100%(3)100% found this document useful (3 votes)
1K viewsHistology Slides
Histology Slides
Uploaded by
DhruvJaiswalThis document provides information on various epithelial, muscle, nerve, and connective tissues through a series of slides. It describes the key characteristics of simple squamous, simple cuboidal, simple columnar, pseudostratified ciliated columnar, transitional, stratified squamous, and stratified cuboidal epithelia. It also summarizes the characteristics of smooth, skeletal, and cardiac muscle tissues as well as neurons, blood, and several types of cartilage and bone connective tissues. References are provided for additional histology resources.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Histology Slides
Histology Slides
Uploaded by
DhruvJaiswal100%(3)100% found this document useful (3 votes)
1K views26 pagesThis document provides information on various epithelial, muscle, nerve, and connective tissues through a series of slides. It describes the key characteristics of simple squamous, simple cuboidal, simple columnar, pseudostratified ciliated columnar, transitional, stratified squamous, and stratified cuboidal epithelia. It also summarizes the characteristics of smooth, skeletal, and cardiac muscle tissues as well as neurons, blood, and several types of cartilage and bone connective tissues. References are provided for additional histology resources.
Original Description:
Histology manual 2
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
This document provides information on various epithelial, muscle, nerve, and connective tissues through a series of slides. It describes the key characteristics of simple squamous, simple cuboidal, simple columnar, pseudostratified ciliated columnar, transitional, stratified squamous, and stratified cuboidal epithelia. It also summarizes the characteristics of smooth, skeletal, and cardiac muscle tissues as well as neurons, blood, and several types of cartilage and bone connective tissues. References are provided for additional histology resources.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as ppt, pdf, or txt
100%(3)100% found this document useful (3 votes)
1K views26 pagesHistology Slides
Histology Slides
Uploaded by
DhruvJaiswalThis document provides information on various epithelial, muscle, nerve, and connective tissues through a series of slides. It describes the key characteristics of simple squamous, simple cuboidal, simple columnar, pseudostratified ciliated columnar, transitional, stratified squamous, and stratified cuboidal epithelia. It also summarizes the characteristics of smooth, skeletal, and cardiac muscle tissues as well as neurons, blood, and several types of cartilage and bone connective tissues. References are provided for additional histology resources.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as ppt, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 26
Histology Slides
Biology 131 – Anatomy and
Physiology
Instructor: Ruth Williams
Epithelial Tissues
No intercellular matrix.
Avascular
Contains nerve endings
Lie on a basement
membrane.
Able to undergo mitosis.
Develop from all three fetal
tissues.
One surface of cells is
exposed to a space or cavity.
Epithelial Tissues
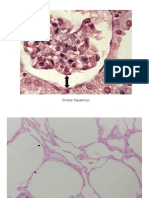
Simple Squamous
Epithelium
Single layer of cells.
Cells are longer than
they are wide.
Nuclei tend to bulge
into a space.
Fxns
Epithelial Tissues
Simple cuboidal
epithelium
Single layer of cells
Width of cell is
roughly equal to
height of cell.
Fxns
Epithelial Tissues
Simple Columnar
Epithelium
Single layer of cells
Height of cells is
greater than cell
width.
Fxns
Epithelial Tissues
Pseudostratified
ciliated columnar
Actually a simple
epithelium – every
cell touches the
basement
membrane.
Contains goblet
cells.
Epithelial Tissues
Transitional
Epithelium
Located in urinary
bladder and ureters
only.
Transitions from
stratified cuboidal to
stratified squamous
Epithelial Tissues
Stratified Squamous
When you are
looking at a stratified
epithelium, to identify
the shape of the cells
always look at the
top most layer.
Stratified Squamous
Epithelium is either
keratinized or non-
keratinized
Epithelial Tissues
Stratified Cuboidal
Located primarily in
ducts of glands
Muscle Tissue
Smooth Muscle
Myocytes lack visible
striations.
Smooth muscle is
located in visceral
organs.
Smooth muscle is
involuntary muscle.
Muscle Tissue
Skeletal Muscle
Myocytes are
multinucleated.
Myocytes run entire
length of muscle.
Myocytes are
striated.
Skeletal muscle is
voluntary muscle.
Muscle Tissue
Cardiac Muscle
Myocardial cells are short
and branched.
Myocardial cells are
striated.
Myocardial cells are
joined by intercalated
disks (note arrow in
picture).
Cardiac muscle is
involuntary muscle.
Nerve Tissue
Neuron
Contains cell body,
axon and dendrites.
In this slide you can
see the cell body of a
neuron and the area
of an axon, called the
axon hillock, where
the axon attaches to
the cell body (note
arrow).
Connective Tissue
Blood
Fluid connective
tissue.
Contains leukocytes
and erythrocytes
Green arrows point
to neutrophils.
Blue arrow points to
a monocyte.
Platelets and
erythrocytes are
also visible.
Connective Tissue
Hyaline Cartilage
Most abundant cartilage.
Located in most joints.
Precursor to most long
bones of body.
Note how cells of
hyaline cartilage ‘bunch
up’.
Note how chondrocytes
‘shrink’ away from their
lacunae (pockets within
semisolid intercellular
matrix of cartilage) –
characteristic of
cartilage.
Connective Tissue
Elastic Cartilage
In order to see
elastic proteins in
elastic cartilage a
special stain is used.
Elastic fibers will stain
gray to black in color.
Connective Tissue
Fibrocartilage
Primarily located in
intervertebral disks
and pubic
symphysis.
Note how
chondrocytes tend to
line up.
Compared to a
herring bone
pattern.
Connective Tissue
Bone
This is a slide of
ground/polished
bone.
Cells of bone are
called osteocytes.
Connective Tissue
Bone
Connective Tissue
Connective Tissue
Proper
Loose areolar
connective tissue.
Found in most tissues
of the body.
Connective Tissue
Connective Tissue
Proper
Dense Regular
Connective Tissue
Collagen fibers run
parallel to one
another.
Note cells of dense
regular c.t., called
fibrocytes, are located
between collagen
fibers.
Connective Tissue
Connective Tissue
Proper
Dense Irregular
connective tissue.
Connective Tissue
Connective Tissue
Proper
Elastic connective
tissue
Connective Tissue
Connective Tissue
Proper
Reticular connective
tissue
ConnectiveTissue
Connective Tissue
Proper
Adipose connective
tissue.
Brown adipose tissue
is found in newborns
and hibernating
animals.
References
Integumentary System
www.udel.edu/Biology/wags/histopage/colorpage/cin/cin.htm
The JayDoc HistoWeb, University of Kansas Medical Center,
1996
www.kumc.edu/instruction/medicine/anaotmy/histoweb/index
.htm
Compact Bone Histology
www.cellbio/utmb.edu/microanatomy/bone/compact_bone_hi
stology.htm
General Histology Images, USC School of Dentistry
www.usc.edu/hsc/dental/ghisto
You might also like
- Color Textbook of Histology - Gartner - Hiatt, 3EDocument569 pagesColor Textbook of Histology - Gartner - Hiatt, 3EPanda Mimi100% (4)
- Histology Question Bank-1Document55 pagesHistology Question Bank-1Abd El-Rahman Salah100% (6)
- Histology NotesDocument4 pagesHistology NotesThonieroce Apryle Jey Morelos100% (5)
- Histology Test Bank PrelimsDocument40 pagesHistology Test Bank Prelimsjed larsen capulong gavino100% (8)
- RENAL HISTOLOGY MCQsDocument6 pagesRENAL HISTOLOGY MCQsMohammad zreadNo ratings yet
- Histology Slides EpitheliumDocument3 pagesHistology Slides EpitheliumNourhan Jamal100% (1)
- Histology UnkownsDocument11 pagesHistology UnkownsBec Jeans100% (3)
- Histology: Lecture NotesDocument97 pagesHistology: Lecture Notessky100% (4)
- Histology For RetardsDocument57 pagesHistology For RetardsDavid Degaetano100% (1)
- Histology World Histology TestbankDocument6 pagesHistology World Histology TestbankRalp Barrios100% (1)
- Histology-World! Histology Testbank-Skin 1aDocument5 pagesHistology-World! Histology Testbank-Skin 1aKat Jornadal100% (1)
- Quiz HistologyDocument28 pagesQuiz HistologyMedShare100% (30)
- Histology Laboratory Manual: Olgga A. Hara MSDocument77 pagesHistology Laboratory Manual: Olgga A. Hara MSMark LopezNo ratings yet
- Embryologypracticequestionswithanswers 140707144050 Phpapp02Document120 pagesEmbryologypracticequestionswithanswers 140707144050 Phpapp02oopie0% (1)
- Histology of Urinary SystemDocument36 pagesHistology of Urinary Systemdiraf100% (2)
- Questions From Previous ExamsDocument6 pagesQuestions From Previous ExamsFaddy Oraha100% (1)
- MCQ BloodDocument7 pagesMCQ BloodMoh Moh Moh100% (6)
- Histology Practice PracticalDocument38 pagesHistology Practice PracticalDeep Patel88% (8)
- Histology Photo AtlasDocument52 pagesHistology Photo AtlasJustin McCormick100% (4)
- Histology - Important NotesDocument32 pagesHistology - Important NotesAbby Aitken100% (7)
- Slide N Label HistologyDocument35 pagesSlide N Label HistologyIsidore Patrick100% (2)
- Histology ImagesDocument10 pagesHistology ImagesLilliana Beltran100% (1)
- A Learning System in HistologyDocument248 pagesA Learning System in HistologyNarcélio Júnior100% (3)
- Histology Quiz 3Document10 pagesHistology Quiz 3Nick JacobNo ratings yet
- Histology LabDocument207 pagesHistology LabDandali100% (3)
- General Histology FinalDocument60 pagesGeneral Histology FinalDr P N N Reddy100% (1)
- HD 201 E1 20140127 Histology of The Male Reproductive SystemDocument7 pagesHD 201 E1 20140127 Histology of The Male Reproductive SystemMaxine Alba100% (1)
- JP Gunasegran HistologyDocument454 pagesJP Gunasegran Histologykarthi keyan100% (7)
- Histology Questions QuizDocument28 pagesHistology Questions QuizminervamoonNo ratings yet
- Essential HistologyDocument520 pagesEssential Histologyv@r0_5100% (7)
- Introduction To HistologyDocument32 pagesIntroduction To HistologyPushparaj ShettyNo ratings yet
- Histology Exam IV Review Part 2Document26 pagesHistology Exam IV Review Part 2ashdmb217No ratings yet
- HistologyDocument57 pagesHistologyAnonymous 9xheGVRM1100% (2)
- Human HistologyDocument128 pagesHuman HistologyBreane Denece LicayanNo ratings yet
- Histology StainsDocument7 pagesHistology StainsFrozenMan100% (2)
- Histology Slide GuideDocument50 pagesHistology Slide GuideEldar Sulejmanovic100% (3)
- Histology ExamsDocument2 pagesHistology Examsqarafi4007No ratings yet
- Histology Model ADocument7 pagesHistology Model AOzgan SüleymanNo ratings yet
- Histology Mock ExamDocument73 pagesHistology Mock ExamRozen GaiserNo ratings yet
- Histology Seminar 3 MCQDocument31 pagesHistology Seminar 3 MCQNeo ShiriNo ratings yet
- Practical Slides Under MicroscopeDocument57 pagesPractical Slides Under MicroscopeAziz Bosteen100% (2)
- Practical Histopathology Made Easy For Laboratory ProfissionalsDocument102 pagesPractical Histopathology Made Easy For Laboratory ProfissionalsAnonymous PizJCvW86% (7)
- Histology QuestionsDocument3 pagesHistology QuestionsAlec Maquiling100% (1)
- Key Histology Exam 2 Fall 2007wDocument18 pagesKey Histology Exam 2 Fall 2007wlogang48100% (4)
- Histology SlidesDocument72 pagesHistology SlidesLilliana BeltranNo ratings yet
- Histology, Lecture 1, Introduction To Histology (Lecture Notes)Document6 pagesHistology, Lecture 1, Introduction To Histology (Lecture Notes)Ali Al-Qudsi100% (8)
- SMS..exam 1Document8 pagesSMS..exam 1Ozgan SüleymanNo ratings yet
- Histology-World! Histology Testbank-Nervous System 1Document3 pagesHistology-World! Histology Testbank-Nervous System 1Kat JornadalNo ratings yet
- Histology Notes 2Document13 pagesHistology Notes 2Lukas BüchlerNo ratings yet
- 1st Year MBBS Histology Slides and Identification Points (FINAL)Document57 pages1st Year MBBS Histology Slides and Identification Points (FINAL)Lucas Victor Almeida50% (6)
- Histology, Lecture 5, Muscular Tissue (Slides)Document17 pagesHistology, Lecture 5, Muscular Tissue (Slides)Ali Al-Qudsi100% (6)
- Histology Worksheets All in OneDocument15 pagesHistology Worksheets All in OneGabriel ParasNo ratings yet
- ThreePointer's Guide To Histology Steeple Chase For 022 ClassDocument54 pagesThreePointer's Guide To Histology Steeple Chase For 022 ClassNnaemeka Neboh100% (1)
- Histology-World! Histology Testbank-Cartilage 2aDocument7 pagesHistology-World! Histology Testbank-Cartilage 2aAya AhmedNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic Criteria Handbook in Histopathology: A Surgical Pathology Vade MecumFrom EverandDiagnostic Criteria Handbook in Histopathology: A Surgical Pathology Vade MecumNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 7 Structural Organisation in Animals - WatermarkDocument21 pagesChapter - 7 Structural Organisation in Animals - WatermarkMehak ShireenNo ratings yet
- Cuizon Lab Act 3Document18 pagesCuizon Lab Act 3Clarizza Joy J. CuizonNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument23 pagesAnatomy and Physiologyapi-464344582100% (4)
- 03 - Blood - and - Blood - Stains Forensic ChemistryDocument21 pages03 - Blood - and - Blood - Stains Forensic ChemistryEmelie TipayNo ratings yet
- Blood and Bloodstains: Harry Danny L. Aspillaga Instructor Forensic Chemistry and ToxicologyDocument50 pagesBlood and Bloodstains: Harry Danny L. Aspillaga Instructor Forensic Chemistry and ToxicologyHarry Danny AspillagaNo ratings yet
- Rose Waaler Test: Jayan Bajracharya - B.SC - MLT 3 YearDocument10 pagesRose Waaler Test: Jayan Bajracharya - B.SC - MLT 3 YearRajkishor Yadav100% (1)
- Blood ReportDocument39 pagesBlood Reportputri Mentari100% (1)
- Blood Bank International Standard ISBT Science Series - 2008 - Hardwick - Blood ProcessingDocument29 pagesBlood Bank International Standard ISBT Science Series - 2008 - Hardwick - Blood ProcessingShan AhmadNo ratings yet
- Blood TransfusionDocument6 pagesBlood TransfusionSophia Mae RoseteNo ratings yet
- PBM Guidelines 4 Template Explanation of Base Excess Measurement Apr21Document2 pagesPBM Guidelines 4 Template Explanation of Base Excess Measurement Apr21Ricardo Antonio Rivas SánchezNo ratings yet
- 761 2107 2 PBDocument7 pages761 2107 2 PBAlvia QothrunnadaNo ratings yet
- Fun For Movers 4th EditionDocument1 pageFun For Movers 4th EditionDushitha JayakumarNo ratings yet
- Blood Donation System Report in C++Document44 pagesBlood Donation System Report in C++vickyvermaNo ratings yet
- L2-SURG-Hemostasis, Surgical Bleeding, - Transfusion (Aug2521)Document8 pagesL2-SURG-Hemostasis, Surgical Bleeding, - Transfusion (Aug2521)Marc Lyndon CafinoNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Flowering PlantsDocument16 pagesAnatomy of Flowering PlantsSadik FsNo ratings yet
- Blood Transfusion ReactionsDocument33 pagesBlood Transfusion Reactionsmarianne.bilaoen09100% (1)
- Handout 3.1 Cell Animal Vs Plant TissueDocument60 pagesHandout 3.1 Cell Animal Vs Plant Tissuearianeleurienee.poralanNo ratings yet
- Thromboelastography (TEG) or Thromboelastometry (ROTEM) To Monitor Haemostatic Treatment Versus Usual Care in Adults or Children With BleedingDocument149 pagesThromboelastography (TEG) or Thromboelastometry (ROTEM) To Monitor Haemostatic Treatment Versus Usual Care in Adults or Children With Bleedingjuancar90No ratings yet
- ملخص اناتومي مهم مليونDocument7 pagesملخص اناتومي مهم مليونSaif AltamareNo ratings yet
- Amoeba Sisters: Video Recap Multiple Alleles (Blood Types)Document2 pagesAmoeba Sisters: Video Recap Multiple Alleles (Blood Types)Kate PruessmannNo ratings yet
- Blood Disorders: LeukemiaDocument134 pagesBlood Disorders: LeukemiaPhan KhoiNo ratings yet
- Erythrocyte Sedimentation RateDocument2 pagesErythrocyte Sedimentation RateLecture NotesNo ratings yet
- Animal Tissues - DPP (00-00-2022)Document14 pagesAnimal Tissues - DPP (00-00-2022)mahir malikNo ratings yet
- MTAP ISBB - Sir JJ (Merged)Document9 pagesMTAP ISBB - Sir JJ (Merged)Nathan DrakeNo ratings yet
- (Stasi) How To Approach Thrombocytopenia PDFDocument7 pages(Stasi) How To Approach Thrombocytopenia PDFrodtobingNo ratings yet
- Blood Products. Preparation of Blood ComponentsDocument32 pagesBlood Products. Preparation of Blood ComponentsSanthiya MadhavanNo ratings yet
- Tissue ClassworkDocument5 pagesTissue ClassworkRajesh Kanna A亗No ratings yet
- QC ABO RH BloodDocument62 pagesQC ABO RH BloodrhoderickNo ratings yet
- Scenario 2 Excited To Observe Skeletal Muscle, A Sprinter, Marathon Runner, and Weightlifter AthleteDocument15 pagesScenario 2 Excited To Observe Skeletal Muscle, A Sprinter, Marathon Runner, and Weightlifter AthleteAisyah FawNo ratings yet
- Ahg NotesDocument5 pagesAhg NotesRonron GarciaNo ratings yet
- Blood DonationDocument11 pagesBlood DonationSagar AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Data Alkes KalibrasiDocument41 pagesData Alkes Kalibrasianisa13No ratings yet