Cucurbitaceae & apaiceae
- 1. PRESENTED BY, SELVAM G I M.Sc BOTANY BHARTHIDASAN UNIVERSITY TRICHY, TAMILNADU
- 2. It is the science that finds, identifies, describes, classifies & naming of plants. It is concerned with laws governing the classification of plants. Taxonomy includes 2 greek words. Taxos-arrangement, nomos-laws. Its defining group is based on the distinguishing characteristics & giving names to those groups. i.e. taxonomic hierarchy.
- 3. The swedish botanist ‘’Carl Linnaeus’’is regarded as the ‘’Father of Taxonomy’’ as he developed a system known as ‘’Linneaen Classification’’ for categorization of plants & its binomial nomenclature.
- 5. SYSTEMATIC POSITION: DIVISION : Spermatophyta. SUB-DIVISION : Phanerogams. CLASS : Dicotyledons. SUB-CLASS : Polypetalae. SERIES : Thalamiflorae. ORDER : Passiflorales. FAMILY : Cucurbitaceae.
- 6. Distribution: Includes 100 genera & 850 species, widely distributed in tropical & sub-tropical regions of the world. In India 86 species only represented. The family cucurbitaceae also called as ‘’Cucurbits’’ popularly known as ‘’Gourd family’’. Utilized mainly as vegetables. The most importants are squash, pumpkin, gourds, watermelons & cucumber.
- 7. The plants are weak stemmed, tendril climbers. Leaves are simple, alternate, exstipulate, palmately lobed. Inflorescence is racemose or solitary axillary cyme. Flowers are unisexual, actinomorphic, epigynous & incomplete.
- 8. Calyx consists of 5 fused sepals, gamosepalous, aestivation is imbricate or valvate. Corolla consists of 5 united petals, gamopetalous, aestivation is valvate or imbricate,campanulate type. Stamens are usually 3 & inserted on the calyx tube, anthers are free or connate.
- 9. Gynoecium is tricarpellary, inferior, syncarpous ovary, trilocular in female flowers. Each locule contains many anatropous ovules in parietal placentation. Style is simple. Stigma is trilobed and papillose. Fruit is pepo. Seeds are dicotyledonous & ex-albuminous.
- 11. SYSTEMATICMIC POSITION: DIVISION : Spermatophyta. SUB-DIVISION : Phanerogams. CLASS : Dicotyledons. SUB-CLASS : Polypetalae. SERIES : Thalamiflorae. ORDER : Passiflorales. FAMILY : Cucurbitaceae. GENUS: Cucurbita SPECIES: maxima
- 12. Habitat: Tropical & sub-tropiical region. Habit: Annual or perennial herbs, mostly are tendril climbers. Root: Tap root system. Stem: Herbaceous, usually climbing, glabarous. It has tendrils. Leaves: Simple, alternate, exstipulate, petiolate, palmately lobed, palmately reticulate venation.
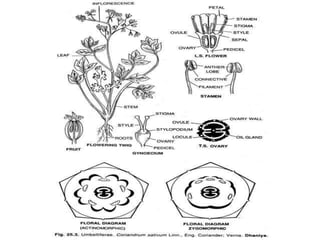
- 15. Inflorescence: solitary axillary cyme. Flowers: unisexual, regular, epigynus, incomplete, actinomorphic. Calyx: 5 sepals, gamosepalous, green in colour and campanulate. Corolla: 5 petals, united, gamopetalous, yellow or white in colour.
- 17. Stamens in male flowers: 3 to 5 stamens, united by variouc degrees, anthers are very long, stamens are borne on calyx tube. Carpels in female flowers: 3 fused carpels, syncarpous inferior ovary, parietal placentation. Fruits: Fleshy berry. Seeds: Non-endospermic seeds. Floral formula: Male flowers: Ebr, k₍₅₎,C₍₅₎,A₍₃₋₅₎,G₀ Female flowers: Ebr, k₍₅₎,C₍₅₎,A ₀,G₃
- 19. Vegetables: Immature fruits of several cucurbits are eaten raw or cooked as vegetables. Fruits: Ripe fruits of some plants are eaten as desserts or used to making refreshing juices. Medicines: Fruit pulp of pumpkin used as a poultice on boils, burns & inflammations. Fruits of Momordica charantia are used for stomach ache, rheumatism, liver & spleen problems & diabetes. Fibrous pericarp of some fruits are taken from dried fruits & used as bath sponge.
- 21. SYSTEMATICMIC POSITION: DIVISION : Spermatophyta. SUB-DIVISION : Angiosperms. CLASS : Dicotyledons. SUB-CLASS : Polypetalae. SERIES : Calyciflorae. ORDER : Umbellales. FAMILY : Apiaceae.
- 22. Distribution: Temperate regions of the world. It includes 295 genera & 2,850 species. This family is commonly known as the ‘’Carrot family’’. The common plants are Daucas carota (carrot), Ferula asafoetida (asafoetida), Carum copticum (omum), Cuminum cyminum (cumin) etc…
- 23. Plants are annual or biennial herbs. Leaves are compound,alternate,exstipulate, with sheathing leaf bases, aromatic, pinnately or palmately dissected. Inflorescence: terminal or axillary. Flowers are bisexual, small, regular, bracteate, epigynous & zygomorphic.
- 24. Calyx consists of 5 sepals, polysepalous, valvate aestivation. Corolla consists of 5 petals,, polysepalous, imbricate aestivation. Androecium consists of 5 free stamens. They are bent inwards in the bud. Gynoecium is bicarpellary, syncarpous. Ovary is inferior, axile placentation. Fruit is schizocarp, which splits into 2 mericarps.
- 26. SYSTEMATICMIC POSITION: DIVISION : Spermatophyta. SUB-DIVISION : Angiosperms. CLASS : Dicotyledons. SUB-CLASS : Polypetalae. SERIES : Calyciflorae. ORDER : Umbellales. FAMILY : Apiaceae. GENUS: Coriandrum SPECIES: sativum
- 27. Habitat: Tropical & sub-tropical regions. Habit: Annual herbs. Stem: Green, cylindrical & flexible in nature. Leaves: Pinnately compound leaf, presence of dissected leaf, exstipulate, having sheathing leaf bases, aromatic due to the presence of schizogenous oil ducts.
- 29. Inflorescence: Compound umbel. Flowers: Pedicellate, bracteate, hermaphrodite, complete, epigynous, the outer flowers of the inflorescence are zygomorphic, i.e., with large and unequal petals, whereas the central flowers are actinomorphic with equal and small petals. Calyx: 5 sepals, polysepalous, valvate aestivation, odd sepal is posterior. Corolla: 5 petals, irregular, polysepalous, outer petals are much exaggerated, they are in curved or forked, imbricate aestivation.
- 30. Androecium: 5 stamens that are alternate with petals, stamens are free, dithecous anther & introse, dorsifixed.. Gynoecium: bicarpellary, syncarpous inferior ovary, axile placentation, bilocular. Fruit: schizocarp.
- 33. These are useful in medicines, culinary purposes because of its essential oils & gums found in the root, stem & fruit. Daucas carota- carrot is used as a vegetable. Carum copticum- omum fruits are used as carminative. Coriander sativum- friuts are used as condiment & spice. Their leaves are aromatic.