0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
42 viewsApplications of Computers in Hospital Pharmacy Practice
Applications of Computers in Hospital Pharmacy Practice
Uploaded by
patil dewanshi kThis document discusses the applications of computers in hospital pharmacy practices. It describes how computer systems can manage patient record databases, enter medication orders, prepare lists like patient profiles and fill lists, and monitor drug use and therapy. Key functions of hospital computer systems include patient data management, order entry, generating labels and reports, and maintaining patient medication profiles that include medical history and prescription records. The computerization of health records through electronic health record systems can improve patient care, coordination, and outcomes while increasing efficiency and cost savings for healthcare providers.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Applications of Computers in Hospital Pharmacy Practice
Applications of Computers in Hospital Pharmacy Practice
Uploaded by
patil dewanshi k0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
42 views12 pagesThis document discusses the applications of computers in hospital pharmacy practices. It describes how computer systems can manage patient record databases, enter medication orders, prepare lists like patient profiles and fill lists, and monitor drug use and therapy. Key functions of hospital computer systems include patient data management, order entry, generating labels and reports, and maintaining patient medication profiles that include medical history and prescription records. The computerization of health records through electronic health record systems can improve patient care, coordination, and outcomes while increasing efficiency and cost savings for healthcare providers.
Original Title
Untitled
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
This document discusses the applications of computers in hospital pharmacy practices. It describes how computer systems can manage patient record databases, enter medication orders, prepare lists like patient profiles and fill lists, and monitor drug use and therapy. Key functions of hospital computer systems include patient data management, order entry, generating labels and reports, and maintaining patient medication profiles that include medical history and prescription records. The computerization of health records through electronic health record systems can improve patient care, coordination, and outcomes while increasing efficiency and cost savings for healthcare providers.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
42 views12 pagesApplications of Computers in Hospital Pharmacy Practice
Applications of Computers in Hospital Pharmacy Practice
Uploaded by
patil dewanshi kThis document discusses the applications of computers in hospital pharmacy practices. It describes how computer systems can manage patient record databases, enter medication orders, prepare lists like patient profiles and fill lists, and monitor drug use and therapy. Key functions of hospital computer systems include patient data management, order entry, generating labels and reports, and maintaining patient medication profiles that include medical history and prescription records. The computerization of health records through electronic health record systems can improve patient care, coordination, and outcomes while increasing efficiency and cost savings for healthcare providers.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 12
APPLICATIONS OF COMPUTERS IN
HOSPITAL PHARMACY PRACTICE
INTRODUCTION
Computers have played an important role in the
development of clinical pharmacy practice and basic
pharmacy research.
The use of computers in hospital administration are medical
research becomes the need of large hospitals.
The computer is a processor whit processes large quantity of
data which may be numbers, letters or picture elements Very
fastly and accurately.
The modern physician is so busy that he does not have
enough time to give personal attention to the patients.
Todays pharmacist's responsibilities are also increased.
Following a list of common capabilities and
functions of modern hospital computer system.
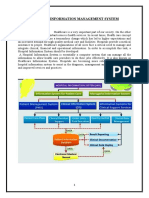
1. Patient record database management.
2. Entries of medication orders.
3. Preparation of lists.
4. Patient medication profile.
5. Drug use review.
6. Drug therapy monitoring and problem detection.
7. Purchasing and inventory control.
8. Billing procedures.
9. Drug formulary search and update.
Applications of Computers In
hospital pharmacy practice
1. Patient Record Data Base Management:
pharmacy computer system must manage that the
pharmacy's patient record database is continually
updated to reflect the current status of all
patients.
The computer system should be capable of
producing the other information such as: Present
diagnosis, allergies, weight. height, name of
attending physician and other special notes
regarding the patient.
2. Entries of Medication Orders:
Rapid processing of drug orders is the
essential function of computer system.
Formatted data entry screens should allow
easy entry and retrieval of orders.
A pharmacist should be able to retrieve
orders for review prior to administration to
patient.
Data may be entered by use of codes for
drug name, dosing schedule. All the drug
orders should contain the following:
• Drug name (code)
• Drug generic name and strength
• Route of administration
• Dosage schedule
• Starting date
• Stopping date
• Physician code
• Pharmacist verification code
3. Preparation of Lists
The computer system should be capable of
producing the labels and reports in the form of
(I) Patient medication profile
(ii) ''Fill-lists" for preparation of individual doses
(iii) List of medications charged
(iv) Drug order renewal lists for the prescriber and
(v) Medication Administration Record (MAR).
Orders entered for 11/ solutions, admixtures and
total parenteral nutrition (TPN) should be
separately prepared.
4. Patient's Medication Profile
A pharmacist keeps prescription records
of patients which are referred to as pa,
history medication profile.
The purpose of patient medication profile
is to provide the patient's previous
medication
This enables patient's medication to be
monitored and provides the data for
consultation. The patient medication profile
contains the following basic information.
The patient medication profile contains the following basic
information
Patient's name
Address
Telephone No.
Age Date of birth
Allergy
Sensitivities
Special diet
Chronic Medical Conditions
Date of Prescription Dispensed
Prescription item
Dosage instruction
Quantity
ELECTRONIC HEALTH RECORDS (EHRs)
1. Digital technology has radically transformed
our lives.
2. Fortunately, we are witnessing the use of
smart phones, tablets and web-enabled
devices in our daily life activities in todays
modern world.
3. Information explosion and availability at single
click, is possible due to these digital
technologies
Medicines and healthcare are information rich
enterprises today.
allergies, radiology images and laboratory test
results EHR workflow.
broader view of a patient's care. V beyond
Standard Clinical data collected in a provider's
office and can be inclusive 0" EHR contains a
patient's medical history, diagnoses,
medications, treatment
Benefits of EHRs
Followings are the important benefits of HER
1. improved patient care.
2. Increase patient participation.
3. Improved care coordination.
4.Improved diagnostics and patient
outcomes.
5, Practice efficiencies and cost savings.
You might also like
- Hospital Pharmacy NotesDocument15 pagesHospital Pharmacy NotesChunnie JakosalemNo ratings yet
- Prescription Handling at Retail Pharmacy and Record KeepingDocument13 pagesPrescription Handling at Retail Pharmacy and Record KeepingMaryam AzizNo ratings yet
- Module 1Document21 pagesModule 1mannan100% (2)
- Pseudoacromegaly Induced by The Long-Term Use of MinoxidilDocument4 pagesPseudoacromegaly Induced by The Long-Term Use of MinoxidilheightdocNo ratings yet
- Application of Computer in PharmacyDocument8 pagesApplication of Computer in PharmacyHashim MohammedNo ratings yet
- 5#application of Computers in Hospital PharmacyDocument14 pages5#application of Computers in Hospital PharmacySamra BatoolNo ratings yet
- Pharmacy Informatics NotesDocument3 pagesPharmacy Informatics NotesSmoi Liver100% (2)
- Unit 3 Computer Applications in PharmacyDocument8 pagesUnit 3 Computer Applications in PharmacyHiba MohammedNo ratings yet
- Application of Computer in PharmacyDocument4 pagesApplication of Computer in Pharmacybryankachocho17100% (1)
- HCP Capter 7 BlackDocument4 pagesHCP Capter 7 BlackDrx Brajendra LodhiNo ratings yet
- Computer System in Hospital Pharmacy 1Document9 pagesComputer System in Hospital Pharmacy 1Sreya Sanil100% (4)
- PharmacyDocument5 pagesPharmacyalepikinsamsonNo ratings yet
- What Is PharmacoinformaticsDocument11 pagesWhat Is PharmacoinformaticsDRx Sonali TareiNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 CompleteDocument32 pagesUnit 3 CompleteKGC PESHAWARNo ratings yet
- Computer Assignment1Document9 pagesComputer Assignment1AlizaNo ratings yet
- 221 Unit 1&2Document10 pages221 Unit 1&2Ning BalderasNo ratings yet
- UNIT 6 Pharmacy TrendsDocument3 pagesUNIT 6 Pharmacy TrendsJenilyn FarnacioNo ratings yet
- Unit - III Part - IIDocument5 pagesUnit - III Part - IImotupat90No ratings yet
- Technologies in PharmacologyDocument6 pagesTechnologies in Pharmacologylaila111No ratings yet
- CPP 463 Pharmacy InformaticsDocument3 pagesCPP 463 Pharmacy Informaticsstephamazony5No ratings yet
- The Role of Technology in The Medication Use ProcessDocument6 pagesThe Role of Technology in The Medication Use Processhadukenryu9761100% (1)
- Project Seminar Hospice FedoraDocument3 pagesProject Seminar Hospice FedoralalithaNo ratings yet
- Use of Computer in Medical Field: Pharmacy Practice-IiiDocument4 pagesUse of Computer in Medical Field: Pharmacy Practice-IiiZaid RazaNo ratings yet
- Role of Computer in HospitalsDocument50 pagesRole of Computer in HospitalsLaiba KhalidNo ratings yet
- Session ThreeDocument19 pagesSession ThreeFrankdavid07No ratings yet
- Himms Copy KoDocument5 pagesHimms Copy KoRochelle Anne Abad BandaNo ratings yet
- Online Patient Management SystemDocument6 pagesOnline Patient Management SystemPrashant Pratap SinghNo ratings yet
- Design and Implementation of Automated PDocument19 pagesDesign and Implementation of Automated PAbubakar Bin AliyuNo ratings yet
- Computerized Medical Lab Record SystemDocument41 pagesComputerized Medical Lab Record SystemUmar Ridwan saniNo ratings yet
- Overview of Pharmacy Information SystemsDocument4 pagesOverview of Pharmacy Information SystemsMasinovTale0% (2)
- Application of Computer in Hospital PharmacyDocument3 pagesApplication of Computer in Hospital PharmacyAyesha LiaqatNo ratings yet
- Hospital Prescription SystemDocument21 pagesHospital Prescription SystemdamtishhilcoetechNo ratings yet
- Hospital Prescription SystemDocument13 pagesHospital Prescription SystemAbraham Damtew0% (1)
- HIMMSDocument5 pagesHIMMSRochelle Anne Abad BandaNo ratings yet
- Hostpital PharmacyDocument9 pagesHostpital PharmacyFallen AngelNo ratings yet
- New Design - and - Implementation - of - A - ComputeriDocument30 pagesNew Design - and - Implementation - of - A - ComputeriAkorede OlasunkanmiNo ratings yet
- Computer in Community Pharmacy by Adnan Sarwar ChaudharyDocument10 pagesComputer in Community Pharmacy by Adnan Sarwar ChaudharyDr-Adnan Sarwar Chaudhary100% (1)
- Importance of Proficiency in Navigating The Patient'S Medical RecordDocument4 pagesImportance of Proficiency in Navigating The Patient'S Medical RecordWulan WulanNo ratings yet
- Application of Compute in Hospital PhamacyDocument9 pagesApplication of Compute in Hospital Phamacymunim008No ratings yet
- Requirements For An Open-Source Pharmacy Dispensing and Stores Management Software Application For Developing CountriesDocument14 pagesRequirements For An Open-Source Pharmacy Dispensing and Stores Management Software Application For Developing CountriesGFBMGFBLKNGMDSBGFNFHNFHNMHDNo ratings yet
- Diagnosis, and TherapiesDocument6 pagesDiagnosis, and TherapiesHoney MacabuhayNo ratings yet
- Chapter Two Literature Review: 2.1 Background Theory of StudyDocument3 pagesChapter Two Literature Review: 2.1 Background Theory of StudyAyinde AbiodunNo ratings yet
- Pharmacy Information SystemsDocument3 pagesPharmacy Information SystemsEköw Santiago Javier60% (5)
- Importance of Proficiency in Navigating The Patient'S Medical RecordDocument4 pagesImportance of Proficiency in Navigating The Patient'S Medical RecordHikmah khanza PutriNo ratings yet
- Hospital PharmacoepidemiologyDocument15 pagesHospital PharmacoepidemiologyAswin DamodaranNo ratings yet
- .Pharmacy Management System A ReviewDocument6 pages.Pharmacy Management System A ReviewsnehaNo ratings yet
- Design and Implementation of Web Base Hospital Management SystemDocument36 pagesDesign and Implementation of Web Base Hospital Management SystemMikel KingNo ratings yet
- Applications of Computer Science in PharmacyDocument33 pagesApplications of Computer Science in PharmacyPaul DavidNo ratings yet
- Application of Computer in Community PharmacyDocument6 pagesApplication of Computer in Community PharmacyAlizaNo ratings yet
- Drug Procurement and Institution Tracking SystemDocument78 pagesDrug Procurement and Institution Tracking SystemLatifa AmeirNo ratings yet
- Wa0008.Document21 pagesWa0008.elementalagni1728No ratings yet
- Hospital Information Management SystemDocument13 pagesHospital Information Management SystemSarita yadavNo ratings yet
- Patient Management System (New Reviewed)Document39 pagesPatient Management System (New Reviewed)Ajewole Eben Tope100% (1)
- Health Information TechnologyfinalDocument8 pagesHealth Information TechnologyfinalFranzia Izandra Alkuino Mojica100% (1)
- DRUG PROCUREMENT AND INSTITUTION TRACKING SYSTEM (Copy)Document8 pagesDRUG PROCUREMENT AND INSTITUTION TRACKING SYSTEM (Copy)Jibreen AlanjiroNo ratings yet
- Med2X - ON-PAGE REQUIREMENT - PHARMACY PAG...Document2 pagesMed2X - ON-PAGE REQUIREMENT - PHARMACY PAG...vishwaparthNo ratings yet
- Online Patients Record Platform Using PHPDocument31 pagesOnline Patients Record Platform Using PHPAmaan B EydreesNo ratings yet
- Analysis Phase: 1. AbstractDocument6 pagesAnalysis Phase: 1. AbstractNaveed Younas RathoreNo ratings yet
- Hospital Prescription SystemDocument24 pagesHospital Prescription SystemAbraham DamtewNo ratings yet
- Asignment of APTS, 2014Document4 pagesAsignment of APTS, 2014amenure4No ratings yet
- Hospital Management SystemDocument12 pagesHospital Management SystemSingh Vadan0% (1)
- Newman's Certified Electronic Health Records Technician Study GuideFrom EverandNewman's Certified Electronic Health Records Technician Study GuideNo ratings yet
- Stok Benang Kamar OperasiDocument5 pagesStok Benang Kamar OperasirendyNo ratings yet
- Respironics Innospire Elegance Compressor ManualDocument11 pagesRespironics Innospire Elegance Compressor ManualJose Guillermo Muñoz CamachoNo ratings yet
- Breakthrough Devices Program Draft Guidance For Industry and Food and Drug Administration StaffDocument28 pagesBreakthrough Devices Program Draft Guidance For Industry and Food and Drug Administration Staffkarunakaran09No ratings yet
- GastricDocument6 pagesGastricMohsin ShahbazbuttNo ratings yet
- Kinematica IndustryDocument12 pagesKinematica IndustryJonathan Escalant SoloNo ratings yet
- IDMP Stands For "Identification of Medicinal Products"Document2 pagesIDMP Stands For "Identification of Medicinal Products"Atthaphon KhamwangprukNo ratings yet
- Syllabus ClinPhar143Document2 pagesSyllabus ClinPhar143Angel GoNo ratings yet
- CM BannuDocument8 pagesCM BannuYounis KhanNo ratings yet
- Medical English Tests UBELTDocument1 pageMedical English Tests UBELTpatriciawidd0% (1)
- Instructions To Author-REACH2020Document2 pagesInstructions To Author-REACH2020pharma xlNo ratings yet
- Current Analytical Methods For Determination of KetoconazoleDocument14 pagesCurrent Analytical Methods For Determination of Ketoconazoleiabureid7460No ratings yet
- Daftar Barang 29-05-2021Document14 pagesDaftar Barang 29-05-2021Apotek VictoryNo ratings yet
- Migraine EbmDocument10 pagesMigraine EbmAfni Panggar BesiNo ratings yet
- Prof Dr. Zhari - Halal Pharma IngredientsDocument82 pagesProf Dr. Zhari - Halal Pharma IngredientsHisyamuddin Kamarudin100% (1)
- Treatment of Diabetes MellitusDocument31 pagesTreatment of Diabetes MellitusIrfan Idealist100% (2)
- Guidelines For Registration of Allopathic Drugs CTDDocument98 pagesGuidelines For Registration of Allopathic Drugs CTDankitasaxena055No ratings yet
- PCOL 2 FLModule #2 (AntiHTNsive Agents) PDFDocument10 pagesPCOL 2 FLModule #2 (AntiHTNsive Agents) PDFAngel de la VictoriaNo ratings yet
- Parp Inhibitors: (Poly Adp-Ribose Polymerase)Document45 pagesParp Inhibitors: (Poly Adp-Ribose Polymerase)Gumus MedelaineNo ratings yet
- MarketLineIC Aurobindo Pharma LTD Profile 100122Document45 pagesMarketLineIC Aurobindo Pharma LTD Profile 100122Smarajeet DasNo ratings yet
- Immediate download Understanding Pharmacology for Pharmacy Technicians 1st Edition Mary Ann Stuhan ebooks 2024Document40 pagesImmediate download Understanding Pharmacology for Pharmacy Technicians 1st Edition Mary Ann Stuhan ebooks 2024dyadyamalet100% (3)
- Platinum Formulary 2016Document61 pagesPlatinum Formulary 2016jNo ratings yet
- Accredited Philippine Importers As of Feb 4 2015Document245 pagesAccredited Philippine Importers As of Feb 4 2015PortCalls100% (3)
- Daftar Barang Astro 19 JUNI 2023Document32 pagesDaftar Barang Astro 19 JUNI 2023ngawi farmasiNo ratings yet
- GingivitisDocument30 pagesGingivitisSharon DingNo ratings yet
- Comparison of Acid-Neutralizing Capacity of Commonly Antacids in Erbil CityDocument5 pagesComparison of Acid-Neutralizing Capacity of Commonly Antacids in Erbil CityNimesh ModiNo ratings yet
- Practical and Experimental PharmacologyDocument4 pagesPractical and Experimental Pharmacologyritika sonareNo ratings yet
- Otezla Epar Product Information - CsDocument41 pagesOtezla Epar Product Information - CsziipiikNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Biopharmaceutical ScienceDocument295 pagesIntroduction To Biopharmaceutical ScienceNgoc Loi NguyenNo ratings yet