23.3.d sedimentary rocks ppt.ppt
- 2. ROCK CYCLE
- 3. Relative Percentages of Sedimentary Rocks
- 4. SEDIMENT From Weathering & Erosion Precipitation from saturated solution calcite, quartz Product of evaporation halite, gypsum Unconsolidated- NOT cemented
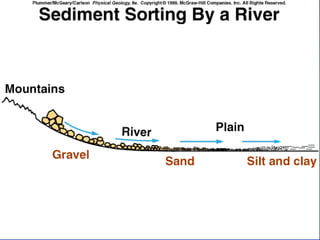
- 5. SEDIMENT Particle size Pebbles, cobbles, boulders Gravel- > 2mm Sand- 2mm - 0.063mm Silt - 0.063mm - 0.004mm Clay- < 0.004 Deposition Clay-sized particle vs. clay mineral
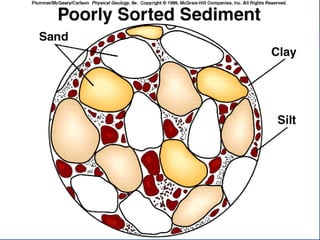
- 6. SEDIMENT Transportation Abrasion Rounding Sorting Deposition Environment of deposition- specific Preservation
- 10. SEDIMENT Transportation Abrasion Rounding Sorting Deposition Environment of deposition- specific Preservation
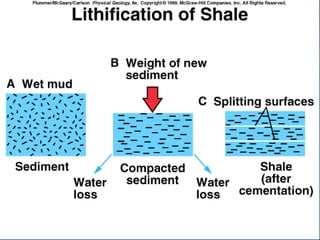
- 13. SEDIMENT Lithification Compaction Decrease in pore space for very fine grain size (clay) Cementation Clastic texture Cements- silica, calcite, iron oxide Crystallization Crystalline texture
- 15. SEDIMENT Lithification Compaction Decrease in pore space for very fine grain size (clay) Cementation Clastic texture Cements- silica, calcite, iron oxide Crystallization Crystalline texture
- 17. SEDIMENT Lithification Compaction Decrease in pore space for very fine grain size (clay) Cementation Clastic texture Cements- silica, calcite, iron oxide Crystallization Crystalline texture
- 19. TYPES OF SEDIMENTARY ROCKS Clastic or Detrital Chemical- inorganic precipitation or evaporation Biochemical- Organic remains shells, charcoal, plant fragments
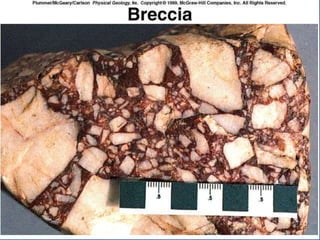
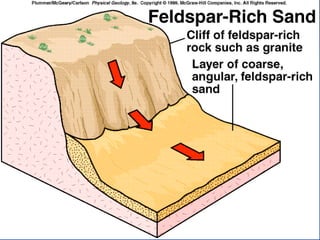
- 20. CLASTIC (Detrital) ROCKS Breccia and Conglomerate (> 2mm) Sedimentary Breccia- angular fragments Conglomerate- rounded fragments Sandstone (2mm - 0.063mm) Quartz sandstone Arkose (feldspar) Graywacke (appreciable amounts of silt/clay) Fine-grained Matrix Usually from turbidity currents
- 23. CLASTIC (Detrital) ROCKS Breccia and Conglomerate (> 2mm) Sedimentary Breccia- angular fragments Conglomerate- rounded fragments Sandstone (2mm - 0.063mm) Quartz sandstone Arkose (feldspar) Graywacke (appreciable amounts of silt/clay) Fine-grained Matrix Usually from turbidity currents
- 24. Quartz Sandstone
- 28. CLASTIC ROCKS Fine-grained Rocks Shale- fissile (in ‘sheets’) Siltstone Claystone Mudstone (silt and clay)
- 31. CHEMICAL SEDIMENTARY ROCKS Carbonate Rocks Limestone- made of calcite Inorganic varieties micrite, oolites, travertine Dolomite Recrystallization Chert- silica Evaporites Rock gypsum Rock salt
- 34. BIOCHEMICAL SEDIMENTARY ROCKS Coal Develops from peat plant fragments Lignite Bituminous Coal Carbonate Rocks Limestone- made of calcite organic varieties Coquina Fossiliferous Limestone Chalk
- 36. BIOCHEMICAL SEDIMENTARY ROCKS Coal Develops from peat plant fragments Lignite Bituminous Coal Carbonate Rocks Limestone- made of calcite organic varieties Coquina Fossiliferous Limestone Chalk
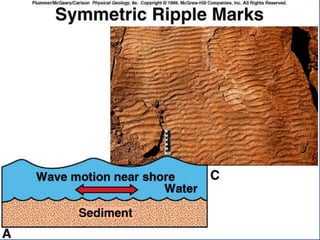
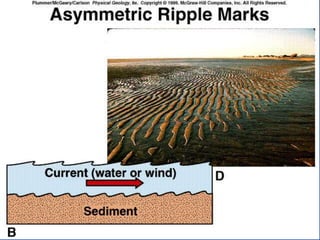
- 40. SEDIMENTARY STRUCTURES BEDDING- Principle of Original Horizontality Bedding plane Cross-bedding Graded bed Mud cracks Ripple marks Fossils
- 43. SEDIMENTARY STRUCTURES BEDDING- Principle of Original Horizontality Bedding plane Cross-bedding Graded bed Mud cracks Ripple marks Fossils
- 44. DUNES
- 47. SEDIMENTARY STRUCTURES BEDDING- Principle of Original Horizontality Bedding plane Cross-bedding Graded bed Mud cracks Ripple marks Fossils
- 50. SEDIMENTARY STRUCTURES BEDDING- Principle of Original Horizontality Bedding plane Cross-bedding Graded bed Mud cracks Ripple marks Fossils
- 51. Mudcracks
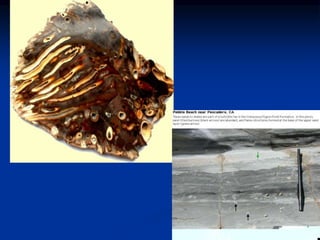
- 55. SEDIMENTARY STRUCTURES BEDDING- Principle of Original Horizontality Bedding plane Cross-bedding Graded bed Mud cracks Ripple marks Fossils Body Fossils Trace Fossils
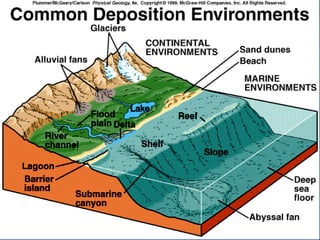
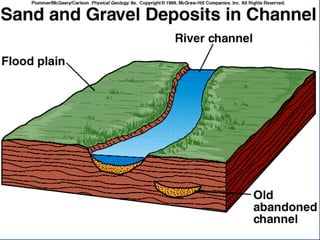
- 61. INTERPRETATION OF SEDIMENTARY ROCKS Source Area Environment of Deposition Glacial environments Tillites Alluvial fan Arkose River channel and flood plain Interbedded shales and sandstones; cross-bedded Lake Shales; interbedded siltstones and mudstones Delta
- 63. Glacial Environment & Till
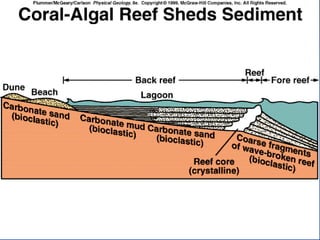
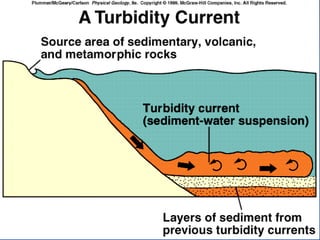
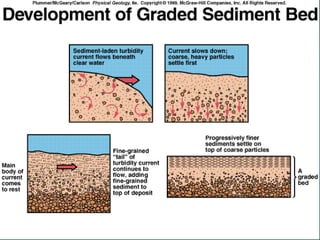
- 66. INTERPRETATION OF SEDIMENTARY ROCK Environment of Deposition Beach, Barrier Island, Dune Very well sorted quartz sandstones Lagoon Shales Shallow marine shelf Interbedded sandstones and shales; burrowed Reef Skeletal Limestones Deep marine environment Turbidites- sequence of GRADED sandstones to shales
- 68. INTERPRETATION OF SEDIMENTARY ROCK Environment of Deposition Beach, Barrier Island, Dune Very well sorted quartz sandstones Lagoon fine grained sediment Shallow marine shelf Interbedded sandstones and shales; burrowed Reef Skeletal Limestones Deep marine environment Turbidites- sequence of GRADED sandstones to shales
- 71. CALCAREOUS
- 74. INTERPRETATION OF SEDIMENTARY ROCK Environment of Deposition Beach, Barrier Island, Dune Very well sorted quartz sandstones Lagoon Shales Shallow marine shelf Interbedded sandstones and shales; burrowed Reef Skeletal Limestones Deep marine environment Turbidites- sequence of GRADED sandstones to shales
- 77. INTERPRETATION OF SEDIMENTARY ROCK Plate Tectonics and Sedimentary Rocks At convergent boundaries Uplift results in Very rapid rates of erosion Thick accumulations of clastic sediment At transform boundaries Rapid rates of erosion, deposition and burial Good basins for petroleum exploration At divergent boundaries Initial stages of rifting- thick wedges of gravel and coarse sediment
- 78. Resources Non-Metallic Sand and gravel Limestone Clay Gypsum Energy Resources Oil and gas Coal
- 79. Formation of Oil and Gas
- 80. Thank you…