Leadership ppt
- 1. A Presentation by Arijit Ghosh LEADERSHIP
- 2. Introduction What is Leadership? The ability to influence a group toward the achievement of goals. According to Peter Drucker, “Leadership is shifting of own vision to higher sights, the rising of man’s performance to higher standards, the building of man’s personality beyond its normal limitations.” What is Management? Use of authority inherent in designated formal rank to obtain compliance from organizational members.
- 3. Importance Leadership transforms potential into reality. Leadership is not mere using people and their potential for realising an organization’s goals. It has the ultimate aim of raising the level of human conduct and ethical aspiration of both the leader and the lead. The leader should elevate, inspire and Initiates action. Providing guidance Creating confidence Effective planning
- 4. Characters Of Leadership Empathy Consistency Honesty Direction Communication Needs support from all Assume obligation
- 6. 1. TRAIT THEORIES Focuses on individual characteristics of successful leaders. Leaders possess a set of traits which make them distinct from followers. Leadership traits are: Ambition and Energy The desire to lead Honest and integrity Self-confidence Intelligence High self-monitoring Job-relevant knowledge
- 7. 2. Behavioral Theories Main focus is behaviors of actual leaders. Determine how various kinds of specific leaders behavior affect the performance and satisfaction of followers. Theories proposing that specific behaviors differentiate leaders from non-leaders.
- 8. a. Ohio State Studies Initiating structure: The extent to which a leader is likely to define and structure his or her role and those of subordinates in the search for goal attainment. Consideration: The extent to which a leader is likely to have job relationships characterized by mutual trust, respect for subordinates ideas, and regard their feelings.
- 9. b. University Of Michigan Studies Employee-Oriented Leader: Emphasizing interpersonal relations; taking a personal interest in the needs of employees and accepting individual differences among members. Production-Oriented Leader: One who emphasizes technical or task aspects of the job.
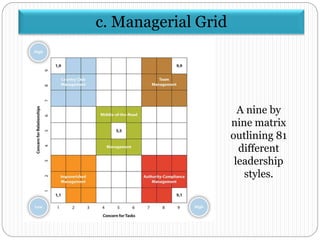
- 10. c. Managerial Grid A nine by nine matrix outlining 81 different leadership styles.
- 11. 3. Contingency Theories a. Fiedler’s Model: Defining the Situation b. Hersey and Blanchard’s Situational Leadership Theory c. Leader–Member Exchange Theory d. The Path-Goal Theory
- 12. a. Fiedler’s Model: Defining the Situation Leader-Member Relations: Relations The degree of confidence, trust, and respect subordinates have in their leader. Task Structure: The degree to which the job assignments are procedurized. Position Power: Influence derived from one’s formal structural position in the organization; includes power to hire, fire, discipline, promote, and give salary increases.
- 13. Findings From Fiedler’s model
- 14. b. Hersey and Blanchard’s Situational Leadership Theory
- 15. c. Leader–Member Exchange Theory Leader-Member Exchange (LMX) Theory Leaders create in-groups and out-groups, and subordinates with in-group status will have higher performance ratings, less turnover, and greater job satisfaction.
- 16. d. The Path-Goal Theory
- 17. Leadership Styles Autocratic management style Democratic management style Laissez Faire management style Transactional Leadership Transformational Leadership
- 18. Autocratic Management Style An autocratic manager dictates orders to their staff and makes decisions without any consultation. The leader likes to control the situation they are in. Decision are quick. This type of management style can decrease motivation and increase staff turnover.
- 19. Democratic Management Style A democratic manager delegates authority to the staff, giving them responsibility to complete the task. Staff will complete the tasks using their own work methods on time. Employees are involved in decision making giving them a sense motivating individuals. Increases job satisfaction by involving employees or team members . Slow decision making process.
- 20. Laissez Faire Management Style A laissez faire manager sets the tasks and gives staff complete freedom to complete the task as they see fit. “leave it be”. It works for teams in which the individuals are very experienced and skilled self-starters. There is minimal involvement from the manager. The manager coaches or supply information if required. Benefits - staff are developed to take responsibility. Staff feel lost and not reach the goals set within the time frame.
- 21. Transactional and Transformational Leadership Transactional Leaders: Leaders who guide or motivate their followers in the direction of established goals by clarifying role and task requirements. Transformational Leaders: Leaders who provide individualized consideration and intellectual stimulation, and who possess charisma.
- 22. THANK YOU