Distance Relay Psps
Distance Relay Psps
Uploaded by
Adhi0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
91 views33 pagesDistance relays are commonly used to protect transmission lines. They provide faster fault clearing than overcurrent relays. There are different types of distance relays including impedance, reactance, and admittance relays. Impedance relays measure the ratio of voltage to current, which represents impedance, and trip if the impedance is below a preset value. This allows them to detect faults along the transmission line. Distance protection can provide both primary and backup protection in a single scheme.
Original Description:
Psps
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentDistance relays are commonly used to protect transmission lines. They provide faster fault clearing than overcurrent relays. There are different types of distance relays including impedance, reactance, and admittance relays. Impedance relays measure the ratio of voltage to current, which represents impedance, and trip if the impedance is below a preset value. This allows them to detect faults along the transmission line. Distance protection can provide both primary and backup protection in a single scheme.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
91 views33 pagesDistance Relay Psps
Distance Relay Psps
Uploaded by
AdhiDistance relays are commonly used to protect transmission lines. They provide faster fault clearing than overcurrent relays. There are different types of distance relays including impedance, reactance, and admittance relays. Impedance relays measure the ratio of voltage to current, which represents impedance, and trip if the impedance is below a preset value. This allows them to detect faults along the transmission line. Distance protection can provide both primary and backup protection in a single scheme.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 33
DISTANCE OR IMPEDENCE RELAY
DISTANCE PROTECTION SCHEME
Distance protection is comparatively
simple to apply and it can be fast in
operation for faults located along most of a
protected circuit. It can also provide both
primary and remote back-up functions in a
single scheme. It can easily be adapted to
create a unit protection scheme when
applied with a signalling channel.
Why distance relays are used?
Distance protection is very commonly
used in protection of transmission lines.
Distance relays are used where
overcurrenting relaying is too slow and is not
so selective. Distance relays are used for both
phase fault and ground fault protection and
they provide higher speeds for clearing faults
than overcurrent relays.
Why is distance protection necessary?
The protection of transmission line from
any type of fault is very important because any
mis-operation or mal- operation of protection
relays can give a great effect on the stability of
power system entirely. One of the
main protection used to protect transmission
line is distance or impedance relay.
DISTANCE OR IMPEDENCE!!
•Distance relays finds its application in
transmission systems.
•The functioning of this relay depends upon the
distance of fault in the line .
•Particularly impedance between the point of
fault and the point where relay is installed.
•Since impedance proportional to
distance(length) , it is also known as impedance
relay.
DISTANCE RELAY OPERATING
CURVE
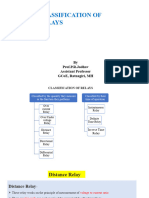
Types of distance relays
1.Impedance Relay.
2.Admittance Relay.
3.Reactance Relay.
TYPES OF DISTANCE RELAYS:
Dependent on the ratio of V and I there are
three types of distance relays which are,
1.Impedance relay which is based on
measurement of impedance Z.
2.Reactance relay which is based on
measurement of reactance X.
3.Admittance or mho relay which is based on
measurement of component of admittance Y.
TYPES:
There are mainly two types of distance relay.
• Definite distance relay
• Time distance relay
DEFINITE DISTANCE RELAY:
This is simply a variety of balanced
beam relay.Here one beam is placed horizontally and
supported by hinge on the middle.One end of the
beam is pulled downwards by magnetic force of
current coil fed from current transformer.Due to
torque produced by these two downward forces,the
beam stays at an equilibrium position.The torque due
to voltage coil serves as restraining torque and torque
due to current coil serves as deflecting torque.
TIME DISTANCE IMPEDANCE
RELAY:
This relay automatically adjust its
operating time according to the distance of the
relay from the fault point.The time distance
impedance relay will not only be operated
depending upon voltage to current ratio.Its
operating time also depends upon the value of
this ratio.
WORKING PRINCIPLE !!!
•PRINCIPLE : Ratio of system voltage and current
which is nothing but impedance so called
impedance relay.
PRINCIPLES
• It involves the division of voltage at the
relaying point by the measured current.
• The calculated apparent impedance is
compared with the reach point impedance.
• If the measured impedance is less than the
reach point impedance ,it is assumed that a
fault exists on the line between the relay and
the reach point.
WORKING
•The operation of such relay depends on the
predetermined value of voltage to current ratio.
Z= V/I
•It only operates when the impedance is less
than its predetermined value.
•Since impedance of transmission line is directly
proportional to its length, distance relay
operates only within a predetermined distance.
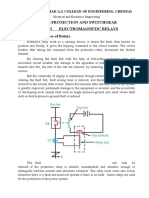
OPERATION
• There is one voltage element from potential
transformer and a current element fed from current
transformer of the system. The deflecting torque is
produced by secondary current of CT and restoring
torque is produced by voltage of potential
transformer.
•In normal operating condition, restoring torque is
more than deflecting torque. Hence relay will not
operate. But in faulty condition, the current becomes
quite large whereas voltage becomes less.
OPERATION
Consequently, deflecting torque becomes more
than restoring torque and dynamic parts of the
relay starts moving which ultimately close the No
contact of relay.
TRIPPING CHARACTERISTICS
IMPEDANCE RELAY:
It works corresponding to the ratio of V
and I of the circuit to be protected.There are two
elements in this relay ,the one produces a torque
proportional to current while the other produces
a torque proportional to voltage.The torque
produced by the current element is balanced
against torque produced by the voltage element.
The current element produces operating
torque , pickup torque which can be said to be
+ve torque.The voltage element produces
restraining torque ,reset torque which can be said
to be –ve torque.So this relay is voltage
restrained overcurrent relay.
WORKING OF IMPEDANCE RELAY:
When the fault occurs at point F in the protected zone
then the voltage drops while current increases.Thus the
ratio V/I i.e. the impedance reduces drastically.This is the
impedance of line between the point at which relay is
connected and the point F at which fault occurs.So when
the impedance reduces than its predetermined value Z ,it
trips and makes the circuit breaker open.
OPERATING CHARACTERISTICS:
As the effect of spring is dominating for the lower values
of currents ,the characteristics shows a noticiable bend at lower
curren. But for all practical purposes,the dotted line which
represents a constant value of Z may be considered as an operating
characteristics.The impedance Z which is predetermined set value is
given by,
Z=1/slope of characteristics
OPERATING CHARACTERISTICS ON R-X DIAGRAM:
DIRECTIONAL IMPEDANCE RELAY:
The directional impedance relay can
be obtained by adding a directional element in
the basic impedance relay.
DIRECTIONAL IMPEDANCE RELAY
CHARACTERISTICS:
MODIFIED DIRECTIONAL IMPEDANCE RELAY
CHARACTERISTICS:
REACTANCE RELAY:
In this relay the operating torque is
obtained by current while the restraining torque
due to a current –voltage directional relay.The
overcurrent element develops the positive torque
and directional unit produces negative torque.
Thus the reactance relay is an overcurrent
relay with the directional restraint.
The directional element is so designed
that the maximum torque angle is 90degree.
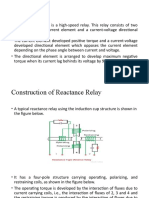
CONSTRUCTION OF REACTANCE RELAY:
The structure used for the reactance relay can be
of induction cup type.It is a four ole structure.It has
operating coil,polarizing coil and a restraining coil.
The current I flows from pole 1,through
ironcore stacking to lower pole 3.The winding
on pole 4 is fed from voltage V.The operating
torque is produced by interaction of fluxes
due to the windings carrying current coils
i.e.interaction of fluxes produced by poles1,3
and 4.Hence the operating torque is
proportional to the square of current while
the restraining torque is proportional to the
product of V and I.
OPERATING CHARACTERISTICS:
MHO RELAY OR ADMITTANCE RELAY:
The mho relay is made inherently directional by
adding a voltage winding called polarizing winding.This
relay is also called angle impedance relay.
In this relay the operating torque is obtained
by V and I element while the restraining
torque is produced by a voltage element.The
operating torque is produced by the
interaction of the fluxes due to the windings
carried by the poles 1,2 and 3.While the
restraining torque is produced by the
interaction of the fluxes due to the windings
carried by the poles 1,3 and 4.
OPERATING CHARACTERISTICS:
ADVANTAGES AND DISADVANTAGES
•High speed fault clearance which over current
relay cannot do.
•This distance protection has both primary and
backup protection.
•If the number of sections in the line is quite
large, the time setting of relay nearest to the
source would be very long. So during any fault
nearer to the source will take much time to be
isolated.
ADVANTAGE:
• The key advantage of distance protection is that
its fault coverage of the protected circuit which
is virtually independent of source impedance
variation.
DISADVANTAGE:
• It gives the resonse of both the CT and PT.Thus
it becomes difficult for the breaker to
determine whether the fault is external or
internal.
• The relay is easily affected by the arc resistance
of the line.
• It is very sensitive to power swing.
THANK YOU !!!
You might also like
- About Impedance RelayDocument8 pagesAbout Impedance RelayVikas GuptaNo ratings yet
- Distance and Differential RelayDocument15 pagesDistance and Differential RelayHimanshu Tiwari100% (1)
- Work in Substations - GeneralDocument25 pagesWork in Substations - GeneralJulian Zuluaga0% (1)
- 800 KVA Transformer SpecificationsDocument3 pages800 KVA Transformer SpecificationsRavi Bapodra100% (1)
- RelaysDocument261 pagesRelaysዛላው መናNo ratings yet
- Distance Relay or Impedance Relay Working Principle TypesDocument4 pagesDistance Relay or Impedance Relay Working Principle TypesLaurence MalanumNo ratings yet
- GROUP 7 Types of Distance ProtectionDocument18 pagesGROUP 7 Types of Distance ProtectionJohn Rey RillonesNo ratings yet
- Working Principle of Distance or Impedance RelayDocument16 pagesWorking Principle of Distance or Impedance Relayrobertovm2002No ratings yet
- SGP 9Document10 pagesSGP 9Soumajit PoddarNo ratings yet
- 15EE72 PS UNIT 2 Distance RelayDocument20 pages15EE72 PS UNIT 2 Distance RelayDr. Srinivas MNo ratings yet
- Classification of RelaysDocument17 pagesClassification of RelaysDurgesh TeredesaiNo ratings yet
- PSG Module IIDocument47 pagesPSG Module IIDr. Srinivas MNo ratings yet
- PBC Slide 2Document53 pagesPBC Slide 2Arnold SNo ratings yet
- Distance RelaysDocument14 pagesDistance RelaysSoham LohiyaNo ratings yet
- Reduced Distance RelayingDocument12 pagesReduced Distance Relayingmmorgenwaine9No ratings yet
- Different Types of RelaysDocument34 pagesDifferent Types of RelayssupriyarakshitNo ratings yet
- Distance Protection Relay - FinalDocument16 pagesDistance Protection Relay - FinalDilina Iroshan DissanayakeNo ratings yet
- Protection of Transmission LineDocument31 pagesProtection of Transmission LineEE166Srushti Vibhute.No ratings yet
- SGP 8Document9 pagesSGP 8Soumajit PoddarNo ratings yet
- Ee8602 PSG Notes - New - Unit2Document30 pagesEe8602 PSG Notes - New - Unit2Vairaperumal KNo ratings yet
- Electrical Power System ProtectionDocument8 pagesElectrical Power System ProtectionZain AbbasNo ratings yet
- RyanDocument10 pagesRyanLuis Javier PenetranteNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1-2-3Document170 pagesChapter 1-2-3Nitish Nageshwara RaoNo ratings yet
- Unit - IIDocument35 pagesUnit - IIthota nagajyothiNo ratings yet
- PS Lab ManualDocument49 pagesPS Lab Manual18-206 Ajay KumarNo ratings yet
- RelaysDocument27 pagesRelaysRakibul hossainNo ratings yet
- Important TermsDocument45 pagesImportant TermsrameshsmeNo ratings yet
- Presentation UPPTCL 400KV Substation Motiram Adda, GorakhpurDocument23 pagesPresentation UPPTCL 400KV Substation Motiram Adda, GorakhpurAnik Goyal50% (6)
- Types of Differential RelayDocument26 pagesTypes of Differential RelayEngr. Nasir AliNo ratings yet
- Static RelaysDocument11 pagesStatic RelaysBharathwaj SreedharNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Relay Types - and Characterstics Con'tDocument54 pagesChapter 2 - Relay Types - and Characterstics Con'tNamee BekeleNo ratings yet
- Long Transmission Lines: Since Long Lines Are Highly Subjected To Power Swings (Load SheddingDocument4 pagesLong Transmission Lines: Since Long Lines Are Highly Subjected To Power Swings (Load Sheddingkrishna chaitanyaNo ratings yet
- REG NO 23 (Talha Saleem)Document4 pagesREG NO 23 (Talha Saleem)Talha ChaudryNo ratings yet
- Revision Notes: By: Marta Ihuhwa PeeeDocument21 pagesRevision Notes: By: Marta Ihuhwa PeeeIhuhwa Marta TauNo ratings yet
- Assignment No 4Document4 pagesAssignment No 4NomanNo ratings yet
- Reactance RelayDocument15 pagesReactance RelayAngel RacasaNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Q and A SupplementaryDocument25 pagesTutorial Q and A SupplementaryKhadar A. FarahNo ratings yet
- Power System Protection - Part 08Document16 pagesPower System Protection - Part 08Rahul MandalNo ratings yet
- Power System Protection RelayDocument36 pagesPower System Protection RelayBikash DasNo ratings yet
- SGP PPT1Document100 pagesSGP PPT1Anley NigissieNo ratings yet
- Impedance RelaysDocument7 pagesImpedance RelaysDiseño y Gestión de ProyectosNo ratings yet
- 02 Relay Operating PrinciplesDocument16 pages02 Relay Operating PrinciplesAHMED BILALNo ratings yet
- PSG 2Document146 pagesPSG 2Shiva PavanNo ratings yet
- 13th LectureDocument73 pages13th LectureNaveed RabbaniNo ratings yet
- Transformer ProtectionDocument23 pagesTransformer ProtectionVinayak PolNo ratings yet
- Line ProtectionDocument91 pagesLine Protectionhafiz_hazreen100% (1)
- Unit-Ii Operating Principles And Relay Construction: ωt cos I I K 2 1 I k FDocument26 pagesUnit-Ii Operating Principles And Relay Construction: ωt cos I I K 2 1 I k FpdselvamNo ratings yet
- Relays - Open ElectricalDocument5 pagesRelays - Open Electricalstalin63No ratings yet
- Electrical Engineering Department Bachelor of Electrical & Biomedical EngineeringDocument74 pagesElectrical Engineering Department Bachelor of Electrical & Biomedical EngineeringGildenNo ratings yet
- PSP MODULE 3 Diffl Gener Trans BusDocument169 pagesPSP MODULE 3 Diffl Gener Trans BusJeevan N BNo ratings yet
- Module 6Document78 pagesModule 6JASPER PAYAPAYANo ratings yet
- Lesson 10Document25 pagesLesson 10Mohammad KhazaalNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Relay1Document39 pagesElectromagnetic Relay1Allen Kyle PrielaNo ratings yet
- Protective RelayDocument57 pagesProtective RelayVivek100% (1)
- Directional Overcurrent RelayDocument22 pagesDirectional Overcurrent RelayJoseph Delos ReyesNo ratings yet
- Protective RelaysDocument79 pagesProtective RelaysMd Saif AliNo ratings yet
- Exp 8 ADocument2 pagesExp 8 Asadmansaquib12No ratings yet
- Lightning Impulse Test in - Precise: Presented by S.M.G.Muthar Hussain Transformer EngineerDocument39 pagesLightning Impulse Test in - Precise: Presented by S.M.G.Muthar Hussain Transformer Engineerchaima haddoudiNo ratings yet
- RelaysDocument7 pagesRelaysRajeev RawatNo ratings yet
- Transformer Protection - 2Document34 pagesTransformer Protection - 2Naveed RabbaniNo ratings yet
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2No ratings yet
- STEM: Science, Technology, Engineering and Maths Principles Teachers Pack V10From EverandSTEM: Science, Technology, Engineering and Maths Principles Teachers Pack V10No ratings yet
- Synchronization of A Single-Phase Photovoltaic Generator With The GridDocument5 pagesSynchronization of A Single-Phase Photovoltaic Generator With The GridAdhiNo ratings yet
- Three Phase Inverter-1Document9 pagesThree Phase Inverter-1AdhiNo ratings yet
- Univ QNSDocument14 pagesUniv QNSAdhiNo ratings yet
- Compact Florescent Lamp-2Document5 pagesCompact Florescent Lamp-2AdhiNo ratings yet
- 7SR224 - Argus Complete Technical Manual (301-350)Document50 pages7SR224 - Argus Complete Technical Manual (301-350)Rosa MiñanoNo ratings yet
- Sma Installation smc7000hv Vers70 enDocument88 pagesSma Installation smc7000hv Vers70 enJuanTrenadosTorresNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2: Diode and ApplicationDocument11 pagesChapter 2: Diode and Applicationসায়েম মুহাম্মাদNo ratings yet
- 6 Adjustable Tripping Settings of A Circuit BreakerDocument14 pages6 Adjustable Tripping Settings of A Circuit BreakerBENJAMIN DULAYNo ratings yet
- Eeng448 Lab1Document3 pagesEeng448 Lab1Osama RaufNo ratings yet
- Lorentz PS4000Document2 pagesLorentz PS4000SINES FranceNo ratings yet
- 2 TRDocument2 pages2 TRbaapmatsikha5No ratings yet
- Eco Aqua LEDDocument4 pagesEco Aqua LEDthunderhossNo ratings yet
- Types of Wires and CablesDocument23 pagesTypes of Wires and CablesTanya67% (3)
- DALI Power Module: Upto64 DALI Bus 1 DALI Bus 2Document6 pagesDALI Power Module: Upto64 DALI Bus 1 DALI Bus 2Yasir ArfatNo ratings yet
- Steca Solarix PRS Instruction English - Uputstvo Solarni PaneliDocument10 pagesSteca Solarix PRS Instruction English - Uputstvo Solarni PaneliAleksandar StankovićNo ratings yet
- HRN-54, HRN-54N - : 96 Voltage Monitoring Relays in 3P With Adjustable LevelsDocument1 pageHRN-54, HRN-54N - : 96 Voltage Monitoring Relays in 3P With Adjustable LevelsN_LocusNo ratings yet
- Three Phase Fully Controlled and Half Controlled Bridge RectifierDocument10 pagesThree Phase Fully Controlled and Half Controlled Bridge RectifierGökhan KAYANo ratings yet
- Three Phase Synchronous Generators: 160 - 900 FRAME SIZES Industrial / Marine ApplicationsDocument20 pagesThree Phase Synchronous Generators: 160 - 900 FRAME SIZES Industrial / Marine ApplicationsRobiNo ratings yet
- VFD Trainer With Motor Features:: SiemensDocument6 pagesVFD Trainer With Motor Features:: Siemenshimanshu mohapatraNo ratings yet
- Understanding The Purpose of Some Electronic Components in EDocument6 pagesUnderstanding The Purpose of Some Electronic Components in EMassolo RoyNo ratings yet
- Case Studies of Power Quality Surveys Using Model 3196 Power Quality AnalyzerDocument32 pagesCase Studies of Power Quality Surveys Using Model 3196 Power Quality AnalyzerElvins AguilarNo ratings yet
- Test Report IEC 60950-1 Information Technology Equipment - Safety - Part 1: General RequirementsDocument58 pagesTest Report IEC 60950-1 Information Technology Equipment - Safety - Part 1: General Requirementsprakash barikNo ratings yet
- Connecting Other Lithium Systems To Multis and Quattros: ManualDocument5 pagesConnecting Other Lithium Systems To Multis and Quattros: ManualandresNo ratings yet
- Qatar Power Transmission System Expansion - Phase Viii: CONTRACT #GTC / 144D / 2006Document6 pagesQatar Power Transmission System Expansion - Phase Viii: CONTRACT #GTC / 144D / 2006துரைராஜ் இலட்சுமணன்No ratings yet
- Complete With DocuSign FOR TRANSFER-Asset TRDocument11 pagesComplete With DocuSign FOR TRANSFER-Asset TRLeo Tabita Jr.No ratings yet
- Technical Aptitude SetDocument7 pagesTechnical Aptitude SetSubhajit Basu0% (1)
- Three-Leg DCDC Converter For Efficient Inductive Power Transfer of Electric Vehicles For Wide-Range Battery ApplicationsDocument5 pagesThree-Leg DCDC Converter For Efficient Inductive Power Transfer of Electric Vehicles For Wide-Range Battery ApplicationsBinit ShresthaNo ratings yet
- Power System and Operation ControlDocument2 pagesPower System and Operation ControlAtul TekadeNo ratings yet
- Dist Distribution Substation EarthingDocument15 pagesDist Distribution Substation Earthinglovedeep161No ratings yet
- 4896 E EEM 3.3 Single-Phase Induction Motor With Bifilar Starting Winding ShortDocument6 pages4896 E EEM 3.3 Single-Phase Induction Motor With Bifilar Starting Winding ShortMuhamad FaizalNo ratings yet
- Orbis CatalogueDocument56 pagesOrbis CatalogueejirobaNo ratings yet
- Paper Laporan KP (English)Document7 pagesPaper Laporan KP (English)Kurniawan Prasetya NugrohoNo ratings yet