0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 viewsHW-1
HW-1
Uploaded by
adityab230761ceCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
HW-1
HW-1
Uploaded by
adityab230761ce0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views3 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views3 pagesHW-1
HW-1
Uploaded by
adityab230761ceCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 3
Mechanics of Solids (CE1012E)
(Winter 2023-24)
HW-1
Topic: Equilibrium of deformable bodies, Stress-Strain and Material Properties
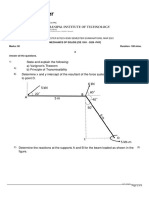
1. Determine the resultant internal normal and shear
force in the member at (a) section a-a and (b) section
b-b, each of which passes through point A. The 500
N load is applied along the centroidal axis of the
member.
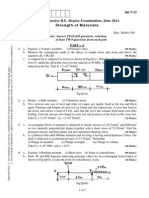
2. Determine the resultant internal loadings acting on
the cross section through point D of member AB.
3. The 800 N load is being hoisted at a constant
speed using the motor M, which has a weight of
90 N. Determine the resultant internal loadings
acting on the cross section through point B in the
beam. The beam has a weight of 40 N/m and is
fixed to the wall at A. (Ans: 0.4 kN, 0.84 kN,
0.728 kNm)
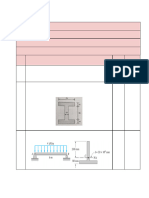
4. The main beam AB supports the load on the wing
of the airplane. The loads consist of wheel
reaction of 175000 N at C, the 6000 N weight of
the fuel in the tank of the wing, having a center
of gravity at D, and the 2000 N weight of the
wing, having a center of gravity at E. If it is fixed
to the fuselage at A, determine the resultant
internal loadings on the beam at this point.
Assume that the wing does not transfer any of the
loads to the fuselage; except through the beam.
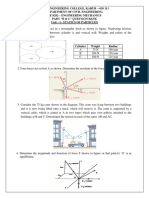
5. Determine the largest load P that can be applied to the frame
without causing either the average normal stress or average shear
stress at section a-a to exceed 150 MPa and 60 MPa, respectively.
Member CB has a square cross section of 25 mm on each side. (Ans:
62.5 kN)
6. The wooden specimen is subjected to the pull of 10 KN in a tension
testing machine. If the allowable normal stress for the wood is 12
MPa and the allowable shear stress is 1.2 MPa, determine the
required dimensions b and t so that the specimen reaches these
stresses simultaneously. The specimen has a width of 25 mm. (Ans:
167 mm and 33.3 mm)
7. The guy wire AB of a building frame is originally
unstretched. Due to an earthquake, the two columns of the
frame tilt 2 degrees. Determine the approximate normal
strain in the wire when the frame is in this position. Assume
the columns are rigid and rotate about their lower supports.
(Ans: 16.8 milli m/m)
8. The corners B and D of the square plate are given the
displacement indicated. Determine the shear strains at A
and B. (Ans: 0.206 rad and -0.206 rad)
9. The acrylic plastic rod is 200 mm long and 15 mm in
diameter. If an axial load of 300 N is applied to it,
determine the change in its length and the change in its
diameter. 𝐸𝑃 = 2.70 𝐺𝑃𝑎, 𝜈𝑃 = 0.4. (Ans: 0.126 mm and
-0.00377 mm)
10. The elastic portion of the stress-strain diagram for a steel
alloy is shown in the figure. The specimen from which it
was obtained had an original diameter of 13 mm and a gauge
length of 50 mm. When the applied load on the specimen is
50 kN, the diameter is 12.99265mm. Determine the
Poisson’s ratio for the material. (Ans: 0.300)
You might also like
- Tutorial Sheets SOMDocument20 pagesTutorial Sheets SOMPriyanshu Sharma100% (1)
- Çalışma SorularıDocument161 pagesÇalışma SorularıSude FilizNo ratings yet
- Ce 603 Set DDocument12 pagesCe 603 Set DJade Paul D. BesanaNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 5Document7 pagesTutorial 5A SкNo ratings yet
- TUTORIAL 1 AMJ10404Document8 pagesTUTORIAL 1 AMJ10404Maisarah JafriNo ratings yet
- SOM AssignmentDocument1 pageSOM Assignmentrohit7abcdNo ratings yet
- 23MECH02I - Tutorial 1Document7 pages23MECH02I - Tutorial 1elwakilwkwNo ratings yet
- Solid Mechanics - DM23801Document41 pagesSolid Mechanics - DM23801Michael MeashoNo ratings yet
- DOC-20240911-WA0055.Document8 pagesDOC-20240911-WA0055.sahilchouhan103No ratings yet
- Assignment 1 FinalDocument6 pagesAssignment 1 FinalshishirNo ratings yet
- Solid MechanicsDocument25 pagesSolid MechanicstvkbhanuprakashNo ratings yet
- MoS Tutorial QuestionsDocument13 pagesMoS Tutorial QuestionsMarxim Rahula BharathiNo ratings yet
- ME 212 Tutorial 4Document2 pagesME 212 Tutorial 4Mihir Kumar MechNo ratings yet
- 212-Chpt 8Document5 pages212-Chpt 8zainabcomNo ratings yet
- Som - Am2200 Assignment - 2Document3 pagesSom - Am2200 Assignment - 2Sai naveenNo ratings yet
- Som FinalDocument3 pagesSom FinalRajaram ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Engineering MechanicsDocument8 pagesEngineering MechanicsNanna ShivuNo ratings yet
- Assignment 5 (Group) - 220110 - 003126Document7 pagesAssignment 5 (Group) - 220110 - 003126MOHAMMAD AELEEF BIN PATRICK A20ET0356No ratings yet
- Solid Mechanics 1: July-Nov 2019 Indian Institute of Technology Guwahati Tutorial-3Document2 pagesSolid Mechanics 1: July-Nov 2019 Indian Institute of Technology Guwahati Tutorial-3Kamini GoyalNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Tutorial QuestionsDocument4 pagesUnit 1 Tutorial QuestionsMarxim Rahula BharathiNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of MaterialDocument3 pagesMechanics of MaterialChhaya Sharma100% (1)
- More Practice ProblemsDocument3 pagesMore Practice Problemsjohnnnie0402No ratings yet
- Mechanics of Solids (CIE 1051)Document4 pagesMechanics of Solids (CIE 1051)aryansorout1612No ratings yet
- ME 201 Assignment R1Document7 pagesME 201 Assignment R1myandonlymeNo ratings yet
- SOM Assignments-3,5Document5 pagesSOM Assignments-3,5ASHISH SINGH SENGARNo ratings yet
- Draw The SFD BMDDocument12 pagesDraw The SFD BMDAshok PradhanNo ratings yet
- Previous Year Question Paper With AnswersDocument108 pagesPrevious Year Question Paper With AnswersTejasPatilNo ratings yet
- ME 201 Assignment 1R2Document10 pagesME 201 Assignment 1R2synuser12No ratings yet
- Question Paper Code:: (10×2 20 Marks)Document3 pagesQuestion Paper Code:: (10×2 20 Marks)annamalai_s873323No ratings yet
- Problem Sets No.4Document1 pageProblem Sets No.4Glenn PabionaNo ratings yet
- Se130a HW03Document3 pagesSe130a HW03Lilia HynaiNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Chapter 1Document3 pagesTutorial Chapter 1ACC SHNo ratings yet
- Mechanical PapersDocument23 pagesMechanical PapersSachin AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Tutorial No. 4-Axial Load & Temp StressesDocument4 pagesTutorial No. 4-Axial Load & Temp Stressesgodsake.mtengaNo ratings yet
- B.Tech Assgn-1Document6 pagesB.Tech Assgn-1K Pushpendu PrashantNo ratings yet
- At Least TWO Questions From Each Part.: (06 Marks)Document2 pagesAt Least TWO Questions From Each Part.: (06 Marks)nvnrevNo ratings yet
- Strength of Materials: at Least TWO Questions From Each PartDocument2 pagesStrength of Materials: at Least TWO Questions From Each PartnvnrevNo ratings yet
- SE - 2019 - Solid MechanicsDocument12 pagesSE - 2019 - Solid MechanicsMANDAR KATOLKARNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document5 pagesChapter 1Fizz MartinNo ratings yet
- Score 1265 HPS 1716 X 70 %: Final AnswerDocument5 pagesScore 1265 HPS 1716 X 70 %: Final AnswerChristian M. MortelNo ratings yet
- Practise Problems Set01Document7 pagesPractise Problems Set01rohit kumarNo ratings yet
- Problem statements-MODSDocument36 pagesProblem statements-MODSrz12138No ratings yet
- Mechanics of Solids Feb Mar 2022Document3 pagesMechanics of Solids Feb Mar 2022SabareeshNo ratings yet
- Gujarat Technological University: InstructionsDocument3 pagesGujarat Technological University: InstructionsBhavesh PipaliyaNo ratings yet
- Question BankDocument9 pagesQuestion Bankpragash100% (1)
- Unit 1 Tutorial Questions With AnsDocument21 pagesUnit 1 Tutorial Questions With AnsMarxim Rahula BharathiNo ratings yet
- Theory of Structures PDFDocument4 pagesTheory of Structures PDFfrancis dimakilingNo ratings yet
- Refresher Psad Preboard Exam 2Document14 pagesRefresher Psad Preboard Exam 2Steven Valerio100% (1)
- AMMDocument3 pagesAMMRajesh Kumar PNo ratings yet
- Es 13 THR: Problem Set Part I. Stresses and Strains (Submission Is On February 5, 2018 Before 5 PM)Document3 pagesEs 13 THR: Problem Set Part I. Stresses and Strains (Submission Is On February 5, 2018 Before 5 PM)akosikapitansinoNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 1 - Introduction - Concept of Stress - Class ExamplesDocument10 pagesChapter - 1 - Introduction - Concept of Stress - Class ExamplesCandice MdakaNo ratings yet
- Sheet 1Document3 pagesSheet 1محمد معوضNo ratings yet
- Design Preboard Exam NOV 2021Document17 pagesDesign Preboard Exam NOV 2021Glaiza Marie100% (1)
- ME 332 Tutorial QuestionsDocument5 pagesME 332 Tutorial Questionsohagwasi davidNo ratings yet
- Strength of Materials - Task 1. Chapter 4-IiDocument4 pagesStrength of Materials - Task 1. Chapter 4-IiMilton CobaNo ratings yet
- CHE2167 Tutorial (Week 2) : Stress TransformationDocument2 pagesCHE2167 Tutorial (Week 2) : Stress TransformationBlue JunNo ratings yet
- Strength of Materials: at Least TWO Questions From Each PartDocument2 pagesStrength of Materials: at Least TWO Questions From Each PartnvnrevNo ratings yet
- O level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2From EverandO level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Class 10th Chemistry Paper CompleteDocument3 pagesClass 10th Chemistry Paper CompleteShaman AliNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Vibration Analysis Applications PDFDocument3 pagesChapter 2 - Vibration Analysis Applications PDFpanxo90007No ratings yet
- Chapter Nineteen Base Plate: 19.1 Base Plates For Axially Loaded ColumnsDocument84 pagesChapter Nineteen Base Plate: 19.1 Base Plates For Axially Loaded ColumnsCarl LacanilaoNo ratings yet
- York Recovery ChillerDocument4 pagesYork Recovery ChillerBen MusimaneNo ratings yet
- 07 SunergyDocument2 pages07 SunergyTedyNo ratings yet
- Volumetric Properties of Pure FluidsDocument3 pagesVolumetric Properties of Pure Fluidscarl0% (1)
- Elasticity 04 Isotropic HyperelasticityDocument14 pagesElasticity 04 Isotropic Hyperelasticityxaaabbb_550464353100% (1)
- Design and Analysis of Gearless Transmission Through Elbow MechanismDocument7 pagesDesign and Analysis of Gearless Transmission Through Elbow MechanismAung Khin ZawNo ratings yet
- 2.acids and Bases Lecture 2Document8 pages2.acids and Bases Lecture 2Protusha RakshitNo ratings yet
- Structure and Deformation Mechanisms in UHMWPE-fibresDocument8 pagesStructure and Deformation Mechanisms in UHMWPE-fibresJust4545100% (1)
- Rocket Lab ReportDocument15 pagesRocket Lab Reportapi-235151902No ratings yet
- Industrial CatalystDocument26 pagesIndustrial CatalystAritra SenNo ratings yet
- CTLG 3ag008 1507e Split PDFDocument40 pagesCTLG 3ag008 1507e Split PDFAditya VashishtNo ratings yet
- Pemeliharaan BOILER CFBDocument62 pagesPemeliharaan BOILER CFBMinanda ArfiansyahNo ratings yet
- Esab Stainless Steel ElectrodeDocument1 pageEsab Stainless Steel Electrodeanupmenon menonNo ratings yet
- Quiz 1 SolutionDocument21 pagesQuiz 1 SolutionChong Ray JieNo ratings yet
- Ordinary Shear WallDocument1 pageOrdinary Shear WallArwen CerenoNo ratings yet
- OceanographyDocument16 pagesOceanographyA S Verma100% (1)
- Spectroscopic Studies: Barc Highlights Barc Highlights Barc Highlights Barc Highlights Barc HighlightsDocument8 pagesSpectroscopic Studies: Barc Highlights Barc Highlights Barc Highlights Barc Highlights Barc HighlightsThuan PhanNo ratings yet
- Spacecraft Dynamics Homework 1Document6 pagesSpacecraft Dynamics Homework 1TrevorNo ratings yet
- Energy Conversion and Management: G. Raveesh, R. Goyal, S.K. TyagiDocument19 pagesEnergy Conversion and Management: G. Raveesh, R. Goyal, S.K. TyagiEng MohammedNo ratings yet
- Archi Board IRR Rule VIII - Light and VentilationDocument7 pagesArchi Board IRR Rule VIII - Light and VentilationCh-47JDZNo ratings yet
- Awadallah-F2019 Article ONTheNaNogate-opeNiNgPressuresDocument15 pagesAwadallah-F2019 Article ONTheNaNogate-opeNiNgPressuresbrianNo ratings yet
- Equipo BardDocument12 pagesEquipo BardanahijanethNo ratings yet
- 1 irrigationDocument1 page1 irrigationer.rizwanbashirNo ratings yet
- Al-Hassan y Norziah 2012Document10 pagesAl-Hassan y Norziah 2012AlexRiveraNo ratings yet
- Jurnal Analisa Kegagalan Pada Rangka TrukDocument13 pagesJurnal Analisa Kegagalan Pada Rangka TrukBaskara Surya WidagdoNo ratings yet
- Colorimetric Estimation of KMnO4Document2 pagesColorimetric Estimation of KMnO4bshabreenshaikNo ratings yet
- Vc07 Vc08 Axitub Solid 2 355m 45 8 - UkDocument2 pagesVc07 Vc08 Axitub Solid 2 355m 45 8 - UkConstantin294No ratings yet