Cellular Structures and Their Functions
- 1. Cells: Factories of Life
- 3. There are some key parts common to most eukaryotic cells: 1. Cell Membrane 2. Cell Wall 3. Nucleus 4. Cytoplasm
- 4. The Cell Membrane The cell membrane is an important part of all cells, and has 2 major jobs: 1) Separates the interior of the cell from its surrounding environment 2) Regulates what enters and leaves the cell!!!
- 5. Cell Wall In organisms such as plants, algae, and some bacteria, the cell membrane is surrounded by a Cell Wall The cell wall helps to support and protect the cell. It is rigid and serves as the “skeleton” of plants
- 6. The Nucleus The Nucleus is the “information control center” of the eukaryotic cell The Nucleus contains DNA, the genetic material that holds the coded instructions for making thousands of different molecules The nucleus directs the biochemical activities of the cell
- 7. The nucleus is made up of three important structures 1. Nuclear Envelope 2. Nucleolus 3. Chromosomes
- 8. Nuclear Envelope Surrounds the nucleus and separates its contents from the rest of the cell Contains pores, or small openings, that allow certain molecules to move in and out of the nucleus
- 9. The nucleolus is a dark, dense region made up of the genetic material RNA The nucleolus where ribosomes are made
- 10. Chromosomes Small, threadlike structures made up of proteins and DNA molecules Contain the hereditary information that is passed from one generation to the next
- 11. Cytoplasm Jellylike fluid made up of water and chemicals that fills the interior of the cell and holds the cell’s organelles
- 12. All Eukaryotic Cells Contain Special Structures Called Organelles Organelles do the “work” of the cell.
- 13. Power Stations of the Cell All living things require energy Energy comes from the sun or food substances This energy is made available to cells in the: Mitochondria Chloroplast
- 14. Mitochondria The “Powerhouse” of the Cell Mitochondria convert the chemical energy stored in food molecules into ATP, the cellular energy molecule
- 15. Chloroplasts Organelles found only in plants, algae, and some bacteria that contain the light absorbing pigment chlorophyll Photosynthesis occurs here as plants convert solar energy into the food substance glucose
- 16. Ribosomes Ribosomes are cellular machines that produce proteins , important biological molecules Ribosomes are either free in the cytoplasm or attached to the Endoplasmic Reticulum
- 17. Cell Highway : The Endomembrane System A series of structures that connect the nucleus to the cell membrane and aid in transporting cellular products
- 18. Endoplasmic Reticulum A network of membrane sacs that transports materials through the inside of the cell 2 types: Rough ER Smooth ER
- 19. Rough ER ER is covered with ribosomes Involved in the synthesis and chemical modification of proteins
- 20. Smooth ER Enzymes and special biochemicals are stored in the smooth ER
- 21. Golgi Apparatus Modifies, collects, packages, and distributes molecules made at one location of the cell and used at another
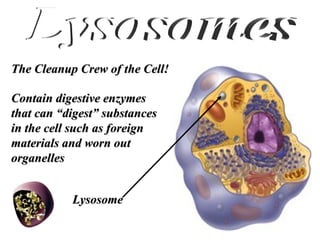
- 22. Lysosomes The Cleanup Crew of the Cell! Contain digestive enzymes that can “digest” substances in the cell such as foreign materials and worn out organelles Lysosome
- 23. Vacuoles Cellular storage tanks that may hold water, salts, proteins, and carbohydrates Plants have a large central vacuole to hold water. The pressure of the water helps to keep the plant upright
- 24. The Cytoskeleton The Cytoskeleton is a tiny network of tubules that support the cell’s structure and drive cellular movement Microtubules provide support for cell shape, help move organelles through the cytoplasm, and play a special role in cell division by forming centrioles
- 25. Centrioles Centrioles are found in animal cells and play a role in mitotic cell division
- 26. Let's Practice!!! Follow the link to a great practice activity at the Biology Place At the site, click on the practice button and follow the directions to test your knowledge!!!
- 27. 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13
- 28. 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15
- 29. Study Here!!! 1. Go to www.biology.com 2. Login username: dgsbiostudent password: darwin 3. Practice and have fun!!!