Disease
- 1. Disease
- 2. A disease is defined as any change (other than an injury) that interferes with the normal functioning of the body. The Germ Theory of Disease states that an infectious disease is caused by a certain agent.There are different types of infectious agents which cause specific symptoms from which the disease may be identified.
- 3. Koch’s postulates is a set of rules that is used to determine whether a specific pathogen is the cause of specific disease.There are various ways in which diseases are spread.The human body has specific and non-specific mechanisms that defend the organism against infectious diseases
- 4. DiseaseA pathological condition of a part, organ, or system of an organism InfectionGeneticEnvironmental stress
- 5. Infectious diseaseClinically evident illness resulting from the presence of pathogensVirusBacteriaFungiProtozoaParasitesprions
- 8. Infectious diseaseCan be slow or fast when it spreadsCan be transferred through different vectors
- 9. Disease vs infectionWhich is which?Type of DiseasesGeneticAgeInfectious
- 10. Manner of infectionEntrance to the host bodyAdhere to specific host cellsInvade and colonizeMultiply between host cells or body fluidsTissue damageProduction of toxins or destructive enzymes
- 11. Germ TheoryMicroorganisms can cause diseasesInfectious disease is caused by an infectious agent
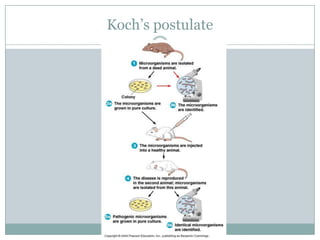
- 12. Koch’s PostulateSeries of experimental steps to determine the cause of a disease
- 13. Koch’s PostulateThe microorganism must be found in abundance in all organisms suffering from the disease, but should not be found in healthy animals.The microorganism must be isolated from a diseased organism and grown in pure culture.The cultured microorganism should cause disease when introduced into a healthy organism.The microorganism must be reisolated from the inoculated, diseased experimental host and identified as being identical to the original specific causative agent.
- 14. Koch’s postulate
- 15. Modes of InfectionDirect contactIndirect contactfecal oral routeAirborne (droplet infection)Vector