Herb (2)
- 2. Mentha Herb (Peppermint) Mentha piperitae الفلفلى النعناع عشب • Origin: • The dried leaves and flowering tops of Mentha piperita Linn., Family: Labiatae. • There are more than one species of Mentha, e.g. Mentha spicata ( spearmint) and M. aquatica (water • mint), Mentha vulgaris and others.
- 4. Morphological characters: • Odour: aromatic characteristic. • Taste: aromatic followed by cooling sensation. • Stem: - Herbaceous, perennial. - Quadrangular - Green to dark purple - Nearly glabrous, with scattered deflected hairs.
- 6. • Leaves: - opposite decussate - petiolate. - ovate lanceolate. - Light or dark green with purplish tinge. - upper surface: dark green nearly glabrous. - lower surface: light green, hairy especially on the veins - Apex: acute. - Base: acute or rounded. - Margin: sharply serrate. - Petiole: long slightly hairy.
- 7. - small - purple - Zygomorphic - Spike. Flowers
- 8. - Calyx: long, tubular, equally 5-toothed green to dark purple, hairy. • Corolla: dark purple, bilabiate. • Stamens: 4 short and equal. • Ovary: superior, bicarpellary tetralocular. • Fruit: blackish-brown, ellipsoidal.
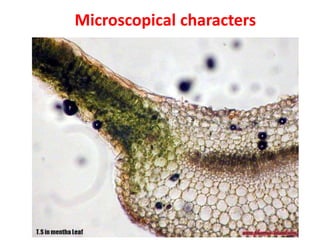
- 10. T.S in Mentha Stem
- 11. T.S in Mentha Stem
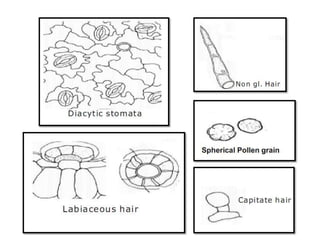
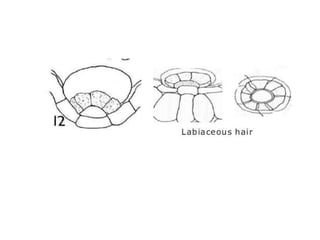
- 12. T.S in Mentha Stem Outline: quadrangular. Cortex: collenchyma in the corners only. Narrow xylem & wide pith. Less hairy; Glandular hair:(Labiaceous& Capitate). Non-glandular hair: (multicellular uniserriate).
- 13. Powdered Mentha Herb • Physical characters: • Color: green to light olive green. • Odour: aromatic characteristic. • Taste: aromatic followed by a sensation of cold in the mouth.
- 18. It is characterized microscopically by the presence of the following fragments: 1. Epidermal cells with wavy walls and diacytic stomata. 2. Non-glandular hairs. 3. Glandular labiaceous hair, unicellular stalk multicellular head consists of 8-16 cells radiating from a common center. 4. Different types of xylem vessels, fibres and wood parenchyma. 5. Smooth spherical pollen grains. 6. NO CALCIUM OXALATE.
- 19. Active constituents: 1- Volatile oil ( 0.7-1.5%) contains free Menthol (78%) Menthol esters (20%). 2- Tannins (6 to 12 %). 3- Flavonoids.
- 20. Uses & actions: 1-G.I.T. - Spasmolytic. -Carminative. - Digestive. -Anti-emetic. -Promotion of liver & gall bladder function (choleretic & cholagogue). -2- Externally: - Local anesthetic -Anti-parasitic. -Anti-pruritic. 3- Respiratory tract: Decongestant.
- 21. 4- In Pharmaceutical preparations: 1. Tooth paste. 2. mouth washes & gargles. 3. Soft gelatin capsules. 4. Aromatherapy •Aromatherapy is now a significant Complementary therapy involving the use of volatile oils to heal or improve well being
- 22. is used in pharmaceutical preparations as local antipruritic, counter-irritant and antiseptic. Mechanism of action Menthol act as calcium channel blocker. It affect the smooth muscles of vessels GIT or neuron cells and heart. It blocks the calcium channels and prevent the influx of calcium channel and leads to the relaxation of smooth muscles. 5- Recently the oil is used for treatment of colitis.
- 23. Contraindications: 1- In cases of gastro-esophageal reflux disease (GERD). 2- Not given to infants or small children. 3- Never apply peppermint oil to the face of an infant or small child as it may cause spasm that inhibit breathing. 4- cause gallstones worse. 5- Pure menthol is poisonous and should never be taken orally. 6- Excessive peppermint oil on the skin may cause allergic reactions (skin rash). 7- Do not use on broken or irritated skin & Avoid use near the eyes or mucous membranes.
- 24. Chemical tests: 1- Positive microchemical test with Sudan III. 2- Special chemical test: Menthol crystals + H2SO4 + vanillin orange yellow color + H2O violet color. Menthol Crystals Few dps of conc. H2SO4 Few dps of vanillin/H2SO4 Few dps of H2O Orange yellow colour Violet colour
- 26. Herba Thymi Thyme الزعتر عشب • Origin: The dried aerial parts of Thymus vulgaris and other Thymus species, Family: Labiatae. - should contain not less than 1.2% w/w v.o
- 27. Morphological characters: • Odour: agreeable aromatic • Taste: aromatic somewhat pungent. - Stem: quadrangular, grayish-brown or purplish. - Leaves: opposite decussate, sessile or shortly petiolate.
- 28. • Flowers: - zygomorphic, shortly pedicillate. - Calyx: tubular showing a ring of stiff hairs in the throat. - Corolla: bilabiate. - Stamens: 4 didynamous. - Ovary: superior, bicarpellary tetralocular.
- 29. Stem: Quadrangular or circular. Collenchyma is one continuous layer. Narrow pith & wide xylem Hairy; as in Mentha Non-glandular hair (Unicellular conical & bent hair). Diacytic stomata. Powder: Color: greenish brown Odor: aromatic. Taste: aromatic somewhat pungent. Microscopical characters
- 33. Active constituents: • 1- Volatile oil (1%): contain phenolic compounds mainly: - Thymol, - Carvacrol. • 2- Tannins. • 3- Flavonoids.
- 35. Antiseptic, antibacterial, antifungal and antioxidant properties. • Contraindications: • Thymol, at high doses, can cause liver toxicity, albuminuria and hematuria. • Prolonged use of thymol-based mouthwash can cause thyrotoxicosis. Antimicrobial, Anti-thrombotic.
- 36. Drug interactions: 1- Thyme interact with anti-coagulants increase risk of bleeding. 2- thyme interact with anti-hyperglycemic drugs may cause severe hypoglycemia. 3- Thyme interact with sedatives and CNS- depressants, increase dowsiness.
- 37. Chemical tests: 1- positive microchemical test with Sudan III. 2- Special chemical test: Thymol crystals + glacial acetic acid + conc. H2SO4 + HNO3 a deep bluish green colour is developed.
- 38. Ergot of Rye Origin: Ergot is the sclerotium of Claviceps purpurea, Family: Clavicipitaceae, developed in the ovary of rye plant, Secale cereale, Family Graminae. What is ergotism?
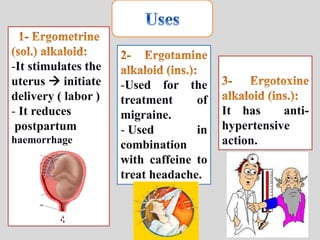
- 43. -It stimulates the uterus initiate delivery ( labor ) - It reduces postpartum haemorrhage -Used for the treatment of migraine. - Used in combination with caffeine to treat headache. It has anti- hypertensive action.
- 44. Shake the ergot with Na2CO3 and CHCl3. Separate the chloroform layer and shake it with PDMAB and FeCl3 in H2SO4 where a blue colour is developed in the acid layer. (used to detect ergot in flour). Shake the ergot with ether &5 drops of H2SO4, add NaHCO3and shake well where a reddish violet colour is given in the aqueous layer. Digest the sclerotium with NaOH to give chitosan , acetic acid and ammonia. Chitosan + Iodine + H2SO4 gives violet colour.