Plastics
- 1. By: Jesús Castillo, Bruno Koster and Sergio Vicente.
- 2. Student One Raw materials: COAL, NATURAL GAS, MINERALS, PLANTS and CRUDE OIL. With the synthesis of monomers you obtain a polymer.
- 3. METHODS. Thermocompression: Ex: doorknob
- 4. METHODS. Extrusion molding: Ex: tubes
- 5. METHODS. Blow molding: Ex: bottle
- 6. Student Two SYNTHESIS OF BASIC POLYMERS: Plastics change shape and for. ADDITIVES: Chemical products to give plastic new qualities.
- 7. INJECTION MOLDING: Process consisted in injecting materials into a mould.
- 8. FOAM MOLDING: Is a process in which you make soft plastics.
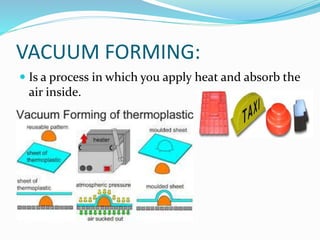
- 9. VACUUM FORMING: Is a process in which you apply heat and absorb the air inside.
- 10. CALENDERING: A sheet of plastic passes between two rolls.
- 11. Student Three PHYSICAL PROPERTIES OF PLASTIC Electical conductivity:Capacity of a material for allowing the electric current to pass. It has a high capacity of insulation. Used for protecting the wires. Thermal conductivity:It describes the behaviour of the polymers against the action of heat
- 12. PHYSICAL PROPERTIES OF PLASTICS Density: Discovered by Arquimedes. (not for plastics) Low Density Polyethylene also known as LDPE Low density polymer High thermal , chemical resistance. Expansion:Plastics expand if you increase their temperature. Melting point:If the plastic is made of LDPE the melting point would be 150·c If the plastic is made of HDPE the meltin point would be 135·c
- 13. MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF PLASTICS There are different types of stress: Traction: The resistance to traction is the highest effort a material can resist Compression: Mold because of compression is the oldest.You put a plastic on a mold with a cavity Bending:You can bend a plastic by using an electric resistance Shearing: Torsion: A plastic would be resistance to torsion if you can bend the plastic without breaking it.
- 14. MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF PLASTICS Elasticity: Plastics have a high capacity of elasticity. Used for wheels Malleability:When you can deform a plastic althought it is cold. Ductility:When plastic can be elongated with out breaking. Hardness:Is the capacity for penetrating in plastic. Weldability:The ability of welding plastics depends on time, temperature and pressure and the design of the plastic
- 15. CHEMICAL PROPERTIES OF PLASTIC Permeability: Is the ability of passing through a solid without changing its structure. A plastic bag is NOT permeable. Solubility: Plastics do not have the ability of solubility , except polyethenol and polyalcohol. Combustibility: Plastic , when it reaches certain temperatures , can be defored or melted.
- 16. BIOLOGICAL PROPERTIES OF PLASTIC Recyclability :Is the process of recycling plastic , and making other new products. Toxicity:
- 17. BIOLOGICAL PROPERTIES OF PLASTIC Biodegradability : Biodegradation of plastics by microorganisms and enzymes seems to be the most effective process.
- 18. Student Four Thermosetting Contains polymers Cross-linking process eliminates remlting in a product Improve meterials chemical properties Provides chemical resistance , heat resistance and structural.
- 19. THERMOSETING
- 20. THERMOPLASTICS Soften heated and become more fluid They can be remolded and recycled High strength, shrink resistance , easy weldability
- 21. ELASTOMER Polymer with viscoelasticity Weaker intermolecule forces It has a thin structure , slightly reticulated.