PHYSICAL EDUCATION & SPORTS FOR ALL
- 1. 1 Physical Education & Sports For All By DR. DEVINDER K. KANSAL Head, Deptt. of Physical Education & Sports Sciences (University of Delhi) & Principal, Indira Gandhi Institute of Physical Education & Sports Sciences
- 2. 2 Physical Education & Sports Facts Fact 1 : Physical education (PE) the know- how of utilizing physical activities for the prevention of chronic diseases and promotion of health, fitness & wellness – is the most potential subject but most neglected due to ignorance of the present day educated people.
- 3. Fact 2: Health Wellness Continuum Worst Death Poorest Health Obesity Serve Illness Heart Disease Poor Health Illness Negative Health Health B.P. Blood Sugar etc. with Medi- cine Deter- iorating Life Style Neutral Say You are in the Middle Here Physi- cally Educa- ted Lifestyl e Positive Health Health B.P. Blood Sugar etc. without Medi- cine Fitness Regular Physical Activity & Active Sports & Recrea- tion Best Best Health Fitness & Wellnes s Active & Happy Lifestyle
- 4. 4 Fact 3: Health Wellness Lifelong H = Health & Wellness E = for Everyone L = Life-Long P = Personalized
- 5. 5 Fact 4: Inactivity Problem H = Heart Diseases O = Obesity L = Lower back Pain D = Diabetics
- 6. 6 Fact 5: An Educated Person An Educated Person is one who knows four subjects i.e. PALM (i. Personality development, ii. Art of Living by ABC (Aiming Fitness, Building healthy base and Choosing Sensibly) iii. Learning right lifestyle of daily scheduling and iv. Management through Sr. MEN’S firm no to SAID; Smoking, Alcohol, Illegal Sex & Drugs).
- 7. 7 Fact 6: A Physically Educated Person NAPES-1992 (USA) A Physically Educated Person is one who knows the Benefits of Physical Activity & Sports (PAS); Skills necessary for variety of PAS; is Fit ; and is Regular in participation, knows the Implications of non-participation & Contributions of PA in Healthful living & Wellness; Values the regular participation in physical activities. Easy Recall Acronym = BSF - RICH Values
- 8. 8 Fact 7: Delhi Govt. Opinions “Students welfare and regard is the highest law” - Sheila Dikshit A Teacher is an agent of Change in attitudes - Deptt. of Education, GNCTD A Teacher takes care of not only the physical class room management but also the behaviour management of students.
- 9. 9 Fact 8: Natural Laws The law of gravity was operative since the existence of world, but discovered only three countries ago by Isacc Newton (1642-1727). Similarly Laws of Physical Fitness & Wellness are operative since dawn of life but are yet to be taught to humanity in regular channel of education.
- 10. 10 Vision With the fast developments, and provision of computers, laptops and internet facility, the above facts will soon be known and will subsequently help the entire public in addition to bring Physical Education in the front line of education.
- 11. 11 Mission To expedite (i) the spread of the above facts to masses and (ii) to adopt regular physical exercises daily for remaining well, fit and healthy and to help others to remain so. Note : 10000 steps or 6 km of daily walk, may be in installments is an insurance to HOLD i.e. Heart Diseases, Obesity, Low back pain and Diabetes.
- 12. 12 Specific Objectives To make the above fact known to at least the following : (a) Departments of Education. (b) Ministries of Education & so called Higher Education. (c) All relatives, friends and students coming in contact. (d) To follow systematic steps prescribed by PETs in lesson plan. (e) To develop potential personalities hardware (body - the vehicle of human activities) on priority. (f) To promote the methods of maintaining physical personality excellence among the members of local society and public at large.
- 13. 13 Objectives (Contd) (g) To utilize the seven habits (Stephen Covey) and the behaviour change stages (PCPACT) (claiming these, as part of P.E.) for the promotion of self & others wellness. (h) To make impact of P.E. on education by making efforts to get one paper of education (including P.E.) compulsory for any graduation degree to be awarded by universities. (i) To promote relation, distinction and importance of education and physical education (which includes spiritual education in the form of sports).
- 14. 14 Objectives (Contd) (j) To promote the know-how of relation, difference and role of health, fitness and wellness on the following concept: (i) Health : It is the minimal state of adequacy of body work performance as depicted by health markers like Blood pressure, Vital capacity, Body composition, Blood Cholesterol levels etc. (ii) Fitness : It is the developed status of health promoted through the knowledge of P.E. and application of regular exercise with right techniques resulting in one’s excellence in the desired sport or activity as a sum of general physical fitness and specific physical fitness. (iii) Wellness : Taking self responsibility for one’s good health and best fitness by following right lifestyle habits and behaviours including regular exercise, right food, stress management, weight management, meditation, hygienic behaviour, safety first aid, health education etc. with firm no to ‘SAID’ i.e. Smoking, Alcohol, Illegitimate sex and Drugs.
- 15. 15 Objectives (Contd) (k) To develop students into leaders and social heroes by developing altruistic nature, truthful performance & team work of sports excellence.
- 16. 16 Conclusion i. Implement Application course in all colleges of D.U. ii. Make maximum efforts to introduce discipline course by 2012 in all colleges. iii. Implement BMI, Exercise prescription and all other applied practicals properly by refreshing teachers’ through hands on experience of using sports science equipments needed for practicals. iv. Promote real P.E. (not only sports excellence, but sports for all) for human wellness.Teach & promote P.E. seriously and sincerely so that we are able to see a good turn with in 3-4 years, during sports- culture environment of CWG-2010.
- 17. Conclusion (Contd.) v. Read & thoroughly understand the concepts to teach the same to our students with the hands on experience using best books like (i)Wellness by Corbin et al. (ii) Fitness & Wellness by Hoeger & Hoeger, (iii) Seven habits by S.Covey (iv) Textbook of Applied Measurement & Evaluation by D.K. Kansal. vi. Remember that semester system will help the promotion of new utilitarian subjects like P.E. through inter-disciplinary approach and provision of Add-On Courses. 17
- 18. Conclusion (Contd.) vii. SEMESTER SYSTEM IS THE KEY • Vice Chancellor Deepak Pental’s zeal of improving standards of higher education by implementing semester system, is a very good opportunity to us to get introduced an inter- disciplinary subject paper on Physical Wellness in each course. • This will help everyone through the learning of daily self-responsibilities towards getting right personal exercise, stress management , essential health education and learning to say a firm no to ‘SAID’ i.e. an acronym for Smoking, Alcohol, Inadequate/ inappropriate sex and Drugs. 18
- 19. Citizens Responsibilities (Not Exclusive) • How to make behavior changes for your specific personal problems. • How to predict the adult height of your child at the age of 8,9,10 years. • How to know which is the best sport for a specific child. • How to select the best team members for a particular sport as per its scientific sport requirements. 19
- 20. Contd.. • How to test your Physique. • What is ‘3S’ Fitness literacy, How to measure your and others’ Strength, Stamina & Suppleness(Flexibility). • How to measure your food requirements and eat healthy for your specific body type. • To learn what are Serving Size measures to plan your meals. 20
- 21. Contd.. • How can you easily remember the meanings of holistic education, personality, personality development with the help of easy acronyms. • How to remain healthy, fit and well and how to keep track (measure) your health, fitness and wellness. • How to find your BMI (Body Mass Index). • How to find your disease risks. 21
- 22. Mass Participation in Countries Advanced in Sports Participation in Sports on scientific lines is promoted by dividing school children around age 10 in two groups:- • Group-I: Consists children having potential to excel in Sports Competitions. • Group-II: Consists all remaining children who must also participate in Recreational Sports for Health and Fitness benefits.
- 23. WORLD SPORTS FOR ALL CONGRESS (November 1-3, 2006) • PHYSICAL INACTIVITY (ALONG WITH UNHEALTHY DIET AND TOBACCO USE) IS A MAJOR PREVENTABLE RISK FACTOR IN CHRONIC NON COMMUNICABLE DISEASE (NCD) AROUND THE WORLD. • 11th WORLD SPORT FOR ALL CONGRESS CALLS FOR URGENT AND CONCRETE ACTIONS.
- 24. SPORTS FOR ALL The Concept : Sports participation is obligatory for all not because each one is required to win medals but because each one is enjoyably required to remain fit, healthy, happy, and to treat and prevent diseases and muscular pains.
- 25. SPORTS FOR ALL The goal of the sports for all program is to help children develop (i) Basic movement skills and, (ii) Gain confidence in their ability to participate in sports and other beneficial physical activity, as well as, (iii) Learning that participation can be fun. With increased confidence and motivation to participate we hope that children will continue to be active rather than drop out of sports and physical activity, as happens so often in the early teen years.
- 26. WHY DEVELOP SPORT FOR ALL CULTURE? BECAUSE: young people can build healthy bodies and establish healthy lifestyles by including physical activity in their daily lives. However, many young people are not physically active on a regular basis, and physical activity declines dramatically during adolescence. School and community Sport for All programs can help young people get active and stay active.
- 27. BENEFITS OF PHYSICAL ACTIVITY Regular Physical Activity in Childhood and Adolescence:- • Improves strength and endurance. • Helps build healthy bones and muscles. • Helps control weight. • Reduces anxiety and stress and increases self-esteem. • May improve blood pressure and cholesterol levels.
- 28. NATIONAL SPORTS POLICY – 2001 1. Broadbasing of Sports. 2. Integration with Education. 3. Infrastructure Development. 4. Excellence in Sports. 5. National Sports Federations (NSFs). 6. Scientific Back-up to Sports Persons. 7. Sports Equipment. 8. Training and Development of Coaches, Sports Scientists, Judges, Referee and Umpires. 9. Incentives to Sports Persons. 10. Sports and Tourism. 11. Resource Mobilization for Sports.
- 29. YOUNG PEOPLE SAY THEY LIKE PHYSICAL ACTIVITY BECAUSE IT IS FUN; THEY DO IT WITH FRIENDS; AND IT HELPS THEM LEARN SKILLS, STAY IN SHAPE, AND LOOK BETTER.
- 30. MODERN TECHNOLOGY HAS ALMOST ELIMINATED THE NEED FOR PHYSICAL ACTIVITY
- 31. CONSEQUENCES OF PHYSICAL INACTIVITY • The percentage of young people who are overweight has almost doubled in the past 20 years. • Inactivity and poor diet cause at least 300,000 deaths a year in the united states. Only tobacco use causes more preventable deaths. • Adults who are less active are at greater risk of dying of heart disease and developing diabetes, colon cancer, and high blood pressure.
- 32. PHYSICAL ACTIVITY AMONG YOUNG PEOPLE • Almost half of young people aged 12-21 and more than a third of high school students do not participate in vigorous physical activity on a regular basis. • Seventy-three percent of 9th graders participate in vigorous physical activity on a regular basis, compared with only 58% of 12th graders. • Daily participation in physical education classes by high school students dropped from 42% in 1991 to 27% in 1997. • The time students spend being active in physical education classes is decreasing; among high school students enrolled in a physical education class, the percentage who were active for at least 20 minutes during an average class dropped from 81% in 1991 to 74% in 1997.
- 33. HOW MUCH PHYSICAL ACTIVITY DO YOUNG PEOPLE NEED? Examples of Moderate Activity Include:- • Walking 2 miles in 30 minutes or running 1½ miles in 15 minutes. • Bicycling 5 miles in 30 minutes or 4 miles in 15 minutes. • Dancing fast for 30 minutes or jumping rope for 15 minutes. • Playing basketball for 15-20 minutes or volleyball for 45 minutes.
- 34. PURPOSE OF ‘SPORTS FOR ALL’ ACTIVITIES: The purpose of the sports for all program is to provide practice of sport-related skills for young people in developmentally appropriate ways, resulting in positive experiences that help children develop lifelong patterns of health-enhancing physical activity. The goal of the sport for all program is the provide children the appropriate practice to develop these skills, resulting in increased confidence in their ability to participate as well as developing an appreciation for participating in physical activity.
- 35. SPORTS FOR ALL IS ALREADY A PROVEN PROGRAM. THE FINAL PROGRAM REPRESENTS A COLLABORATIVE EFFORT OF NASPE, HUMAN KINETICS, AND SPORTIME. IN ADDITION TO THE ACTIVITY CARD PACKETS, SPORT FOR ALL OFFERS COMPREHENSIVE TRAINING THROUGH NASPE AND CHILD-FRIENDLY EQUIPMENT FROM SPORTIME DESIGNED TO ENHANCE THE SUCCESS AND SAFETY OF THE CHILDREN.
- 36. Sports For All programme, especially in our country, is lacking in attracting and motivating people towards Sports. An effort is being made through this small serial write- ups to help all the readers of “The AISGD” in developing motivation towards sports resulting in their enduring physical fitness, health, glory, prestige, personality development, easy treatment to common physical ailments of lower back, neck and shoulder pains etc.
- 37. 1. Sports for Fitness Promotion & Maintenance. 2. Sports for Health Promotion & Maintenance. 3. Sports and Exercises for Treatment (at least of Common postural, joints, muscular lower back, neck and shoulder pain etc. e.g. Yoga). 4. Sports for Competitive excellence. 5. Sports for Recreation Friendship and Co- operation . 6. Sports for Personality and Figure Development
- 38. PHYSICAL EDUCATION FOR ALL
- 39. Sports For All Steps Needs:- I. Two-way Administration:- 1. Health Excellence Channel, 2. Sports Excellence Channel. II. Three compulsory paper in each course i.e. 1. Sports For All (SFA). 2. Fitness & Wellness. 3. Measurement & Evaluation. III. Distance Education in Sports:- 1. Contact Programme. 2. Lessons. 3. Assignments. IV.Placement Cell including old students updating.
- 40. I. Two-way Administration:- 1. Health Excellence Channel. 2. Sports Excellence Channel.
- 41. II. Three compulsory paper in each course i.e. 1. Sports For All (SFA). 2. Fitness & Wellness. 3. Measurement & Evaluation.
- 42. III. Distance Education in Sports:- 1. Contact Programme. 2. Lessons. 3. Assignments.
- 43. IV. Placement Cell including old students updating.
- 44. Six Steps to Problem Behaviour change with Physical Education I. Pre-contemplation Unconvinced for benefits of Physical activity. II. Contemplation Accepting Benefits. III. Preparation Stage Seeking equipment & guidance. IV. Action Started Exercise routines with company. V. Maintenance Consistency for five years. VI. Adoption Behaviour changed to regular life long activity.
- 45. Pre-contemplation Unconvinced for Benefits of Physical Activity Contemplation Accepting Benefits
- 46. Preparation Stage Seeking Equipment & Guidance Action Started Exercise Routines with Company
- 47. Maintenance Consistency for Five Years Adoption Behaviour Changed to Regular Life Long Activity
- 48. SPORTS TALENT SELECTION & PHYSICAL EDUCATION TEACHERS’ NO.1 POSITION IN SCHOOLS DEVINDER. K. KANSAL PRINCIPAL, (Ph.9971883044) INDIRA GANDHI INSTITUTE OF PHYSICAL EDUCATION & SPORTS SCIENCES E-mail= kansalvandana@yahoo.co.in Refresher Course SCERT School Teachers, Feb.25, 2008
- 49. LESSON PLAN=UGC.COL.VAR • WHERE • U = Unit name. • G = Grade standard. • C = Concept statement. • C =Contents: O=Objectives: L=Learning activity • V = Valid evaluation. • A = Achievement record. • R = Reference materials of all four domains. • Domains = SH.MB = Soul, Heart, Mind & Body (or Spiritual, Affective, Cognitive & Physical)
- 50. TODAY’S LESSON • U = SPORTS TALENT SELECTION • G = School Teachers. • C =PET can counsel students for sports. • C = Measurement, PhysicalGrowth,Selections. • O = Teaching A.S.K. of Lab. & Theory classes. • L = Finding sports talent among 6th class boys. • V = Ability to teachsports selection method two . new persons. • A = Notes taken inspected by peers/examiner. • R = Textbook by Dr. Devinder K.Kansal.
- 51. P.E. NEGLECTED IN SCHOOLS The formal physical education (which is the only means of teaching fundamentals of physical activity) has been neglected by the educationists and educational curriculum developing agencies by not conducting the examinations in Physical Education at school level, till date.
- 52. S.N o. Universities in India Number Percentag e 1. Number of Universities Literate in Physical Education. 61 17% 2. Number of Universities illiterate in Physical Education. 297 83% 3. Total Universities 358 100% P.E. NEGLECTED IN UNIVERSITIES
- 53. LAW OF LEARNING COMPLETE RECEPTIVITY TO THE TEACHER’s SAYING i.e. Listening carefully to accept all as true with trust. “Rain can fill your pot only if you keep it upright”.
- 54. NO ARGUEMENT BUT AGREEMENT TWO PEOPLE MUST DIFFER IN VIEWS USUAL APPROACH IS I AM ALWAYS RIGHT CHANGE TO OTHERS MAY BE RIGHT.
- 55. A TEACHER CAN NEVER TRULY TEACH UNLESS HE IS STILL LEARNING HIMSELF A LAMP CAN NEVER LIGHT ANOTHER LAMP UNLESS IT CONTINUES TO BURN ITS OWN FLAME • RABINDRANATH TAGORE
- 56. KEY (Descriptive): I have to perform a full-dress rehersal of the potentials of Physical Education by learning human growth patterns & sports talent identification. I will be No.1 Teacher in my school, most sought after teacher for help.
- 57. MY LOCKED UP PALACE 1. PE has the biggest portions of human HAPPINESS Palace. 2. PE has the biggest portion of Human Recreation Palace. 3. PE has the biggest portion of Wealth Palace. 4. PE has the biggest portion of Fitness Palace. 5. PE has the biggest portion of Sports Palace. 6. PE has the biggest portion of Health Palace.
- 58. PHYSICAL EDUCATION IS HEALTH AND HEALTH IS H = HAPPINESS. E = ENTERTAIN & EDUCATE. A = AFFLUENCE (WEALTH). L = LEAN TISSUE VS FAT (FITNESS). T = TRAINING (SPORTS). H = HUMANISM.
- 59. YOUR PRACTICAL KEY TEST = Tool OR QUESTIONNAIRE MEASUREMENT = Measured Value (ANY READING) EVALUATION = Giving Meaning TO THE READING 1. Human Growth Patterns. 2. Anthropometry (Kinanthropometry) 3. Fitness Measurement. 4. Training Methods 5. Sincerity & Spirituality in Exercise Prescription for Training.
- 60. • IT MAY BE DEFINED AS THE “SCIENTIFIC SELECTION OF THE MOST APPROPRIATE SPORT • FOR THE SPECIFIC CHILD • MOST SUITED TO HIS/HER ADULT BODY POTENTIALS, • PREFERABLY AT THE PRE- ADOLESCENT AGE” SPORT - SELECTION FOR A CHILD
- 61. TALENT SELECTION-for a sport • “THE SCIENTIFIC SELECTION OF THE MOST APPROPRIATE TEAM OF PLAYERS • FOR A DESIRED SPORT, • AT PRE-TRAINING STAGE”
- 62. SPORTS COUNSELLING • SCIENTIFIC GUIDANCE PROVIDED BY THE PHYSICAL EDUCATION TEACHER OR A SPORTS COACH • TO INDIVIDUALS IN SELECTING THE MOST APPROPRIATE SPORT OR PHYSICAL ACTIVITIES
- 63. MAJOR USES OF PHYSICAL EDU • MAJOR USES ARE REPRESENTED BY • CRPF HTC • C =COMPITITIVE SPORTS(GENETICALLY-TALENTED). • R = RECREATIONAL SPORTEX . (SPORTEX=SP.+EX.) • P = PERSONALITY-SHAPING EXERCISES. • F = FITNESS PROMOTION SPORT EX. • H = HEALTH PROMOTION SPORTEX. • T = TREATMENT EXERCISES (FOR INJURY/DISEASE). • C = CO-OPERATION & FRIENDSHIP PROMOTION SPORTS
- 64. AND IDENTIFICATION 1. Knowledge of Growth patterns and Maturity Status. 2. Methods of Predicting Adult Physique & Performance Potentials at young age. 3. Specific Physique & Physiological Requirements of each sports event. 4. Scientific Methods of Evaluation. STEPS OF TALENT SELECTION
- 65. STEPS OF TALENT SELECTION-2 1. Measurment of present status. 2. Testing the development stage . 3. Projection of predicted adult potentials d. 4. Comparing the predicted status with the specific sports requirementss. 5. Seeking child's interests and preferences 6. Making the final recommendations to the
- 66. KNOWLEDGE OF GROWTH PATTERNS EXISTING STATUS: Physical growth is least utilised in Physical Education, Fitness and Sports fields. DESIREBLE STATUS: 1. Measurement and Physical Growth patterns should be an essential paper of each Graduate and Postgraduate Physical Education and Coaching Course. 2. Coaches and Physical Education Teachers must learn practical measurement of Physique and Growth Status.
- 67. 1. DIFFERENCE: GROWTH = Change in Size. MATURITY = Change in proportions and Functional Capacity. 2. EVALUATION: GROWTH = From individual size Measurement like Height , Weight, Lengths, Widths, Circumferences etc. MATURITY = From Body Proportions (B.B.I., BMI, Sitting Ht/Height) functional capacity indicators (VC, PR etc.) and Secondary Sex characters (Menarche, Pubic Hair, Auxillary Hair, Facial Hair etc.) GROWTH & MATURITY STATUS
- 68. AGE VARIATIONS 1. Chronological Age = Passage of time in years, months, days after birth. (Measure from Calendar). 2. Biological Age = Milage covered on the Path of Maturity (Measured from skeletal Age, Secondary Sex characters, Dental Age, Physiological, Morphological or Bio- chemical markers etc.).
- 69. AGE CALCULATOR • Any subject’s exact age correct up to three decimal places can easily be calculated with the help of an age calculating table. • If we want to calculate age on 25th Feb., 2008 for a person born on 7th august,1985. • Consulting the table, we find • Age =25.2.2008-7.8.1985 = 2008.151-1985.597 • =22.554 Years.
- 70. PHYSICAL GROWTH CURVES GENERAL PATTERNS
- 71. ADULT HEIGHT PREDICTIONS Measured Height(cm) Predicted Height age Measured Height Predicted Height age 09 10 11 09 age 10 11 120 122 124 126 128 130 132 134 157 159 162 165 167 170 172 175 153 155 157 159 162 164 166 168 -- -- 152 154 156 158 160 163 136 138 140 142 144 146 148 150 178 180 182 184 186 189 191 193 171 173 176 178 181 183 186 188 165 168 170 172 175 177 180 183
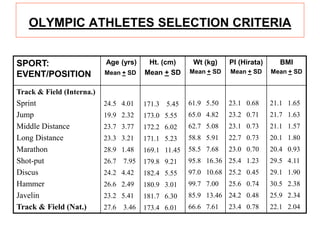
- 72. OLYMPIC ATHLETES SELECTION CRITERIA SPORT: EVENT/POSITION Age (yrs) Mean + SD Ht. (cm) Mean + SD Wt (kg) Mean + SD PI (Hirata) Mean + SD BMI Mean + SD Track & Field (Interna.) Sprint Jump Middle Distance Long Distance Marathon Shot-put Discus Hammer Javelin Track & Field (Nat.) 24.5 4.01 19.9 2.32 23.7 3.77 23.3 3.21 28.9 1.48 26.7 7.95 24.2 4.42 26.6 2.49 23.2 5.41 27.6 3.46 171.3 5.45 173.0 5.55 172.2 6.02 171.1 5.23 169.1 11.45 179.8 9.21 182.4 5.55 180.9 3.01 181.7 6.30 173.4 6.01 61.9 5.50 65.0 4.82 62.7 5.08 58.8 5.91 58.5 7.68 95.8 16.36 97.0 10.68 99.7 7.00 85.9 13.46 66.6 7.61 23.1 0.68 23.2 0.71 23.1 0.73 22.7 0.73 23.0 0.70 25.4 1.23 25.2 0.45 25.6 0.74 24.2 0.48 23.4 0.78 21.1 1.65 21.7 1.63 21.1 1.57 20.1 1.80 20.4 0.93 29.5 4.11 29.1 1.90 30.5 2.38 25.9 2.34 22.1 2.04
- 73. OLYMPIC ATHLETES SELECTION CRITERIA SPORT: EVENT/POSITION Age (yrs) Mean + SD Ht. (cm) Mean + SD Wt (kg) Mean + SD PI (Hirata) Mean + SD BMI Mean + SD Badminton (Internat.) Gymnastics (Internat) Kabbadi (International) Basketball (Internat) Volleyball (Internat) Volleyball (National) Boxing (International) Football (National) Forwards Halves Backs Goalkeepers 19.0 2.93 22.4 3.47 26.0 3.16 18.6 0.95 22.1 4.09 29.6 4.81 18.6 0.75 27.8 5.04 26.2 3.18 29.1 4.52 27.3 3.63 170.8 7.67 164.4 4.34 173.4 6.11 184.9 6.28 188.6 6.60 178.0 6.22 166.4 6.76 171.3 3.97 166.0 3.77 173.7 4.94 174.8 1.77 60.9 6.99 53.7 3.34 70.9 7.27 71.4 6.22 72.2 7.52 68.3 7.64 56.1 6.19 61.6 4.72 58.1 7.32 67.6 7.09 64.5 2.12 23.0 0.67 22.9 0.41 23.9 0.68 22.4 0.70 22.1 0.62 22.9 0.68 23.0 0.54 23.0 0.83 23.3 0.80 23.4 0.92 23.0 0.48 20.8 1.57 19.8 0.87 23.6 1.82 20.9 1.60 20.3 1.58 21.5 1.79 20.2 1.26 21.0 1.96 21.0 2.28 22.4 2.35 21.1 1.12
- 74. OLYMPIC ATHLETES SELECTION CRITERIA SPORT: EVENT/POSITION Age (yrs) Mean + SD Ht. (cm) Mean + SD Wt (kg) Mean + SD PI (Hirata) Mean + SD BMI Mean + SD Hockey (International) Forwards Halves Backs Goalkeepers Judo (International) 65 kg 71 kg 78 kg 86 kg 21.2 2.09 22.7 2.51 22.7 3.23 20.6 2.00 21.0 5.60 21.6 4.92 27.2 6.24 27.2 0.47 169.4 8.18 170.6 6.52 172.8 5.64 179.1 4.53 168.4 4.68 168.8 4.73 172.1 3.66 179.3 4.88 66.5 4.26 65.6 4.94 72.9 4.63 74.2 8.87 63.8 1.97 71.1 1.60 81.2 1.64 88.0 0.00 23.9 1.09 23.6 0.84 24.2 0.62 23.4 0.74 23.7 0.71 24.6 0.85 25.2 0.58 24.8 0.68 23.3 2.18 22.6 1.90 24.4 1.35 23.1 2.30 22.6 1.45 25.0 1.92 27.5 1.35 27.4 1.49
- 75. 1. Percent Mature Status Method = 2. Percentile Follow-up Method = Centile Established & Adult value. 3. Multiple Regression Equation Method (e.g. Predicted Adult Height PAH = 1.22 height (cm) – 7.2 Age (yrs) – 0.4 RUS Bone Age (yrs) +82.) 4. Combination Method = Quite Advance cannot be considered now. PREDICTION METHODS OF ADULT STATUS
- 76. NEW PAPERS TO BE ADDED IN ALL PHYSICAL EDUCATION PROGRAMMES (As compulsory Foundation Courses) 1. Sports Talent Selection & Counselling. 2. Physical Fitness & Wellness. 3. Exercise Prescription. 4. Exercise & Nutrition. 5. Sports for All. 6. CBSE Prescribed School PE Curriculum FOCUS. New Paper to be added in all Teacher Training Programmes like B.P.Ed., B.El.Ed. M.P.Ed. Etc. 1. Physical Fitness, Wellness & Active Lifestyle.
- 77. SPIRITUALITY IS THE SCIENCE OF ART OF TRUTHFULL EXECUTION OF DUTIES WITH RIGHT SPIRITS AND IS SYNONYMOUS WITH ONE’S RELIGION TO WHICH ONE IS SINCERELY DEVOTED WITH FULL TRUST & SURRENDER.
- 78. SPIRITUALITY (OR DHARAM) MEANS A DISCIPLINED LIFE. - Shantha Ramaswami
- 79. SWOT ANALYSIS OF A SCHOOL P.E.T. Strengths = 1. Approach to all Children. 2. Fitness and Growth interests all. 3. No.1 Position Potential. Weakness = Syllabi prescribed in P.E. not taught in B.P.Ed., M.P.Ed. etc. unavoidable incompetence. Opportunity = Plentiful by determination to learn and do of Refresher Courses & Internet availability of E-mail, Telephone to contact modern experts. Threats = Negative & demotivating thoughts of mind. e.g.It does not pay to give attention to children/students.
- 80. FURTHER DETAILS • ARE AVAILABLE IN THE FOLLOWING BOOK • A TEXTBOOK OF • TEST MEASUREMENT & EVALUATION • BY • Dr. DEVINDER K. KANSAL • SPORTS & SPIRITUAL SCIENCE PUBLISHERS JEEVAN PARK ,NEW DELHI. • Ph.011-25643801
- 81. Teacher Guidance to Students Learning to Learn. Learning to Unlearn. Education for Life. Education through Life. Education throughout Life.
- 82. Balanced Education (UNESCO’s Treasure With-in Learning to Know (Cognitive Domain). Learning to Do (Psychomotor Domain). Learning to Become. Learning to Live Together.
- 83. Personality Personal + Identity P = Physical E = Emtional R = Recreative S = Spiritual O = Occupational N = Nutritional A = Affective L = Learning (Cognitive) I = Iness (Internal) D = Developer E = Educational N = National & Dhayan T = Transcendental I = Intensity/Intentional T = Training Technology Y = Yoga/Attachment