SQL Commands X (1)
Uploaded by
topg51253SQL Commands X (1)
Uploaded by
topg51253Unit – 3 – Databases
My SQL Commands and Statements
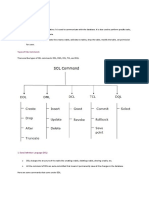
1. Show: Used to show databases and tables.
Syntax: show databases; or show tables;
2. Use: Used to get into a database.
Syntax: use <dbname>;
3. Desc: It describes a database, table. It shows all the properties of a table.
Syntax: desc <tablename>;
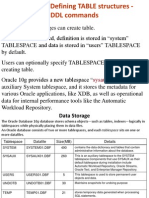
4. CREATE command: It is used to create a database or a table.
Syntax: create database <dbname>;
Or
Create table <tablename>
(
<colname> <datatype>(<size>) <constraints>,
<col2name><datatype>(<size>) <constraints>,
……
);
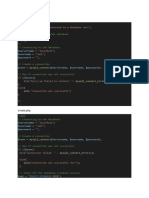
5. INSERT command: Used to enter data into the table.
Syntax: INSERT INTO <tablename>
(<Col1name>,<Col2name>,…….)
VALUES
(<value1>,<value2>,…….)
;
6. SELECT command: Used to query into the table and extract data.
Syntax: SELECT <Col1name>,<Col2name>,…… FROM <tablename>;
OR
SELECT * FROM <tablename>;
7. ALTER command: Used to alter the structure of the table.
List of Alter commands:
a. ALTER <tablename> ADD <colname> <datatype><(size)> <constraint>;
b. ALTER <tablename> DROP <colname>;
c. ALTER <tablename> MODIFY <colname> <datatype><(size)> <constraint>;
d. ALTER <tablename> RENAME <oldcolname> <newcolname>;
8. UPDATE command: It is used to update or change values in a table.
Syntax: UPDATE <tablename>
SET <colname> = <newdata>
WHERE <colname> = <olddata>;
9. DROP Command: It is used to drop or delete databases or tables.
Syntax: DROP DATABASE <databasename>;
OR
DROP TABLE <tablename>;
10. DELETE Command: It is used to delete data from a table.
Syntax: DELETE from <tablename>
WHERE <condition>;
My SQL Clauses:
11. FROM Clause: It is used to retrieve values from the specified table
Eg: SELECT * FROM <tablename>;
12. WHERE Clause: It is used to specify a condition to the query
Eg: SELECT * from <tablename> WHERE <condition>;
13. DISTINCT Clause: It is used to omit repeated values in the query result.
Eg. SELECT DISTINCT <columnname> FROM <tablename>;
14. BETWEEN Clause: It is used to specify the range from which values are to be queried.
Eg: SELECT * FROM <tablename>
WHERE <condition> BETWEEN <value1> AND <value2>;
15. LIKE Clause: It is used to search for a particular character or word and then run the query.
Eg: SELECT * FROM <tablename> WHERE <condition> LIKE ‘A%’;
(LIKE Clause has 3 types of searches.
1. “A%”: Means it will start from A
2. “%A”: Means it will end at A
3. “%A%”: Means the word or value contains the letter A.)
16. LIMIT Clause: It is used to limit the total number of rows.
Eg: SELECT * FROM <tablename> LIMIT 10; (It will show only 10 rows)
17. IN Clause: It is used to specify a condition in a list of values.
Eg: SELECT * FROM <tablename> WHERE <condition> IN (‘value1’, ‘value2’, ‘value3’);
18. GROUP BY clause: It is used to group the result rows into specific groups as specified by a column.
Eg: SELECT * FROM <tablename> GROUP BY <columnname>;
19. HAVING clause: It is used in conjunction with GROUP BY and restricts the grouped results by a
condition.
Eg: SELECT * FROM <tablename> GROUP BY <colname> HAVING <condition>;
20. ORDER BY clause: It is used to determine the order of appearance of rows after a query is
executed. ORDER BY can order by Ascending Order (ASC) of a specific column, Descending order
(DESC) of a specific column or by the values of a specific column.
Eg: SELECT * FROM <tablename> ORDER BY <columnname> ASC / DESC;
You might also like
- Web Application Development 1 - Final Quiz 1No ratings yetWeb Application Development 1 - Final Quiz 14 pages
- SQL Data Manipulation: Prepared By: Dr. Vipul VekariyaNo ratings yetSQL Data Manipulation: Prepared By: Dr. Vipul Vekariya49 pages
- Chapter-6 SQL Concepts: Data Manipulation LanguageNo ratings yetChapter-6 SQL Concepts: Data Manipulation Language3 pages
- EX - NO:1a Data Definition Languages (DDL) Commands of Base Tables and Views100% (1)EX - NO:1a Data Definition Languages (DDL) Commands of Base Tables and Views44 pages
- Basics of SQL Queries: Dbms Lab (Cs593)No ratings yetBasics of SQL Queries: Dbms Lab (Cs593)20 pages
- Ex - No-1 Data Definition, Table Creation, ConstraintsNo ratings yetEx - No-1 Data Definition, Table Creation, Constraints14 pages
- Introduction of Structured Query Language: SQL Practical FileNo ratings yetIntroduction of Structured Query Language: SQL Practical File18 pages
- B: O: D: / M: A: + S: - : Precedence: BODMASNo ratings yetB: O: D: / M: A: + S: - : Precedence: BODMAS17 pages
- Structured Query Language Prepared By: Reema Agrawal Asst Professor MeriNo ratings yetStructured Query Language Prepared By: Reema Agrawal Asst Professor Meri22 pages
- SQL: Just The Basics: Thursday, February 05, 2009No ratings yetSQL: Just The Basics: Thursday, February 05, 200910 pages
- Introduction To SQL: P212 Information Management100% (1)Introduction To SQL: P212 Information Management30 pages
- DBMS - Paper Solution - CSC403 - R19 - Sem IVNo ratings yetDBMS - Paper Solution - CSC403 - R19 - Sem IV16 pages
- Postgresql Internals Through Pictures: Ruce OmjianNo ratings yetPostgresql Internals Through Pictures: Ruce Omjian72 pages
- Hexagon GSP GeoMedia Professional Basic Training AgendaNo ratings yetHexagon GSP GeoMedia Professional Basic Training Agenda4 pages
- Transaction Processing Concepts and TheoryNo ratings yetTransaction Processing Concepts and Theory56 pages
- Advanced Databases Second Semester: Dr. Jihan A. RasoolNo ratings yetAdvanced Databases Second Semester: Dr. Jihan A. Rasool18 pages
- Writing A Search Strategy For A Literature Review100% (2)Writing A Search Strategy For A Literature Review5 pages
- SQL Worksheet-1 (DDL - Database Related Commands)No ratings yetSQL Worksheet-1 (DDL - Database Related Commands)33 pages
- 2023 12 01 11 57 38 IT Officer - 6 Level - 2080No ratings yet2023 12 01 11 57 38 IT Officer - 6 Level - 20804 pages