Chap 3 global context of business
- 1. Memoona Qadeer Copyright ©2003 Prentice Hall, Inc.
- 2. Today’s Plan Let’s improve- quiz The company Lesson part 1 Break Lesson part 1 Let’s improve- exercise The company Foresee: Next class
- 4. Chapter 2 The Global Context of Business
- 5. Exercise Give me stories of different products and marketing approaches in other countries, and compare them in Palestine? What evidence have we seen in the last ten years of growing international business partnership? Trade agreements- global mergers- joint ventures- licensing
- 6. “We are in the midst of a great transition from narrow nationalism to international partnership.” ~ Lyndon Baines Johnson
- 7. Key Topics The rise of global business Major world marketplaces and Palestine trading partners Influences on international business International business management The impact of differences among nations
- 8. The key drivers to globalization Global market Drivers: Convergence Similar customer needs, Global customers, Transferable marketing Trade policies, Technical Scale economies, GovernmentStandards, host government, Global Sourcing efficiencies Cost Influence policies Strategies Countries costs, Advantages High product development costs Interdependence, Competitors global High exports/imports, Global Competition
- 9. Globalization Is Gaining Speed The world economy is becoming a single, interdependent system Export: Domestic product sold abroad Import: Foreign product sold domestically
- 10. Globalization Is Gaining Speed Example: Asian financial markets in the late 90s directly affects stock markets worldwide. Discussion: what product from other countries do you useconsume? Why have you chosen it? Why not Palestinian product?
- 11. Categorizing Economies High Income Countries: Per capita income greater than $9,386 Middle Income Countries: Per capita income between $765 and $9,386 Low Income Countries: Per capita income of less than $765 Discussion: what countries fall into each category?
- 12. Major World Marketplaces North America NAFTA Europe EU Pacific Asia Do we have any economic agreement with other countries. What are they?
- 13. The North American Marketplace (NAFTA) Canada United States Mexico Copyright ©2003 Prentice Hall, Inc. 2 - 13
- 14. Europe and the Nations of the European Union • Austria • Luxembourg • Portugal • Sweden • Belgium • Netherlands • Spain • United Kingdom • Denmark • Finland • France • Germany • Greece • Ireland • Italy • Ireland • Italy Copyright ©2003 Prentice Hall, Inc. 2 - 14
- 15. The Nations of ASEAN • Brunei • Indonesia • Malaysia • Philippines • Singapore • Thailand • Vietnam Copyright ©2003 Prentice Hall, Inc. 2 - 15
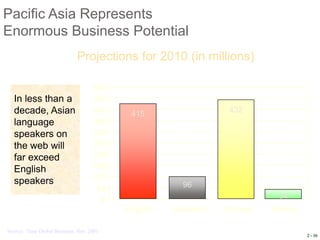
- 16. Pacific Asia Represents Enormous Business Potential Projections for 2010 (in millions) 500 In less than a 450 decade, Asian 400 415 432 language 350 speakers on 300 the web will 250 far exceed 200 English 150 speakers 100 96 50 34 0 English Japanese Chinese Korean Source: Time Global Business, Nov. 2001 2 - 16
- 17. Competitive Advantage Absolute Advantage: when one country can produce a product cheaper andor higher quality than any other country. Ex. OPEC Comparative Advantage: when one country can produce certain goods or services more efficiently and effectively than others. Ex. US software
- 18. Competitive advantages When competitive advantage is materialized? When a firm earns persistently higher rate of profit over its rivals. Determinants of profit level 1- Value of company products in customers’ eyes. 2- Company production cost.
- 19. Competitive advantage It can be created in certain industrial field, through the adoption of low-cost- differentiation strategy. M. Porter
- 20. National Competitive Advantage Factor conditions Demand conditions Related and supporting industries Strategies, structures, an d rivalries Qui. Evaluate Palestine?
- 21. Import/Export Balances Balance of Trade Trade Deficits Trade Surpluses Balance of Payments The total flow of money into or out of an economy
- 22. Exchange Rates Heavily Impact Global Trade When an economy’s currency is strong: Domestic companies find it harder to export products Foreign companies find it easier to import products Domestic companies may move production to cheaper sites in foreign countries Implications for balance of trade?
- 23. Exchange Rates Heavily Impact Global Trade When an economy’s currency is weak: Domestic companies find it easier to export products Foreign companies find it harder to import products Foreign companies may invest in production facilities Implications for balance of trade?
- 24. The U.S. Economy Has a Growing Trade Deficit U.S. Imports & Exports U.S. Trade Deficit (in billions) (in billions) 1600 $400,000 1400 350,000 344,716 1200 300,000 1000 250,000 255,971 800 200,000 600 150,000 166,898 400 100,000 35,666 105,932 102,113 200 28,266 97,039 95,947 78,857 50,000 68,949 0 0 1990 1991 1992 1993 1994 1995 1996 1997 1999 2000 1998 1990 1991 1992 1993 1994 1995 1996 1997 1998 1999 2000 Imports Exports Copyright ©2003 Prentice Hall, Inc. 2 - 24
- 25. Does It Make Sense to Go International? Is there Can the Is the foreign Does the international product be business firm have or demand for YES modified to fit YES YES climate suited can it get the the firm’s a foreign to imports? necessary product? market? skills and NO NO NO knowledge to do business NO abroad? YES Stay Domestic Go International Copyright ©2003 Prentice Hall, Inc. 2 - 25
- 26. Levels of International Involvement Importer & Exporter International Firms Multinational Firms
- 27. International Organizational Structures HIGH INVOLVEMENT Foreign Investment Strategic Alliances Branch Offices Licensing Arrangements Independent Agents LOW
- 28. Barriers to International Trade Legal & Political Social & Cultural Differences Differences Economic Differences
- 29. Take Time to Learn the Culture Thoroughly! Este es nuestro nuevo auto: Ha, ha, ha, ha, h el NOVA! a, ha!!!
- 30. The Customer’s Language A Critical Business Success Factor In the U.S. alone, 18% of the population does not speak English at home. Only 48% of the world’s Web users are native English speakers. Consumers are four times more likely to buy a product on the Internet if the website is in their preferred language. Source: Time Global Business, Nov. 2001
- 31. Economic Differences To operate effectively in another country, businesses must know when, and to what extent, the government is involved in a given industry.
- 32. Legal & Political Differences Quotas, Tariffs, & Subsidies Protectionism Local Content Laws Business Practice Laws Day to day operations Cartels Dumping
- 33. Definitions Quota: restriction on the number of certain type of product that can be imported into a country. Embargo: complete ban on imports and exports, imposed by a government for political reasons. Tariff: tax levied on imported products. Subsidy: government payments to help a domestic business compete with foreign firms. Protectionism: the practice of protecting domestic business against foreign competition.
- 34. Chapter Review Discuss the rise of international business, describe the major world marketplaces. Explain how competitive advantage, import-export balances, exchange rates, and foreign competition shape international business strategies.
- 35. Chapter Review Discuss what factors influence whether a company should engage in international business. Identify different levels of international involvement and international organizational structure. Describe key barriers to international trade.