Wireless Application Protocol
Uploaded by
BibinMathewWireless Application Protocol
Uploaded by
BibinMathewSEMINAR REPORT 2010
WIRELESS APPLICATION PROTOCOL
ABSTRACT
The primary means of communicating information of these days are voice and Internet. The unlimited accesses to Internet and sheer number of people connected to the Internet have made industry captain realize its potential. The industry now plans its marketing and communication strategies around the Internet. Today every banking to education, research to health-care is affected by it. E-mail is the way to communicate today. Practically who use the Internet uses E-mail. The wireless technologies and the Internet were growing separately. The wireless industry initially struggled within a number of issues like low bandwidth and low connection stability, to bring Internet to its users. They came together to form a common forum to tackle these issues. This forum is called the WAP.The wireless application protocol.
Dept.of COMPUTER SCIENCE
CAS, KDTY
SEMINAR REPORT 2010
WIRELESS APPLICATION PROTOCOL
CONTENTS
1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12.
INTRODUCTION THE WAP MODEL MOTIVATION FEATURES OF WAP ARCHITECTURE WAE APPLICATIONS THE PROBLEM AREAS FUTURE OUTLOOK OF WAP MARKET POTENTIAL CONCLUSION REFERENCES
3 6 10 11 12 15 19 20 22 23 24 25
Dept.of COMPUTER SCIENCE
CAS, KDTY
SEMINAR REPORT 2010
WIRELESS APPLICATION PROTOCOL
INTRODUCTION
The primary means of communicating information of these days are voice and Internet. The unlimited accesses to Internet and sheer number of people connected to the Internet have made industry captain realize its potential. The industry now plans its marketing and communication strategies around the Internet. Today every banking to education, research to health-care is affected by it. E-mail is the way to communicate today. Practically who use the Internet uses E-mail. The wireless technologies and the Internet were growing separately. The wireless industry initially struggled within a number of issues like low bandwidth and low connection stability, to bring Internet to its users. They came together to form a common forum to tackle these issues. This forum is called the WAP.The wireless application protocol. The Wireless Application Protocol is a standard developed by the WAP Forum, a group founded by Nokia, Ericsson, Phone.com (formerly Unwired Planet), and Motorola. The WAP Forums membership roster now includes computer industry heavyweights such as Microsoft, Oracle, IBM, and Intel along with several hundred other companies. According to the WAP Forum, the goals of WAP are to be:
Independent of wireless network standard. Open to all. Proposed to the appropriate standards bodies. Scalable across transport options. Scalable across device types. Extensible over time to new networks and transports.
Dept.of COMPUTER SCIENCE
CAS, KDTY
SEMINAR REPORT 2010
WIRELESS APPLICATION PROTOCOL
WAP defines a communications protocol as well as an application environment. In essence, it is a standardized technology for crossplatform, distributed computing. It sound similar to the World Wide Web. WAP is very similar to the combination of HTML and HTTP except that it adds in one very important feature: optimization for low-bandwidth, lowmemory, and low-display capability environments. These types of environments include PDAs, wireless phones, pagers, and virtually any other communications device. Wireless Application Protocol (WAP) is a result of continuous work to define an industry-wide specification for developing applications that operate over wireless communication networks. The scope for the WAP Forum is to define market is growing very quickly and reaching new customers and providing new services. To enable operators and manufacturers to meet the challenges in advanced services, differentiation, and fast/flexible service creation, WAP defines a set of protocols in transport, session and application layers.
WAP AS AN EXTENSION OF THE INTERNET MODEL
The WAP model closely resembles the Internet model of working. In Internet a WWW client requests a resource stored on a web server by identifying it using a unique URL, that is, a text string constituting an address to that resource. WAP client applications make requests very similar in concept to the URL concept in use on the Web.Standard communication protocols, like HTTP and Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) manage these requests and transfer of data between the two ends. The content that is transferred can either be static like html pages or dynamic like Active Server Pages (ASP), Common Gateway Interface (CGI), and Servlets.
Dept.of COMPUTER SCIENCE
CAS, KDTY
SEMINAR REPORT 2010
WIRELESS APPLICATION PROTOCOL
The following figure helps draw a parallel to the Internet protocols. You can see how WAP extends or reuses Internet protocols to achieve mobile Internet access.
The strength of WAP (some call it the problem with WAP) lies on the fact that it very closely resembles the Internet model. In order to accommodate wireless access to the information space offered by the WWW, WAP is based on well-known Internet technology that has been optimized to meet the constraints of a wireless environment. Corresponding to HTML, WAP specifies a markup language adapted to the constraints of low bandwidth available with the usual mobile data bearers and the limited display capabilities of mobile devices - the Wireless Markup Language (WML). WML offers a navigation model designed for devices with small displays and limited input facilities (no mouse and limited keyboard). WAP also provides a means for supporting more advanced tasks, comparable to those solved by using for example JavaScript in HTML.
Dept.of COMPUTER SCIENCE
CAS, KDTY
SEMINAR REPORT 2010
WIRELESS APPLICATION PROTOCOL
THE WAP MODEL
A WAP request is routed through a WAP gateway which acts as an intermediary between the bearer used by the client (GSM, CDMA, TDMA, etc.) and the computing network that the WAP gateway resides on (TCP/IP in most cases). The gateway then processes the request, retrieves contents or calls CGI scripts, Java servlets, or some other dynamic mechanism, then formats data for return to the client. This data is formatted as WML (Wireless Markup Language), a markup language based directly on XML. Once the WML has been prepared (known as a deck), the gateway then sends the completed request back (in binary form due to bandwidth restrictions) to the client for display and/or processing. The client retrieves the first card off of the deck and displays it on the monitor. The deck of cards metaphor is designed specifically to take advantage of small display areas on handheld devices. Instead of continually requesting and retrieving cards (the WAP equivalent of HTML pages), each client request results in the retrieval of a deck of one or more cards. The client device can employ logic via embedded WMLScript (the WAP equivalent of client-side JavaScript) for intelligently processing these cards and the resultant user inputs. To sum up, the client makes a request. This request is received by a WAP gateway that then processes the request and formulates a reply using WML. When ready, the WML is sent back to the client for display.
Dept.of COMPUTER SCIENCE
CAS, KDTY
SEMINAR REPORT 2010
WIRELESS APPLICATION PROTOCOL
As mentioned earlier, this is very similar in concept to the standard stateless HTTP transaction involving client Web browsers.
Three are three essential product components that you need to extend your host applications and data to WAP-enabled devices. These three components are: 1. WAP Microbrowser residing in the client handheld device 2. WAP Gateway typically on wireless ISPs network infrastructure 3. WAP Server - residing either on ISPs infrastructure or on enduser organizations infrastructure .
Dept.of COMPUTER SCIENCE
CAS, KDTY
SEMINAR REPORT 2010
WIRELESS APPLICATION PROTOCOL
1.WAP Microbrowser
A WAP micro-browser is a client software designed to overcome challenges of mobile handheld devices that enables wireless access to services such as Internet information in combination with a suitable network server.
2.WAP Gateway
The idea behind WAP specifications is to connect the mobile networks to the Internet.To connect these two mega-networks, the WAP Specification assumes there will be a WAP Gateway. At its simplest level, this is a stack converter, which will convert the WAP request into a Web request and the Web response into a WAP response. WAP Gateway is a piece of software that sits between the mobile device and the external network like the Internet. The gateway does the job of converting Internet content i.e. the WML pages into byte code (WMLC) to reduce the size and number of packets, which can be understood by a WAP device. Usually located on a server of a mobile operator it handles incoming requests from your WAP phone, takes care of the conversion required during WTLS/SSL sessions and handles incoming requests from your WAP phone.It decreases the response time to the handheld device by aggregating from different servers on the web, and catching frequently used information.
Dept.of COMPUTER SCIENCE
CAS, KDTY
SEMINAR REPORT 2010
WIRELESS APPLICATION PROTOCOL
A WAP Gateway typically includes the following functionality : Protocol Gateway: The protocol Gateway translates requests from the WAP protocol stack to the WWW protocol stack(HTTP and TCP/IP). Content Encoders And Decoders:The content encoders translate web content into compact encoded formats to reduce the size and number of packets travelling over the wireless data network. The infrastructure ensures that mobile terminal users can browse a variety of WAP content and applications regardless of the wireless network they use. Application authors are able to build content services and applications that are network and terminal independent, allowing their applications to reach the largest possible audience. Because of the WAP proxy design, content and applications are hosted on standard WWW servers and can be developed using proven Web technologies such as CGI Scripting. The WAP Gateway can also interface with subscriber databases and use information from the wireless network, such as
Dept.of COMPUTER SCIENCE
CAS, KDTY
SEMINAR REPORT 2010
10
WIRELESS APPLICATION PROTOCOL
location, to dynamically customize WML pages for a certain group of users.
3.WAP server
It is simply a combined web server and WAP gateway. WAP devices do not use SSL. Instead they use WTLS. Most existing web servers should be able to support WAP content as well. Some new MIME types need to be added to your web server to enable it support WAP content. MIME stands for Multipurpose Internet Mail Extension, and in the web context, MIME can be thought of as a piece of header information that comes down with every file sent from a web server to a browser.
Dept.of COMPUTER SCIENCE
CAS, KDTY
SEMINAR REPORT 2010
11
WIRELESS APPLICATION PROTOCOL
MOTIVATION
During the last couple of years, the Internet has grown at a tremendous pace and has proved to be an easy and efficient way for delivering services to millions of wireline users. Parallely, wireless voice communication has grown at an equally rapid pace and gained wide acceptance. shortcomings: 1. The Internet requires a wireline connectivity for accessing the services,posing a problem to those users who spend substantial amount of their time on the move. 2. Todays wireless network infrastructure does not have the flexibility required for rapid deployment of wireless data services like telephony services. The Internet and wireless industries realised that Wireless Internet can be a single solution that can effectively address the shortcomings of both these technologies. Wireless Internet not only enables accessing the services offered by Internet from mobile phones thereby overcoming the constraint imposed by the Internet, but also allows the network operators to host wireless data services on Internet platform. Early efforts at unifying the Internet and wireless technologies to launch wireless services were not very successful. Such attempts were made by independent wireless data carriers using proprietary technologies that were bound to fail due to a fragmented market and low economies of scale. The WAP Forum was founded by Ericsson, Motorola, Nokia and Unwired Planet (now Phone.com) to develop standards to make universal wireless Internet access a reality. The WAP specification was developed by WAP Forum to adapt the Internet technology to address issues specific to wireless environment. The inherent constraints of wireless network technology like limited bandwidth, high latency, However, both these technologies have certain
Dept.of COMPUTER SCIENCE
CAS, KDTY
SEMINAR REPORT 2010
12
WIRELESS APPLICATION PROTOCOL
unpredictable availability and less reliable connection stability are adequately addressed by the WAP specification. The WAP specification also deals with issues related to wireless devices like limited computational capability, small memory size, limited battery power, limited input mode and small display size.eb server to a browser.
Dept.of COMPUTER SCIENCE
CAS, KDTY
SEMINAR REPORT 2010
13
WIRELESS APPLICATION PROTOCOL
FEATURES OF WAP
Some of the key features of WAP are :
1. Interoperability: WAP is an open license-free standard, which ensures that WAP-compliant devices are interoperable. 2. Scalability: WAP applications scale across a variety of wireless transport options like GSM SMS, GSM USSD, IP, CDMA, etc., and also across a wide range of wireless terminals from hand sets to powerful PDAs. 3. Extensibility: WAP has been designed as a future-proof technology. It is extensible over time to new networks and transports thereby protecting the mobile network 4. Flexibility: WAP is a flexible solution that caters to the requirements of various types of applications by providing service options like connection mode and connection-less services, with or without end-toend security. 5. Reusability: WAP specification extends and adapts existing Internet standards such as HTTP, IP, Proxy technology, SSL, TLS, XML, HTML,etc., to wireless environment instead of defining a new set of standards.
Dept.of COMPUTER SCIENCE
CAS, KDTY
SEMINAR REPORT 2010
14
WIRELESS APPLICATION PROTOCOL
ARCHITECTURE
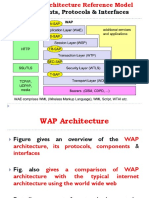
The WAP Protocol Stack is implemented via a layered approach (similar to the OSI network model). These layers consist (from top to bottom) of:
Wireless Application Environment (WAE) Wireless Session Protocol (WSP) Wireless Transaction Protocol (WTP) Wireless Transport Layer Security (WTLS) Wireless Datagram Protocol (WDP) Bearers (GSM, IS-136, CDMA, GPRS, CDPD, etc.) The WAP stack can be configured in four different ways to provide
four different types of services. Following are the four types of services offered by WAP : 1. Connectionless service: The WAP protocol stack used for this service consists of only WSP layer operating directly over WDP layer. 2. Connectionless service with security: This configuration is similar to connectionless service but provides security by having WTLS layer between WSP and WDP layers. 3. Connection oriented service: The configuration of protocol stack used for this service consists of WSP, WTP and WDP layers with ordering of the layers same as that shown in Figure WTP and WDP layers together provide a connection oriented transport service in this configuration.
Dept.of COMPUTER SCIENCE
CAS, KDTY
SEMINAR REPORT 2010
15
WIRELESS APPLICATION PROTOCOL
4.Connection oriented service with security: This configuration consists of all the layers of WAP stack.
Different protocol layers and application environment of WAP: 1. Wireless Datagram Protocol (WDP)
WDP provides the higher layers of the stack with a consistent interface to underlying bearer. WDP operates transparently over one of the available bearer services there by making the upper layers of the WAP stack independent of the bearer. Since the services offered by underlying bearers vary widely, WDP contains adaptation layers to map WDP functions to services offered by different bearers. The functionality of WDP when operating on IP bearer is exactly same as the Internet standard User Datagram Protocol (UDP). WDP provides a connectionless, unreliable datagram service. WDP supports underlying bearer service. WDP uses port numbers to address higher layer entities as in transport layer of the Internet protocol stack. WDP can be extended to support optional error reporting mechanism by adding Wireless Control Message Protocol (ICMP).
2. Wireless Transaction Layer (WTP)
WTP layer provides a lightweight transaction service, i.e., a request/response service, which can operate efficiently over a secure, or insecure datagram service. It provides three classes of service, namely, 1. unreliable push service
Dept.of COMPUTER SCIENCE
CAS, KDTY
SEMINAR REPORT 2010
16
WIRELESS APPLICATION PROTOCOL
2. reliable push service 3 . reliable transaction service The features of WTP are selective retransmissions, duplicate removal, segmentation/reassembly, port number addressing, user-touser reliability (through user-to-user acknowledgements) in addition to protocol acknowledgements, asynchronous transactions, optional out-ofband information, delayed acknowledgements and message concatenation to improve over-the-air efficiency. WTP is message oriented protocol, which makes it suitable for interactive browsing applications.
3. Wireless Session Protocol (WSP)
WSP layer provides mechanisms and semantics based on the Internet standard, Hyper Text Transfer Protocol (HTTP/1.1) along with additional functionalities such as: 1. protocol feature negotiation (capability negotiation) 2. compact encoding of data 3. session suspend/resume 4. long lived session states 5. asynchronous request
Dept.of COMPUTER SCIENCE
CAS, KDTY
SEMINAR REPORT 2010
17
WIRELESS APPLICATION PROTOCOL
Dept.of COMPUTER SCIENCE
CAS, KDTY
SEMINAR REPORT 2010
18
WIRELESS APPLICATION PROTOCOL
WIRELESS APPLICATION ENVIRONMENT (WAE)
WAE provides a network neutral and device independent
application environment framework, which enables a wide range of applications (user-agents) to be used on wireless terminals. WAE is consistent with the Internet/WWW programming model including authoring and publishing methods. WAE allows the MMI to be controlled by the vendor of the handset. WAE is designed to leverage on standard Web Servers (origin servers) to host content and services. The content is addressed using the Internet standard URLs and URIs. Following are the various components of WAE: 1. Wireless Markup Language (WML) 2. WMLScript 3. WAP Content Types 4.Wireless Telephony Application (WTA) environment
WML
It is a tag based markup language, which is derived from XML and is similar to the Internet standard HTML. WML addresses the constraints such as small displays, limited user-input capability, narrow-band network connections, limited processing power and limited memory resources in a wireless device. The key features of WML are navigation support, hyperlinks, soft-button support, screen management (displaying formatted text, images) and user data input (text, selection lists).
Dept.of COMPUTER SCIENCE
CAS, KDTY
SEMINAR REPORT 2010
19
WIRELESS APPLICATION PROTOCOL
The following gives the characteristics of WML: a) WML performs the same as HTML on the Internet. b) WML is also a tag-based language. c) WML is a case-sensitive language. d) WML organizes the document that is cards and decks. Cards specify any one or more units of user interface. Cards are grouped together into deck. Cards are same as HTML file and deck is same as HTML page. e) <WML> tag identifies a deck. </WML>. f) <Card> to create a card, </Card> to close the card. g) Card has two attributes ID and title. The ID attribute is used to identify card in a deck, and title attribute takes a text string to display as the title of the card. EX: <WML> <card id = card1 title= first card> <p> WELCOME TO CARD1 </p> </card> </WML> it will print on the screen of the WAP device. Similarly the various applications can be implemented through WML.
Dept.of COMPUTER SCIENCE
CAS, KDTY
SEMINAR REPORT 2010
20
WIRELESS APPLICATION PROTOCOL
WMLScript
WMLScript is a lightweight procedural scripting language. It is an extended subset of JavaScript TM scripting language. It enhances the presentation facilities offered by WML and supports advanced dynamic UI behavior by adding intelligence on the client side. WAP defines several content formats based on standard WWW content formats that facilitate interoperable data exchange. All WAP content is specified in one of the defined content formats. As in WWW content formats, a header contain-ing content type field allows the micro-browser to process the content based on its type. The two most important formats defined by WAP are encoded WML and WMLScript formats. The purpose of WMLScript is to provide client-side procedural logic. It is based on ECMAScript (which is based on Netscapes JavaScript language), however it has been modified in places to support low bandwidth communications and thin clients. The inclusion of a scripting language into the base standard was an absolute must. While many Web developers regularly choose not to use client-side JavaScript due to browser incompatibilities (or clients running older browsers), this logic must still be replaced by additional server-side scripts. This involves extra roundtrips between clients and servers which is something all wireless developers want to avoid. WMLScript allows code to be built into files transferred to mobile client so that many of these round-trips can be eliminated. According to the WMLScript specification, some capabilities supported by WMLScript that are not supported by WML are:
Check the validity of user input Access to facilities of the device. For example, on a phone, allow the programmer to make phone calls, send messages, add phone numbers to the address book, access the SIM card etc.
Dept.of COMPUTER SCIENCE
CAS, KDTY
SEMINAR REPORT 2010
21
WIRELESS APPLICATION PROTOCOL
Generate messages and dialogs locally thus reducing the need for expensive round-trip to show alerts, error messages, confirmations etc.
Allow extensions to the device software and configuring a device after it has been deployed.
WMLScript is a case-sensitive language that supports standard variable declarations, functions, and other common constructs such as if-then statements, and for/while loops. Among the standards more interesting features are the ability to use external compilation units (via the use url pragma), access control (via the access pragma), and a set of standard libraries defined by the specification (including the Lang, Float, String, URL, WMLBrowser, and Dialogs libaries). The WMLScript standard also defines a bytecode interpreter since WMLScript code is actually compiled into binary form (by the WAP gateway) before being sent to the client.
WTA
It provides extensions for telephony services like call and feature control mechanisms, voice mail, messaging, phone-book management, etc., to make them accessible to WAP content developers. WTA framework also allows real-time processing of events important to the end-user while browsing. WTA provides a library of telephony-related functions called Wireless Telephony Application Interface (WTAI) that can be invoked from WML/WMLScript. MLScript formats. WAE typically consists of two user-agents: a micro-browser and a telephony application. A micro-browser is similar to a web browser such
Dept.of COMPUTER SCIENCE
CAS, KDTY
SEMINAR REPORT 2010
22
WIRELESS APPLICATION PROTOCOL
as Netscape Navigator or Internet Explorer with additional optimizations required to run on a consumer handset. A micro-browser interprets WML/WMLScript content types. A telephony application is used for providing telephony services offered by WTA to end-user. WWW content (e.g., HTML), a filter is used to translate the WWW content to WAP content.
APPLICATIONS
Some of the interesting applications of WAP (already existing or being worked on) are:
Computer Sciences Corporation (CSC) and Nokia are working with a Finnish fashion retailer who plans to send clothing offers direct to mobile telephones using a combination of cursors, touch screen technology and WAP to allow would-be shoppers to hot-link to order-entry pages on the web.
In Finland, children already play new versions of competitive games such as "Battleships", via the cellular networks. In the music world, Virgin Mobile in the UK offers to download the latest pop hits to customers in a daily offering.
Scala has developed several WAP products for small to mediumsized companies which would allow, for example, a field sales force to access customer order information and stock availability details via a WAP handset.
A key growth area for the technology will be business-toworkforce, with companies using WAP applications to reach employees at any time. Scala is currently working on time-sheet applications and techniques for entering and filing expense claims via the mobile phone.
Dept.of COMPUTER SCIENCE
CAS, KDTY
SEMINAR REPORT 2010
23
WIRELESS APPLICATION PROTOCOL
Nokia says applications that will benefit from WAP include customer care and provisioning, message notification and call management, e-mail, mapping and location services, weather and traffic alerts, sports.
Dept.of COMPUTER SCIENCE
CAS, KDTY
SEMINAR REPORT 2010
24
WIRELESS APPLICATION PROTOCOL
THE PROBLEM AREAS
One of the problem, basically to do with infrastructure (and not WAP) is that as the mobile Internet access. A live example is I-mode services in Japan, where the mobile data access has seen a unprecedented rate of growth. So, unless the infrastructure is geared up to expect unexpected volumes, this can have significant impact on these data services since most of these systems are simply inadequate for big volumes. So there is a possibility of unsatisfactory performances observed by mobile data users. Another problem area is that the delay in the delivery of longpromised terminals and service launches are narrowing the window of opportunity for WAP, while the proposed developments in faster mobile networks and more sophisticated terminals come closer. Further developments in WAP are still required and in the meantime, other solutions will emerge. Also as with many other technologies what matters most and what guides the development of a technology is the emergence of killer applications. So, unless some killer applications hit the market, which influence the mood of the enduser, WAP just like other technologies has a difficult path ahead. Already due to lots of hype WAP proponents find them selves in a little tight position. So, this presents a big opportunity for the developer community to develop new and innovative applications that can realize the advantage of WAP. It is very, very early on in the ballgame and already vendor toolkits are offering proprietary tags that will only work with their microbrowser. Given the history of the computing industry and competition, in general, this was to be expected. However, further
Dept.of COMPUTER SCIENCE
CAS, KDTY
SEMINAR REPORT 2010
25
WIRELESS APPLICATION PROTOCOL
differentiation between vendor products and implementations may lead to a fragmented wireless Web. WAP also could be found lacking if compared to more powerful GUI platforms such as Java, for instance. For now, processor speeds, power requirements, and vendor support are all limiting factors to Java deployment but its not hard to imagine a day in the near future where Java and WAP exist side-by-side just as Java and HTML do today. In that circumstance, Java would hold a clear advantage over WAP due to the fact that a single technology could be used to build applications for the complete range of operating devices. Of course, on the flip side, the world is not all Java and there will always be a place for markup languages in lieu of full-blown object-oriented platforms.
Dept.of COMPUTER SCIENCE
CAS, KDTY
SEMINAR REPORT 2010
26
WIRELESS APPLICATION PROTOCOL
FUTURE OUTLOOK OF WAP
The point brought about by many analysts against WAP is that with the emergence of next generations networks (including GPRS), as the data capabilities of these networks evolve, it will make possible the delivery of full-motion video images and high-fidelity sound over mobile networks. Thus the technical significance of WAP (designed keeping in mind the low bandwidths available in the present mobile networks). On the other hand many believe that with the introduction of packetswitched data networks will kick-start the take-up of WAP services. Japan and South Korea are forging ahead, having already introduced packet data on their networks. Europe and other regions that adhere to the GSM standard are close on their heels, with many GPRS contracts now confirmed. What should be understood is that the limitations in mobile Internet access is not just the low bandwidths available. The very nature of mobile devices presents limitations like display etc. As I have already mentioned in the introduction, power consumption is a very critical issue and even if high speeds are available power considerations may limit the data speeds. Services like GPRS are bearer services. Internet access via WAP should infact become much more easier with WAP. Currently, WAP access needs a specific connection via an Internet service provider (ISP) in much the same way as a PC accesses. But the system will come into its own with the introduction of another enabling technology, general packet radio services (GPRS), a method of sending Internet information to mobile telephones at high speed. At present, services such as BT Cellnet's Genie deliver information at a speed of
Dept.of COMPUTER SCIENCE
CAS, KDTY
SEMINAR REPORT 2010
27
WIRELESS APPLICATION PROTOCOL
9,600 bits of information a second. With GPRS the speed will rise to 100,000.
Dept.of COMPUTER SCIENCE
CAS, KDTY
SEMINAR REPORT 2010
28
WIRELESS APPLICATION PROTOCOL
MARKET POTENTIAL
As WAP aims at bridging two of the most successful technologies of the communication revolution - Internet and Wireless, the success of WAP is assured. Market studies show that the share of global wireless communication revenues as a percentage of the total telecommunication revenues - is consistently on the rise (from a mere 5% in 1992 to around 20% in 2000). With telecommunication industry revenues touching the US $1000 billion mark and growing at a rate of 7%, the industry is all set to reach the US $1.5 trillion size by 2004. Close to a quarter of these revenues would be from the wireless domain - where WAP enabled product vendors, service providers and network operators would meet the advanced data needs of over 500 million subscribers. 04, there could be more than 700m mobile commerce users. 04, there could be more than 700m mobile commerce users.
Dept.of COMPUTER SCIENCE
CAS, KDTY
SEMINAR REPORT 2010
29
WIRELESS APPLICATION PROTOCOL
CONCLUSION
The primary focus of WAP technology is to create a global wireless internet by bringing services offered by internet to mobile phone users. Industry leaders in handset manufacturing representing over 90% of the world market and mobile network operators representing about 300 million subscribers are adopting this technology. WAP has been designed to benefit wireless subscribers, handset vendors, network operators and service providers. Subscribers get access to a wide range of services available on Internet from their mobile phones and other wireless interoperable open standard, whichis is handset vendor independent. Some critics and second-guessers have pondered the need for a technology. WAPs use of the deck of cards pattern and use of binary file distribution meshes well with the display size and bandwidth constraints of typical wireless devices. Scripting support gives us support for client-side user validation and interaction with the portable device again helping to eliminate round trips to remote servers. WAP is a young technology that is certain to mature as the wireless data industry as a whole matures; however, even as it exists today, it can be used as an extremely powerful tool in every software developers toolbox.
Dept.of COMPUTER SCIENCE
CAS, KDTY
SEMINAR REPORT 2010
30
WIRELESS APPLICATION PROTOCOL
REFERENCES
1) www.google.com 2) www.mobileinfo.com 3) www.wapforum.org 4) www.wiprotechnologies.com
Dept.of COMPUTER SCIENCE
CAS, KDTY
You might also like
- Network Performance Optimization: A Case Study of Enterprise Network Simulated in OPNETNo ratings yetNetwork Performance Optimization: A Case Study of Enterprise Network Simulated in OPNET7 pages
- Networking Technologies and Its Design and Implementation: A Summer Training Synopsis Based ON80% (5)Networking Technologies and Its Design and Implementation: A Summer Training Synopsis Based ON46 pages
- Unit 1 Introduction To WML and WAP: StructureNo ratings yetUnit 1 Introduction To WML and WAP: Structure17 pages
- Building the Internet of Things with IPv6 and MIPv6: The Evolving World of M2M CommunicationsFrom EverandBuilding the Internet of Things with IPv6 and MIPv6: The Evolving World of M2M CommunicationsNo ratings yet
- Technical Seminar Report On Wireless Application Protocol100% (4)Technical Seminar Report On Wireless Application Protocol25 pages
- Mobile Computing: Introduction:: Unit - INo ratings yetMobile Computing: Introduction:: Unit - I4 pages
- Handoff Strategies in Cellular System PDFNo ratings yetHandoff Strategies in Cellular System PDF7 pages
- Cs 718 Wireless Networks Syllabus - Virtual University of PakistanNo ratings yetCs 718 Wireless Networks Syllabus - Virtual University of Pakistan4 pages
- Experiment No 6 Display Calculator Using WML: Theory100% (1)Experiment No 6 Display Calculator Using WML: Theory9 pages
- CS 515 Mobile and Wireless Networking: Ibrahim Korpeoglu Computer Engineering Department Bilkent University, AnkaraNo ratings yetCS 515 Mobile and Wireless Networking: Ibrahim Korpeoglu Computer Engineering Department Bilkent University, Ankara82 pages
- BE-IT - Elec-3 - 414444-A - Mobile Computing Syllabus - ZNo ratings yetBE-IT - Elec-3 - 414444-A - Mobile Computing Syllabus - Z3 pages
- GSM Based SMS Driven Automatic Display Tool KitNo ratings yetGSM Based SMS Driven Automatic Display Tool Kit120 pages
- Notes For Unit 5 Mobile Computing ArchitectureNo ratings yetNotes For Unit 5 Mobile Computing Architecture29 pages
- Syllabus of MCA - Bridge Course (Mangt) (2020patt.) 2020 - 2022 - 13.05.2021No ratings yetSyllabus of MCA - Bridge Course (Mangt) (2020patt.) 2020 - 2022 - 13.05.202113 pages
- CV - Telecom Site Engineer or SupervisorNo ratings yetCV - Telecom Site Engineer or Supervisor4 pages
- Ai Based Rush Collision Prevention in Railways Abstract:: Keywords: Arduino, RFID Reader, GSM, Railway TrackNo ratings yetAi Based Rush Collision Prevention in Railways Abstract:: Keywords: Arduino, RFID Reader, GSM, Railway Track6 pages
- 2745JPA004 - Bluetooth Based Chatting System Using Android PDF100% (1)2745JPA004 - Bluetooth Based Chatting System Using Android PDF8 pages
- Information: Call Handling Mobile Originated Call/Mobile Termi-Nated Call MOC/MTCNo ratings yetInformation: Call Handling Mobile Originated Call/Mobile Termi-Nated Call MOC/MTC17 pages
- Coral Ipx Modular Communications Server Combining Ip Technology With Traditional TDM Telephony100% (1)Coral Ipx Modular Communications Server Combining Ip Technology With Traditional TDM Telephony4 pages
- What Are Clusters?: High Cost of Traditional' High Performance ComputingNo ratings yetWhat Are Clusters?: High Cost of Traditional' High Performance Computing24 pages
- Artificial Neural Network Based Power System Restoratoin50% (2)Artificial Neural Network Based Power System Restoratoin22 pages
- Clos Architecture in OPS Seminar Report '04No ratings yetClos Architecture in OPS Seminar Report '0422 pages
- "Civilization Advances by Extending The Number of Important Operations Which We Can Perform Without Thinking About Them." - Alfred North WhiteheadNo ratings yet"Civilization Advances by Extending The Number of Important Operations Which We Can Perform Without Thinking About Them." - Alfred North Whitehead44 pages
- Intrusion Detection Systems: ANN For Misuse DetectionNo ratings yetIntrusion Detection Systems: ANN For Misuse Detection25 pages
- Adaptive Active Phased - Array 'Multifunction' Radars Seminar ReportNo ratings yetAdaptive Active Phased - Array 'Multifunction' Radars Seminar Report21 pages
- Adaptive Optics in Ground Based TelescopesNo ratings yetAdaptive Optics in Ground Based Telescopes24 pages
- Lec - MAC Protocols For Ad Hoc Wireless Networks - ppt13!11!17No ratings yetLec - MAC Protocols For Ad Hoc Wireless Networks - ppt13!11!1718 pages
- How To Sniff HTTP POST Password Via Network Using Wireshark Network Analyzer - Ethical Hacking Tutorials, Tips and Tricks100% (1)How To Sniff HTTP POST Password Via Network Using Wireshark Network Analyzer - Ethical Hacking Tutorials, Tips and Tricks9 pages
- IBM DS8886 Storage Hardware IntroductionNo ratings yetIBM DS8886 Storage Hardware Introduction16 pages
- Installing & Using Aspera Faspex With VantageNo ratings yetInstalling & Using Aspera Faspex With Vantage10 pages
- HDTVI DVR 3MP Resolution: Features and FunctionsNo ratings yetHDTVI DVR 3MP Resolution: Features and Functions2 pages
- Bizhub C454e: Colour A3 Multifunctional Up To 45 Pages Per MinuteNo ratings yetBizhub C454e: Colour A3 Multifunctional Up To 45 Pages Per Minute4 pages
- Advertising and Sales Promotion Assignment 2No ratings yetAdvertising and Sales Promotion Assignment 29 pages
- Network Performance Optimization: A Case Study of Enterprise Network Simulated in OPNETNetwork Performance Optimization: A Case Study of Enterprise Network Simulated in OPNET
- Networking Technologies and Its Design and Implementation: A Summer Training Synopsis Based ONNetworking Technologies and Its Design and Implementation: A Summer Training Synopsis Based ON
- The IMS: IP Multimedia Concepts and ServicesFrom EverandThe IMS: IP Multimedia Concepts and Services
- New Telecom Networks: Enterprises and SecurityFrom EverandNew Telecom Networks: Enterprises and Security
- Building the Internet of Things with IPv6 and MIPv6: The Evolving World of M2M CommunicationsFrom EverandBuilding the Internet of Things with IPv6 and MIPv6: The Evolving World of M2M Communications
- Technical Seminar Report On Wireless Application ProtocolTechnical Seminar Report On Wireless Application Protocol
- Cs 718 Wireless Networks Syllabus - Virtual University of PakistanCs 718 Wireless Networks Syllabus - Virtual University of Pakistan
- Experiment No 6 Display Calculator Using WML: TheoryExperiment No 6 Display Calculator Using WML: Theory
- CS 515 Mobile and Wireless Networking: Ibrahim Korpeoglu Computer Engineering Department Bilkent University, AnkaraCS 515 Mobile and Wireless Networking: Ibrahim Korpeoglu Computer Engineering Department Bilkent University, Ankara
- BE-IT - Elec-3 - 414444-A - Mobile Computing Syllabus - ZBE-IT - Elec-3 - 414444-A - Mobile Computing Syllabus - Z
- Syllabus of MCA - Bridge Course (Mangt) (2020patt.) 2020 - 2022 - 13.05.2021Syllabus of MCA - Bridge Course (Mangt) (2020patt.) 2020 - 2022 - 13.05.2021
- Ai Based Rush Collision Prevention in Railways Abstract:: Keywords: Arduino, RFID Reader, GSM, Railway TrackAi Based Rush Collision Prevention in Railways Abstract:: Keywords: Arduino, RFID Reader, GSM, Railway Track
- 2745JPA004 - Bluetooth Based Chatting System Using Android PDF2745JPA004 - Bluetooth Based Chatting System Using Android PDF
- Information: Call Handling Mobile Originated Call/Mobile Termi-Nated Call MOC/MTCInformation: Call Handling Mobile Originated Call/Mobile Termi-Nated Call MOC/MTC
- Coral Ipx Modular Communications Server Combining Ip Technology With Traditional TDM TelephonyCoral Ipx Modular Communications Server Combining Ip Technology With Traditional TDM Telephony
- CAMEL: Intelligent Networks for the GSM, GPRS and UMTS NetworkFrom EverandCAMEL: Intelligent Networks for the GSM, GPRS and UMTS Network
- IP Multimedia Subsystem IMS A Complete GuideFrom EverandIP Multimedia Subsystem IMS A Complete Guide
- What Are Clusters?: High Cost of Traditional' High Performance ComputingWhat Are Clusters?: High Cost of Traditional' High Performance Computing
- Artificial Neural Network Based Power System RestoratoinArtificial Neural Network Based Power System Restoratoin
- "Civilization Advances by Extending The Number of Important Operations Which We Can Perform Without Thinking About Them." - Alfred North Whitehead"Civilization Advances by Extending The Number of Important Operations Which We Can Perform Without Thinking About Them." - Alfred North Whitehead
- Intrusion Detection Systems: ANN For Misuse DetectionIntrusion Detection Systems: ANN For Misuse Detection
- Adaptive Active Phased - Array 'Multifunction' Radars Seminar ReportAdaptive Active Phased - Array 'Multifunction' Radars Seminar Report
- Lec - MAC Protocols For Ad Hoc Wireless Networks - ppt13!11!17Lec - MAC Protocols For Ad Hoc Wireless Networks - ppt13!11!17
- How To Sniff HTTP POST Password Via Network Using Wireshark Network Analyzer - Ethical Hacking Tutorials, Tips and TricksHow To Sniff HTTP POST Password Via Network Using Wireshark Network Analyzer - Ethical Hacking Tutorials, Tips and Tricks
- Bizhub C454e: Colour A3 Multifunctional Up To 45 Pages Per MinuteBizhub C454e: Colour A3 Multifunctional Up To 45 Pages Per Minute