Project cycle
- 1. Subject: Project Formulation and Environmental Impact Assessment Dhwani Shah,Assistant Professor Bhaikaka Centre for Human Settlements, APIED,VallabhVidyanagar. PROJECT CYCLE
- 2. What is a Project? ‘A unique set of co-ordinated activities/jobs, with definite starting and finishing points, undertaken by an individual or organization to meet specific objectives within defined schedule, cost and performance parameters.
- 3. Types of Project Personal Projects Preparation from your Exam Local Projects Cleanliness drive in your neighborhood Organizational Projects Construction of a highway taken up by an organization National Projects Literacy Campaign Preparation of Annual budget Global Projects Environmental protection
- 5. Identification Stage Understanding of the likely causes and linkages between existing problems and the needed actions. In depth knowledge and experience of local conditions – Source of suggestions for project formulation
- 6. Identification Stage Example: Existing Problem: High Pollution level in Delhi Needed action: ReduceTransport and Industrial Pollution To ReduceVehicular Pollution Mass RapidTransit System (MRTS) like Metro/BRTS Better Infrastructure for Using Non MotorizedTransport (NMT) like good side walks, cycle tracks, cycle sharing Restrict registration of new vehicles Ban DieselVehicles on the road Enforce strict emission norms, Pollution Under Control Certificate Encourage use of Car pool Grow more trees/ green belts in the city Declaring no traffic zone in the city. Eg- Chandni Chowk Ban vehicles with age of 10yrs or more plying on roads Traffic curbing measures like odd-even number plates
- 7. Preparation Projects that survive successful identification are prepared and analyzed before money is allocated to them. Criteria for Screening of ideas Effectiveness to achieve objective Cost of proposal/Resources available Ease of Implementation Time needed Scoring Alternate projects based on the criteria. Projects with maximum points selected for further Screening/ Appraisal.
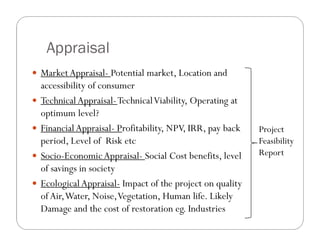
- 8. Appraisal MarketAppraisal- Potential market, Location and accessibility of consumer TechnicalAppraisal-TechnicalViability, Operating at optimum level? FinancialAppraisal- Profitability, NPV, IRR, pay back period, Level of Risk etc Socio-EconomicAppraisal- Social Cost benefits, level of savings in society EcologicalAppraisal- Impact of the project on quality of Air,Water, Noise,Vegetation, Human life. Likely Damage and the cost of restoration eg. Industries Project Feasibility Report
- 9. Project Selection Multi Criteria Evaluation After theAppraisal a project is selected for Implementation on the basis of Expected life Environmental Impact Net PresentValue/Rate of Return Flexibility Investment required etc. Points are given to each criteria and as per the weightage decided for each criteria an overall score is worked out for each project.
- 10. Ideas from Identification to Selection
- 11. Implementation & Monitoring Implementation A project that is considered to be worthwhile at the appraisal stage qualifies for implementation It is considered to have three phases: • Investment • Development • Operation Monitoring It requires an effective information gathering and management system that can check the progress of the project according to the plans that have been drawn up and the project objectives. Monitoring- 3 key parameters Time Cost Performance
- 12. Evaluation Evaluation is an ex-post assessment of whether the project was worthwhile. It seeks to answer such questions as: • Has the project been successful in attaining its objectives? • If not, in what respect has it failed? • How might its design and/or implementation have been improved? Evaluation helps to identify elements of strength and weakness, success or failure.The results are valuable in planning future projects and in attempts to avoid repeating or committing ‘mistakes’.