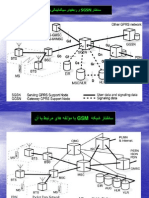
راتخاس Sgsn اتیدو یگنیلانگیس یاهطبار و
راتخاس Sgsn اتیدو یگنیلانگیس یاهطبار و
Uploaded by
rahmani12Copyright:
Available Formats
راتخاس Sgsn اتیدو یگنیلانگیس یاهطبار و
راتخاس Sgsn اتیدو یگنیلانگیس یاهطبار و
Uploaded by
rahmani12Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Copyright:
Available Formats
راتخاس Sgsn اتیدو یگنیلانگیس یاهطبار و
راتخاس Sgsn اتیدو یگنیلانگیس یاهطبار و
Uploaded by
rahmani12Copyright:
Available Formats
SGSN
GSM
Figure 3-1 Protocol interfaces provided by the MSOFTX3000 in a mobile network
BSC: Base Station Controller BC: Billing Center SG: Signaling Gateway MGW: Media Gateway
GMLC: Gateway Mobile Location Center SCP: Service Control Point SGSN: Serving GPRS Support Node PLMN: Public Land Mobile Network
HLR: Home Location Register SMC: Short Message Center RNC: Radio Network Controller
Table 3-5 Interfaces and protocols supported by the MSOFTX3000 in a mobile network
Connected Entities
MSC ServerMGW
MSC ServerRNC MSC ServerBSC (GSM) MSC ServerVLR MSC ServerHLR VLRHLR MSC ServerMSC Server MSCMSC (GSM) MSC ServerSMC VLRVLR MSC ServerGMLC SSPSCP GMSC ServerPSTN GMSC ServerPLMN MSC ServerSGSN MSC ServerNMS MSC ServerBC
Interface
Mc
lu-CS A B C D Nc E E G Lg Gs -
Protocol
H.248
RANAP BSSAP Internal protocol MAP MAP MAP, TUP/ISUP/BICC MAP, TUP/ISUP/BICC MAP MAP MAP CAP TUP/ISUP BSSAP+ MML FTP/FTAM
Figure 5-7 H.248 stack structure (H.248 over M3UA)
Figure 5-8 H.248 stack structure (H.248 over SCTP)
Figure 6-1 MSC networking
BSS: GSM Base station subsystem
UTRAN: UMTS terrestrial radio access network
GMSC: Gateway mobile switching center
BC: Billing center
GMLC: Gateway mobile location center PSTN: Public switched
HLR: Home location register
SCP: Service control point PLMN: Public land mobile
SMC: Short message center
SGSN: Serving GPRS support node
Figure 3-1 MA networking with multiple MSC numbers and multiple SPs
MS
2.2.1 Signaling Flow Figure 2-2 shows the signaling flow of the GMSC NPI scheme. Figure 2-2 Signaling flow of the GMSC NPI scheme
Line type
It indicates the office to which the A-interface circuit belongs.
Trunk group name
Equipment type CIC status Uninstall
It indicates the trunk group to which the A-interface circuit belongs.
It indicates that the A-interface equipment type is BSSAP. It indicates the identifier of the A-interface circuit. It indicates that A interface circuits are not configured or A interface data configuration is incomplete. For example, A interface circuits are configured but the circuits are in the unavailable state, or the circuits are configured on dualhoming non-activated nodes. It indicates that A interface circuits are normal or can be used for calls. It indicates A interface circuits are abnormal. The reason is a transmission problem due to abnormal physical connection of E1.
Idle Fault Oam block
It indicates that A interface circuits are abnormal. When you run BLK AIETKC to block the circuits, the circuits in the free state are transferred to the blocked state When circuits are in this state, you cannot make calls through there circuits except circuits specified by an operator. It indicates that circuits on the BSC side are blocked. When circuits are in this state, you cannot make calls through the circuits. It indicates that A interface circuits are normal. When circuits are occupied for calls, the circuits are in this state. It indicates that A interface circuits on the BSC side and local maintenance console are blocked. It indicates that A interface circuits are both in the oam block and the fault state. l This occurs when you block A interface circuits in the fault state on the maintenance console. l This occurs when you block circuits in the free state on the maintenance console but the circuits lead to E1 failure due to circuit gateway failure. It indicates that A interface circuits are both in the peer block and the fault state. It indicates that A interface circuits are both in the oam peer block and the fault state.
Remotely blocking Busy Oam peer block Oam block fault
Peer block fault Oam peer block fault
nce number) BSN
tor bit) BIB
vlr
Figure 3-9 Protocol stack processed by the WCCU/WCSU
Figure 3-19 Protocol stack processed by the WSGU
You might also like
- Ericsson Training PDFDocument118 pagesEricsson Training PDFNuwan100% (1)
- ASTM A775 - A775M-07b Std. Specs For Epoxy Coated Reinforcing BarsDocument11 pagesASTM A775 - A775M-07b Std. Specs For Epoxy Coated Reinforcing BarsILSEN N. DAET100% (2)
- Mass Limits For Trucks in VictoriaDocument2 pagesMass Limits For Trucks in VictoriaTanvir Shahrier Mahmud33% (3)
- Extec S5 PDFDocument24 pagesExtec S5 PDFlandago100% (1)
- Automated Broad and Narrow Band Impedance Matching for RF and Microwave CircuitsFrom EverandAutomated Broad and Narrow Band Impedance Matching for RF and Microwave CircuitsNo ratings yet
- From GSM to LTE-Advanced Pro and 5G: An Introduction to Mobile Networks and Mobile BroadbandFrom EverandFrom GSM to LTE-Advanced Pro and 5G: An Introduction to Mobile Networks and Mobile BroadbandNo ratings yet
- Design of Crane Steel BeamsDocument134 pagesDesign of Crane Steel Beamsshak54389% (9)
- Principles of Eddy Current TestingDocument1 pagePrinciples of Eddy Current Testingpcotfas100% (1)
- راتخاس Sgsn اتیدو یگنیلانگیس یاهطبار وDocument101 pagesراتخاس Sgsn اتیدو یگنیلانگیس یاهطبار وrezafaNo ratings yet
- Verifying The Iu-CS Interface: About This ChapterDocument8 pagesVerifying The Iu-CS Interface: About This ChapterMohsenNo ratings yet
- ASR ImprovementDocument22 pagesASR Improvementsureshkumar1912No ratings yet
- Guidelines For ASR Improvement Security LevelDocument22 pagesGuidelines For ASR Improvement Security LevelRohit SinghalNo ratings yet
- Verifying The Iu-PS Interface: About This ChapterDocument8 pagesVerifying The Iu-PS Interface: About This ChapterMohsenNo ratings yet
- CISCO Port Failure TroubleshootingDocument3 pagesCISCO Port Failure TroubleshootingmukiveNo ratings yet
- 418-00. Electrical Elecrtical Distribution Module Communications Network Diagnosis and Testing (Document83 pages418-00. Electrical Elecrtical Distribution Module Communications Network Diagnosis and Testing (LIRO ROMANo ratings yet
- GSM Channel StructureDocument4 pagesGSM Channel Structurebdrajubd0% (1)
- GB BT05 E1 0 GSM Signaling System-31Document27 pagesGB BT05 E1 0 GSM Signaling System-31se7en_csNo ratings yet
- RNCDocument22 pagesRNCUmesh Yadav100% (2)
- WO - NAST3015 - E01 - 0 UMTS Call Drop Analysis P26Document24 pagesWO - NAST3015 - E01 - 0 UMTS Call Drop Analysis P26noumizredhaNo ratings yet
- UMTS Interview Questions and AnswerDocument16 pagesUMTS Interview Questions and AnswerSuhelSiddiquiNo ratings yet
- Operator E CA (Carrier Aggregation) Feature Test GuideDocument8 pagesOperator E CA (Carrier Aggregation) Feature Test GuideAkhtar KhanNo ratings yet
- Troubleshooting IBM: Internetworking Troubleshooting Handbook, Second Edition 1-58705-005-6Document54 pagesTroubleshooting IBM: Internetworking Troubleshooting Handbook, Second Edition 1-58705-005-6Fahim Hyder SayedNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6: GB InterfaceDocument43 pagesChapter 6: GB Interfacesonchoy17No ratings yet
- 3G IUB ParametersDocument3 pages3G IUB ParametersMohan OletiNo ratings yet
- Extending The SPI Bus For Long Distnce CommDocument7 pagesExtending The SPI Bus For Long Distnce CommFelipe Ademir Aleman Hdez100% (2)
- SDH AlarmsDocument141 pagesSDH AlarmsDerrick Senyo100% (2)
- Verifying The Iur Interface: About This ChapterDocument8 pagesVerifying The Iur Interface: About This ChapterMohsenNo ratings yet
- SAN Troubleshooting (11) - Common SAN IssueDocument8 pagesSAN Troubleshooting (11) - Common SAN IssuePurushothama GnNo ratings yet
- QL ServiceManualDocument98 pagesQL ServiceManualOscar Arthur KoepkeNo ratings yet
- Take Assessment CCNP BCMSN Final 3: (Version 5.0)Document14 pagesTake Assessment CCNP BCMSN Final 3: (Version 5.0)Manuel Valdés100% (2)
- SDH Alarms & Performance MonitoringDocument141 pagesSDH Alarms & Performance MonitoringSanjay Yadav100% (1)
- GSM Signaling System: Course ObjectivesDocument31 pagesGSM Signaling System: Course ObjectivesBsskkd KkdNo ratings yet
- Cdot An-RaxDocument46 pagesCdot An-Raxneeraj kumar singh100% (2)
- 7 7302 5523 VLAN Setup and IBDocument67 pages7 7302 5523 VLAN Setup and IBbelbel4321No ratings yet
- Brocade San Switch TroubleshootingDocument7 pagesBrocade San Switch TroubleshootingMohaideenNo ratings yet
- Switching (HEXCO) QUE AND ANSWERSDocument17 pagesSwitching (HEXCO) QUE AND ANSWERSLaison BlaimNo ratings yet
- 13 WO - NA05 - E1 - 0 UMTS Call Drop Analysis-26 PDFDocument27 pages13 WO - NA05 - E1 - 0 UMTS Call Drop Analysis-26 PDFsyrish2622No ratings yet
- ATM For IUBDocument15 pagesATM For IUBoucht79No ratings yet
- AN3947 DaisyChaining SPI DevicesDocument8 pagesAN3947 DaisyChaining SPI DevicesrockymaxdeemannNo ratings yet
- 21801FDocument88 pages21801FJorge GarabanNo ratings yet
- DBZ6J User's ManualDocument14 pagesDBZ6J User's ManualchiviprogamerNo ratings yet
- How Reliable Is The Routing Inyour SDH Network?: Application Note 64Document12 pagesHow Reliable Is The Routing Inyour SDH Network?: Application Note 64Ilay VelNo ratings yet
- Stand-Alone CAN Controller With SPI Interface: Features DescriptionDocument84 pagesStand-Alone CAN Controller With SPI Interface: Features DescriptionjismagicNo ratings yet
- Dms Axe Level1Document28 pagesDms Axe Level1Arpit Shah100% (1)
- Zigbee Body SensorDocument7 pagesZigbee Body SensorsunilsmcsNo ratings yet
- 4department 5electronics: Communication System For Controlling Smart Appliances Using Power Line CommunicationDocument6 pages4department 5electronics: Communication System For Controlling Smart Appliances Using Power Line CommunicationNeel SomudroNo ratings yet
- Engineering Instruction Atm C-Dot System - An IntroductionDocument36 pagesEngineering Instruction Atm C-Dot System - An IntroductionApoorv VermaNo ratings yet
- PPTDocument34 pagesPPTMariam MugheesNo ratings yet
- Presentation: OF Base Station System (BSS)Document30 pagesPresentation: OF Base Station System (BSS)wakeonlanNo ratings yet
- Channel ElementsDocument6 pagesChannel ElementsVikas DwivediNo ratings yet
- WAN TECHNOLOGY FRAME-RELAY: An Expert's Handbook of Navigating Frame Relay NetworksFrom EverandWAN TECHNOLOGY FRAME-RELAY: An Expert's Handbook of Navigating Frame Relay NetworksNo ratings yet
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2No ratings yet
- High-Performance D/A-Converters: Application to Digital TransceiversFrom EverandHigh-Performance D/A-Converters: Application to Digital TransceiversNo ratings yet
- Signal Integrity: From High-Speed to Radiofrequency ApplicationsFrom EverandSignal Integrity: From High-Speed to Radiofrequency ApplicationsNo ratings yet
- Gain-Cell Embedded DRAMs for Low-Power VLSI Systems-on-ChipFrom EverandGain-Cell Embedded DRAMs for Low-Power VLSI Systems-on-ChipNo ratings yet
- LEARN MPLS FROM SCRATCH PART-B: A Beginners guide to next level of networkingFrom EverandLEARN MPLS FROM SCRATCH PART-B: A Beginners guide to next level of networkingNo ratings yet
- Advanced Multicarrier Technologies for Future Radio Communication: 5G and BeyondFrom EverandAdvanced Multicarrier Technologies for Future Radio Communication: 5G and BeyondNo ratings yet
- Exploring BeagleBone: Tools and Techniques for Building with Embedded LinuxFrom EverandExploring BeagleBone: Tools and Techniques for Building with Embedded LinuxRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)
- 10 - 6255 - NAK - HSDPA Code ManagementDocument8 pages10 - 6255 - NAK - HSDPA Code Managementrahmani12No ratings yet
- IratDocument50 pagesIratrahmani12No ratings yet
- 15 6255 Nak Hsupa MobilityDocument19 pages15 6255 Nak Hsupa Mobilityrahmani12No ratings yet
- 13 6255 NAK HSUPA Protocol FeaturesDocument104 pages13 6255 NAK HSUPA Protocol Featuresrahmani12No ratings yet
- TBFDocument4 pagesTBFrahmani12No ratings yet
- Base Line Week 20 Week 22 Week 27 Week 29 Week 30 Week 33 Week 34 Week 35 Week 36 Week 37 Week 38Document2 pagesBase Line Week 20 Week 22 Week 27 Week 29 Week 30 Week 33 Week 34 Week 35 Week 36 Week 37 Week 38rahmani12No ratings yet
- 4.BSC GPRS Cutover ExampleDocument5 pages4.BSC GPRS Cutover Examplerahmani12No ratings yet
- Bad RX QualDocument5 pagesBad RX Qualrahmani12No ratings yet
- 5 Tcsm2eDocument22 pages5 Tcsm2erahmani12No ratings yet
- IN OUT Extra On Leave: Year DAYDocument2 pagesIN OUT Extra On Leave: Year DAYrahmani12No ratings yet
- Ebmpapst Cooling Fan D2D146-BG03-14 ATV61 - 71 For Schneider Frequency Converter Fan - Computers & AccessoriesDocument2 pagesEbmpapst Cooling Fan D2D146-BG03-14 ATV61 - 71 For Schneider Frequency Converter Fan - Computers & AccessoriesubaiNo ratings yet
- A002-003 Drawing ListDocument2 pagesA002-003 Drawing ListyehtetkyawstanzadecorationNo ratings yet
- IYI-Seismic Protection of Structures With Modern Base Isolation Technologies PDFDocument10 pagesIYI-Seismic Protection of Structures With Modern Base Isolation Technologies PDFmelseNo ratings yet
- Astm A767-09Document5 pagesAstm A767-09poulmackNo ratings yet
- History and Development of Discipline Engineering IndustryDocument11 pagesHistory and Development of Discipline Engineering IndustrySiti Nur JanahNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Engineering Seismology: KeywordsDocument34 pagesIntroduction To Engineering Seismology: Keywordsdiyan soloNo ratings yet
- Guidance On Use of Producer Statements: PS1 DesignDocument1 pageGuidance On Use of Producer Statements: PS1 DesignErsel KizilayNo ratings yet
- 16 Optimizing Linux System Performance 7043Document5 pages16 Optimizing Linux System Performance 7043gabjonesNo ratings yet
- Sugar ProjectDocument7 pagesSugar ProjectVidushi ShuklaNo ratings yet
- Kobra 260.1 S4Document1 pageKobra 260.1 S4Mishmash PurchasingNo ratings yet
- Mac Puarsa MRL Othyssone PDF Electric Motor Capacitor 2Document1 pageMac Puarsa MRL Othyssone PDF Electric Motor Capacitor 2dejan.bimbeNo ratings yet
- MS Access 2010 Tutorial PDFDocument141 pagesMS Access 2010 Tutorial PDFpganoel100% (2)
- Name: Digital Logic Circuits (Common To ICE) Part A (20X2 40 Marks) Answer All QuestionsDocument2 pagesName: Digital Logic Circuits (Common To ICE) Part A (20X2 40 Marks) Answer All QuestionsAnonymous yO7rcec6vuNo ratings yet
- Fz7 (Paga and FGDS) BoqDocument3 pagesFz7 (Paga and FGDS) BoqAlla Naveen KumarNo ratings yet
- AquacultureDocument2 pagesAquaculturesamtomNo ratings yet
- Dbms ProjectDocument10 pagesDbms Projectsagarvk70No ratings yet
- Dr. J. J. Magdum College of Engineering, Jaysingpur.: Course - OutlineDocument10 pagesDr. J. J. Magdum College of Engineering, Jaysingpur.: Course - OutlinedspNo ratings yet
- Designer Training Record-CompDocument7 pagesDesigner Training Record-CompWilliam Boyle Jr.No ratings yet
- Exercise Form 1 Chapter 5 Air Around UsDocument9 pagesExercise Form 1 Chapter 5 Air Around UsAimi Nadia Yusof100% (1)
- An Articulated Robotic ArmDocument74 pagesAn Articulated Robotic ArmVishwajit Nandi100% (1)
- Nablus City My PlaceDocument24 pagesNablus City My PlaceMay SayrafiNo ratings yet
- Chap004 1 PDFDocument91 pagesChap004 1 PDFMR no oneNo ratings yet
- C++ Pointers - C++ Programming Concepts at Little Drops at ThiyagaraajDocument9 pagesC++ Pointers - C++ Programming Concepts at Little Drops at Thiyagaraajankur9359saxenaNo ratings yet
- 300 2013 6.4LDocument302 pages300 2013 6.4LLuis Ramon Arguello RealNo ratings yet