Finance AS Business full shebang
- 1. Sources of finance Business Unit 1
- 2. Why do firms need finance? – To – To – To – To – To – To – To – To expand buy new equipment start up a new business pay workers buy premises survive buy stock cover a fall in demand (recession)
- 3. Sources of Finance Sources of Finance can be either: Internal Internal can be cheaper, but spending this money on the business means the money can’t be spent on other projects like investing External Comes from outside the business. This usually costs more as interest may be charged
- 4. Types of Finance • Internal – Personal savings – Retained profit – Working capital (money – Sale of assets – Debt Factoring in the till)
- 5. Types of Finance • External – Shares capital – Debentures (secured loan) – Mortgage (secured loan) – Other loans – Overdraft facilities – Hire purchase / leasing – Trade credit – Venture Capital – Grants
- 6. How much finance can a business get? • It depends on risk assessment based on: – The type of business – Stage of development – State of the economy
- 7. Choosing the right type of finance is based on How long the money is needed for The legal structure of the business • The duration of the loan should reflect the time they expect to need the purchase for • A sole trader can’t sell shares – You would not take a 5 year loan for a van that you expect to last 3 years • The liability of the owners must also be taken into account
- 8. Liability Unlimited Liability – The owners of the business are personally liable for any debts which the business may have (Can be risky) Limited Liability – The liability of the owners (the shareholders) to pay off debts is limited to the amount of money which they have invested in the business (Safer)
- 9. Time Periods for Finance Finance is generally considered to be either: Short-term Short/Medium Long-term 1 year 2 to 5 years Over 5 years
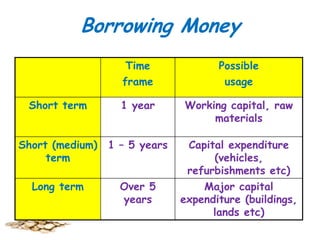
- 10. Borrowing Money Time frame Possible usage Short term 1 year Working capital, raw materials Short (medium) term 1 – 5 years Long term Over 5 years Capital expenditure (vehicles, refurbishments etc) Major capital expenditure (buildings, lands etc)
- 11. Types of finance • Long term finance – Normally for large projects like expanding, research or producing a new product. – Often less interest to pay back on this type of finance • Short term finance – Often used to fill gaps in the cash flow of a business, like paying rent. – Often flexible and comes at a higher rate of interest
- 12. Long Term Finance • Share capital (5 – 25 years) (PLC & LTD only) • Shares are sold by the business to raise capital. In a PLC this is done on the London Stock Exchange, LTD you must know the seller, the profit share they get is called a dividend • Venture Capital (PLC & LTD only) • Someone will buy shares in the business to help them grow faster and sell them at a profit (Dragons Den)
- 13. Long Term Finance • Debentures (5 – 25 years) (PLC & LTD only) • Is a secured loan. Interest is paid to each holder, this is paid before any money is paid to share holders • Mortgages • Is secured a contract that means the loan is secured on property and that the party buying it will not own the property till its fully paid
- 14. Long Term Finance • Loans (5 – 25 years) (this can be a short term source too) • Normally given out by the bank, will have to repay over a set number of years with interest, paid at the same time every month • Retained Profit • Profit the business has made and is reinvesting in the business, this is often used to buy stock, and pay wages on a weekly basis
- 15. Long Term Finance • Grants (5 – 25 years) • This is money given to the firm by the government, this money does not have to be repaid
- 16. Short Term Finance (up to 5 years) • Leasing equipment • Will allow you to rent out equipment over time instead of buying it, useful if you only need equipment for a short time, but you never own it • Hire Purchase • Like leasing but you pay every month for the product / equipment, instead of paying in one go, it means you don’t have to spend a large amount at once, and you keep it after
- 17. Short Term Finance (up to 5 years) • Bank overdrafts • is a negative balance that the bank allows you to use in emergencies, this is repaid when money goes in to your account, high interest but flexible • Trade credit • is an amount of time that firms give you to repay them for items they have sold you (normally 30 days)
- 18. Short Term Finance (up to 5 years) • Factoring • A factoring firm will buy a firms debts and assume the risk on non-payment. The factor collects the debts directly from the businesses customers. (But pays less for the debt than owed)
- 19. Question Time • All students must have one question !! • Write 3 down in case somebody else asks it. What’s Business
- 20. Did you bring your text book? And Homework!!
- 21. Owner’s funds Benefits Explanation Drawbacks Money put into the No need to Could have been business by the pay interest invested elsewhere, owner earning a higher profit on the money Owner may not have enough funds to meet the needs of the business
- 22. Retained Profit Explanation Money kept in the business by the owners Benefits Drawbacks No need to Could have been pay interest invested elsewhere, earning a higher profit on the money Known as retained The business may not profit on the have enough retained balance sheet profit to meet its needs Shareholders may become unhappy if this means lower dividend payments
- 23. Selling Assets Benefits Explanation Drawbacks Items owned by The business is The business has to the business are using money it have something sold and the already has – worth selling for this to be an option money made used so no need to to finance the take on loans or The business may business pay any interest sell something they or charges later need
- 24. Overdraft Benefits Explanation Drawbacks The bank allows Very quick to Only suitable for arrange the business to smaller amounts and draw more money A good short has to be repaid from their bank within a short term solution amount of time account than they to a cash flow actually have in it problem Interest or charges are paid
- 25. Trade Credit Explanation Items are bought from suppliers on a ‘buy now pay later’ basis Benefits Gives the business more cash to use in the immediate future Drawbacks Can only be used to buy certain goods Bills usually have to be settled within 30,60 or 90 days, usually 30!
- 26. Debt Factoring Benefits Explanation Drawbacks The company sells Allows the Time consuming to arrange a debt it is owed business to get to a debt factoring money for debts The business company who pay that might receives less the business a otherwise never money than it have been paid smaller sum than was originally they were owed Saves the business owed – this may time chasing affect profitability customers etc for money owed
- 27. Leasing Benefits Explanation Drawbacks Used to help Cost of the May be more obtain new asset is expensive than equipment eg cars spread over buying the asset – its life the owner will want The business rents No need to to profit from the the item from its deal find a lumpowner sum of money The business does to purchase it not own the asset so it does not appear on the balance sheet
- 28. Debentures Explanation Long term borrowing similar to selling shares, but with the promise of repaying the amount lent at a fixed period in time, usually for a set amount of interest Benefits Drawbacks A very Usually ‘secured’ onto structured assets of the business method such as property, which allows therefore if the the business interest on the debt, to know or the debt itself isn’t exactly how repaid, the debenture much interest holder will claim the item/property will be paid and when the No longer a popular debt has to method of finance for be paid back businesses
- 29. Bank loan Explanation An amount of money is borrowed from the bank, then repaid (with interest) over a set period of time Benefits Drawbacks Easy and quick Interest payable to set up If repayments Large amounts cannot be kept up, of money can the business risks be borrowed getting a poor credit Structured rating or being repayment made bankrupt term
- 30. Issuing Shares Explanation A share in the business is sold to an individual or another business. This money then used to purchase new assets Benefits No need to repay the money invested Cheaper than a loan. Some businesses can raise large sums of money this way Drawbacks Need to pay the shareholders a share of future profits Ownership also means some influence over how the business is run – the original owners may lose control of the business Risky for the shareholder - the investment may be lost if the business fails
- 31. Mortgage Benefits Explanation Long term loan Only method provided by a available to buy property bank in order to buy property Structured repayments over a long term (25 years) Drawbacks Large sums of interest charged Can take a long time to repay debt
- 32. Government Grant Explanation Money given to the business by the government. Used to help finance new projects – especially those that create new jobs Benefits No need to repay the grant Drawbacks Limited funds are available May be restrictions on what the money can be used for
- 33. Hire Purchase Benefits Explanation Drawbacks An item is bought Flexible method – High interest often charged on finance, can hand back repayments are the item if no Item doesn’t made each month longer required belong to the until the final and payment will business until stop payment when the the end of the item becomes the term property of the firm
- 34. Venture Capital Explanation Venture capitalists invest in small, risky business e.g. new business startups Benefits Can raise money from them even when banks have refused to lend to the business Drawbacks Risky for the venture capitalist The VC may want to have some control over how the business operates