Chapter 2 Cells Lesson - Introduction to Cells
- 1. Understanding Biology An introduction Copyright © 2010 All Rights Reserved
- 2. The Subject Understanding of the Human Body - Explains a) how our body functions (with response to the environment) b) why we resemble our parents c) how humans reproduce (the highlight!!!) Understanding of Plants - Explains a) how to locate the xylem and phloem in plants b) how plants transport water ( against gravity!!!) Understand Life Sciences and its Application a) our Singapore government hopes to make this industry the fourth pillar of Singapore’s manufacturing sector after electronics, chemicals and engineering Copyright © 2010 All Rights Reserved
- 3. Copyright © 2010 All Rights Reserved
- 4. Structural hierarchy cell --> tissue --> organ --> system Tissue = a group of similar cells performing a special function (e.g. epithelium/epidermis) Organ = a group of different tissues working together and enabling the organ to perform its function (e.g. stomach) System = several organs working together for a special purpose (e.g. respiratory & digestive system) Copyright © 2010 All Rights Reserved
- 5. Cells: the building block of life Chapter 2 Copyright © 2010 All Rights Reserved
- 6. Cells are the building blocks of life simplest units that have all the characteristics of life Many chemical reactions occur continually inside your cells to keep you alive - it takes in raw materials - it processes these materials to make new molecules - these molecules can either be used by the cell itself or transported to other parts of the body
- 7. Microscopes Light microscope - 1000 x magnification Electron microscope - 200, 000 x magnification Fitting a camera on either microscopes enable us to take micrographs i) light micrograph -> colour images ii) electron micrograph -> black-white images but can be artificially colourised Copyright © 2010 All Rights Reserved
- 8. Introduction to organisms Picture of an amoeba Picture of a paramecium Both of them are called unicellular organisms. Why? Copyright © 2010 All Rights Reserved
- 9. How many cells do you think you have in your body? Humans have about 10 - 100 trillion cells in one body alone! Copyright © 2010 All Rights Reserved
- 10. Introduction Organisms Unicellular (single cell) Multicellular (made up of more than one cell) amoeba bacterium paramecium human being balsam plant can be example example
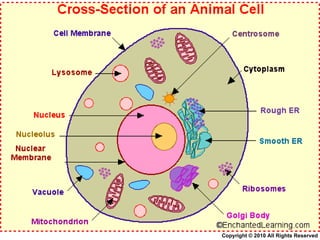
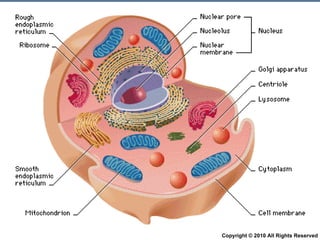
- 11. Animal Cell Components Copyright © 2010 All Rights Reserved
- 12. Lesson objectives Name the different components of an animal cell Describe the function of each part Copyright © 2010 All Rights Reserved
- 13. Generalised Animal Cell 1. 2. 3. 4. 6. 7. 8. 10. 11. 12. Nuclear envelope 5. free ribosomes 9. centriole 13. Copyright © 2010 All Rights Reserved
- 14. Worksheet: Label the animal cells Copyright © 2010 All Rights Reserved
- 15. Copyright © 2010 All Rights Reserved
- 16. Copyright © 2010 All Rights Reserved
- 17. Structure and function of animal cell components Copyright © 2010 All Rights Reserved
- 18. Function of plasma membrane/ cell membrane Partially permeable membrane Regulates movement of materials in and out of the cell Only small molecules are able to be exchanged Copyright © 2010 All Rights Reserved
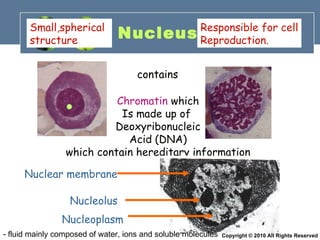
- 19. Nucleus contains Chromatin which Is made up of Deoxyribonucleic Acid (DNA) which contain hereditary information Nuclear membrane Nucleolus Nucleoplasm Small,spherical structure Responsible for cell Reproduction. - fluid mainly composed of water, ions and soluble molecules Copyright © 2010 All Rights Reserved
- 20. Function of the nucleus Controls all cell activities e.g. cell growth and repair of worn-out parts Is essential for cell division. Cells without a nucleus (e.g. RBCs) have a short lifespan and are unable to divide. Copyright © 2010 All Rights Reserved
- 21. Function of chromatin (1) Network of long thread-like structures found within the nucleus that controls the activities of the cell e.g. cell division Each chromatin thread is made up of proteins and deoxyribonucleic acid ( DNA ). Hereditary information is stored in DNA. DNA contains instructions that a cell needs to carry out all the chemical reactions within itself Copyright © 2010 All Rights Reserved
- 22. Function of chromatin (2) When the cell is dividing, chromatin thread condense and become chromosomes (highly coiled structures) Copyright © 2010 All Rights Reserved
- 23. Protoplasm protoplasm refers to all substances and objects contained inside the cell membrane The protoplasm, therefore, includes the organelles, nucleus, and fluid inside the cell Copyright © 2010 All Rights Reserved
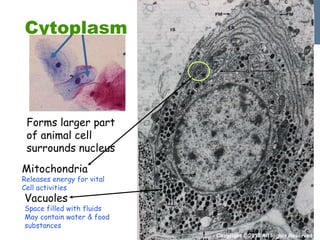
- 24. Function of cytoplasm The protoplasm of a cell between the cell membrane and the nucleus ( The cytoplasm refers to all the structures outside the nucleus but inside the cell membrane) where most chemical reactions take place contains enzymes and organelles e.g. mitochondria and centrioles contains nucleoplasm Copyright © 2010 All Rights Reserved
- 25. Cytoplasm Mitochondria Releases energy for vital Cell activities Vacuoles Space filled with fluids May contain water & food substances Forms larger part of animal cell surrounds nucleus Copyright © 2010 All Rights Reserved
- 26. Parts of the cytoplasm Consist of 1. organelles e.g. mitochondria and vacuoles 2. endoplasmic reticulum (ER) - rough ER - smooth ER Copyright © 2010 All Rights Reserved
- 27. Rough ER (RER) Rough appearance due to ribosomes (small round structures) attached on the outer surface Ribosomes are either i) attached to the membrane of the RER -> make proteins that are usually transported out of the cell ii) lie freely in the cytoplasm (called free ribosomes ) -> makes proteins that are used within the cytoplasm of the cell RER is continuous with the nuclear envelope RER transports proteins made by ribosomes to the Golgi apparatus for secretion out of the cell Copyright © 2010 All Rights Reserved
- 28. Smooth ER (SER) does not have ribosomes attached to its membrane more tubular than RER it is connected to the RER Function(s) of the SER Synthesizes fats and steroids e.g. sex hormones Detoxification i.e. converts harmful substances into harmless materials Copyright © 2010 All Rights Reserved
- 29. Golgi apparatus is shaped like a disc consists of flattened spaces surrounded by membranes ( cisternae ) Vesicles can be seen fusing with one side of the Golgi apparatus and pinching off from the opposite side Function(s) of the Golgi apparatus Stores and modifies substances made by the ER Packages these substances in vesicles for secretion out of the cell http://www.johnkyrk.com/CellIndex.swf Copyright © 2010 All Rights Reserved
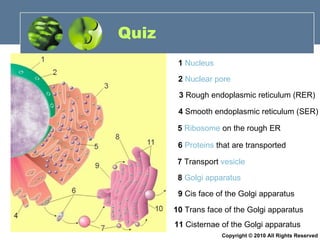
- 30. Quiz 1 Nucleus 2 Nuclear pore 3 Rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER) 4 Smooth endoplasmic reticulum (SER) 5 Ribosome on the rough ER 6 Proteins that are transported 7 Transport vesicle 8 Golgi apparatus 9 Cis face of the Golgi apparatus 10 Trans face of the Golgi apparatus 11 Cisternae of the Golgi apparatus Copyright © 2010 All Rights Reserved
- 31. 1. Vesicles transport substances within the cell. Small vesicles containing substances made by the ER are pinched off from the ER. How substances made by the endoplasmic reticulum enter the Golgi apparatus and are finally secreted out of the cell rough endoplasmic reticulum vesicle forming Processes in the Golgi Apparatus Copyright © 2010 All Rights Reserved
- 32. 1. Vesicles transport substances within the cell. Small vesicles containing substances made by the ER are pinched off from the ER. How substances made by the endoplasmic reticulum enter the Golgi apparatus and are finally secreted out of the cell rough endoplasmic reticulum vesicle forming vesicle pinched off Processes in the Golgi Apparatus Copyright © 2010 All Rights Reserved
- 33. 1. Vesicles transport substances within the cell. Small vesicles containing substances made by the ER are pinched off from the ER. 2. Vesicles then fuse with the Golgi apparatus and release their contents into the Golgi apparatus. The substances made by the ER may be modified inside the Golgi apparatus. How substances made by the endoplasmic reticulum enter the Golgi apparatus and are finally secreted out of the cell rough endoplasmic reticulum vesicle forming vesicle fusing with Golgi apparatus Golgi apparatus vesicle pinched off Processes in the Golgi Apparatus
- 34. 1. Vesicles transport substances within the cell. Small vesicles containing substances made by the ER are pinched off from the ER. 2. Vesicles then fuse with the Golgi apparatus and release their contents into the Golgi apparatus. The substances made by the ER may be modified inside the Golgi apparatus. How substances made by the endoplasmic reticulum enter the Golgi apparatus and are finally secreted out of the cell 3. Secretory vesicles containing these modified substances are pinched off from the Golgi apparatus. They then move to fuse with the cell surface membrane. rough endoplasmic reticulum vesicle forming vesicle fusing with Golgi apparatus Golgi apparatus secretory vesicle pinched off vesicle pinched off Processes in the Golgi Apparatus Copyright © 2010 All Rights Reserved
- 35. 1. Vesicles transport substances within the cell. Small vesicles containing substances made by the ER are pinched off from the ER. 2. Vesicles then fuse with the Golgi apparatus and release their contents into the Golgi apparatus. The substances made by the ER may be modified inside the Golgi apparatus. 4. Secretory vesicles fuse with the cell surface membrane and their contents are released outside the cell. How substances made by the endoplasmic reticulum enter the Golgi apparatus and are finally secreted out of the cell 3. Secretory vesicles containing these modified substances are pinched off from the Golgi apparatus. They then move to fuse with the cell surface membrane. rough endoplasmic reticulum vesicle forming vesicle fusing with Golgi apparatus Golgi apparatus secretory vesicle pinched off substances released outside the cell vesicle pinched off secretory vesicle fuses with cell surface membrane Processes in the Golgi Apparatus Copyright © 2010 All Rights Reserved
- 36. Function of vacuoles Contains air, liquid or food particle Acts as a storage of food Small but many in numbers inside animal cells Membrane enclosing vacuole = tonoplast Copyright © 2010 All Rights Reserved
- 37. Function of mitochondria Energy release during cell respiration Copyright © 2010 All Rights Reserved
- 38. Centrioles (only found in animal cells) Play a part in cell division Absent in most plants Note: Centrioles are not visible under a light microscope Centrioles are visible under an electron microscope
- 39. Lysosomes Derived from the Greek words lysis , which means dissolution or destruction, and soma , which means body spherical organelles that contain enzymes ( acid hydrolases ) are found in animal cells, while in yeast and plants the same roles are performed by lytic vacuoles are created by the addition of hydrolytic enzymes to early endosomes (membrane-bound compartments a.k.a. vesicles) from the Golgi apparatus Function Lysosomes digest 1 excess or 2 worn-out organelles, food particles, and engulfed viruses or bacteria
- 40. Lets recap Animal cells cell membrane cytoplasm vacuoles nucleus consist of partially permeable membrane to control movement of material in and out of the cell fills the cell and allow chemical reactions to take place storage of food control all the chemical reactions inside the cell chromosomes determine the characteristics of the organism functions as a function is to functions as a function is to function is to centrioles cell division mitochondria Energy release during cell respiration
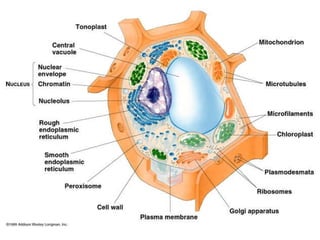
- 41. Plant Cell Copyright © 2010 All Rights Reserved
- 42. Lesson objectives Name the parts of the plant cell Describe the function of each part Copyright © 2010 All Rights Reserved
- 43. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 11. 12. 14. 15. centriole 13. free ribosomes 10. Copyright © 2010 All Rights Reserved
- 44. Worksheet: Label the plant cells Copyright © 2010 All Rights Reserved
- 45. Copyright © 2010 All Rights Reserved
- 47. Can you identify this organelle? Copyright © 2010 All Rights Reserved
- 48. Structure and function of plant cell components Copyright © 2010 All Rights Reserved
- 49. Function of cell wall Made up of cellulose Has 2 functions: protects the cell from injury supports and gives a plant cell its natural shape (provides mechanical support ) Is fully permeable Looking at the cell wall, do you think it is very flexible? Copyright © 2010 All Rights Reserved
- 50. Function of vacuole Forms the biggest part of the plant cell Reduces the amount of cytoplasm in the cell to a thin lining Function is same as vacuole in animal cells Contains cell sap which contains water, dissolved sugars and salt
- 51. Function of vacuole Why is it that plants have larger vacuoles? Ans: Plants are food producers and produce food constantly by photosynthesis. A large amount of food produced ends up being stored for later usage Copyright © 2010 All Rights Reserved
- 52. Function of chloroplast Contains chlorophyll which is green in colour Chlorophyll traps sunlight for the plant to photosynthesize Do all plants have chlorophyll? Ans: Yes! All plants can carry out photosynthesis. This is a main characteristic of plants chloroplast Copyright © 2010 All Rights Reserved
- 53. Function of starch grain Tiny grains that can be found in the cytoplasm This is a form of stored food for the plant cell Copyright © 2010 All Rights Reserved
- 54. Lets recap Plant cell cell membrane vacuole nucleus chromosomes cytoplasm Mitochondria *centrioles chloroplast cell wall starch grain supports the cell and gives a regular shape traps sunlight for photosynthesis as a form of food storage consist of function is to function is to function is * Only some plant cells Copyright © 2010 All Rights Reserved
- 55. Comparision between a plant and animal cell Copyright © 2010 All Rights Reserved
- 56. In pairs, draw a table stating the similarities and differences between the 2 cells below: animal cell plant cell Copyright © 2010 All Rights Reserved 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13.
- 57. Activity: Complete the table in the worksheet provided Copyright © 2010 All Rights Reserved
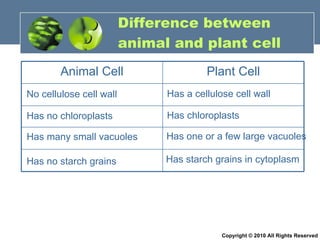
- 58. Difference between animal and plant cell No cellulose cell wall Has a cellulose cell wall Has no chloroplasts Has chloroplasts Has many small vacuoles Has one or a few large vacuoles Has no starch grains Has starch grains in cytoplasm Copyright © 2010 All Rights Reserved Plant Cell Animal Cell
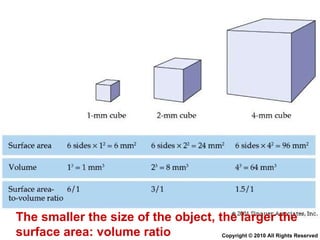
- 59. Surface area: volume ratio Copyright © 2010 All Rights Reserved
- 60. The smaller the size of the object, the larger the surface area: volume ratio Copyright © 2010 All Rights Reserved
- 61. Specialised cells Copyright © 2010 All Rights Reserved
- 62. Activity: Suggest function of these structures RBC Root hair cell Xylem vessels Copyright © 2010 All Rights Reserved
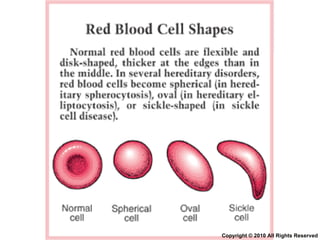
- 63. Red blood cell Copyright © 2010 All Rights Reserved
- 64. Red blood cell function Involved in gaseous transport of dissolved O 2 or CO 2 or CO Copyright © 2010 All Rights Reserved
- 65. Red blood cell Copyright © 2010 All Rights Reserved
- 66. Root hair cell Copyright © 2010 All Rights Reserved
- 67. Root hair cell Long & narrow -> increases surface area:volume ratio For efficient absorption of water and mineral salts Copyright © 2010 All Rights Reserved
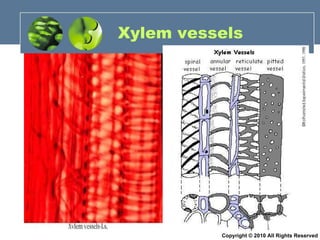
- 68. Xylem vessels Copyright © 2010 All Rights Reserved
- 69. Xylem vessels 1. Long hollow tubes formed from xylem cells laid end to end Transports 1 water and 2 mineral salts from roots to stem and leaves absence of cross walls and protoplasm -> enables water to move easily through the lumen 2. Walls strengthened by lignin which prevents the vessels from collapsing Xylem vessels bundled together provide mechanical support to the plant
- 70. Copyright © 2010 All Rights Reserved 1. Enables water to move easily through the lumen 2. Prevents collapse of xylem vessels 3. Provides mechanical support to the plant 1. Increases s.a.:volume ratio of cell for efficient absorption of water and mineral salts from soil Enable transport of O 2 from the lungs to all parts of the body Enabling it to carry more haemoglobin and hence more O 2 Increases s.a:volume ratio for efficient O 2 exchange) Function 1. Absence of cross walls and protoplasm in the long hollow tubes 2. Walls strengthened by lignin 3. Xylem vessels bundled together 1. Long and narrow Contains haemoglobin No nucleus 3. Circular, biconcave shape Structure Xylem vessels Root hair cell Red blood cell
- 71. Tissues, Organs and Systems Copyright © 2010 All Rights Reserved
- 72. Structural hierarchy cell --> tissue --> organ --> system Tissue i) Simple tissue : a group of similar cells performing a special function (e.g. epithelium/epidermis) ii) Complex tissue : tissues that contain several types of cells (e.g. connective tissue/ nervous tissue/ glandular tissue/ bone tissue/ vascular tissue e.g. xylem and phloem tissue) Organ = a group of different tissues working together and enabling the organ to perform its function (e.g. stomach/ leaf/ root/ stem/ flower) System = several organs working together for a common purpose (e.g. respiratory & digestive system) Copyright © 2010 All Rights Reserved
- 73. Examples of simple tissues Epithelium – sheet of cells that cover the internal and external surfaces of the body ii) Epidermis – sheet of cells that cover the external surface of the body Copyright © 2010 All Rights Reserved
- 74. 4 basic tissues Epithelium, Connective, Muscular and Nervous tissues Copyright © 2010 All Rights Reserved
- 75. Types of organs found in the digestive system Copyright © 2010 All Rights Reserved
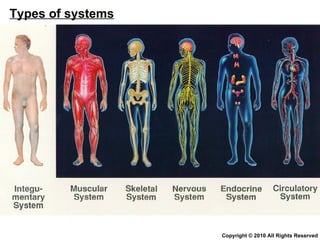
- 76. Copyright © 2010 All Rights Reserved Types of systems
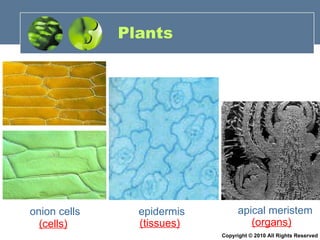
- 77. Plants onion cells epidermis apical meristem (cells) (tissues) (organs) Copyright © 2010 All Rights Reserved
Editor's Notes
- Teacher’s note: Here we can just bring a box with some ping pong balls and shake it as ask the students what they can tell from the sound of the balls moving Relate this to how a cell would be like if there were to be no cytoplasm
- Teacher’s note: Here take a box (eg shoe box) and ask the student what would happen to the shape of the box if put a book inside Next take a plastic bag and put a book inside This would demonstrate the function of a cell wall