atoms and elements
- 1. In this presentation, you will learn more about: -Atoms -Elements -Compounds -Symbols -Properties of elements -The periodic table -Molecules -Formulae -Chemical reaction -Word equation
- 2. Everything around us is made up of particles . These particles are known as atoms and are so small that they can only be seen with a powerful microscope. There are about 100 different types of atoms for example: Oxygen, Hydrogen, Gold, Platinum, Scandium and Sulfur atoms. Each type of atom is an element . Some objects are composed of only one element. Some objects also contain more than one element. These objects contain two or more elements joined together. The object is then known as a compound . Atoms
- 3. Scientists around the world use a common set of symbols to represent all the different elements. In some cases the symbol of the element is the first letter of the name of the element. It is written in capital. Symbols#1 oxygen O sulfur S boron B iodine I fluorine F hydrogen H Element Symbol
- 4. Several elements begin with the same letter for example Scandium and Silicon. To identify any of these as a separate element, its symbol has the first letter of the name followed by the second letter from within the name. Scandium has the symbol Sc, while silicon has the symbol Si. T he first letter is always a capital one and the second letter is in lower case. Symbols#2 Br bromine Be beryllium Ca calcium Cl chlorine Mn manganese Mg magnesium Symbol Element
- 5. Sometimes the symbol for an element is derived from the Latin name for that element. Symbols#3 K ( kalium) Potassium Fe ( ferrum) Iron Pb ( plumbum) Lead Na ( natrium ) Sodium Symbols Element
- 6. Different elements can have very different properties . Some are solids , some are liquids and some are gases . Some are essential to our health and well being, but some are highly toxic. Early scientists examined the elements that had been discovered and tried find links and patterns between them. Properties of elements
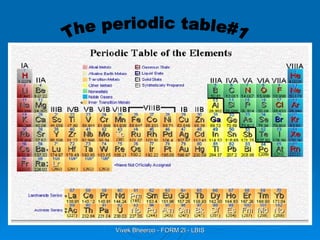
- 8. The periodic table was invented by Dimitri Mendeleev . He used the properties of each element to decide where to place them in his table. On the left and middle part of the table, there are the metal elements and on the left part of the table, there are the non- metal elements. Dimitri Iwanowitsch Mendeleev The periodic table#2
- 9. We have seen that when the atoms of two or more elements are joined together they form a compound. Water is a compound because it contains atoms of two different elements, hydrogen and oxygen. When hydrogen and oxygen join together to make this compound, the water has completely different properties of either hydrogen or oxygen. When the two elements join together, they are arranged in a particular way. It consists of two hydrogen atoms joined to one oxygen atom. This is then called a molecule . A water molecule Molecules
- 10. The compound we call water has the formula H 2 O . This is a shorthand way of saying that every water molecule consists of two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom. The gas we call oxygen has the formula O 2. This means that an oxygen molecule consists of two oxygen atoms joined together. Oxygen molecule Formulae
- 11. New compounds are made when atoms of elements are joined together during chemical reactions . These new compounds can have very different properties from the elements that formed them. We can describe chemical reactions that make new compounds using word equations. Chemical reaction
- 12. When a balloon of hydrogen explodes, we are seeing and hearing a very vigorous chemical reaction between the hydrogen in the balloon and oxygen in the air. We describe this reaction with the following word equation. Hydrogen + oxygen Water Water
- 13. The metal sodium reacts with chlorine to produce the compound sodium chloride . Sodium + chloride sodium chloride Sodium chloride
- 14. When a slice of toast is overcooked, the surfaces become covered with black carbon. This carbon may react with the oxygen in the air to form the gas carbon dioxide. Carbon + oxygen carbon dioxide Carbon dioxide
- 15. When heated, the metal copper reacts with the non- metal sulfur to produce the compound copper sulfide . Copper sulfide Copper + sulfur copper sulfide Copper sulfide
- 16. References Books Brian Arnold, Geoff Jones, Mary Jones, Emma Poole. Absolute Science: Pupil Book 2, 2003. Martin Sherwood, Wendy Allen, Nigel Davis, Mick Gillah. Chemistry Today: The World Book Encyclopedia of Science, 1989. Ministry of Education and Scientific Research; Editions de L’Ocean Indien: Form 3, 2005. Tony Eugene, Ellis D. Miner. Discover Stars & Planets; Publications International Ltd, 2003. Chancellor Press. Tell me Why? Octopus Publishing Group Ltd, 2001. Internet(Yahoo) Atoms and Elements users.rcn.com/jkimball.ma.ultranet/BiologyPages/E/ Elements .html www.karentimberlake.com/ atomsand .htm www.chem4kids.com/files/elem_intro.html hyperphysics.phy-astr.gsu.edu/hbase/chemical/atom.html www.pslc.ws/macrog/kidsmac/ atoms .htm www.colorado.edu/physics/2000/ elements _as_ atoms /index.html www.st and ards.dfes.gov.uk/schemes2/secondary_science/sci08e/?view
- 17. THE END