Agile Methodology Vs. Others by Sara Berrada
- 1. Agile Vs. Other Methodologies Presented by Sara Berrada
- 3. Agenda 1. Agile Overview 2. Traditional 3. Comparison of 4 Agile Methodologies 4. Advantages 5. Disadvantages 6. Industry examples
- 4. Agile Overview What’s Agile? Agile means small teams working collectively and collaboratively with this mission: To deliver frequent, incremental releases of innovation functions and features, prioritized for need and affordability; evolved iteratively from a vision according to user reflection and feedback, and produced at the best possible value. – John C. Goodpasture Adaptedfromedge.papercutpm.com/ Change Adaptation Flexibility
- 5. When is it used? Continuous Change & Uncertainty Aggressive deadlines: Urgency High degree of complexity High degree of novelty (uniqueness) to them. If it's something the team has done before over and over then the team probably doesn't need an agile approach.
- 8. Comparing Agile and Traditional Approaches to Governing of Agile Teams (Scale: -10 to +10) -4.7 -6.2 -1.7 -2.6 -4.1 -2.1 4.5 1.2 2.8 3.9 4.3 3.4 Copyright 2017 Scott Ambler + Associates Decreases Morale Reduces Quality Wastes IT Investment Decreases Productivity LightweightHeavyweight Improves Productivity Increases Quality Promotes Wise IT Investment Improves Morale AgileTraditional Focused on Business Value Not focused on Business Value Source: 2017 Agile Governance Survey
- 9. Scrum XP Crystal EVO 4 Agile Methodologies Builds on the Waterfall. Embraces the Deming Plan- Do-Check-Act cycle - PDCA Disciplined Approach. Less prescriptive than SCRUM practices. Management framework in the main. Not prescriptive of actual technical practices. Most Empathetic. People Powered. Address the Scalability issue by a ladder of colors.
- 11. People Adapted from Project Management the Agile Way by John C. Goodpasture EVO
- 12. Process Adapted from Project Management the Agile Way by John C. Goodpasture
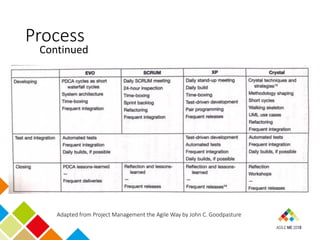
- 13. Process Continued Adapted from Project Management the Agile Way by John C. Goodpasture
- 14. Technology Practices Adapted from Project Management the Agile Way by John C. Goodpasture EVO
- 15. Adapted from Segue Technologies
- 16. Disadvantages Weak commitment to scope & cost Vulnerable to turn-over in the team staffing Not architectural driven so there are may be dependencies discover later Difficult to scale the small team dynamic to an enterprise scope project Difficult to scale without commitment of documentation Testing is not independent Verification is by testing, not traceable to specifications High reliability and mission-critical requires strong verification that is missing
- 17. Advantages 1. Flexibility-The ability to become flexible and delivery of quality software that fulfilling the requirements of costumer is recognized as key benefit of agile development 2. Increased productivity- costumer’s frequent feedback with changing requirements allows developer team to create better quality product with minimum risk of error. 3. Early detection of feasibility and error- agile process execute the design, analysis and implementation in repeated iterations that give clear visibility of project progress. On behalf of progress stage costumer can take decision to continue or cancel, if they find that it is not going as expected to save the extra investment. 4. High software quality- short iterations, frequent feedback and test driven development help to improve the overall quality of software. 5. Project control- main focus of agile is on people over process and less stress on documentation gives the opportunity to developers improve process activities like: short iteration, knowledge sharing, continuous integration and feedback with full project control. 6. Knowledge transfer- regular meetings in which they mainly discuss on developing project issues. => increases the communication between team and they remain updated with current scenarios.
- 18. Industries
- 19. Adopted from Agilitrix - CC Mountain Goat Software LLC Use of Scrum by different companies
- 20. Use of Scrum in different types of projects Adopted from Agilitrix - CC Mountain Goat Software LLC
- 23. Thank you!