Come flying on Divergence Airways with Mike Biggs -"We always land"
- 2. Today I aim to • Show that Discoveries can be so much more. • Define some ‘How tos’ of great Discoveries. • Provide the core elements that will make them easier to understand and sell. WHY we always land…
- 3. Known fact finding Truly new stuff Discoveries (today) result in
- 4. Known fact finding Truly new stuff My goal for Discoveries
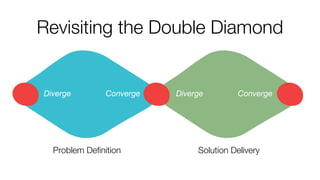
- 6. Revisiting the Double Diamond Diverge Converge Problem Definition Solution Delivery Diverge Converge
- 7. Introducing the all-new Double Diamond Machine….
- 8. Revisiting the Double Diamond Diverge Converge Sensemaking Feel uncomfortable Fuzzy Compounding Constraints Contradiction Complex Feel coherent Understood A path forward Defined problems Problem Definition Generative thinking Inductive thinkingAbductive Thinking Example activities Prototyping Testing Example activities Research Finding meaning Certainty
- 10. “It is not the mountain we conquer, but ourselves.” Edmund Hillary, Explorer
- 11. Principles of a great Discovery • Diversity of the team. • Intentional Divergence where we aim to Discover completely new information and push boundaries in: • Product • Process • Ourselves • Explicit Sensemaking. • Radical Editing resulting in models that provide clarity. • Problems to solve. • Validation of insights or solution ideas. • Focus
- 12. Diversity of team How we achieve it: GOOD: Racial, Culture, Gender, extrovert, introvert. BETTER: Role / function, area of expertise, level of experience, radical vs incremental innovators., Horizon 1 vs Horizon 3 thinkers. SUPER-CHARGED: No common language, extremely unrelated domain expertise, use children as focus group participants.
- 13. Intentional Divergence How we achieve it: GOOD: Question everything, call bullshit. BETTER: Use specific generative thinking tools such as: • Provocative Operations: e.g. “People are robots” • Random word. e.g “Lemon” + Interface =? • 6 Thinking Hats, CVS2BVS, X10, GBB, etc…. SUPER-CHARGED: Mexican Shaman Don Juan recommends ‘Not-Doings’ - an intentional act that will break your current way of perceiving.
- 15. Explicit Sensemaking How we achieve it: GOOD: Genius’ staring into the middle distance whilst listening to Jazz. BETTER: Collective discussion and formation of a shared view. Randomly putting elements together. SUPER-CHARGED: Using a repeatable formulas such as ‘narratvies’ which ensures the underlying equation is used. +
- 16. Ambiguity Ahead… Fasten your Seatbelts.
- 17. It’s ok. We have equations.
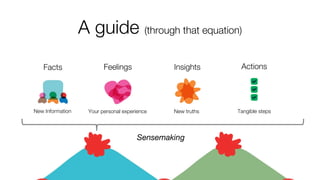
- 18. Sensemaking Equation New information + Stuff we know = Insights • Research • Facts • Constraints • Mental models • Design / Development models • Other Facts • Goals • Values / Meaning • Explanations that provide new meaning • A model that can be used to make decisions • A truth that is actionable beyond the immediate circumstances
- 19. A guide (through that equation) Sensemaking Facts New Information Feelings Your personal experience Insights New truths Actions Tangible steps
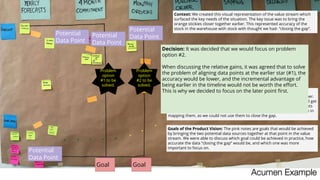
- 20. Potential Data Point Goal Acumen Example Potential Data Point Potential Data Point Potential Data Point Context: We created this visual representation of the value stream which surfaced the key needs of the situation. The key issue was to bring the orange stickies closer together earlier. This represented accuracy of the stock in the warehouse with stock with thought we had- “closing the gap”. Potential Data Points: The purple notes are potential data points that we learnt were available in the system and were important in one way or another. We mapped them along the value stream to understand how early we could get (and use) that point. It’s important to note that there are potential data points on both sides of the stream. If there were not, there would be no advantage in mapping them, as we could not use them to close the gap. Goals of the Product Vision: The pink notes are goals that would be achieved by bringing the two potential data sources together at that point in the value stream. We were able to discuss which goal could be achieved in practice, how accurate the data “closing the gap” would be, and which one was more important to focus on. Goal Problem option #2 to be solved. Problem option #1 to be solved. Decision: It was decided that we would focus on problem option #2. When discussing the relative gains, it was agreed that to solve the problem of aligning data points at the earlier star (#1), the accuracy would be lower, and the incremental advantage of being earlier in the timeline would not be worth the effort. This is why we decided to focus on the later point first.
- 21. Bresic Whitney Example After conducting value stream mapping to identify the primary waste in the system, we had a hunch about what would improve it the most; Internet speed, and virtual system access. But it was a hunch, and we wanted to be sure. So we created a chart (shown on the left) that plotted the pain points (including gains), against the desired future state that would support strategic goals. Contrary to our hunch, the area we could have the most impact was Workflows. We were able to prioritise workflow as an initial project which would release the most value in the shortest amount of time. PainPoints Gains Future Capabilities (visioned)
- 22. FUNK
- 23. FUNK IFICATION
- 25. Discovery_
- 26. DiscoveryProduct
- 28. DiscoveryService
- 31. Discoveries can happen anywhere at any time The further upstream they occur the more value they provide
- 32. Level of Abstraction Strategic Risks identified to be monitored Goals & types of learning required ⟩ • Generative Thinking • FutureSpectives • Personal Reflection • Sensemaking • Framing Changes in Society Our Identity Our Assets Coverage not metrics ActivitiesFocus Area(s) Hypothesis for new business models = Product / Market fit ⟩ • Service Blueprinting • Business Model Canvas • Market Analysis • Competitive Analysis • How Now Wow Competitive Environment Business Models The Org, the Market Key Metrics Hypotheses for new customers / new problems to be solved = Problem / Solution fit ⟩ • Design Thinking • Kano analysis • Qualitative Interviews • Jobs to be Done • Empathy Maps Customer problems/ needs Key metrics Hypotheses for process improvement and/or feature-based product improvement ⟩ • Value Stream Mapping • Theory of Constraints • Contextual Enquiry Internal process/ value streams Alignment to strategy KPIs TACTICAL STRATEGIC MANDATORYFORINNOVATIONCATALYSTSFORINNOVATION Outcomes Desired
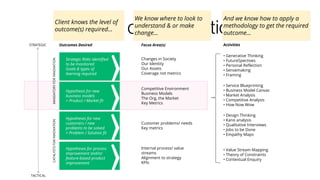
- 33. Level of Abstraction Strategic Risks identified to be monitored Goals & types of learning required ⟩ • Generative Thinking • FutureSpectives • Personal Reflection • Sensemaking • Framing Changes in Society Our Identity Our Assets Coverage not metrics ActivitiesFocus Area(s) Hypothesis for new business models = Product / Market fit ⟩ • Service Blueprinting • Business Model Canvas • Market Analysis • Competitive Analysis • How Now Wow Competitive Environment Business Models The Org, the Market Key Metrics Hypotheses for new customers / new problems to be solved = Problem / Solution fit ⟩ • Design Thinking • Kano analysis • Qualitative Interviews • Jobs to be Done • Empathy Maps Customer problems/ needs Key metrics Hypotheses for process improvement and/or feature-based product improvement ⟩ • Value Stream Mapping • Theory of Constraints • Contextual Enquiry Internal process/ value streams Alignment to strategy KPIs TACTICAL STRATEGIC MANDATORYFORINNOVATIONCATALYSTSFORINNOVATION Outcomes Desired Client knows the level of outcome(s) required... We know where to look to understand & or make change... And we know how to apply a methodology to get the required outcome...
- 34. Selling Formula Service Blueprinting Business Model Canvas Market Analysis Competitive Analysis How Now Wow Hypothesis for new business models = Product / Market fit ⟩ Competitive Environment Business Models The Org, the Market Key Metrics Define the value Prove we’ve done it before Have a method Be specific about the outputs
- 35. And now for something completely different BUT AMAZING
- 36. Suncorp Example Suncorp are practicing a radical discovery as an ongoing function within their organisation. They are reducing their strategic risk by constantly scanning industries that could affect them in the future. They do this through: ● Constant broad coverage of potential signals. ● No sense of what’s most important and no prioritisation.
- 37. Suncorp Example
- 38. Going up into the clouds can feel like magic. But it isn’t. And because we have methods. We always land.
- 43. Links and Resources ● ‘Narratives’ - Sensemaking Method by Mike Biggs ● Reflection Cards by Mathias Jakobsen & Dave Gray ● Shultz hour Article ● Suncorp Strategic Risk/ Innovation Model ● CVS 2 BVS Thinking Tool ● X10 Thinking Tool ● Provocative Operation Thinking Tool ● 6 Thinking Hats Thinking Tool ● http://alangullette.com/essays/philo/stopping.htm ● Great Jazz Playlist: