Approach to case of arthritis
- 1. APPROACH TO ARTHRITIS Guide:Dr.Sanjay Dubey Canditate:Dr.Sarath Menon.R DEPT.MEDICINE,RHEUMATOLOGY DIVISION, MGM MEDICAL COLLEGE ,INDORE.
- 2. OUTLINE Rheumatological history and clinical examination Inflammatory /non-inflammatory arthritis Mono/ Oligo arthritis Polyarthritis Soft tissue rheumatism Lab investigations Synovial fluid analysis Imaging
- 3. EVALUATION OF A PATIENT WITH ARTHRITIS IN RHEUMATOLOGY OPD Articular or non articular Inflammatory or non inflammatory Acute or chronic Monoarticular or polyarticular Extra articular signs
- 4. ARTICULAR NONARTICLAR - localised pain - Deep or diffuse pain. - Point or local tenderness - Painful or limited range of - Painful active movements but movemnt - both active and not on passive passive - Physical findings are remote - Swelling of joint from joint capsule. - Crepitation. - swelling,crepitation,joint - Joint instability. instability, deformity are rare. - Locking of joint. - Deformity.
- 5. ARTHRITIS inflammatory Non- inflammatory Cardinal signs NO signs Systemic symptoms Stiffness-<60 mnt Stiffness- >1 hr - intermittent - prolon. rest -brief rest Lab evidences Trauma,rept.use, ESR Degenerative,tumor CRP
- 6. THE RHEUMATOLOGIC HISTORY h/o presenting complaints - Onset - progression - distribution of disease - stiffness - aggravating or relieving factor - diurnal variation - other systemic feature - functional disability General systematic medical history. Past medical and surgical history. Family history. Drug history.
- 7. RHEUMATIC DISEASE SIGNS Swelling Posture of joint Deformity Warmth Redness Tenderness Limitation of joint movement Crepitus Stability Function
- 8. EXTRA ARTICULAR SIGNS & SYMPTOMS Constitutional symptoms Skin rashes Mucous membrane lesions Ocular Nails Raynauds Serositis
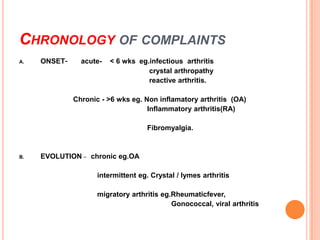
- 9. CHRONOLOGY OF COMPLAINTS A. ONSET- acute- < 6 wks eg.infectious arthritis crystal arthropathy reactive arthritis. Chronic - >6 wks eg. Non inflamatory arthritis (OA) Inflammatory arthritis(RA) Fibromyalgia. B. EVOLUTION – chronic eg.OA intermittent eg. Crystal / lymes arthritis migratory arthritis eg.Rheumaticfever, Gonococcal, viral arthritis
- 10. CHRONOLOGY OF COMPLAINTS C. Extent of articular involvement - Monoarticular (one joint involved) - Oligo or pauciarticular (two or three joint) - Polyarticular (> 3 joints) D. Distribution of joint involvement -symmetrical- upper and lower limb eg. RA, SLE -Asymmetrical-eg. psoriatic arthritis, spondyloarthropathy, gout -Involvement of axial skeletal-eg AS, OA, RA(only cervical spine)
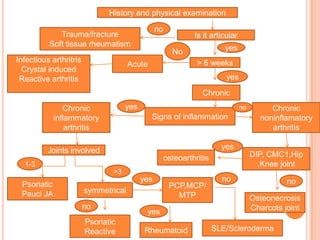
- 11. History and physical examination no Trauma/fracture Is it articular Soft tissue rheumatism yes No Infectious arthritris > 6 weeks Acute Crystal induced Reactive arthritis yes Chronic Chronic yes no Chronic inflammatory Signs of inflammation noninflamatory arthritis arthritis Joints involved yes osteoarthritis DIP, CMC1,Hip 1-3 ,Knee joint >3 yes no no Psoriatic PCP,MCP/ Pauci JA symmetrical MTP Osteonecrosis no Charcots joint yes Psoriatic Reactive Rheumatoid SLE/Scleroderma
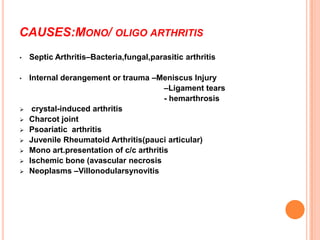
- 12. CAUSES:MONO/ OLIGO ARTHRITIS • Septic Arthritis–Bacteria,fungal,parasitic arthritis • Internal derangement or trauma –Meniscus Injury –Ligament tears - hemarthrosis crystal-induced arthritis Charcot joint Psoariatic arthritis Juvenile Rheumatoid Arthritis(pauci articular) Mono art.presentation of c/c arthritis Ischemic bone (avascular necrosis Neoplasms –Villonodularsynovitis
- 13. SEPTIC ARTHRITIS: RISK FACTORS Prosthetic hip joint. Prosthetic knee joint. Skin Infection. Joint surgery. Rheumatoid Arthritis. Elderly patients over age 80 years old. Diabetes Mellitus. Intravenous drug use (unusual joints affected). Large vein catheterization (unusual joints affected).
- 14. CAUSES OF SEPTIC ARTHRITIS Young sexually active adults –Neisseria gonorrhoeae (most common) More common in women –Staphylococcus aureus –Streptococcus Older adults –Staphylococcus aureus(50%) –Streptococcus species -Gram Negative Bacilli
- 15. SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS Rapid onset monoarticular joint inflammation Joints affected in bacterial infection –Septic Knee (50% of cases),hip (children), ankle, - shoulder Joints affected with intravenous Drug Abuse –SI joint, SC joint.pubic symphysis,vertebral spaces
- 16. GOUT: URIC ACID CRYSTALS RISK FACTOR -Obesity -Diabetes Mellitus -Hyperlipidemia -Hypertension -Atherosclerosis -Alcohol use -Thiazide Diuretics -Renal insufficiency -Myeloproliferativedisease
- 17. GOUT :SIGN AND SYMPTOMS •Acute onset of lower extremity joint pain –First Metatarsophalangeal joint (great toe) - Affected in 50% of first gout attacks •Fever and chills •Joint Inflammation - Asymmetric joint involvement - May only involve one side with the first attack
- 18. GOUTY ARTHRITIS
- 19. GOUT SynovialFluid •Polarizing Microscopy •Negatively birefringent Needle shaped Uric Acid crystals • Gram Stain and Culture •Rule out Septic Arthritis
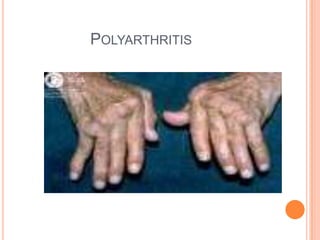
- 20. POLYARTHRITIS
- 21. POLYARTHRITIS Acute Polyarthritis - < 6 wks - Viral - Borrelia burgdorferi Chronic Polyarthritis: - >6 weeks <60yrs age : RA, SLE, psoriatic arthritis, spondyloarthropathies >60yrs age : crystal induced, OA
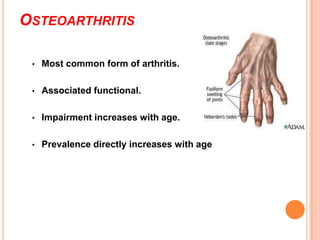
- 22. OSTEOARTHRITIS • Most common form of arthritis. • Associated functional. • Impairment increases with age. • Prevalence directly increases with age
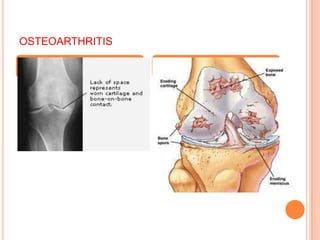
- 23. PATHOPHYSIOLOGY Primary lesion resides in the articular cartilage –Abnormal cartilage repair and remodeling –Chondrocytes proteolytic enzymes destroy cartilage subchondral subchondral sclerosis cysts Marginal osteophytes
- 24. OSTEOARTHRITIS
- 25. SIGN AND SYMPTOMS • Pain on motion that worsens with increasing joint usage • • Slowly progressive deformity and possibly pain • No systemic manifestations Associated muscle spasm, contractures and atrophy Symptoms uncommon before age 40 • Morning stiffness of short duration (<30 minutes)
- 26. DISTRIBUTION OF OSTEOARTHRITIS • Joints spared –Wrist –Metacarpal-phalangeal (except thumb) –Elbow –Ankle • Joints commonly involved • knee • hip • foot • hand –DIP (Heberden'sNodes) –PIP (Bouchard's Nodes) –First CMC jt(thumb) •Cervical and lumbar spine
- 27. RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS Affects all ethnic groups Peak incidence 4-6th decades Most widely used criteria ACR Diagnosis is based on the clinical criterion and cant be made until symptoms present for several weeks positive RF supports Diagnosis (20% are seronegative)
- 28. ACR RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS CRITERIA NEED TO HAVE 4 OF 7 1. Morning stiffness:-in and around the joint lasting 1 hr before maximal improvement. 2. Arthritis of 3 or more joint area observed by the physician. 14 possible joint area involved are rt < PIP,MCP, wrist, elbow, knee, ankle and MTP joint. 3. Arthritis of hand joints- wrist,mcp &pip joint. 4. Symmetrical arthritis. 5. Rheumatoid nodule. 6. Serum Rheumatoid factor. 7. Radiographic changes – erosion or bony decalcification in or adjacent to involved joints. Criteria 1 to 5 must be present for at least 6 wks Criteria 2 to 5 must be observed by physician
- 29. GUIDELINES FOR CLASSIFICATION 1. Four of the seven criteri are required to classify a pts is having RA. 2. Pts with two or more clinical diagnoses are not excluded.
- 30. DISTRIBUTION OF RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS •Affects small and medium sized joints •Typical patient has symmetrical inflammation in the wrists and/or MCP joints •Spares DIP •Morning stiffness, inactivity stiffness
- 31. DEFORMITIES Z deformity Swan neck deformity Boutonniere deformity
- 32. DEFORMITY- RA Swan neck deformity
- 34. Z - deformity Subcutaneous nodules
- 36. SYSTEMIC ERYTHEMATOSUS LUPUS Immune complex deposition disease, involving many organs Female:Male 10:1 ANA and other criterion will make the diagnosis
- 37. CRITERION FOR DIAGNOSIS OF SLE NEED 4 OUT OF 11 TO MAKE THE DIAGNOSIS MalarRash :Rash spares nasolabialfolds Discoid Rash Photosensitivity Oral Ulcers: Painless observed by physician Arthritis: Nonserosive 2 or > joints Serositis: Pleuritis, Pericarditis Renal Disorder: Proteinuria> o.5g/day or casts Neurologic Disorder: seizures/ psychosis HematologicDisorder: Hemolysis, Leukopenia<4000, Lymphopenia <1500,Thrombocytopenia <100000 ANA Immunologic disorder: Anti-DNA, Anti-Sm, APS
- 38. SLE- NON EROSIVE ARTHRITIS Intermittent polyarthritis Soft tissue & muscle involv. Myositis,tendonitis Hand,wrist,knee
- 39. SERONEGATIVE SPONDOARTHROPATHIES Psoriatic arthritis Reactive arthritis Enteropathic arthritis Ankylosing sponylosis
- 40. FEATURES OF SPONDOARTHROPATHIES Absence of RA Factor,subcut nodules Sacroiliatis/spondylitis + Assymetric peripheral joints Extra articular- ocular,oral,skin,enthesitis Familial aggregation HLA-B27 +
- 41. DISTRIBUTION OF SPONDOARTHROPATHIES Assymetric arthritis r Axial spine & lower limb joints Soft tissues involvmnt Bursitis,achilles tendonitis,epichondyliti s,plantar fascitis
- 42. PSORIATIC ARTHRITIS Psoriasis precedes in 60-70% Wright & Molls 5 patterns of arthropathy Nail changes in 90% INVOLVEMENT OF DIP joints Dactylitis,enthesitis,tenosynovitis Arthritis mutilans
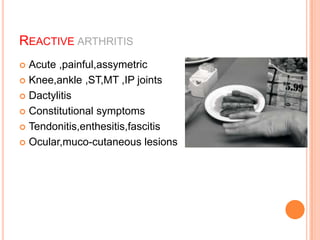
- 44. REACTIVE ARTHRITIS Acute ,painful,assymetric Knee,ankle ,ST,MT ,IP joints Dactylitis Constitutional symptoms Tendonitis,enthesitis,fascitis Ocular,muco-cutaneous lesions
- 45. ANKYLOSING SPONDYLITIS Sacroiliatis Syndesmophytes Bamboo spine Inflamm. Backache Age<50 Improves with exercise not with rest
- 46. ENTEROPATHIC ARTHRITIS Ankylosing spondylitis Peripheral arthritis-acute oligo & chronic polyarthritis Joint invl same in UC &CD Erosion and deformity rare
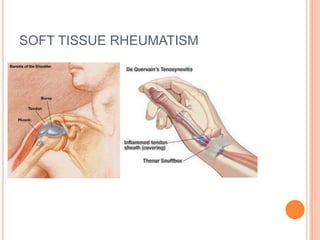
- 47. SOFT TISSUE RHEUMATISM Most common cause of MSK pain Enthesopathy,bursitis,tedonitis,tenosynovitis Mostly associated with fibromyalgia Improves with local steriod inj.
- 49. LAB INVESTIGATIONS Routine blood tests ESR,CRP Rheumatoid factor,CCP ANA Autoimmune antibodies Complement levels
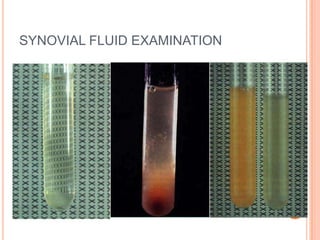
- 51. INTERPRETATION OF SYNOVIAL FLUID EXAMINATION Strongly consider synovial fluid examination if Monoarthritis Trauma with joint effusion Mono arthritis in a pt. with chronic arthritis Suspicion of joint infection,crystal induced Inflammatory or non arthritis,heamarthrosi inflammatory articular condition Appearance Is the effusion is Viscocity hemorrhagic? Is wbc . 2000/ μl WBC count ? Crystal identification Gram Consider Consider noninflamm. stain,culture if neded Trauma or Condition Consider inflamm. Or mechanical Osteoarthritis septic arthritis derangement Trauma Consider Coagulopathy Other noninflamm is the % Neuropathic articular PMNs.75% arthropathy conditions ? Osteoarthrutis Trauma Are crystals Consider other inflamm. Or other present? septic arthritides.gram stain ,culture Is WBC .50000/μl ? Crystal identification for specific diagnosis Gout or pseudogout Probable inflamm arthritis Possible septic arthritis
- 52. DIAGNOSTIC IMAGING Plain X-ray Ultrasonography Scintigraphy-Tc-99,Ga-67 CT Scan MRI