stevenson download pdfDocument49 pagesAn Atlas of Osteoporosis Third Edition John C. Stevenson download pdfholmekodatkn100% (3)
- Wa0035.Document73 pagesWa0035.hamzaali227004No ratings yet
- Cuddon - Electrophysiology in Neuromuscular Disease - 2002Document32 pagesCuddon - Electrophysiology in Neuromuscular Disease - 2002paula gonzalezNo ratings yet
- 134 - Neurology Pathology) Pons LesionsDocument5 pages134 - Neurology Pathology) Pons LesionsTamaraNo ratings yet
- GmailDocument1 pageGmailjayakantharushanNo ratings yet
- Hendy 2009Document65 pagesHendy 2009msannodominiNo ratings yet
- 1st QUARTER GRADE 9 SCIENCE EXAMINATION 2021 2022Document8 pages1st QUARTER GRADE 9 SCIENCE EXAMINATION 2021 2022Elmar Delos SantosNo ratings yet
- Corticosteroids: Dr.R.Prameela, Assistant Professor of Pharmacology, GMC, SrikakulamDocument64 pagesCorticosteroids: Dr.R.Prameela, Assistant Professor of Pharmacology, GMC, SrikakulamRamadi PrameelaNo ratings yet
- Fat and Protein MetabolismDocument2 pagesFat and Protein MetabolismMark Zedrix MediarioNo ratings yet
- Grades 10 Science SQPDocument6 pagesGrades 10 Science SQPArnav SudhindraNo ratings yet
- MSC BiotechnologyDocument28 pagesMSC BiotechnologypmtsgmlNo ratings yet
- Lympathic System TransesDocument9 pagesLympathic System TransesMonica SabarreNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 10 Science Lab Manual - CO2 Is Released During RespirationDocument7 pagesCBSE Class 10 Science Lab Manual - CO2 Is Released During RespirationSumit BissuNo ratings yet
- Types of Synovial JointsDocument7 pagesTypes of Synovial Jointsaulia nurfadillahNo ratings yet
- Cell Transport Review KEYDocument2 pagesCell Transport Review KEYThanh GáiNo ratings yet
- 10 Life Processes Notes 1Document6 pages10 Life Processes Notes 1Govind Kumar SinghNo ratings yet
- Talbi AmarDocument95 pagesTalbi AmarOum MaNo ratings yet