0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1 viewsPHYLUM Porifera
PHYLUM Porifera
Uploaded by
nirajbaniya757Phylum Porifera, commonly known as sponges, are the first multicellular animals characterized by their porous bodies and aquatic habitats. They exhibit various body forms and canal systems, with three main classes based on the chemical nature of their endoskeleton: Calcarea, Hexactinellida, and Demospongiae. Sponges are hermaphroditic, capable of asexual reproduction, and possess significant regenerative abilities.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
PHYLUM Porifera
PHYLUM Porifera
Uploaded by
nirajbaniya7570 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1 views13 pagesPhylum Porifera, commonly known as sponges, are the first multicellular animals characterized by their porous bodies and aquatic habitats. They exhibit various body forms and canal systems, with three main classes based on the chemical nature of their endoskeleton: Calcarea, Hexactinellida, and Demospongiae. Sponges are hermaphroditic, capable of asexual reproduction, and possess significant regenerative abilities.
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Phylum Porifera, commonly known as sponges, are the first multicellular animals characterized by their porous bodies and aquatic habitats. They exhibit various body forms and canal systems, with three main classes based on the chemical nature of their endoskeleton: Calcarea, Hexactinellida, and Demospongiae. Sponges are hermaphroditic, capable of asexual reproduction, and possess significant regenerative abilities.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1 views13 pagesPHYLUM Porifera
PHYLUM Porifera
Uploaded by
nirajbaniya757Phylum Porifera, commonly known as sponges, are the first multicellular animals characterized by their porous bodies and aquatic habitats. They exhibit various body forms and canal systems, with three main classes based on the chemical nature of their endoskeleton: Calcarea, Hexactinellida, and Demospongiae. Sponges are hermaphroditic, capable of asexual reproduction, and possess significant regenerative abilities.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 13
PHYLUM: PORIFERA
• Derivation of name: (Gr. porus=pore; ferre=to
bear)
• Common name: Sponges
• Parazoology: Study of sponges
• Robert E. Grant coined the term Porifera
• Sponges are called ‘Republic of cells’.
• Sponges are 1st multicellular animals.
General Characters
• Habitat: They are all aquatic, mostly marine and
fresh water (e.g. Spongilla).
• They are sessile, sedentary and may be solitary or
colonial. Larvae are free living.
• Pores: Body is perforated by two types of pores;
ostia and osculum.
• Ostia are smaller and numerous used for entry of
water also called inhalant pores.
• Oscula are larger and few used for exit of water
also called exhalent pores.
• Body organization: First metazoans with cellular
grade of organization and cell aggregate body
plan.
• Body forms: Body is elongated, cylindrical, vae
like, branching and irregular.
• Symmetry: Mostly asymmetrical and few are
radially symmetrical e.g. Leucosolenia
• Germ layers: Diploblastic animal. The body is
derived from outer ectoderm (pinacoderm) and
inner endoderm (chaonaderm).
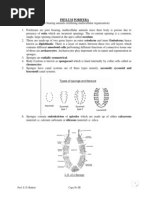
• Coelom: Acoelomate
• Body wall: It consists of three layers;
a) Pinacoderm: Outer layer of pinacocytes and
porocytes
b) Choanoderm: Inner layer of highly specialized
flagellated choanocytes or collar cells
c) Mesenchyme: Middle cellular ge;atinous matrix with
amoebocytes, collagen fibre and spicules.
• Body cavity: The body cavity is called spongocoel or
paragatric cavity lined by choanocytes.
• Water canal system: It is special type of canal system
formed by pores and canals used for ingestion,
respiration, excretion and egestion. It is also called
aquiferous system and is life line for sponge.
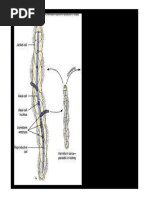
• Canal system may be
a) Ascon type: Simplest and primitive type. Flow or
water; water-ostia- spongocoel-osculum-out. E.g.
Leucosolenia
b) Sycon type: It is more complex type. Flow of water;
water-ostia-incurrent canal-prosopyle-radialcanal-
apopyle-spongocole- osculum-out e.g. Sycon
c) Leucon type: It formed by folding of body wall. Flow
of water; water-ostia-incurrent canal- prosopyle-
radial canal-apopyle-excurrentn canal-spongocoel-
osculum-out e.g. Spongilla
d) Rhagon type: It is found during larval stage and is
changed into leucon type in adult.
• Endoskeleton: Sponges bear three types of
endoskeleton (spicules).
a) Calcerous: Made up of calcium carbonate,
strongest and hardest spicule.
b) Siliceous: Made up of silica
c) Spongin fibres: Protenious fibres, softest
spicules.
• Nutrition: Holozoic and intracellular digestion.
• Respiration and excretion: Occurs through
general body surface. Ammonia chief excretory
waste.
• Reproduction: They are hermaphrodite. Asexual
reproduction by regeneration, budding and
gemmule ( internal bud) formation. Archaeocytes
form gemmule in fresh water sponge like
Spongilla.
• Development: It is indirect with free swimming
ciliated larval forms; amphiblastula (hollow larva)
and parenchymula (solid larva).
• Regeneration: sponges have great power of
regeneration that was observed by H.W. Wilson.
• Archaeocyte are totipotent cells of sponges
responsible for regeneration.
CLASSIFICATION
Phylum Porifera is divided into three classes on the basis
of chemical nature of endoskeleton.
a) Class: Calcarea
• Presence of calcareous spicule.
• Dull coloured and exclusively marine.
• Inhabits shallow water.
• Canal system ascon or sycon.
• Choanocytes are large.
• Body is cylindrical or vase shaped.
• Examples; Sycon (crown sponge), Leucosolenia
(smallest sponge), Grantia
b) Class: Hexactinellida
• Exclusively marine.
• Presence of siliceous spicules.
• Spicules are tiaxon with six rays.
• Canal system leucon .
• Choanocytes are small.
• Body is cup or funnel shaped.
• Examples; Euplectella (venus flower basket),
Hyalonema (glass rope sponge), Pheronema
(bowl sponge)
c) Class: Demospongiae
• Marine as well as fresh water.
• Body is compact, massive and brightly coloured.
• Presence of siliceous spicules or spongin fibres or
both or none (Oscarella).
• Canal system leucon.
• Choanocytes are small.
• Examples; Cliona (boring sponge), Euspongia (bath
sponge), Spongilla (fresh water sponge).
You might also like
- V. Conducting The Review of Related LiteratureDocument26 pagesV. Conducting The Review of Related LiteraturegetteNo ratings yet
- Ratio R2 NP 1Document16 pagesRatio R2 NP 1Konstantin Konstantius100% (5)
- Cable Testing: On-Site TestDocument92 pagesCable Testing: On-Site Testasawinraja100% (4)
- Bio 102 TwoDocument42 pagesBio 102 TwoPraise GodsonNo ratings yet
- Porifera CharactersDocument5 pagesPorifera CharactersPriyashmita RoyNo ratings yet
- 4 PoriferaDocument11 pages4 PoriferadianoktaNo ratings yet
- Phylum Porifera - SpongesDocument11 pagesPhylum Porifera - SpongesArief Hidayat Handytalky GarutNo ratings yet
- Phylum PoriferaDocument8 pagesPhylum Porifera21400744No ratings yet
- PoriferaDocument14 pagesPoriferaNazwa AuliaNo ratings yet
- Phylum Porifera: by Asani Delgahagoda & Sahan UmedaDocument20 pagesPhylum Porifera: by Asani Delgahagoda & Sahan UmedaabheethafNo ratings yet
- PoriferaDocument33 pagesPoriferaRushikesh pawar100% (1)
- Filum Porifera (Hewan Berpori)Document56 pagesFilum Porifera (Hewan Berpori)Silvi valNo ratings yet
- 2 - Academic Script200319070703030303Document6 pages2 - Academic Script200319070703030303Swetalina SarangiNo ratings yet
- Phylum Porifera: by Asani Delgahagoda & Saha N UmedaDocument20 pagesPhylum Porifera: by Asani Delgahagoda & Saha N UmedaabheethafNo ratings yet
- DS - Zoology - Phylum Porifera - Sem1Document11 pagesDS - Zoology - Phylum Porifera - Sem1Mohamed SelemanNo ratings yet
- Lecture 6 MulticellularOrganizationDocument28 pagesLecture 6 MulticellularOrganizationshahbaz zafarNo ratings yet
- PlasmodiumDocument15 pagesPlasmodiummohamedahmedghiat2003No ratings yet
- Phylum Porifera: by Asani Delgahagoda & Sahan UmedaDocument15 pagesPhylum Porifera: by Asani Delgahagoda & Sahan UmedaabheethafNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - PoriferaDocument23 pagesChapter 2 - PoriferaHeilene Ethel AngcayaNo ratings yet
- Clss and GCDocument39 pagesClss and GCsanskritisingh4321No ratings yet
- PoriferansDocument12 pagesPoriferanssammysmiles088No ratings yet
- Exercise 8 Syste LabDocument7 pagesExercise 8 Syste LabP B A TNo ratings yet
- Phylum Porifera Cnidaria Ctenphora 2Document42 pagesPhylum Porifera Cnidaria Ctenphora 2joannaigieborNo ratings yet
- Phylum PoriferaDocument7 pagesPhylum PoriferaLaraib Fatima Al HussainiNo ratings yet
- Invertebrate Gallery of Indian MuseumDocument58 pagesInvertebrate Gallery of Indian MuseumAkash NaskarNo ratings yet
- Exercise 8 Syste LabDocument3 pagesExercise 8 Syste LabPee BeeNo ratings yet
- _mesozoa_and_parazoa_2010 (2)Document26 pages_mesozoa_and_parazoa_2010 (2)drdz181016No ratings yet
- HRCCZoo TS Int To ParaZoaGenCharacteristis 20221220Document45 pagesHRCCZoo TS Int To ParaZoaGenCharacteristis 20221220D4R7H W4D3RNo ratings yet
- Kingdom Animalia (Until Molluscs PDFDocument15 pagesKingdom Animalia (Until Molluscs PDFthetrashwilldoNo ratings yet
- PoriferaDocument22 pagesPoriferaSamuel TosinNo ratings yet
- PoriferaDocument32 pagesPoriferasyedmehrienzia333No ratings yet
- Plant and Animal KingdomDocument9 pagesPlant and Animal KingdomAsim Iftikhar100% (1)
- Larva.: General Characteristics of PoriferaDocument8 pagesLarva.: General Characteristics of PoriferaJether Marc Palmerola GardoseNo ratings yet
- 55 16saczo1 2020121910192848Document30 pages55 16saczo1 2020121910192848Dandy H HerkoNo ratings yet
- Ch-4 Animal Kingdom-NotesDocument7 pagesCh-4 Animal Kingdom-Notes10080No ratings yet
- Phylum Porifera (Sponges) : Dr. Khalid M. SalihDocument25 pagesPhylum Porifera (Sponges) : Dr. Khalid M. SalihMohamed SelemanNo ratings yet
- Phylum EchinodermataDocument88 pagesPhylum EchinodermataIkki PhoenixNo ratings yet
- CH 26 Phylum PoriferaDocument51 pagesCH 26 Phylum Poriferaapi-244168124No ratings yet
- Phylum - Porifera-2308Document45 pagesPhylum - Porifera-2308shaikhaman0674No ratings yet
- Phylum Porifera (Sea Sponges) BIO 102 (02)Document7 pagesPhylum Porifera (Sea Sponges) BIO 102 (02)Amina bello KokoNo ratings yet
- Animals 2: Mollusc A, Ec Hi No Derma Ta, A Rthrop OdaDocument8 pagesAnimals 2: Mollusc A, Ec Hi No Derma Ta, A Rthrop OdaKaylaniNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9Document68 pagesChapter 9contactrafiakhuramNo ratings yet
- CANAL SYSTEM IN SPONGES BY AASIYADocument10 pagesCANAL SYSTEM IN SPONGES BY AASIYAfadeenk9No ratings yet
- CoelenterataDocument10 pagesCoelenteratarudra nayakNo ratings yet
- The Lophophorate Phyla: BryozoaDocument20 pagesThe Lophophorate Phyla: BryozoaEthylNo ratings yet
- Lec 6. PoriferaDocument32 pagesLec 6. PoriferaSikandar JehanNo ratings yet
- Phylum Porifera ClassificationDocument3 pagesPhylum Porifera ClassificationSudesh RathodNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 - PoriferaDocument25 pagesChapter 7 - Poriferaprettymarie floresNo ratings yet
- porifraDocument2 pagesporifraMaruee sahitoNo ratings yet
- 2. PoriferaDocument6 pages2. PoriferasreesivambigaatexNo ratings yet
- Phylum ProtozoaDocument123 pagesPhylum Protozoaยุทธพงษ์ สานต์ศิริNo ratings yet
- Phylum PoriferaDocument5 pagesPhylum Poriferastudent10100No ratings yet
- Diversity of Marine Sponges: Mandapam Regional Centre, ICAR Central Marine Fisheries Research InstituteDocument7 pagesDiversity of Marine Sponges: Mandapam Regional Centre, ICAR Central Marine Fisheries Research InstituteMohamed SelemanNo ratings yet
- Phylum PoriferaDocument13 pagesPhylum PoriferaKennet CruzNo ratings yet
- Phylum PoriferaDocument13 pagesPhylum Poriferapajarillo2433166No ratings yet
- The Three Grades of Metazoan Animals: Kingdom: AnimaliaDocument52 pagesThe Three Grades of Metazoan Animals: Kingdom: AnimaliaTesfaye SimeNo ratings yet
- PHYLUM PORIFERA-WPS OfficeDocument3 pagesPHYLUM PORIFERA-WPS OfficekowsikakaruppasamyNo ratings yet
- BSc Zoology Part I PoriferaDocument6 pagesBSc Zoology Part I Poriferasubghatkhan712No ratings yet
- Chapter6-Phylum Porifera NotesDocument4 pagesChapter6-Phylum Porifera Notesapi-195601294100% (1)
- PoriferaDocument25 pagesPoriferaAmelia MeiriskaNo ratings yet
- MolluscaDocument57 pagesMolluscaRisky Aprilian G100% (1)
- Unit 6 Time To Celebrate Network1 EsoDocument2 pagesUnit 6 Time To Celebrate Network1 EsoFiona TalboomNo ratings yet
- The Importance of Social Studies Education - in Bullet Note FormDocument5 pagesThe Importance of Social Studies Education - in Bullet Note FormMrs_Lovetts_Meat_PiesNo ratings yet
- Declaration of The Truths Relating To Some of The Most Common Errors in The Life of The Church of Our TimeDocument8 pagesDeclaration of The Truths Relating To Some of The Most Common Errors in The Life of The Church of Our TimeNational Catholic ReporterNo ratings yet
- BNS-41 Assignments July 2020Document5 pagesBNS-41 Assignments July 2020Harish Hn HnNo ratings yet
- Interview With Norwegian Eco-Philosopher Arne Naess: WWW - Rerunproducties.nlDocument54 pagesInterview With Norwegian Eco-Philosopher Arne Naess: WWW - Rerunproducties.nlJan Van BoeckelNo ratings yet
- Ariana Grande - Santa Tell Me ChordsDocument3 pagesAriana Grande - Santa Tell Me ChordsJuditCasasPerisNo ratings yet
- Class 9 Science Motion WORKSHEETDocument13 pagesClass 9 Science Motion WORKSHEETEkanshNo ratings yet
- "Los Hombres Son Como Peces" Men Like A FishDocument208 pages"Los Hombres Son Como Peces" Men Like A FishLeito QuintanaNo ratings yet
- Application of Derivatives Class 12 Maths MCQs PDFDocument14 pagesApplication of Derivatives Class 12 Maths MCQs PDFManthanNo ratings yet
- Notes of Chapter 9 The Making of National Movement Study RankerDocument3 pagesNotes of Chapter 9 The Making of National Movement Study Rankersandeepkumuni805No ratings yet
- June 12 in PerspectiveDocument104 pagesJune 12 in Perspectivefemi obayoriNo ratings yet
- Response To Mzati NkolokosaDocument7 pagesResponse To Mzati NkolokosaMalawi2014No ratings yet
- Elementi Vedic MatematikeDocument323 pagesElementi Vedic MatematikeDraganNo ratings yet
- Bachelor of Mass Media Xavier CollegeDocument7 pagesBachelor of Mass Media Xavier CollegearundhangNo ratings yet
- 195 People V TamayoDocument2 pages195 People V TamayoKarenliambrycejego RagragioNo ratings yet
- Dashcode MacDocument30 pagesDashcode MacAnonymous VbzFdYzNo ratings yet
- CS508 Midterm Exam 2017 SolutionDocument3 pagesCS508 Midterm Exam 2017 SolutionMohamed Abdel-AzizNo ratings yet
- Suggested Answers Self-Review Questions (Chapters 1 and 2 Hilton and Platt)Document5 pagesSuggested Answers Self-Review Questions (Chapters 1 and 2 Hilton and Platt)kokomama231No ratings yet
- Research Presentation FinalDocument8 pagesResearch Presentation FinalJulius AlavarNo ratings yet
- RBCW Programme Schedule June 2019Document5 pagesRBCW Programme Schedule June 2019bhargavNo ratings yet
- A Man Called Ove 2015 480p BluRay x264 AAC - (Mkvking Com)Document44 pagesA Man Called Ove 2015 480p BluRay x264 AAC - (Mkvking Com)xoyat75592No ratings yet
- Banu UmmayaDocument29 pagesBanu UmmayaABDUL MOIZ HUSSAIN100% (1)
- Black Schloes FormulaDocument2 pagesBlack Schloes FormulaPhaniraj LenkalapallyNo ratings yet
- 博弈论讲义8 不完全信息动态博弈 PDFDocument46 pages博弈论讲义8 不完全信息动态博弈 PDFLucas PiroulusNo ratings yet
- Financial Analysis of Mozaffar Hossain Spinning Mills: Submitted byDocument12 pagesFinancial Analysis of Mozaffar Hossain Spinning Mills: Submitted byEhsanul AzimNo ratings yet
- TQM-I - 04 - Sampling Plans and Acceptance SamplingDocument54 pagesTQM-I - 04 - Sampling Plans and Acceptance SamplingAjith NB100% (1)
- Res Gestae: Submitted By: Saif Ali 4 Year (SF) Roll No. 43Document25 pagesRes Gestae: Submitted By: Saif Ali 4 Year (SF) Roll No. 43Saif AliNo ratings yet