Module 3 Group Presentation.pptx
- 1. MODULE 3:- ORGANIZING MBAH 401: MODERN ORGANISATION AND MANAGEMENT
- 2. Submitted By: Group NO 6 “Golden Gang” Context: Organizing: Organization, Organizational Structures, Principles of Work Specialization, Departmentalization, Chain of Command, Span of Control, Centralization and Decentralization, Formalization. Mechanistic and Organic Structures, Factors Affecting Structural Choice - Strategy, Size, Technology, Environmental Uncertainty. Traditional Organizational Designs - Simple Structure, Functional Structure, Divisional Structure, Matrix Structure, Team Structures, Project Structure, Adaptive Organizations - Boundary less Organization, Virtual Organizations, Learning Organization, Flexi Work, Tele-working, Global Organizations.
- 3. • Organization is any collection of person • Material, procedures, Ideas or Facts • Arranged and ordered • Combination of these parts • That works towards achieving • Organizational objectives Murali
- 4. According to Theo Haimann, “ Organization is the process of defining and grouping the activities of the enterprise and establishing the authority relationship among them.”
- 5. 1. Group of persons 2. Common Objectives 3. Division of work 4. Cooperative Efforts 5. Communication 6. Rules and regulations 7. Central Authority
- 6. 1. Formal Organization A formal organization is an organization with a fixed set of rules of intra-organization procedures and structures. 2. Informal Organization An informal organization is a group of people who share a common identity and are committed to achieving a common purpose.
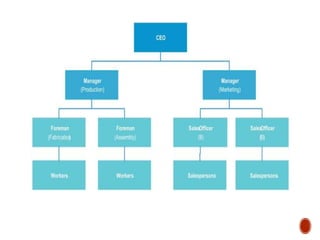
- 7. An organizational structure is a system that outlines how certain activities are directed in order to achieve the goals of an Organization. These activities can include rules, roles, and responsibilities. The organizational structure also determines how information flows between levels within the company.
- 9. When manager develop or change an Organizational structure, they are engaged in Organization designs, a process that involves decisions about six key elements : 1. Work Specialization 2. Departmentalization 3. Chain of command 4. Span of control 5. Centralisation and Decentralization 6. Formalization
- 10. It is also called as division of labour. The degree to which an Organization divides individual task into separate jobs. Every worker is trained specifically on how to perform a small, particular task in the best way. That worker becomes extremely efficient at doing the task.
- 12. DEPARTMENTALIZATION The basis on which jobs are grouped together is called departmentalization. 1. Functional 2. Product 3. Geographical 4. Process 5. customer Five common forms of departmentalization
- 13. Functional Departmentalization Functional Departmentalization- Group Jobs According to Function Advantages: 1. Specialization 2. Optimum Utilization of Resources Disadvantages: 1. Slow Decision Making 2. Lack of Innovation And Creativity
- 14. Product Departmentalization Product Departmentalization- Groups Jobs by Product Line Advantages: 1. Control organization of production 2. Ensures quality products Disadvantages: 1. Duplicate efforts or tasks 2. Not as suitable for smaller organization
- 15. Geographical Departmentalization Geographical Departmentalization-Groups Jobs According to Geographical Region Advantages: 1. Leadership Opportunities 2. Better efficiency for division Disadvantages: 1. More expensive 2. Competition for resources
- 16. Process Departmentalization Process Departmentalization-Group Jobs on the Basis of Product or customer Flow Advantages: 1. Uses specialized technology 2. Utilizes special skills Disadvantages: 1. It is hard to maintain unity of command
- 17. Customer Departmentalization Customer Departmentalization-Groups Jobs on the basis of specific and unique customers who have common needs Advantages: 1. Possible to know the likes and dislikes of customer 2. Ensures full attention to customer Disadvantages 1. May create duplication of resources 2. May face heavy overheads
- 18. Chain of command refers to an organisational structure that indicates how each member of the company or organisation reports to one another - ANANTHAKRISHNA S
- 19. Responsibility: Everyone has their own separate duties, and their own supervisor to keep them accountable. Efficiency: A functional chain of command helps improve efficiency when communicating with workers. Clarity: This lets everyone know which decisions they are allowed to make and which ones to present to their supervisors. Employee Morale: It improves the morale of workers leading to high productivity and low employee turnover. Specialization: Making employees focus on narrow functional areas can create groups of specialists that heavily impact the functions of the company. ADVANTAGES
- 20. Span of control defines how many subordinates each manager or supervisor is responsible for in an organization
- 21. Centralization means concentration of authority at the top level of the administrative system. Centralized organizations have all decisions coming from the same place. Decentralization means dispersal of authority among the lower levels of the administrative system. Decentralized organizations have decisions coming from all levels of management towards the same goal.
- 22. The advantage of such a structure is, it allows employees to have a well-defined framework within which all work needs to carried out. The disadvantage of such a structure is that it increases the time taken to arrive at a decision. As decision-making authority lies with selected people from top management, it may result in biased decision making.
- 23. The Advantage of decentralization is that the employees are empowered to make their own decisions that will benefit the organization, which results in a high level of employee satisfaction and boosts the productivity of an organization. Decentralization enables low-level employees to gain leadership skills, which can contribute to the growth of the organization in the long run.
- 24. Formalization is the extent to which an organization's policies, procedures, job descriptions, and rules are written and explicitly articulated. These structures control employee behavior using written rules, so that employees have little autonomy to decide on a case-by-case basis.
- 26. An advantage of formalization is that it makes employee behavior more predictable. Whenever a problem at work arises, employees know to turn to a handbook or a procedure guideline. Therefore, employees respond to problems in a similar way across the organization; this leads to consistency of behavior. A high degree of formalization may actually lead to reduced innovativeness because employees are used to behaving in a certain manner. Formalization reduces ambiguity and provides direction to employees.
- 27. Formalization is a process occurring in three stages: Stage 1. Creating legal documents for the company, to define its mission, goals, course of action and principles of operation. The result of the first stage is the development of such documents as the statute, procedures and organizational chart. Stage 2. Development of a detailed description of units describing behavioural patterns in specific organizational situations, decision rules, etc., Stage 3.Continuous improvement of organizational documentation, adapting it to changing internal and external conditions.
- 28. Mechanistic and Organic Structure What is a mechanistic organization? A mechanistic organization is an organizational structure with centralized authority, divisions between departments and specialized roles that work independently of each other. Companies that have mechanistic structures run similarly to bureaucracies in which an established chain of command manages business operations. Types of businesses that often implement this type of structure include: When represented visually, mechanistic organizations have a triangular or pyramid structure, and the higher your position on the triangle, the more authority you have. Typically, most company roles comprise entry-level and non-supervisory positions, which make up the bottom section of the triangle. The next, smaller section of the triangle includes their immediate supervisors, followed by senior supervisors. This pattern continues to the top of the pyramid, which includes executives such as the chief executive officer and chief financial officer.
- 29. CONTINGENCY FACTORS: Top managers of most organizations typically put a great deal of thought into designing an appropriate structure. What that appropriate structure is depends on four contingency variables: the organization's strategy, size, technology, and degree of environmental uncertainty. Organic Organizational Structure An organic organizational structure is a flat organization that allows for horizontal communications and interactions and is more suited to creative businesses. This type of organizational structure is decentralized, giving employees at all levels a chance to participate in business- related decision making. Businesses with an organic structure often encourage group participation and the sharing of work responsibilities. Communication channels are open to employees, managers and business owners and contact between all levels of employees usually occurs on a regular basis. Lower-level employees tend to have more face-time with executives than in a mechanistic organization. The type of communication most often used in organic structures is verbal.
- 30. Factorsors Affecting Organization Structure 1. Strategy: Strategy determines a course of action to direct various organizational activities. It makes plans to co-ordinate human and physical resources to work towards a common objective. Strategy is pre-requisite to organization structure and also follows it. The relationship between strategy and organization structure is depicted as follows:
- 31. Strategies to diversify product lines or markets require decentralized transition as decision- making is done at wider level and strategies fororganizations working in stable environment. Where managers do not diversify their operations, require a centralized organization. 2. Technology : The technology for manufacturing goods and services also affects the organization stricture. In case of mass production technology, mechanistic organization structure is more appropriate, while in case of continuous production orsmall scale production technology, the appropriate from is organic structure. This is because mass production technologies involve standardization and specialization of work activities and continuous or
- 32. unit production technologies require low levels of standardization and specialization. 3. People: Organization structure defines work, groups it into departments and appoints people to run those departments. People at different jobs must possess the skill, knowledge and efficiency to accomplish the related tasks. 4.Task: Activities performed by people who transform organizational plans into reality are known as tasks. 5 .Decisions: Questions like who makes decisions-top managers or lower level managers, how information flows in the organization so that decision- making is facilitated, affect the organization structure. Centralized decision-making powers give rise to mechanistic structures and decentralized decision-making processed give rise to organic or
- 33. behavioral structures. 6.Informal organization: Informal organizations are and outgrowth of formal organizations. Social and cultural values, religious beliefs and personal likes and dislikes of members which form informal groups cannot be overlooked by management. 7.Size: A group known as Aston Group conducted research on firms of different sizes and concluded that as firms increase in size, the need for job specialization, standardization and decentralization also increases and organizations are structured accordingly. 8.Environment: Organization structure cannot ignore the effects of environment. Organizations must adapt to the environment, respond to incremental opportunities and satisfy various external parties such as customers, suppliers, layout unions etc.
- 34. In case of stable environment where people perform routine and specialized jobs, which do not change frequently, a closed or mechanistic organization structure is appropriate. 9. Managerial perceptions: Organizations where top managers perceive their subordinated as active, dynamic and talented entrepreneurs, prefer organic form of structure, If they hold negative opinion about their subordinates, they prefer mechanistic organization structure.
- 35. Traditional organization structure is a strategy for organizing a business or other entity in what is known as a hierarchy or a top-down structure. With this approach, the processes of task allocation and management focus on a vertical structure that strictly defines a chain of command. TRADITIONAL ORGANISATIONAL STRUCTURE:
- 36. 1. SIMPLE STRUCTURE: Simple structure consists of owners and employees. A simple structure is an organizational design with low departmentalization ,wide span of control ,authority centralized in a single person and little formulization . Employees often work in several operational areas, and their departmental structure and area of expertise may not be well-defined.
- 37. 2.FUNCTIONAL STRUCTURE: The functional organization is designed on the typical hierarchy system where position and job requirement of every employee is defined. Employees are grouped based on their specific skills ansd knowledge. Functional organization structure is suitable for small as well as those entities that offer one type of services or products regularly; for example, medical clinics, car-repairing shops, hotels, and restaurants.
- 38. 3.DIVITIONAL STRUCTURE : A divisional organizational structure is a system in which a company segments its employees based on products or markets, as opposed to their job roles. It promotes flexibility and initiative as each division functions as an autonomous unit and it leads to further decision making. The divisional organizational structure allows each division of a firm to be accounted for in isolation. Leads to more focused and higher responsiveness. .
- 39. Contemporary Organizational Designs Managers in contemporary organisations are finding that these traditional hierarchical designs often aren't appropriate for the increasingly dynamic and complex environments they face . Managers are finding creative ways to structure and organize work and to make their organizations more responsive to the needs of customers, employees, and other organizational constituents - ANUSHA T
- 40. Team-Based Structures The entire organization is made up of work groups or teams that perform the organization's work. There is no chain of command. Employee teams are free to design work in the way they want to. To improve productivity at the operating level, for instance, companies such as Saturn, Motorola, and Xerox extensively use self-managed teams.
- 41. Matrix Structure Specialists from different functional departments work on one or more projects being led by project managers It creates a dual chain of command It explicitly violates the classical organizing principle of unity of command. An example of the matrix structure used in an aerospace firm. -
- 42. Project Structure Employees continuously work on projects Employees take their specific skills, abilities, and experiences to other work projects Project structures tend to be very fluid and flexible organizational designs. Managers serve as facilitators, mentors, and coaches
- 43. Adaptive organization is an organization or a company that is able to successfully adapt to the rapid and unexpected changes that occur in its environment. Such businesses are flexible able to develop fast tend to entrust more powers (in terms of making decisions) to the employees.
- 44. The Boundaryless Organization It is an organization whose design is not defined by, or limited to, the horizontal, vertical, or external boundaries imposed by a predefined structure In a boundaryless organization, the boundaries that divide employees such as hierarchy, job function, and geography as well as those that distance companies from suppliers and customers are broken down. The goal in a boundaryless organization : To develop greater flexibility and responsiveness to change and To enable the free exchange of information and ideas. Boundaryless organizations are able to achieve greater integration and coordination. It shows in integration of resources and human capital. They are able to adapt to environmental and technological changes faster.
- 45. Virtual Organizations In a virtual organization an alliance of independent companies share skills, costs, and access to one another’s markets. It consists of a network of continually evolving independent companies. Each partner in a virtual organization contributes only in its area of core competencies.
- 46. The Learning Organization Learning Organizations is an organization that has a developed the capacity to continuously adopt and change because all members take an active role in identifying and resolving work related issues. In a Learning Organizations, employees are practicing knowledge management continually acquiring and sharing new knowledge and are willing to apply that knowledge in making decisions or performing works. In learning organizations, employees feel free to openly communicate, share, experiment, and learn without fear of criticism or punishment.
- 47. Tele-Working • Tele working is also known as remote working, future of work, tele work, tele working, work from home, mobile work, remote job, work from anywhere, and flexible workplace. • It is an arrangement in which employees do not commute or travel to a central place of work, such as an office building, warehouse or store
- 48. Advantages/Benefits of Tele-Working • Work-life Balance and flexible working hours. • Saves Time and Money • Pollution Reduction • Reduces Conflicts in Companies • Improves Concentration
- 49. Disadvantages of Tele-Working • Elimination of a good working environment • Emotional Disengagement • Not being able to control the time and work of employees. • Lack of Collaborations b/w work teams • Reduction of Learning
- 50. How to Improve Tele-Working? 1. Keep a regular routine 2. Use the right tools 3. Find a workspace at home 4. Set a work schedule 5. Have little breaks when necessary 6. Eat healthy and at regular times 7. Set goals and deadlines and meet them
- 51. Flexi Work • Flexible working is a way of working that suits an employee's needs, for example having flexible start and finish times, or working from home. • Flexible working, employees can work from anywhere, from home, from cafes, or during their commute.
- 52. Advantages of Flexible Working • Efficiency • Adaptability • Taking control over the schedule • Reduce employee stress • Employee satisfaction • Less cost • Reduced absenteeism • Reduced overtime
- 53. Disadvantages of Flexible Working • Communication Difficulties • It can be Harder for Managers and Employers to Keep Track of what Their Employees are Doing • Can Lead to Less Productivity • Unsuitable for some employee roles • Availability issues
- 54. How to improve flexibility at Work? • Step outside of your comfort zone • Have a Strong Support Network • Encourage Creativity • Lead With Purpose • Plan ahead.