0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
41 viewsSpin A
Spin A
Uploaded by
bajaocSpina bifida is a birth defect where the spinal cord or its coverings do not fully develop. It occurs when the neural tube fails to close during the first month of pregnancy. There are three main types ranging from mild to severe. Signs and symptoms depend on the severity but may include issues with the bladder, bowel, legs and intelligence. It can often be detected before birth through tests like ultrasound and amniocentesis and treated after birth.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Spin A
Spin A
Uploaded by
bajaoc0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
41 views25 pagesSpina bifida is a birth defect where the spinal cord or its coverings do not fully develop. It occurs when the neural tube fails to close during the first month of pregnancy. There are three main types ranging from mild to severe. Signs and symptoms depend on the severity but may include issues with the bladder, bowel, legs and intelligence. It can often be detected before birth through tests like ultrasound and amniocentesis and treated after birth.
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Spina bifida is a birth defect where the spinal cord or its coverings do not fully develop. It occurs when the neural tube fails to close during the first month of pregnancy. There are three main types ranging from mild to severe. Signs and symptoms depend on the severity but may include issues with the bladder, bowel, legs and intelligence. It can often be detected before birth through tests like ultrasound and amniocentesis and treated after birth.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as ppt, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
41 views25 pagesSpin A
Spin A
Uploaded by
bajaocSpina bifida is a birth defect where the spinal cord or its coverings do not fully develop. It occurs when the neural tube fails to close during the first month of pregnancy. There are three main types ranging from mild to severe. Signs and symptoms depend on the severity but may include issues with the bladder, bowel, legs and intelligence. It can often be detected before birth through tests like ultrasound and amniocentesis and treated after birth.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as ppt, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 25
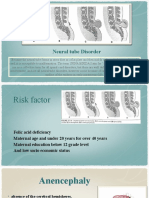
SPINA BIFIDA
Also called as myelodysplasia
it is a condition in which there is
abnormal development of the back
bones, spinal cord, surrounding
nerves and the fluid-filled sac that
surrounds the spinal cord. This
neurological condition can cause a
portion of the spinal cord and the
surrounding structures to develop
outside, instead of inside the body.
Spina bifida is a birth defe ct that involves the incomple te develo pment
of the spinal cord or its coverings. The term spina bifida comes from
Latin and literally means "split" or "open" spine.
Spina bifida occurs at the end of the first month of pregnancy when the
two sides of the embryo's spine fail to jo in together, le aving an open
area. In some cases, the spinal cord or other membranes may push
through this opening in the embryo's back.
The conditio n can typic ally be detected befo re a baby is born and
treated rig ht away.
Types:
1. Spina Bifida Occulta- a mild form of spina bifida in which the spinal cord and the
surrounding structures remain inside the baby, but the back bones in the lower
back area fail to form normally.
2. Meningocele- a moderate form of spina bifida in which a fluid-fil ed sac is visible
outside of the back area.
3. Myelomeningocele- a severe form of spina bifida in which the spinal cord and nerves
develop outside of the body and are contained in a fluid-fil ed sac that is visible outside
the back area.
The condition can typically be detected before a baby is born and
treated right away.
The causes of spina bifida are largely unknown. Some evidence
suggests that genes may be involved, but in most cases there is no
familial connection. A high fever during pregnancy may increase a
woman's chances of having a baby with spina bifida.
Women with epilepsy who have taken the drug valproic acid to control
seizures may have an increased risk of having a baby with spina bifida.
Causes:
- During pregnancy, the human brain and spine begin as a flat plate of cells,
which rolls into a tube called the nueral tube. If all part of the nueral tube fails
to close, leaving an opening, this is known as an open neural tube defect. This
opening may be left exposed or covered eith bone or skin.
- Anencephaly and spina bi Anencephaly and spina bifida are the most types of
ONTD, while encephalocele ( in which there is a protrusion of the brain or its
covering through the skull is much rare. Anencephaly occurs when the neural
tube fails to close at the base of the skull, while spina bifida occurs when the
neural tube fails to close somewhere along the spine.
- ONTD results from combination of genes inherited from both parents, coupled
with environmental factors. For this reason, ONTD are considered multi factorial
traits meaning “many factors” both genetic and environmental, contribute to
their occurrence.
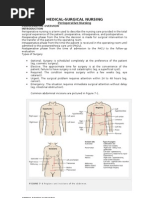
Signs and Symptoms:
- Abnormal appearance of the baby’s back, varying from small, hairy patch or a
dimple birth mark, to a sac-like protrusion that is found along the back bone
area.
- Bowel and Bladder problems
- Loss of feeling below the area of the lesion, especial y in babies born with a
meningocele
- Inability to move the lower legs
- The baby may also have problems related to spina bifida that include the
fol owing:
- Hydrocephalus
- Heart problems
- Heart problems
- Orthopedic problems
- Lower than normal intel igence level
Diagnostic Tests:
- Blood Test, a blood test be offered between 15 to 20 weeks to all women who
are pregnant who have not previously had a child with an ONTD and who do not
have a family history of ONTD. This blood test measures alpha-fetoprotein (AFP)
levels and other biochemical markers in the mother’s blood determine whether
her pregnancy is at increased risk for an ONTD.
AFP is a protein normally produced by the fetus that crosses the placenta into the
mother’s blood. Generally if the fetus an ONTD, the alpha-tetoprotein level in the
mother’s blood wil be increased. Although this test does not tel for certain whether a
fetus has an ONTD, it wil determine which pregnancies are at greater risk, so the
additional testing may be performed.
- Prenatal Ultrasound (Sonography), prenatal ultrasound may be able to detect on
ONTD, and may be used to examine other organs and body systems of the
fetus.
- Amniocentesis- a procedure that involves inserting a long, thin needle through
the mother’s abdomen into the amniotic sac to withdraw a small sample of the
amniotic fluid for examination.
Nursing and Medical Managements:
- repair and closure of the lesion
- treatment of hydrocephalus
- orthopedic problems
- bowel and bladder problems
- examining the skin, especial y over bony areas such as the elbows, buttocks,
back of the thighs, heel and foot areas.
- Ways to feed the baby and monitor baby’s nutrition
- Promoting activity and mobility
- Encouraging age-appropriate growth and development
- Provide comfort measures and sensory stimulation
Complications:
- ankle and foot deformities
- contracted muscles
- hip dislocation
- curvatures of the back
You might also like
- Physiotherapy For Adult Neurological Conditions (Abraham M. Joshua) Bibis - IrDocument909 pagesPhysiotherapy For Adult Neurological Conditions (Abraham M. Joshua) Bibis - IrDharmik PrajapatiNo ratings yet
- Spina Bifida PowerpointDocument15 pagesSpina Bifida Powerpointapi-547884261100% (3)
- Case Analysis Spina BifidaDocument11 pagesCase Analysis Spina BifidaErica Joy Algire VillalunaNo ratings yet
- Pediatric NursingDocument55 pagesPediatric Nursingbajaoc100% (14)
- Nursing Leadership and ManagementDocument43 pagesNursing Leadership and Managementbajaoc95% (22)
- Prevention of Heart DiseaseDocument43 pagesPrevention of Heart DiseaseamitmokalNo ratings yet
- Spina BifidaDocument10 pagesSpina BifidaMike Faustino SolangonNo ratings yet
- Neural Tube Defect: Mrs. Abhilasha Saha Associate Professor-Paediatric Nursing National Medical College, Birgunj, NepalDocument26 pagesNeural Tube Defect: Mrs. Abhilasha Saha Associate Professor-Paediatric Nursing National Medical College, Birgunj, NepalSilvana María Espinoza CuadrosNo ratings yet
- Developmental Anomalies of Spinal CordDocument41 pagesDevelopmental Anomalies of Spinal Cordhamza_shoaib99No ratings yet
- Spina BifidaDocument17 pagesSpina Bifidajessy100% (1)
- Spinalbifida 121213120324 Phpapp02Document28 pagesSpinalbifida 121213120324 Phpapp02Silvana María Espinoza CuadrosNo ratings yet
- Spina BifidaDocument14 pagesSpina BifidaChacha ZakiyaNo ratings yet
- No. 3 - NCM 109LDocument44 pagesNo. 3 - NCM 109LDalene EvangelioNo ratings yet
- Spina BifidaDocument34 pagesSpina BifidaShijin KelambethNo ratings yet
- Spina BifidaDocument6 pagesSpina BifidaAdiel Calsa100% (1)
- Spina Bifida4 @medical._.notesDocument12 pagesSpina Bifida4 @medical._.notesdaxoabhi900No ratings yet
- Spina BifidaDocument28 pagesSpina BifidaIshita MaheyNo ratings yet
- Spinal DiseasesDocument2 pagesSpinal DiseaseschicbeatzNo ratings yet
- Myelomeningocele: By: Jahada GonzalesDocument11 pagesMyelomeningocele: By: Jahada GonzalesJada GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Neural Tube Defects and Folic Acid: Dr. Sukma Sahreni, M.GiziDocument38 pagesNeural Tube Defects and Folic Acid: Dr. Sukma Sahreni, M.GiziGinanjar Putri SariNo ratings yet
- Congenital Neurologic DisordersDocument114 pagesCongenital Neurologic DisordersKirk08No ratings yet
- Spina BifidaDocument3 pagesSpina BifidaANGELICA JOY GATDULANo ratings yet
- Spina Bifida Mayo HandoutDocument3 pagesSpina Bifida Mayo Handoutليلى صيرمNo ratings yet
- RRLDocument14 pagesRRLFreisanChenMandumotanNo ratings yet
- EctopicDocument4 pagesEctopicAb Staholic BoiiNo ratings yet
- Folic Acid in The Prevention of Neural Ube DefectDocument29 pagesFolic Acid in The Prevention of Neural Ube DefectRashmi GoswamiNo ratings yet
- Spina Bbifida: Baguhin, Paul Ceniza, AnneDocument16 pagesSpina Bbifida: Baguhin, Paul Ceniza, AnnePaul Michael BaguhinNo ratings yet
- Neural Tube DefectDocument77 pagesNeural Tube Defectminkmin91No ratings yet
- Neema Rawat Microteaching (Spina Bifida)Document67 pagesNeema Rawat Microteaching (Spina Bifida)Dimple GoyalNo ratings yet
- Neural Tube DefectDocument43 pagesNeural Tube DefectEllen AngelNo ratings yet
- Spina Bifida ModuleDocument5 pagesSpina Bifida ModuleJulliza Joy PandiNo ratings yet
- P1 Facts About AnencephalyDocument8 pagesP1 Facts About AnencephalyAde Cahyo IslamiNo ratings yet
- Spina Bifida - Pediatrics - MSD Manual Professional EditionDocument4 pagesSpina Bifida - Pediatrics - MSD Manual Professional EditionTONY GO AWAYNo ratings yet
- Spina BifidaDocument46 pagesSpina BifidaS G100% (1)
- Neural Tube DefectsDocument2 pagesNeural Tube DefectsVijay SluNo ratings yet
- Neural Tube Defects.Document34 pagesNeural Tube Defects.ChosenNo ratings yet
- Spina BifidaDocument29 pagesSpina Bifidaann dimcoNo ratings yet
- Spina BifidaDocument25 pagesSpina BifidaYumi MacalinaoNo ratings yet
- Congenital Malformations of The New BornDocument14 pagesCongenital Malformations of The New BornMartha LubasiNo ratings yet
- Spina BifidaDocument2 pagesSpina BifidaMI ZINo ratings yet
- Neural tube defectsDocument33 pagesNeural tube defectsJayalakshmi JRNo ratings yet
- AnencephalyDocument10 pagesAnencephalyRm LavariasNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 Child With Congenital DisordersDocument159 pagesUnit 5 Child With Congenital DisordersRenita RichardNo ratings yet
- Congenital AbnormalitiesDocument22 pagesCongenital AbnormalitiesNatukunda DianahNo ratings yet
- S PINABIFIDADocument31 pagesS PINABIFIDAArjun JadejaNo ratings yet
- Neonatology Lec1 2023Document17 pagesNeonatology Lec1 2023khaleelNo ratings yet
- 9.spina BifidaDocument33 pages9.spina BifidaAbdul GhayurNo ratings yet
- Spina BifidaDocument33 pagesSpina BifidaRegine Prongoso DagumanpanNo ratings yet
- Neural Tube Defects: Group 1Document28 pagesNeural Tube Defects: Group 1imneverwrong2492100% (1)
- 4 Anatomibirth DefectDocument51 pages4 Anatomibirth Defectwahyu ashariNo ratings yet
- Spina BifidaDocument18 pagesSpina BifidaIrham KhairiNo ratings yet
- Case GfndyDocument9 pagesCase Gfndyednom12No ratings yet
- Neural Tube Defect (Spina Bifida) : Guided by Presented byDocument41 pagesNeural Tube Defect (Spina Bifida) : Guided by Presented byShreyasi PatankarNo ratings yet
- Neural Tube DefectDocument8 pagesNeural Tube DefectReema Akberali nooraniNo ratings yet
- Pedia Day 2-3Document19 pagesPedia Day 2-3dhknjjppnyNo ratings yet
- Community Medicine PresentationDocument7 pagesCommunity Medicine PresentationAyeshaNo ratings yet
- AnencephalyDocument11 pagesAnencephalyAnironOrionNo ratings yet
- SPINA BIFIDA & MANAGEMENTDocument32 pagesSPINA BIFIDA & MANAGEMENTFatima Ul HassanNo ratings yet
- Homework PreemiDocument8 pagesHomework PreemiTeenie Guerrero-GarciaNo ratings yet
- Myelomeningocele What Is A Myelomeningocele?Document1 pageMyelomeningocele What Is A Myelomeningocele?Solange VillaizanNo ratings yet
- Dental Management of the Pregnant PatientFrom EverandDental Management of the Pregnant PatientChristos A. SkouterisNo ratings yet
- Psych Nursing CompleteDocument31 pagesPsych Nursing CompletebajaocNo ratings yet
- Management of Shock: Role of Inotropic & Vasoactive DrugsDocument50 pagesManagement of Shock: Role of Inotropic & Vasoactive DrugsbajaocNo ratings yet
- Perioperative NursingDocument41 pagesPerioperative Nursingbajaoc100% (8)
- Maternity NursingDocument41 pagesMaternity Nursingbajaoc100% (1)
- Urinary CatheterizattionDocument85 pagesUrinary Catheterizattionbajaoc100% (6)
- SuctioningDocument30 pagesSuctioningbajaoc60% (5)
- NebulizationDocument8 pagesNebulizationbajaocNo ratings yet
- Re YesDocument12 pagesRe YesbajaocNo ratings yet
- Eating Disorders: Anorexia vs. BulimiaDocument17 pagesEating Disorders: Anorexia vs. BulimiabajaocNo ratings yet
- Why Worry About Electricity?Document18 pagesWhy Worry About Electricity?bajaocNo ratings yet
- Cardioversion & DefibrillationDocument14 pagesCardioversion & DefibrillationbajaocNo ratings yet
- Kinemati Cs of TraumaDocument62 pagesKinemati Cs of TraumabajaocNo ratings yet
- Ecg/EkgDocument29 pagesEcg/EkgbajaocNo ratings yet
- Managing Chest DrainageDocument63 pagesManaging Chest DrainagecarlalynneNo ratings yet
- Emergency DrugsDocument17 pagesEmergency Drugsapi-3853350100% (12)
- Health - Occupational Hazards: Back InjuryDocument7 pagesHealth - Occupational Hazards: Back InjurybajaocNo ratings yet
- Administering EnemaDocument35 pagesAdministering Enemabajaoc100% (1)
- Diabetes Patient EducationDocument96 pagesDiabetes Patient EducationbajaocNo ratings yet
- Mrs. Rosario A. Respicio Clinical InstructorDocument52 pagesMrs. Rosario A. Respicio Clinical InstructorbajaocNo ratings yet
- Cesarean Section FinalDocument11 pagesCesarean Section FinalbajaocNo ratings yet
- Anti Hypertensive DrugsDocument13 pagesAnti Hypertensive DrugsbajaocNo ratings yet
- Neuro-Rehabilitation: DR SG Sturman Consultant Neurologist SWBH NHS Trust, Birmingham, UKDocument39 pagesNeuro-Rehabilitation: DR SG Sturman Consultant Neurologist SWBH NHS Trust, Birmingham, UKHassen Kavi IsseNo ratings yet
- DD McqsDocument21 pagesDD McqsSyeda MunazzaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Radio: AbdomenDocument10 pagesAnatomy Radio: AbdomenMonique BorresNo ratings yet
- Senses (Quizziz)Document3 pagesSenses (Quizziz)mariaNo ratings yet
- Module6 All CompressedDocument58 pagesModule6 All CompressedAryanaNo ratings yet
- Language & Language AssessmentDocument20 pagesLanguage & Language AssessmentDee CarballeaNo ratings yet
- Cerebral PalsyDocument37 pagesCerebral Palsykeihoina keihoinaNo ratings yet
- NeuroDocument4 pagesNeuroKrizia R. PingkeNo ratings yet
- Wong2016 PDFDocument17 pagesWong2016 PDFMelissa Peña LópezNo ratings yet
- Health Assessment Skills Check OffDocument4 pagesHealth Assessment Skills Check OffCatalina Cortes100% (2)
- Chapter SixDocument182 pagesChapter Sixtadele10No ratings yet
- Addenbrooke Cognitive ExaminationDocument11 pagesAddenbrooke Cognitive ExaminationAshlin BaijuNo ratings yet
- Destructive Operations. PDFDocument63 pagesDestructive Operations. PDFFeba SajanNo ratings yet
- Journal of Food Biochemistry - 2022 - Xiang - The Bioactivity and Applications of Pomegranate Peel Extract A ReviewDocument24 pagesJournal of Food Biochemistry - 2022 - Xiang - The Bioactivity and Applications of Pomegranate Peel Extract A Reviewmudhra143No ratings yet
- 2023 Multi-class classification of brain tumor types from MR images using EfficientNetsDocument12 pages2023 Multi-class classification of brain tumor types from MR images using EfficientNetsAnsuman AcharyaNo ratings yet
- Case Study On Lung CancerDocument54 pagesCase Study On Lung CancerQusai BassamNo ratings yet
- ANPH M3 CU15. Lymphatic SystemDocument22 pagesANPH M3 CU15. Lymphatic Systemmark tuazonNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument3 pagesNervous SystemMary Rose Ponte FernandezNo ratings yet
- Comfort and Pain ManagementDocument75 pagesComfort and Pain ManagementBeverly Lavilla100% (1)
- Chapter 22 Lymphatic System Transes FinalDocument40 pagesChapter 22 Lymphatic System Transes FinalMohamidin MamalapatNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic Imaging Pediatrics by Lane F. Donnelly, Blaise v. Jones, Sara M. OHara, Christopher G. Anton, Corning Benton, Sjirk J. Westra, Steven J. Kraus, Janet L. Strife, Bernadette L. Koch, Karin L.Document1,148 pagesDiagnostic Imaging Pediatrics by Lane F. Donnelly, Blaise v. Jones, Sara M. OHara, Christopher G. Anton, Corning Benton, Sjirk J. Westra, Steven J. Kraus, Janet L. Strife, Bernadette L. Koch, Karin L.simona mariana dutu100% (1)
- Anatomy Physiology 1st Edition Openstax College All Chapter Instant DownloadDocument64 pagesAnatomy Physiology 1st Edition Openstax College All Chapter Instant Downloadrougefte100% (2)
- Tooth Root FormationDocument10 pagesTooth Root FormationAthenaeum Scientific PublishersNo ratings yet
- Viruses 08 00210Document13 pagesViruses 08 00210Hany ZutanNo ratings yet
- Physical Assessment - QUINDAODocument2 pagesPhysical Assessment - QUINDAOJean QuindaoNo ratings yet
- Body Systems ReviewDocument13 pagesBody Systems ReviewJoseph LinNo ratings yet
- Neuroanatomy Draw It to Know It 2nd Edition Adam Fisch 2024 Scribd DownloadDocument81 pagesNeuroanatomy Draw It to Know It 2nd Edition Adam Fisch 2024 Scribd Downloadgagencudan7mNo ratings yet
- Adult Mesenchymal Stem Cells and Their Exosomes Sources, Characteristics, and Application in Regenerative MedicineDocument9 pagesAdult Mesenchymal Stem Cells and Their Exosomes Sources, Characteristics, and Application in Regenerative MedicinerelbelkasyNo ratings yet
- Biology of Bone Formation, Fracture Healing, and Distraction OsteogenesisDocument10 pagesBiology of Bone Formation, Fracture Healing, and Distraction OsteogenesisenviNo ratings yet