The S Curve of Business: The Key Levers to Sustaining Momentum for Your Brand
- 1. The S Curve of Business: The Key Levers to Sustaining Momentum for Your Brand
- 2. The real path of growth is a sigmoid, or S curve that picks up speed at first then tapers off as growth slows and the company matures. The True Shape of Growth.
- 3. The “hockey stick” of growth you see pictured to the right is a fantasy. Companies simply don’t have crazy success without encountering some growing pains, shifts in the market, or other changes that affect profitability. What Growth Isn’t.
- 4. Looking closer, you’ll see that the S curve has temporary dips called strategic inflection points—moments where growth slows, requiring action by the company to continue moving upward. These inflection points are a natural consequence of growth, and should be treated as an opportunity. The S Curve of Business Growth.
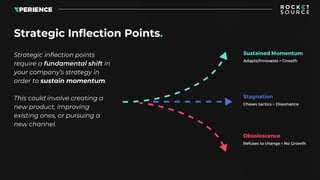
- 5. Strategic inflection points require a fundamental shift in your company’s strategy in order to sustain momentum. This could involve creating a new product, improving existing ones, or pursuing a new channel. Strategic Inflection Points.
- 6. Use data to inform your decision-making during inflection points. The outliers (larger circles) represent innovation loops and outcomes that could be supported with an increased budget. Leveraging Data.
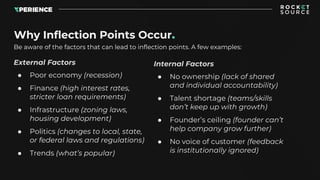
- 7. Why Inflection Points Occur. External Factors ● Poor economy (recession) ● Finance (high interest rates, stricter loan requirements) ● Infrastructure (zoning laws, housing development) ● Politics (changes to local, state, or federal laws and regulations) ● Trends (what’s popular) Be aware of the factors that can lead to inflection points. A few examples: Internal Factors ● No ownership (lack of shared and individual accountability) ● Talent shortage (teams/skills don’t keep up with growth) ● Founder’s ceiling (founder can’t help company grow further) ● No voice of customer (feedback is institutionally ignored)
- 8. The results of a company’s actions in response to an inflection point are determined by the company’s preparedness and ability to adapt. To prepare your business to react to inflection points, you need to start with a Growth Framework. Sustaining Growth on the S Curve of Business.
- 9. Before you can nail any new initiatives, you need to have a solid foundation for growth: ● Analyze product/market fit ● Onboard people who have a growth mindset ● Establish effective processes, and adopt reliable platforms ● Understand the journey your ideal customers follow to become a buyer ● Learn how to constantly optimize the end-to-end customer experience Always Start With a Solid Framework.
- 11. StoryVesting is our own system for improving customer experience and promoting growth by maintaining relationships between: ● Customers and the brand ● Company and the customer ● Employees and the company ● Company and the employees Foster Quality CX With StoryVesting.
- 12. The essential building blocks of any business. Success depends largely on the people you choose and the tools they use. Make sure your growth framework has people (employees and partners) with a growth mindset, processes that have been refined and optimized, and platforms that enable you to deliver the best possible customer experience. Framework: People, Processes, and Platforms.
- 13. The traditional sales funnel is designed for a one-time purchase. Meanwhile, the bowtie funnel is designed to carry your ideal customer from prospect to brand advocacy. By leveraging data-driven insights, you’ll continually optimize the buyer journey and generate incredible momentum by keeping customers coming back for more. Bowtie Funnel.
- 14. Zappos succeeds because they: ● Introduced a new retail experience by offering free shipping, free returns, and a call center focused on quality service. ● Maintain a like-minded team by hiring vested employees and using retention programs. ● Mastered customer retention. Around 75% of sales come from repeat customers. ● Support business culture, nurturing that unique identity with programs and common goals. Zappos as Model for Growth Frameworks.
- 15. Apple provides a good example of how inflection points can be handled. Invent: Scroll wheel, iTunes software. Innovate: iPod touch, App store. Improve: New ideas come directly from customer feedback and user data. Using the Three Is to Handle Inflection Points. https://www.lifewire.com/history-ipod-classic-original-2000732
- 16. A failure to respond to a inflection point can have disastrous results. Some of the more common causes: ● Lack of Recognition ● Panic Paralysis ● Falling into Old Habits Failure to Act During Inflection Points.
- 17. As in-home streaming became more of a reality, Blockbuster stuck with its brick-and-mortar model, unwittingly paving the way for Netflix to take over. Blockbuster: a Failure to Act.
- 18. Risk-taking is a given during inflection points, but avoid making costly mistakes: Channel Chasing Moving away from core channels in order to pursue short-term revenue growth. Non-productive “Innovation” Making changes that fail to introduce something unique or that stray too far from the business’ core values often leads to more problems than solutions. Negative Actions.
- 19. The retail giant (1) abandoned its core channels prematurely in order to explore new channels that strayed from its core focus and (2) failed to invest in computer technology to improve its supply chain, allowing competitors like Walmart to dominate the market. Misguided Actions Accelerated Kmart’s Downfall.
- 20. Companies that excel during inflection points: ● Are aware of shifts in external factors, ● Identify threats to growth, ● Adhere to a growth framework, ● Keep employees vested and on the path to growth, ● And work tirelessly to improve the customer’s buying experience. Reacting to Inflection Points.
- 21. Insulate your business from disruption. Learn more at RocketSource.co