0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
Heat Transfer
Uploaded by
shashinaganurThe document discusses three primary modes of heat transfer: conduction, convection, and radiation. It provides details on each mode, including definitions and relevant equations like Fourier's Law, Newton's Law of Cooling, and the Stefan-Boltzmann Law.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
Heat Transfer
Uploaded by
shashinaganur0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
The document discusses three primary modes of heat transfer: conduction, convection, and radiation. It provides details on each mode, including definitions and relevant equations like Fourier's Law, Newton's Law of Cooling, and the Stefan-Boltzmann Law.
Original Title
Heat Transfer ppt - Copy
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
The document discusses three primary modes of heat transfer: conduction, convection, and radiation. It provides details on each mode, including definitions and relevant equations like Fourier's Law, Newton's Law of Cooling, and the Stefan-Boltzmann Law.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
Heat Transfer
Uploaded by
shashinaganurThe document discusses three primary modes of heat transfer: conduction, convection, and radiation. It provides details on each mode, including definitions and relevant equations like Fourier's Law, Newton's Law of Cooling, and the Stefan-Boltzmann Law.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1/ 10
Date-19/07/2023
HEAT TRANSFER METHOD
Thermax-Sudarshan Chemicals Ltd. Roha
INTRODUCTION
• Heat transfer refers to the process by which thermal energy
is transferred from one object or system to another due to a
temperature difference. It occurs in various forms and plays a
fundamental role in our everyday lives and numerous
industrial processes.
• The driving force behind heat transfer is the temperature
difference between two objects or regions. Heat naturally
flows from a higher temperature region to a lower
temperature region until thermal equilibrium is reached,
where both objects have the same temperature. The goal of
heat transfer is to balance temperatures and equalize
thermal energy distribution.
Type of Heat Transfer
There are three primary modes of heat transfer:
1. Conduction
2. Convection
3. Radiation
Conduction
Conduction is the transfer
of heat through direct
contact between solid
objects. In a boiler,
conduction is important
for the transfer of heat
from the combustion
chamber to the boiler
tubes or heat exchanger
walls. The hot gases or
flames come into contact
with the walls, and heat is
conducted from the
hotter surface to the
cooler surface.
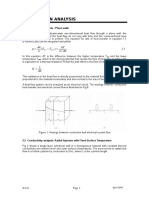
Fourier's Law
• The main condition of heat transfer by conduction is Temperature difference and
always heat flows from a hotter body to colder body.
• Fourier's law state that- “Rate of heat transfer is the product of Area normal to heat
flow path, temperature gradient and thermal conductivity of the material".
Mathematically this can be written as
• q = dQ/dt = -KA dt/dx
Where
• q = Rate of heat transfer
• K = Thermal conductivity of the Conducting material
• A = Area normal to heat flow path
• dt/dx = temperature gradient or the rate of change of temperature with reference to
the distance in the direction of heat flow.
Convection
Convection is the transfer of
heat through the movement
of fluids (liquids or gases). In a
boiler, convection occurs as
the hot gases generated by
combustion rise and carry
heat away from the
combustion chamber. This
convective heat transfer is
responsible for heating the
water or generating steam
inside the boiler. The
movement of the fluid helps
distribute heat more evenly
and improves overall
efficiency.
Newton's Law of cooling
• The rate of heat transfer by convection is product of heat transfer area,
difference of temperature between surface and that of fluid and a
constant called as convective heat transfer coefficient.
The equation can be written as
• q = hAMT
Where
• q = average rate of heat transfer by convection (Watt or J/s)
• A = heat transfer Area (m 2)
• AT = difference of temperature between surface and that of the fluid
(°C).
• h = convective heat transfer coefficient W/ (m2 K).
Radiation
Radiation is the transfer of heat
through electromagnetic waves
without the need for a medium
or direct contact. In a boiler,
radiation plays a minor role
compared to conduction and
convection, but it still contributes
to heat transfer. The hot surfaces
of the boiler, such as the
combustion chamber or heat
exchanger, radiate heat energy in
the form of infrared radiation.
This radiation can be absorbed by
cooler surfaces, contributing to
overall heat transfer in the
system.
Stefan Boltzmann Law
• In 1879 "Stefan" proposed that the total emissive power of a radiating surface
of a black body is proportional to the fourth power of the absolute
temperature of the surface. This was then proofed by "Boltzmann" in 1884.
Mathematically this law may be written as.
• q = αAT^4
Where
• q = rate of heat emission by radiation
• A = Area of the emitting body (m 2)
• T = absolute temperature (K)
• α = a constant known as Stefan — Boltzmann constant
THANK YOU
BY- AMIT KUMAR SINGH
You might also like
- Chapter Outline: Failure Fracture: How Do Materials Break?No ratings yetChapter Outline: Failure Fracture: How Do Materials Break?9 pages
- Dr. Fawad A. Najam - Are We Prepared Enough For The Next Big One PDFNo ratings yetDr. Fawad A. Najam - Are We Prepared Enough For The Next Big One PDF65 pages
- Heat Transfer Conduction Convection RadiationNo ratings yetHeat Transfer Conduction Convection Radiation3 pages
- Choosing The Right Turbulence Model For Your CFD S PDFNo ratings yetChoosing The Right Turbulence Model For Your CFD S PDF6 pages
- Sheet 1 - Introduction To Heat Transfer MechanismsNo ratings yetSheet 1 - Introduction To Heat Transfer Mechanisms2 pages
- MCQ Thermodynamics Part 8 ECE Board ExamNo ratings yetMCQ Thermodynamics Part 8 ECE Board Exam12 pages
- Evaluate Theories of Motivation in Sport - Essay PlanNo ratings yetEvaluate Theories of Motivation in Sport - Essay Plan2 pages
- 68-Radiation Heat Transfer-Terminology and Laws-22-Oct-2019Material - I - 22-Oct-2019 - Radiation PDFNo ratings yet68-Radiation Heat Transfer-Terminology and Laws-22-Oct-2019Material - I - 22-Oct-2019 - Radiation PDF48 pages
- Lec 6 Entropy and The Second Law of Thermodynamics100% (1)Lec 6 Entropy and The Second Law of Thermodynamics77 pages
- Introduction and Basic Concepts: Abdul Adam AbdullahNo ratings yetIntroduction and Basic Concepts: Abdul Adam Abdullah31 pages
- Introduction To Heat Transfer PresentationNo ratings yetIntroduction To Heat Transfer Presentation43 pages
- HEAT and Mass Transfer: Course Code: NME-501No ratings yetHEAT and Mass Transfer: Course Code: NME-50136 pages
- DUPLEX 1500 - 11000 Multi-N Rooftop EN - 2018 - 03No ratings yetDUPLEX 1500 - 11000 Multi-N Rooftop EN - 2018 - 038 pages
- Lesson 1 Kinetic Molecular Model of Liquids and SolidsNo ratings yetLesson 1 Kinetic Molecular Model of Liquids and Solids26 pages
- Consider A Steam Power Plant Operating On The Ideal Rankine CycleNo ratings yetConsider A Steam Power Plant Operating On The Ideal Rankine Cycle1 page
- Modeling and Simulation of Natural Ventilation of Building Using Solar ChimneyNo ratings yetModeling and Simulation of Natural Ventilation of Building Using Solar Chimney6 pages
- Physics Experiment Report (V) Basic Physics "Total Internal Reflection"No ratings yetPhysics Experiment Report (V) Basic Physics "Total Internal Reflection"9 pages
- A. Terminologies:: Geotechnical EngineeringNo ratings yetA. Terminologies:: Geotechnical Engineering5 pages
- Solved Problems in Chemical Process CalculationsNo ratings yetSolved Problems in Chemical Process Calculations19 pages
- Periodic Maintenance Manual - Split UnitsNo ratings yetPeriodic Maintenance Manual - Split Units1 page
- Photometry: Chapter 3: Analytical TechniqueNo ratings yetPhotometry: Chapter 3: Analytical Technique6 pages
- Solids, Liquids and Gases.: - Complete The Spaces in The Table BelowNo ratings yetSolids, Liquids and Gases.: - Complete The Spaces in The Table Below8 pages
- XI Chemistry Sir Waqar Sindh Board Final TermNo ratings yetXI Chemistry Sir Waqar Sindh Board Final Term6 pages
- Chapter Outline: Failure Fracture: How Do Materials Break?Chapter Outline: Failure Fracture: How Do Materials Break?
- Dr. Fawad A. Najam - Are We Prepared Enough For The Next Big One PDFDr. Fawad A. Najam - Are We Prepared Enough For The Next Big One PDF
- Choosing The Right Turbulence Model For Your CFD S PDFChoosing The Right Turbulence Model For Your CFD S PDF
- Sheet 1 - Introduction To Heat Transfer MechanismsSheet 1 - Introduction To Heat Transfer Mechanisms
- Evaluate Theories of Motivation in Sport - Essay PlanEvaluate Theories of Motivation in Sport - Essay Plan
- 68-Radiation Heat Transfer-Terminology and Laws-22-Oct-2019Material - I - 22-Oct-2019 - Radiation PDF68-Radiation Heat Transfer-Terminology and Laws-22-Oct-2019Material - I - 22-Oct-2019 - Radiation PDF
- Lec 6 Entropy and The Second Law of ThermodynamicsLec 6 Entropy and The Second Law of Thermodynamics
- Introduction and Basic Concepts: Abdul Adam AbdullahIntroduction and Basic Concepts: Abdul Adam Abdullah
- DUPLEX 1500 - 11000 Multi-N Rooftop EN - 2018 - 03DUPLEX 1500 - 11000 Multi-N Rooftop EN - 2018 - 03
- Lesson 1 Kinetic Molecular Model of Liquids and SolidsLesson 1 Kinetic Molecular Model of Liquids and Solids
- Consider A Steam Power Plant Operating On The Ideal Rankine CycleConsider A Steam Power Plant Operating On The Ideal Rankine Cycle
- Modeling and Simulation of Natural Ventilation of Building Using Solar ChimneyModeling and Simulation of Natural Ventilation of Building Using Solar Chimney
- Physics Experiment Report (V) Basic Physics "Total Internal Reflection"Physics Experiment Report (V) Basic Physics "Total Internal Reflection"
- Solids, Liquids and Gases.: - Complete The Spaces in The Table BelowSolids, Liquids and Gases.: - Complete The Spaces in The Table Below