Citric Acid Production
- 1. PRESENTED BY, S.KIRUTHIKA, BON SECOURS COLLEGE FOR WOMEN, THANJAVUR. CITRIC ACID PRODUCTION
- 2. CONTENT Introduction History Microbes in Citric acid Production Citric acid fermentation techniques Factors affecting Citric acid production Industrial production of citric acid Applications/Uses of citric acid Side effects Largest producers in the world
- 3. Over view Citric acid is a usually occuring acid found primarily in Several Varieties of fruits and vegetables with citrus fruits such as lemons and limes containing the highest amounts of citric acid. This Organic acid has many uses, including as a food additive /Preservative, ingredient in Cosmetic products and as a powerful cleaving agent.
- 4. Introduction: Citric acid (2-hydroxy-1,2,3- propane tri carboxylic acid) is the most important commercial product, which is found in almost all plant & animal tissues. Citric acid is the most important organic acid produced in tonnage and is extensively used in food and pharmaceutical industries. Citric acid is a weak organic acid found in citrus fruits(lemon). It is good ,natural preservative and is also used to add an acidic taste to food and soft drinks. More than million tonnes are produced every year by fermentation.
- 6. HISTORY: The discovery of citric acid has been credited to the 8th century Muslim alchemist Jabir Ibn Hayyan (Geber). Citric acid was first isolated in 1784 by the Swedish chemist carl Wilhelm Scheele, who crystallize it from lemon juice. Industrial scale citric acid production began in 1890 based on the Italian citrus fruit industry. In 1893, C. Wehmer discovered penicillin mold could produce citric acid from sugar. However, microbial production of citric acid did not become industrially important until world war I disrupted Italian citrus exports.
- 7. Structure of citric acid
- 8. Micro-organisms used for citric acid production: Large number of micro-organisms including bacteria, fungi and yeasts have been employed to produce citric acid. The main advantages of using this micro-organisms are: a) Its easy of handling b) Its ability to ferment a variety of cheap raw materials c) High yields
- 9. Yeasts: Saccahromicopsis lipolytica Candida tropicalis C. oleophila C. guilliermondii C. parapsilosis C. citroformans Hansenula anamosa Micro organisms: Fungi: Aspergillus nagger A. aculeatus A. awamori A. carbonarius A. wentii A. foetidus Penicillium janthinelum Bacteria: Bacillus licheniformis Arthrobacter paraffinens Corynebacterium species
- 10. Citric acid production: Fermentation is the most economical and widely used ay for synthesis citric acid production. The industrial citric acid production can be carried in three different ways: surface fermentation submerged fermentation solid state fermentation
- 11. Surface Fermentation: Surface fermentation using Aspergillus niger may be done on rice bran as is the case in Japan, or in liquid solution in flat aluminium or stainless steel pans. Special strains of Aspergillus niger which can produce citric acid despite the high content of trace metals in rice bran are used.
- 12. SUBMERGED FERMENTATION: In this case , the strains are inoculated of about 15cm depth in fermentation tank. The culture is enhanced by giving aeration using air bubbles. And its allowed to grow for about 5 to 14 days at 27 to 33 degree Celsius. The citric acid produced in the fermentation tank and it is purified.
- 13. Solid state fermentation: It is simplest method for citric acid production. Solid state fermentation is also known as koji process, was first developed in Japan. Citric acid production reached a maximum(88g/kg dry matter)when fermentation as carried out with cassava having initial moisture of 62% at 26degree Celsius for 120 hours.
- 14. Separation: The biomass is separated by filtration. The liquid is transferred to recovery process Separation of citric acid from the liquid precipitation. Calcium hydroxide is added to obtain calcium citrate.
- 15. Tetra hydrate Wash the precipitate Dissolve it with dilute sulfuric acid, yield citric acid and calcium sulfate precipitate Bleach and crystallization Anhydrous or mono hydrate citric acid Separation process:
- 16. PURIFICATION: Purification is a simple form of getting a pure citric acid followed by two simple techniques. Precipitation Filtration React citric acid with calcium carbonate Filter precipitate React precipitate with sulfuric acid Filter precipitate Purified citric Acid
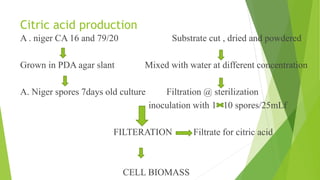
- 17. Citric acid production A . niger CA 16 and 79/20 Substrate cut , dried and powdered Grown in PDA agar slant Mixed with water at different concentration A. Niger spores 7days old culture Filtration @ sterilization inoculation with 1 10 spores/25mLf FILTERATION Filtrate for citric acid CELL BIOMASS
- 18. Factors affecting citric acid production: Nitrogen source pH Aeration Trace elements Temperature
- 19. Industrial production of citric acid: 99% of world production microbial processes surface or submerged culture. 70% of total production of 1.5 million tons per year is used in food and beverage industry as on acidifier or antioxidant to preserve or enhance the flavors and aromas of fruit juices, ice cream and marmalades. 20% used pharmaceutical industry as anti oxidant to preserve vitamins, effervescent, pH corrector, blood preservative, or in the form of iron citrate.
- 20. Tablets, ointments and cosmetic preparations Chemical industry remaining 10% softening and treatment of textile. Also used in the detergent industry as a Phosphate substitute, because of less entropic effect hardening of cement
- 21. Applications/uses of citric acid: Food & drink: Preservative and flavoring agent Emulsifying agent in ice-cream. Household cleaner: Kitchen Bathroom sprays. Cosmetics: Shampoos Body wash WASH CLEANERS: Nail polish Hand soap and other cosmetic products
- 22. To cure kidney disorders: Sodium citrate, acetic acid is used to prevent kidney stones. Side effects: Taking excess of citric acetate in combination with sodium citrate may lead to kidney failure. Taking citric acid with empty stomach may lead to stomach or intestinal side-effects. It may also lead to muscle twisting or cramps. It can also cause weight gain, swelling, fast heart rate, slow or rapid .
- 23. Largest producer in the world: country Fruit crop USA Grape fruit, pummelo China Mandarin Brazil Sweet orange India Acid lime Italy Lemon
- 25. ANY QUESTIONS ?